Method and system for installation of diverse exterior sheathing components of buildings
a technology for building exterior sheathing and components, applied in the direction of roofs, coverings/linings, constructions, etc., can solve the problems of changing size, difficult and time-consuming installation, and felt paper is vulnerable to weather, so as to overcome differences in language, easy and accurate differentiation, and the effect of overcoming the level of education and literacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
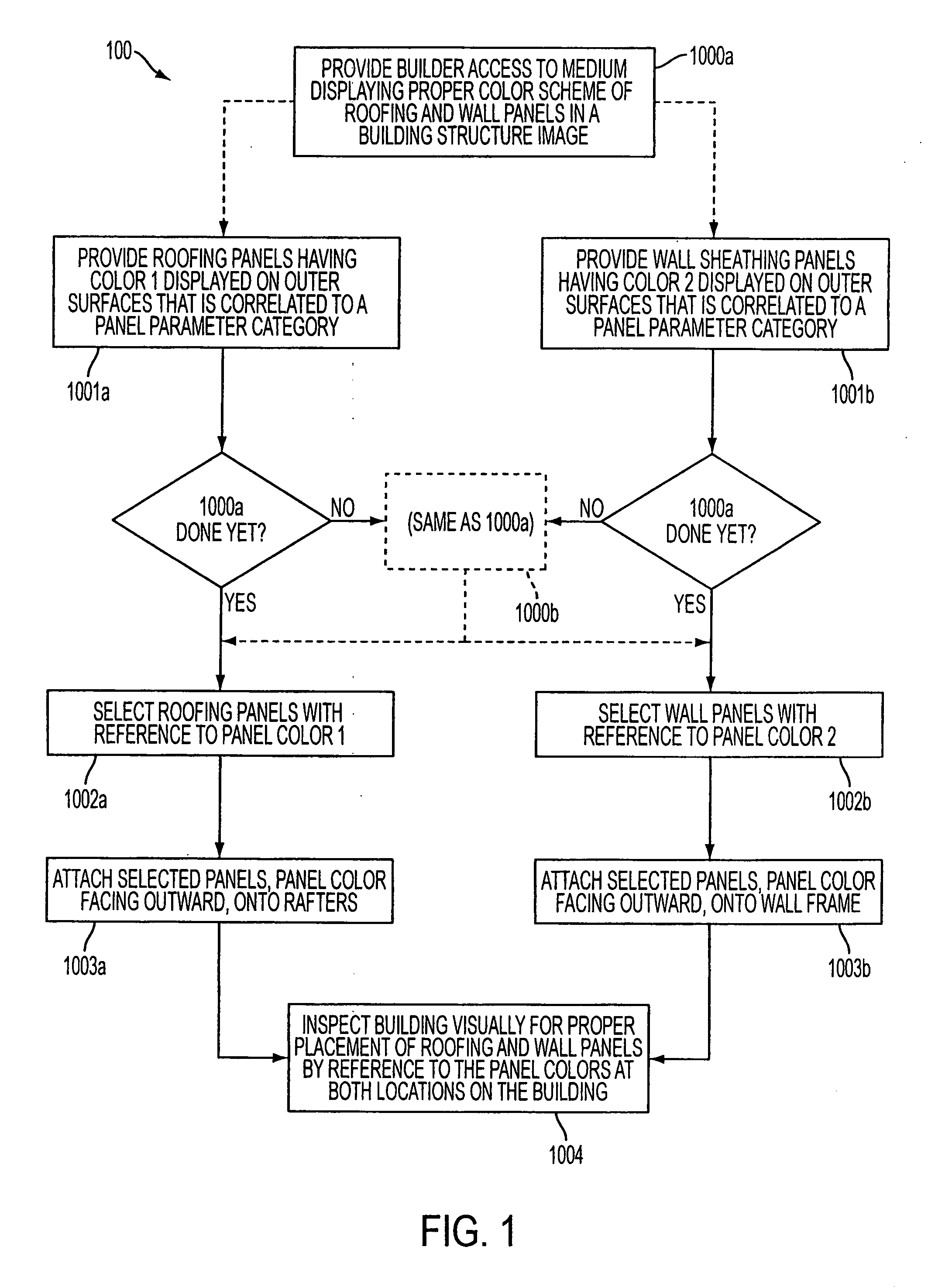
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
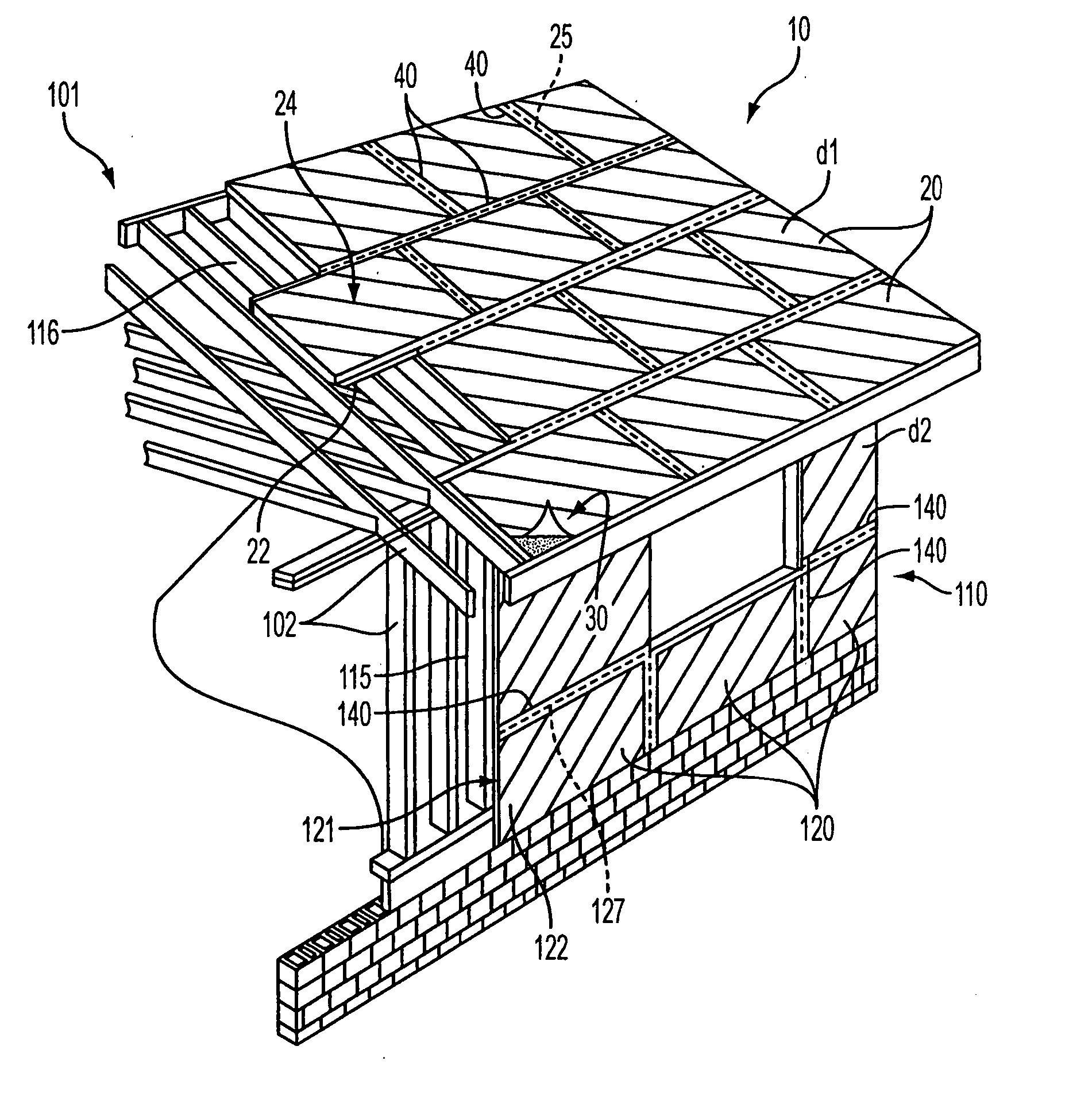
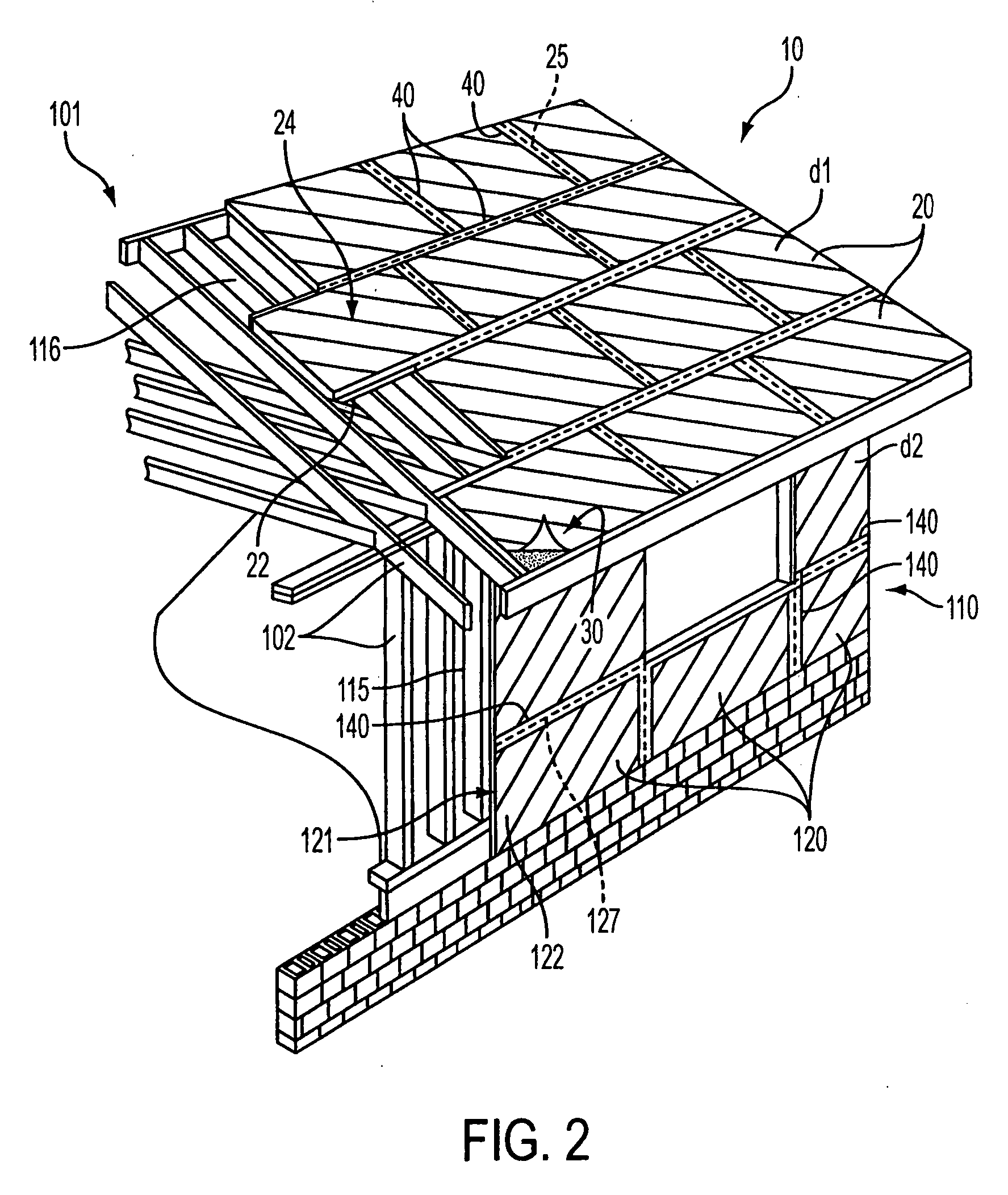
[0024] As used herein, a “color” may be a primary color (a color that cannot be made as a combination of any other colors), a secondary color (a color created from a combination of two primary colors), a tertiary color (a combination of three colors that are primary or secondary) or other intermediates, or black, and includes earth colors. A “color wheel” refers to a traditional color wheel (see, e.g., FIG. 5), such as a Johannes Itten color wheel, based on the RYB model (red / yellow / blue) with secondary colors of orange, green, and violet (purple), and tertiary colors comprising combinations of primary and secondary colors (i.e., yellow-orange, red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet, blue-green, yellow-green). A “color diad” or “diadic color scheme” is one using two colors that are two colors apart on the color wheel (e.g., red and orange). A “complementary color scheme” is one that uses colors or hues that are directly across from each other on the color wheel (e.g., blue and orange)....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com