Active sterilization zone for container filling
a technology of container and active sterilization zone, which is applied in the direction of liquid handling, application, packaging goods type, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome operation of aseptic filling lines, time-consuming, and limiting production capacity,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053]While this invention is susceptible of embodiments in many different forms, there are shown in the drawings and will herein be described in detail exemplary embodiments of the invention with the understanding that the present disclosure is to be considered as an exemplification of the principles of the invention and is not intended to limit the broad aspect of the invention to the embodiments illustrated.
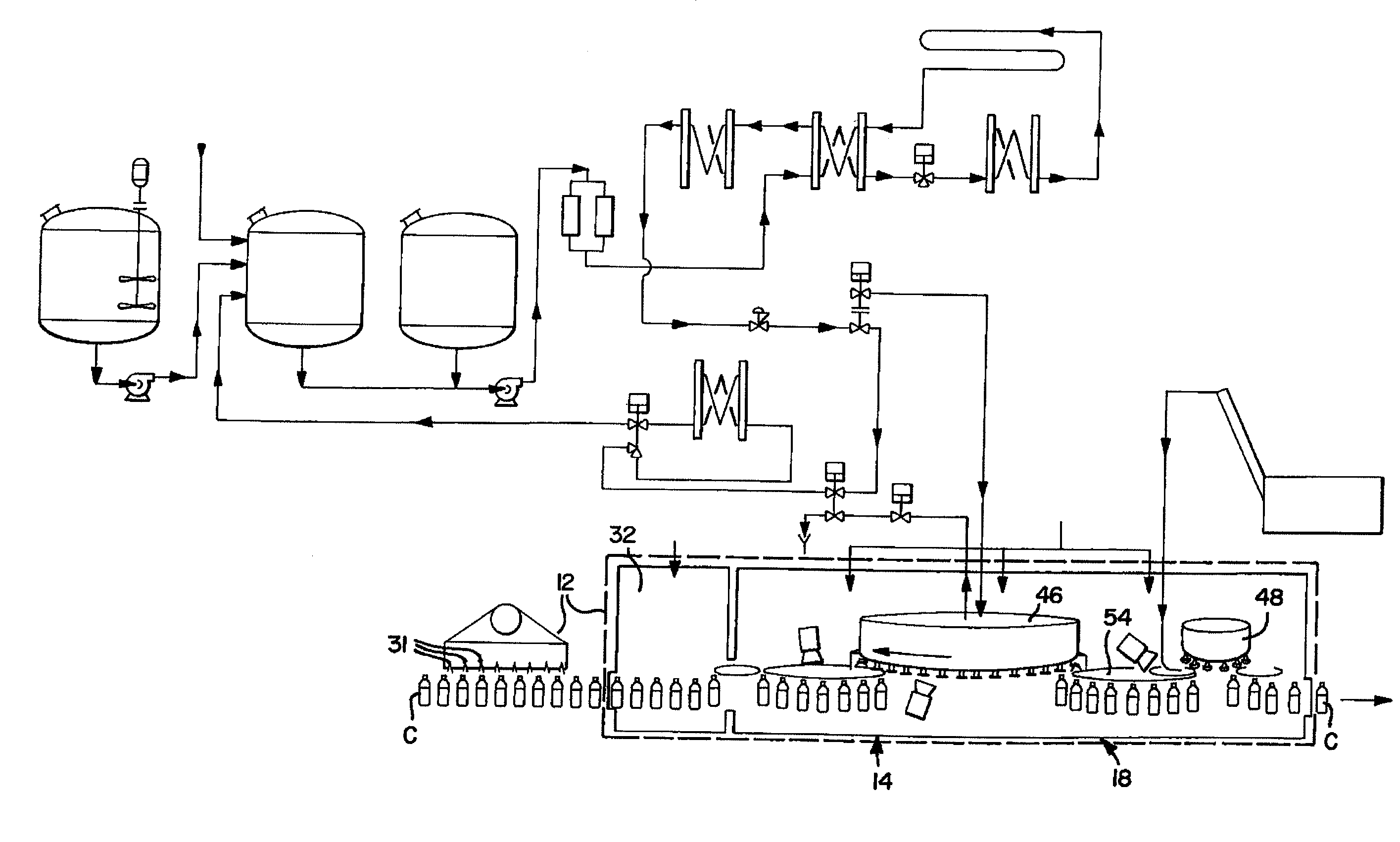
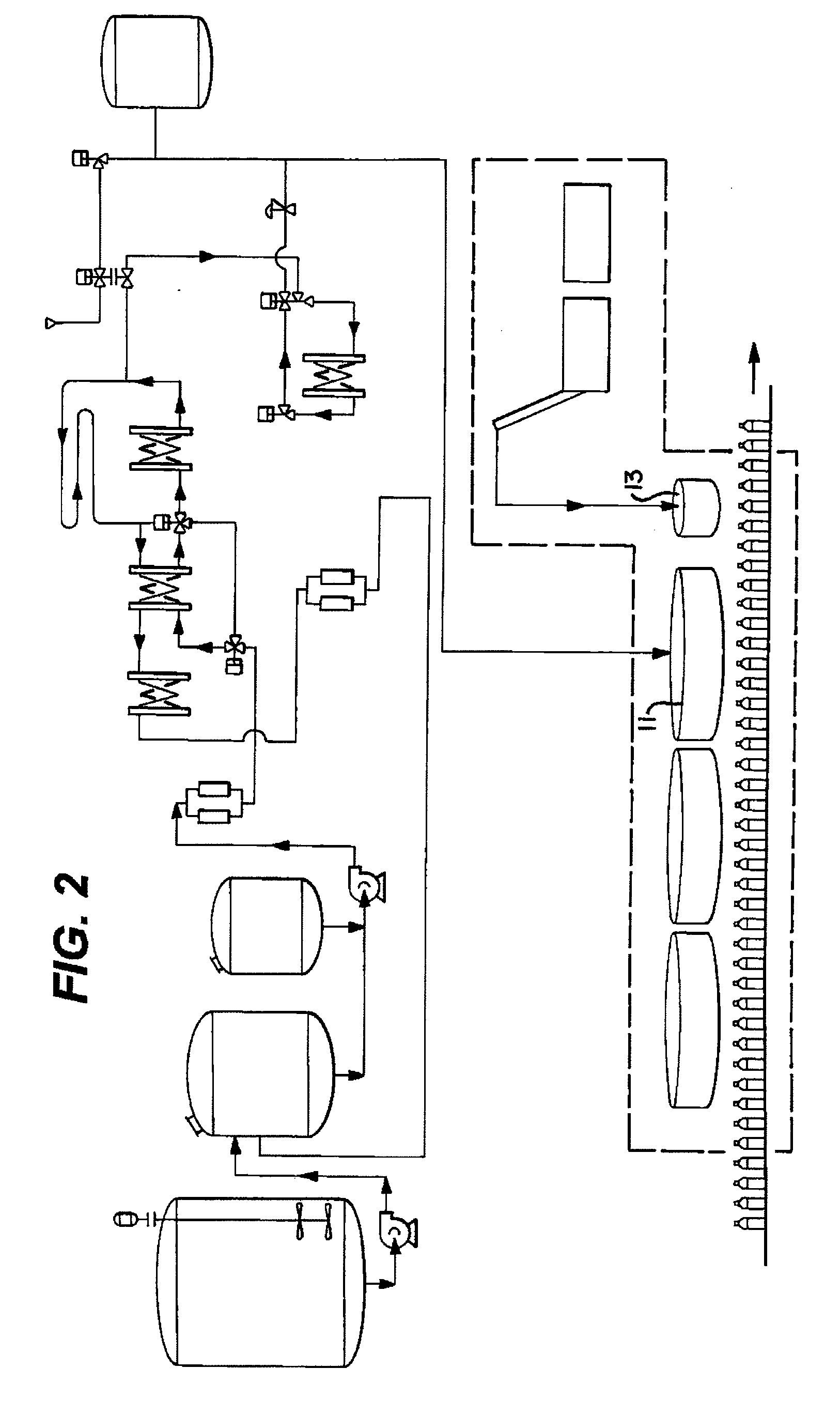
[0054]Referring now to the FIGS., and initially to FIGS. 4-6, there is shown an exemplary embodiment of an apparatus for sterile filling of containers, generally designated with the reference numeral 10. In one exemplary embodiment, the containers are beverage containers, although the system 10 can be used in various other container applications requiring sterile filling and closing. The system 10 generally includes a first module, or station 12 and a second module or station 14. The first station 12 and the second station 14 have certain associated structures 16, as explained...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com