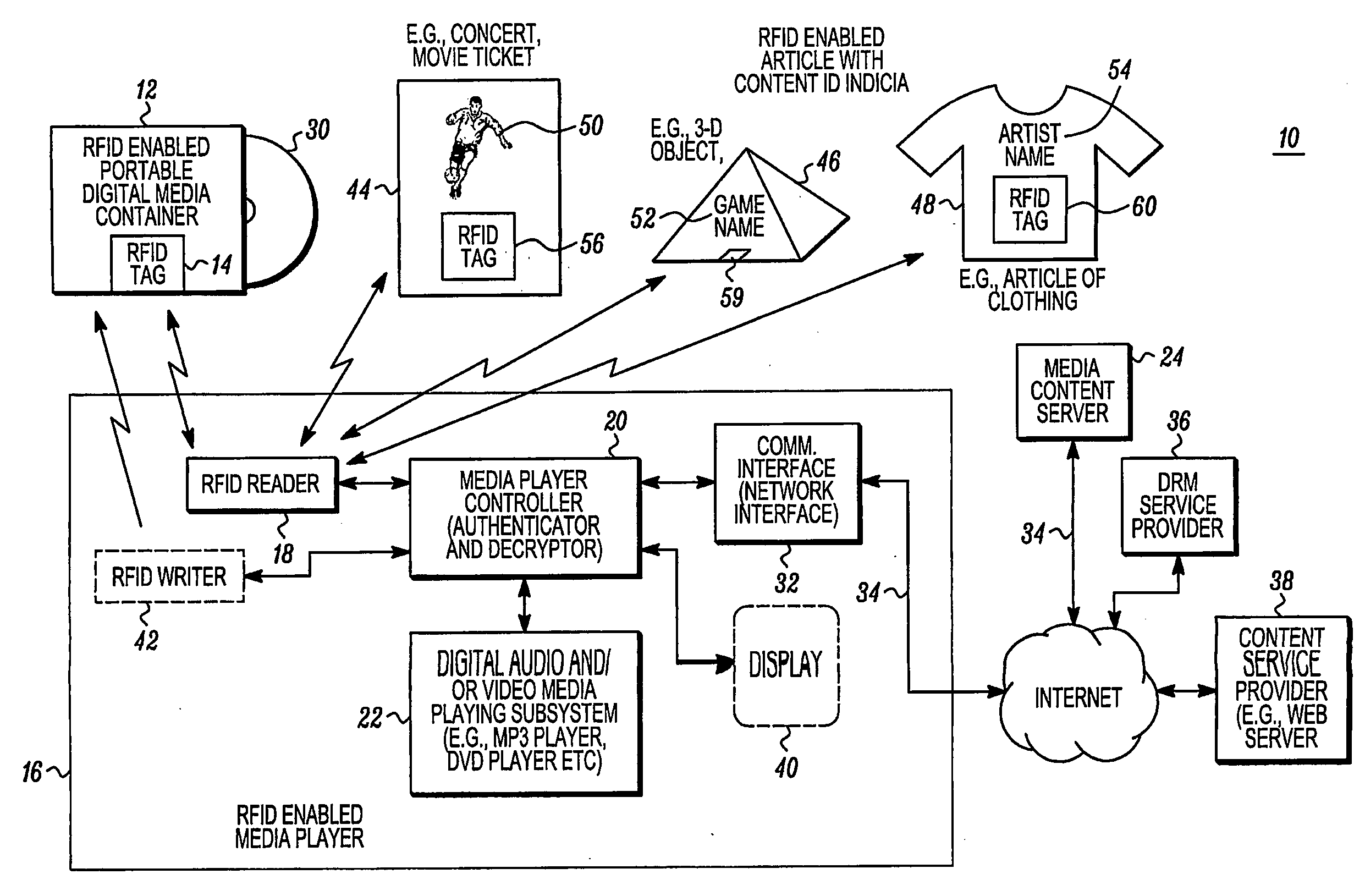
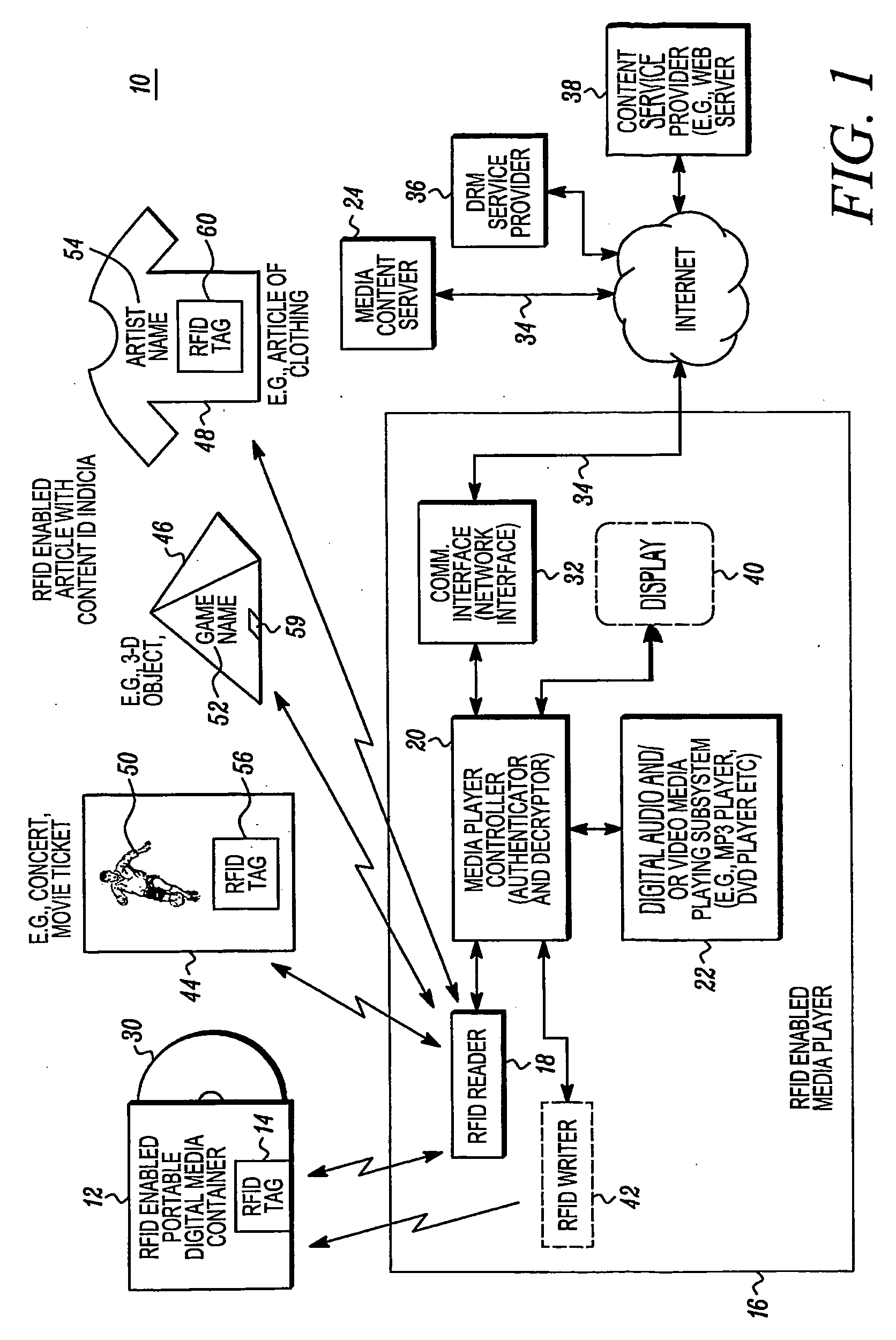
[0088]The media player display interface 600 also includes data representing media player control
graphics 606 for providing media player control to control play of the
media content downloaded from the remote media source. For example, the media player control
graphics 606 may be
graphics buttons that are displayed representing fast forward, stop, play,
volume control or any other suitable controls to control the
digital audio and / or
video media playing subsystem 22. In addition, if desired, the media player
user interface presents data representing indicia from the RFID enabled article 608 which may be found for example in the embodiment where the article is a movie card. The data representing indicia from the RFID enabled article may be the content indicia 50 (which includes a representation thereof), or information that is related to it. Too, for example, the displayed data 608 indicates to the user that they have obtained the proper downloaded
media content. As such, a visual indication allows the user to readily identify whether an error has occurred if the content of the downloaded media that is shown by for example the data 608 matches for example information or other visual indicia on the movie card. As such, the media player
user interface includes data 608 that represents visual indicia located on the RFID tag that's on a portable media object.
[0101]As shown in FIG. 11, the RFID reader of the content media player 1104 reads both RFID enabled objects 1100 and 1102 and the content media player 1104 passes this information to the
network element 1106. For example, if the combination of read content identifiers matches an expected combination of content identifiers (whether an expected
spatial relationship among objects or an expected temporal relationship is detected), the
network element authorizes access to content or media that are different from, or in addition to, media or content that would have been authorized if each of the RFID enabled objects were presented individually to the content player 1104. To help insure that combinations of objects are presented with a short period of time (as opposed to hours or days for example), as is also shown, timing logic 1108 may be introduced in the content media player 1104 as part of, for example, the RFID reader control, to determine whether the RFID reader read the tag information from the RFID tags on the different objects within an allowable period of time which may be any suitable predetermined period of time as desired.
[0115]The RFID enabled object 44, in this example, may be a Top 10 movie card with indicia thereon indicating that it is a Top 10 movie card or it may be a Top 10 song card or a Top 5 song card or any other suitable RFID media object. Similarly, the 3-D object 46 may be a Top 10 movie object, Top 10 song object, Top 10 album object or any other suitable RFID enabled object as desired. In this example an owner of the RFID enabled object purchases a subscription for the service. There may be for example, a one time fee that is paid to obtain the card where after the card may have a predetermined
life span which may be monitored by the
digital rights management
service provider. Any other suitable subscription service and operation may also be employed. The controller (FIG. 12) is responsive to RFID tag based information, such as content identification information, obtained by the
digital audio and / or
video media playing device 16 and operates to facilitate access to immediate content associated with a periodically changing
media content list. In this example, the controller is integrated as part of the
digital rights management
service provider 36, and provides media identification information such as URLs as described earlier so that the media playing device 16 can download the appropriate media from the media contents
server 24. Alternatively, if the controller is located as part of the media contents
server 24, the controller may facilitate access to media content by providing the media content directly for download. The digital audio and / or
video media playing device 16 then plays the audio and / or video that has been retrieved based on the periodically changing media content
list.
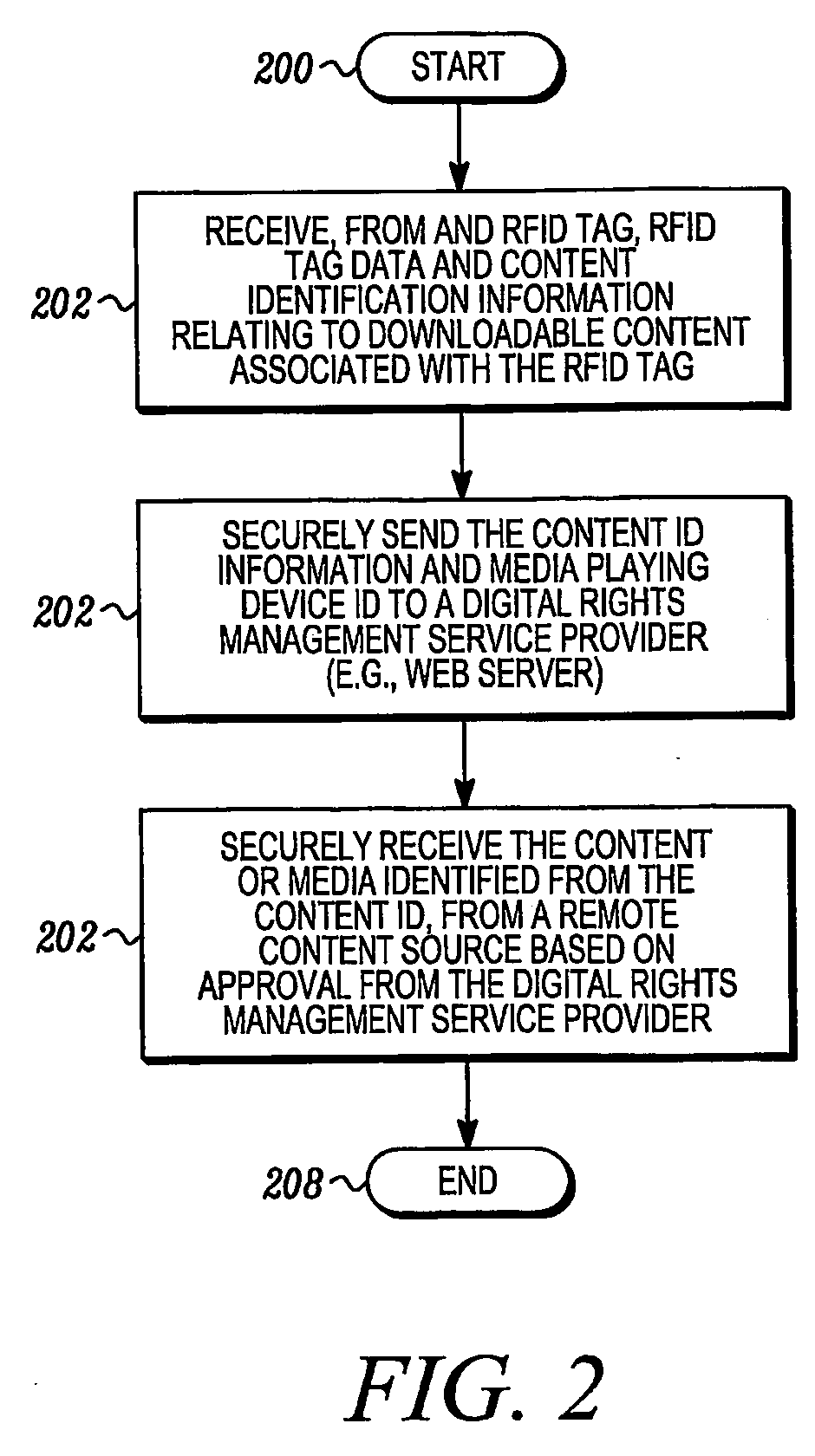
[0116]FIG. 16 illustrates a method for providing digital audio and / or video content that includes, as shown in block 1600, receiving RFID tag based information, such as content identification information, from an RFID enabled media object. As shown on block 1602, the method includes facilitating access to media content associated with a stored periodically changing media content
list. The method may then end by waiting for another red RFD tag.
[0125]FIG. 18 depicts a game
system in which placing a tagged RFID enabled figurine 1800 close to an RFID reader enabled
game console 1802 triggers a game download and starts running the game. The figurine acts as the physical representation of the player in the
video game. It is used in subsequent game sessions to log the user in and to store personal settings and high scores. Today, video games can be downloaded or come in a box with one or more CDs or DVDs and a user manual. A single object (e.g. figurine) materializing the game enhances the way players emotionally relate to the games they own. For example, the user buys a tagged warrior figurine in a
video game shop. When he places the warrior close to his enhanced
game console, the console reads the RFID tag and starts downloading the game
software of an online multi-player heroic fantasy game from a
content server based on media ID's from the DRM
service provider 36. The game starts and the user plays a warrior character, as the figurine indicates. One month later, the user decides to go back to the shop to buy an axe for his figurine as he cannot manage to find one in the digital game world. His digital warrior gets an axe immediately in the
video game after he physically places the RFID enabled axe in the figurine's hand, because the axe contains an RFID tag that links it to the digital game world. The figurine includes an add-on object sensor, such as an optical sensor,
mechanical sensor or other suitable sensor to sense when the RFID enabled add-on object is in the figurine's hand.
[0127]FIG. 20 depicts a
system in which
software license keys could be physically materialized by decorative objects (e.g. tagged figurines) and sit next to RFID reader equipped computers. The installed
software checks against the
license key contained in the RFID tag 2000. Today's software complexity and unpredictable security flaws implies continuous software updates for licensees.
Software licenses are mostly invisible to consumers (as they are digital or take the form of dongles plugged at the back of computers). The system increases
user awareness of
license key presence and limits illegal license
copying and exchange. For example, a figurine watchdog sitting next to a
workstation symbolizes the fact that the
workstation is secure. Indeed, the figurine contains a tag which stores the license for a daily updated antivirus software. The method for secured access to software and dynamic updates is represented as follows:
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More