Anti-cd20 antibodies and methods of use
a technology of anti-cd20 and antibodies, which is applied in the field of anti-cd20 antibodies and methods of use, can solve the problems that current murine and chimeric antibodies do not constitute ideal therapeutic agents, and achieve the effects of improving cdc function, preventing organ and tissue graft rejection, and increasing complement-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (cdc)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Optimization of Humanized Murine Anti-CD20 Antibody
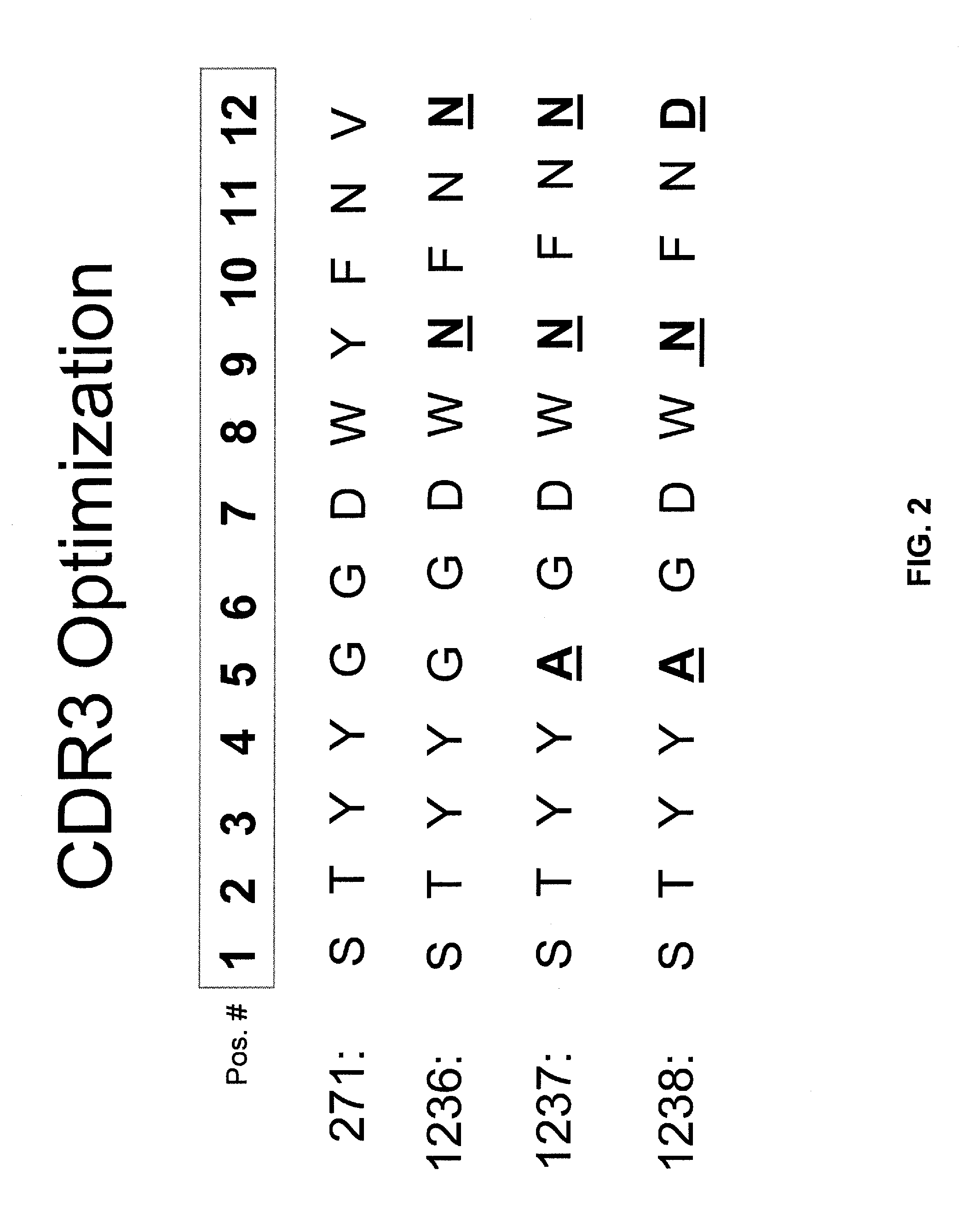
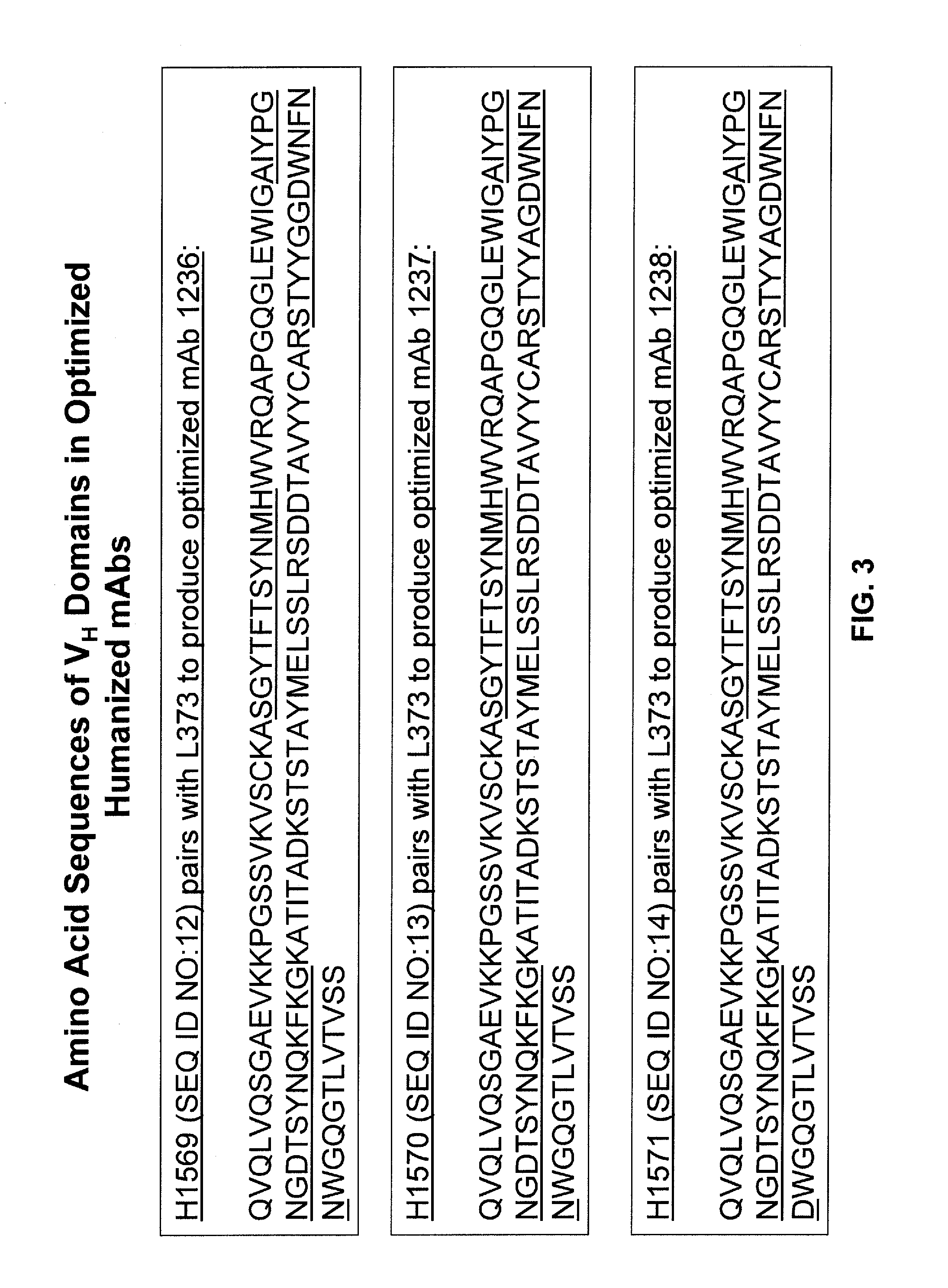
[0335] A humanized murine anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, mAb 1097, was engineered within one or more of the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of its variable heavy (VH; see SEQ ID NO:29) and variable light (VK; see SEQ ID NO:10) domains to yield optimized mAbs having increased CDC function. The initial humanized murine anti-CD20 mAb is a humanized form of the chimeric murine / human anti-CD20 antibody known as rituximab (i.e., mAb C2B8; see U.S. Pat. No. 5,736,137). The three CDRs of the original VH domain (designated H1286) and original VK domain (designated L373) within the humanized murine anti-CD20 mAb are shown in FIG. 1. The CDR2 of L373 (shown in SEQ ID NO:9) was derived from a human VK and not a murine VK.
[0336] Initial optimization steps included modifications to the starting CDR3 (designated as “271” in FIG. 1; SEQ ID NO:30) of the H1286 VH domain (see FIG. 2). The 271 CDR3 sequence is equivalent to that for the C...
example 2
Binding and Functional Characteristics of Optimized Humanized Murine Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibodies
[0342] The optimized humanized mAb 1236, mAb 1237, and mAb 1238 described in Example 1 were assessed for their respective binding and functional characteristics. For each assay, mAb 271, having the identical sequence to rituximab (IDEC-C2B8; Rituxan®; IDEC Pharmaceuticals Corp., San Diego, Calif.), served as the positive control.
[0343] Binding specificity was assessed by Fluorometric Microvolume Assay Technology (FMAT, Applied Biosystems 8200 Cellular Detection System) and Flow Cytometry, which tabulates Mean Fluorescence Intensities (MFI) of staining on CD20 positive (CD20+) and CD20 negative cell lines. FMAT analysis demonstrated binding specificity for CD20 (FIGS. 6A-6D). Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated binding of these optimized humanized anti-CD20 mAbs to CD20+ Daudi and EB1 cells (Table 2).
TABLE 2Binding to CD20 membrane positive and negative cell linesFlow Cytometry Re...
example 3
Further Optimization of mAb 1237
[0352] B-cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (B-CLL) cells express lower levels of CD20 than NHL (Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma) cells. Testing showed that optimized mAb 1236, mAb 1237, and mAb 1238 demonstrate weak CDC of B-CLL cells. As a next step the mAb 1237 was selected and subjected to mutagenesis to screen for improvements in affinity and thus improvements in the lysis of B-CLL cells. The affinity improvement strategy comprised randomizing specific positions in the VH and the VK domains, selecting mutant VH domains with L373, selecting mutant VK domains with H1570, combining separate beneficial mutations in either VH or VK, and combining mutant VH with mutant VK domains. The new mutants identified are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3New mutants identified. Residue positions withinthe VH and VK domains are with reference tothe Kabat numbering system.mAbVHVK1588H1638 (H1570 S31F)L3731589H1639 (H1570 D56A)L3731590H1640 (H1570 D56L)L3731652H1639 (H1570 D56A)L419...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com