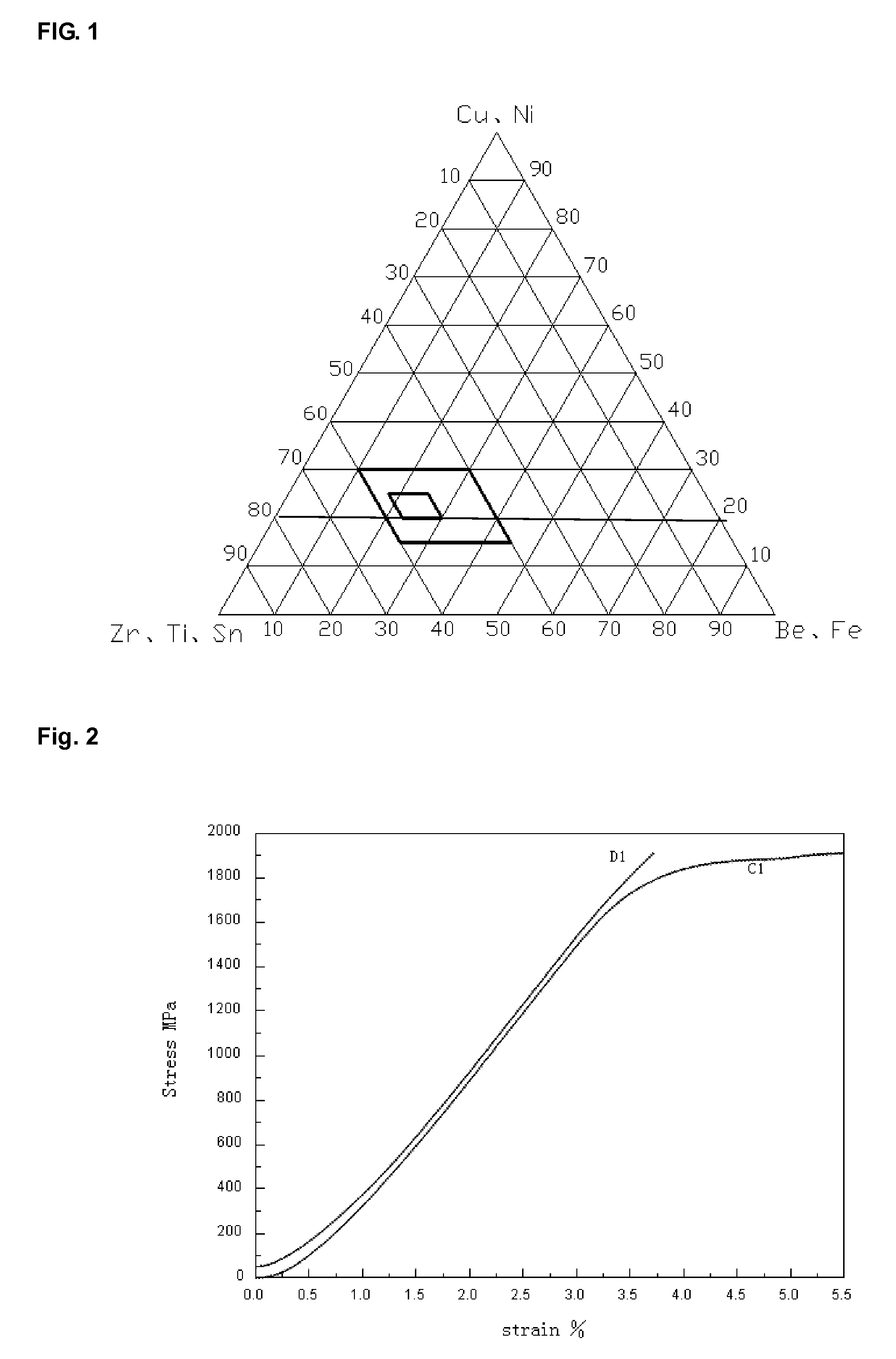
Zr-based amorphous alloy and a preparing method thereof
a technology of amorphous alloys and preparing methods, which is applied in the field of zr-based amorphous alloys and a preparing method thereof, can solve the problems of difficult to manufacture large-scale amorphous alloys, limiting the application of amorphous metallic alloys, and reducing the internal cooling speed of products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0022]A preparation method of a Zr-based amorphous alloy is illustrated in this example.
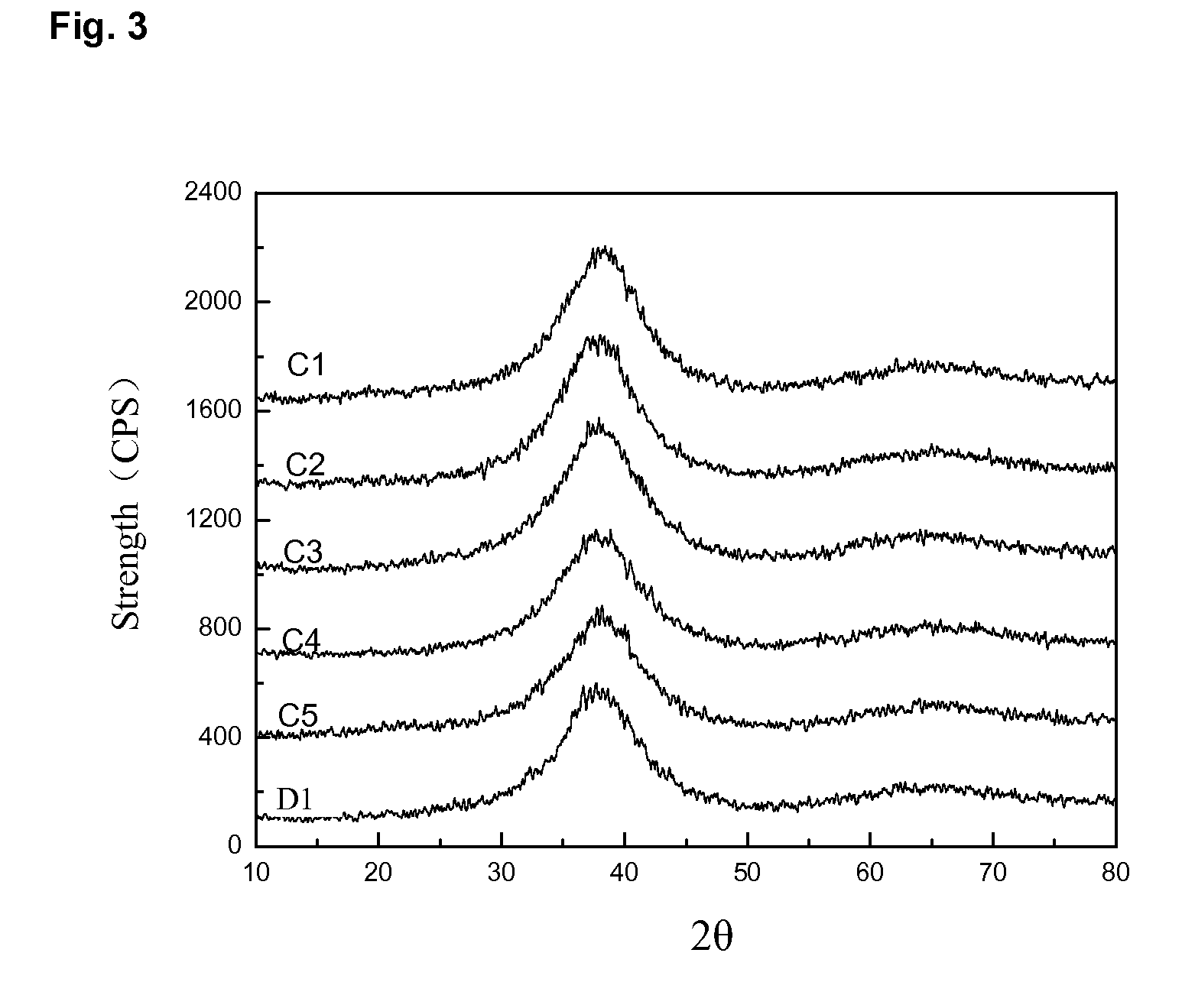
[0023]Raw materials Zr, Ti, Sn, Cu, Ni, Fe, Be (about 25 grams) were added to an electric arc melting equipment (Shen Yang Scientific Instrument Manufacturing Company Limited). The ratios of the raw materials were as follows: (Zr0.74Ti0.25Sn0.01)55.34(Cu0.56Ni0.44)20.65Fe1.96Be22.05. The equipment was vacuumized to about 5 Pa. The raw material was melted at about 2,000° C. under Ar protection for about 6 minutes. The molten master alloy was mixed sufficiently, and then cooled into an ingot. The ingot was re-melted at about 1,500° C. using electric arc melting, and then cooled in a copper mold casting process with a cooling speed of about 102 k / s to obtain the Zr-based amorphous alloy sample C1.
example 2
[0024]Another preparation method of a Zr-based amorphous alloy is illustrated in this example.
[0025]Raw materials Zr, Ti, Sn, Cu, Ni, Fe, Be (about 200 kg) were added to an induction melting equipment (Zhongbei Technology). The ratios of the raw materials were as follows: (Zr0.74Ti0.25Sn0.01)55.34(Cu0.56Ni0.44)20.65Fe1.96Be22.05. The equipment was vacuumized to about 5 Pa. The raw materials were melted at about 1,800° C. under Ar protection for about 10 minutes. The molten master alloy was mixed sufficiently, and then cooled into an ingot. The ingot was re-melted at about 1,200° C. using resistance heating, and then cooled in a die-casting process with a cooling speed of about 104 k / s to obtain the Zr-based amorphous alloy sample C2.
example 3
[0026]Yet another preparation method of a Zr-based amorphous alloy is illustrated in this example.
[0027]Raw materials Zr, Ti, Sn, Cu, Ni, Fe, Be (about 20 g) were added to a quartz tube (Zhongbei Technology). The ratios of the raw materials were as follows: (Zr0.80Ti0.17Sn0.03)40Y5Nb5(Cu0.64Ni0.36)25Fe5Be20. The tube was vacuumized to about 200 Pa. The raw materials were melted at about 2,000° C. by induction heating under Ar protection for about 5 minutes. The molten master alloy was mixed sufficiently, and then cooled into an ingot. The ingot was re-melted at about 1,500° C. by induction heating, and then cooled in a water quenching process with a cooling speed of about 103 k / s to obtain the Zr-based amorphous alloy sample C3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com