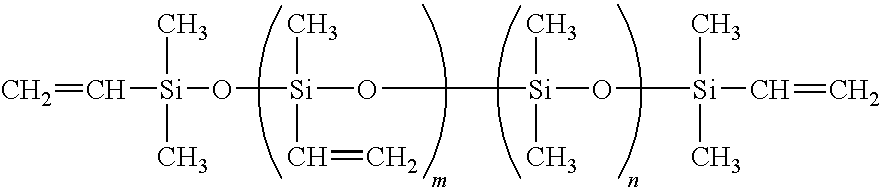Glass substrate with protective glass, process for producing display device using glass substrate with protective glass, and silicone for release paper
a technology of glass substrate and release paper, which is applied in the direction of non-linear optics, instruments, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the production of display devices, optical defects, and the strength decrease of glass substrate caused by such a step, and achieves good adhesion properties, easy laminate of both substrates, and inclusion of bubbles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
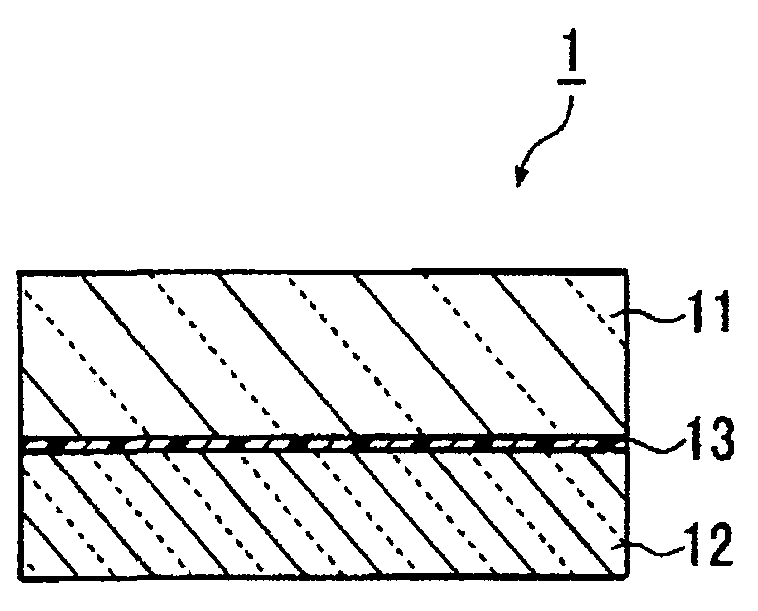
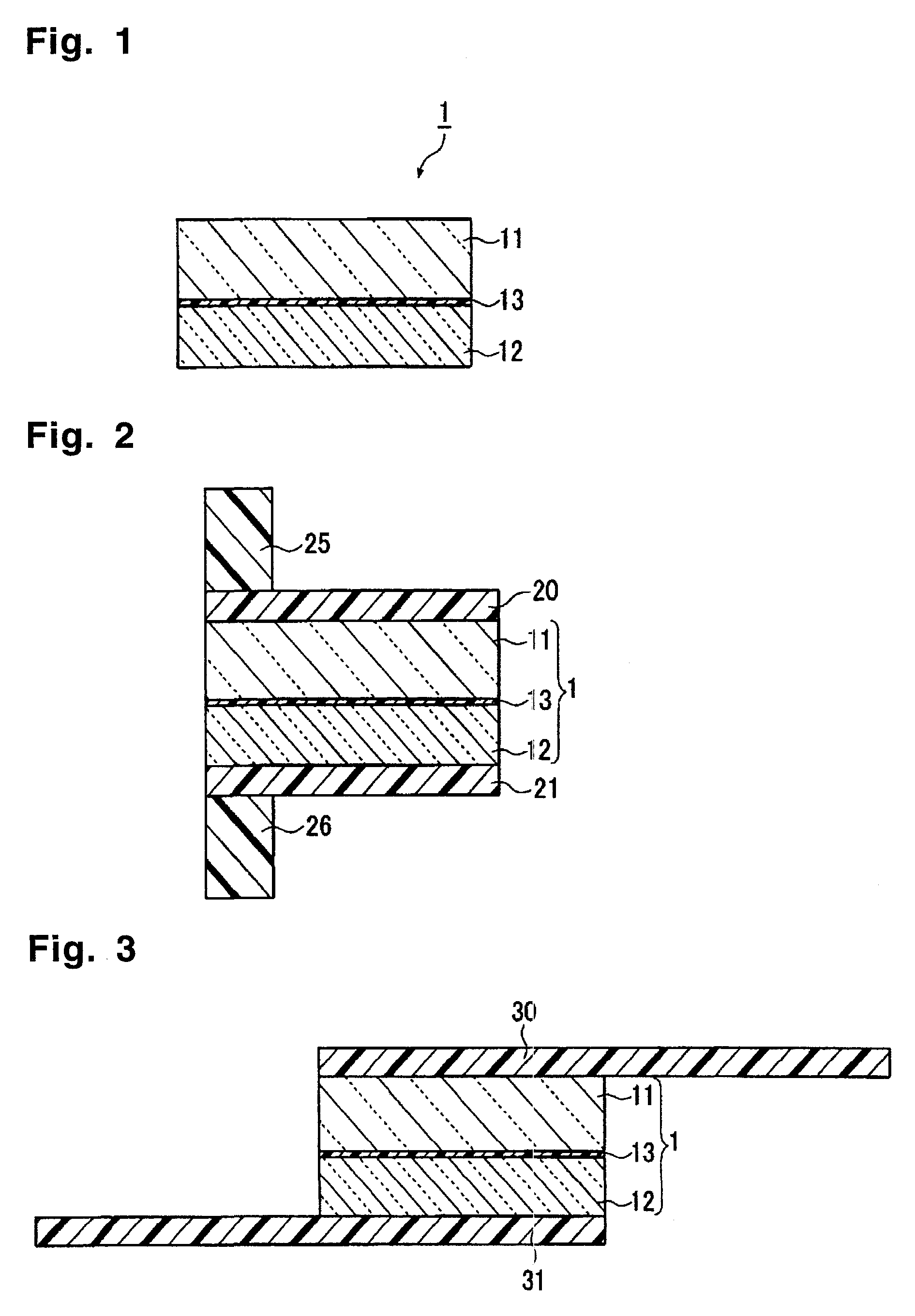
[0130]The protective glass substrate (AN100, manufactured by Asahi Glass Company, Limited) having 400 mm×300 mm×0.3 mm thick and having a linear expansion coefficient of 38×10−7 / ° C., was cleaned by e.g. purified water washing and UV washing, and then, a mixed product (application amount 30 g / m2) of 100 parts by mass of a non-solvent addition reaction type silicone for release paper (KNS-320A, viscosity: 400 cs, manufactured by Shin-Etsu Silicone) and 2 parts by mass of a platinum type catalyst (CAT-PL-56, manufactured by Shin-Etsu Silicone), was applied on the above protective glass substrate by a screen printing machine, and was heat-cured at 180° C. for 30 mins in the atmospheric air to obtain a silicone resin layer of 20 μm thick.
[0131]A surface of a glass substrate (AN100, manufactured by Asahi Glass Company, Limited) having 400 mm×300 mm×0.4 mm thick and having a linear expansion coefficient of 38×10−7 / ° C., which is to be contacted with the silicone resin layer, was cleaned b...
example 2
[0144]The glass substrate with protective glass (a glass substrate 2 with protective glass) of the present invention was obtained by carrying out the same procedures as in Example 1 except that the substrate thickness of the protective glass substrate was 0.4 mm.
[0145]In the glass substrate 2 with protective glass, the glass substrate was bonded to the silicone resin layer without forming bubbles, and it had no convex defects and had suitable smoothness.
[0146]When the simple peel test was carried out on the glass substrate 2 with protective glass, it was easy to peel the back surface protective glass substrate. Further, with respect to the glass substrate 2 with protective glass after being heat-treated at 300° C. for 1 hour in an atmosphere, the simple peel test was carried out, and it was easy to peel the back surface protective glass substrate, and the heat resistance was also suitable.
[0147]Further, in the same manner as in Example 1, with respect to the glass substrate 2 with p...
example 3
[0149]The protective glass substrate (AN100, manufactured by Asahi Glass Company, Limited) having 400 mm×300 mm×0.2 mm thick and having a linear expansion coefficient of 38×10−7 / ° C. was cleaned by e.g. purified water washing and UV washing, and then, a mixed product (application amount 20 g / m2) of a linear polyorganosiloxane having vinyl groups at both terminals (tradename “8500”, manufactured by Arakawa Chemical Industries, Ltd.), methylhydrogen polysiloxane having hydrosilyl groups in its molecule (tradename “12031” manufactured by Arakawa Chemical Industries, Ltd.), and a platinum catalyst (tradename CAT12070”, manufactured by Arakawa Chemical Industries, Ltd.), was applied on the above protective glass substrate by a screen printing machine, and was heat-cured at 180° C. for 30 minutes in an atmosphere to obtain a silicone resin layer of 20 μm thick.
[0150]Here, the mixing ratio of the linear polyorganosiloxane to methylhydrogen polysiloxane was adjusted so that the molar ratio ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| total thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com