Nonpolar phase-soluble methathesis catalysts
a catalyst and phase-soluble technology, applied in the direction of organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complexes catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem that the product of the reaction is less soluble in the solvent than the molecule, and achieve the effect of less solubl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
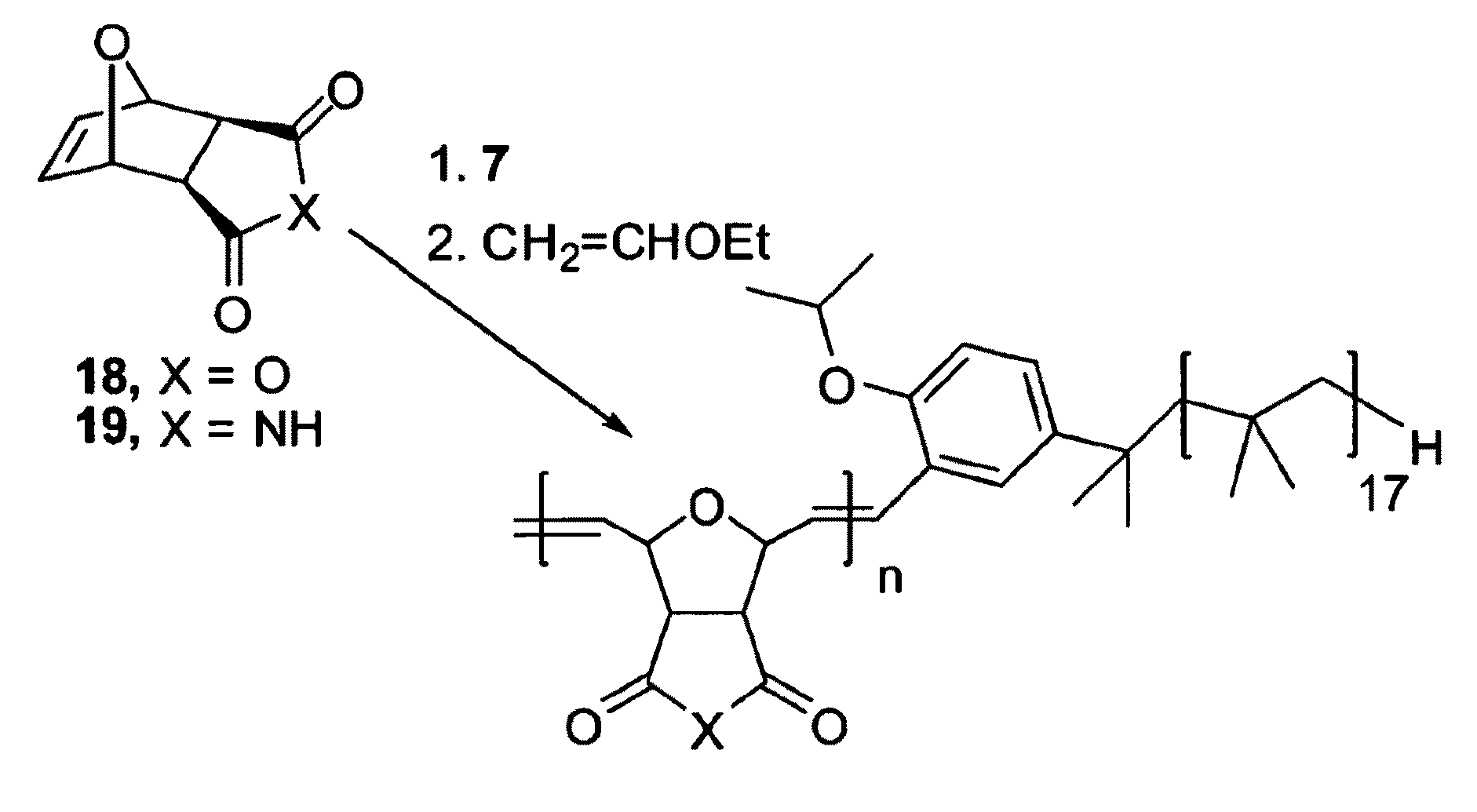
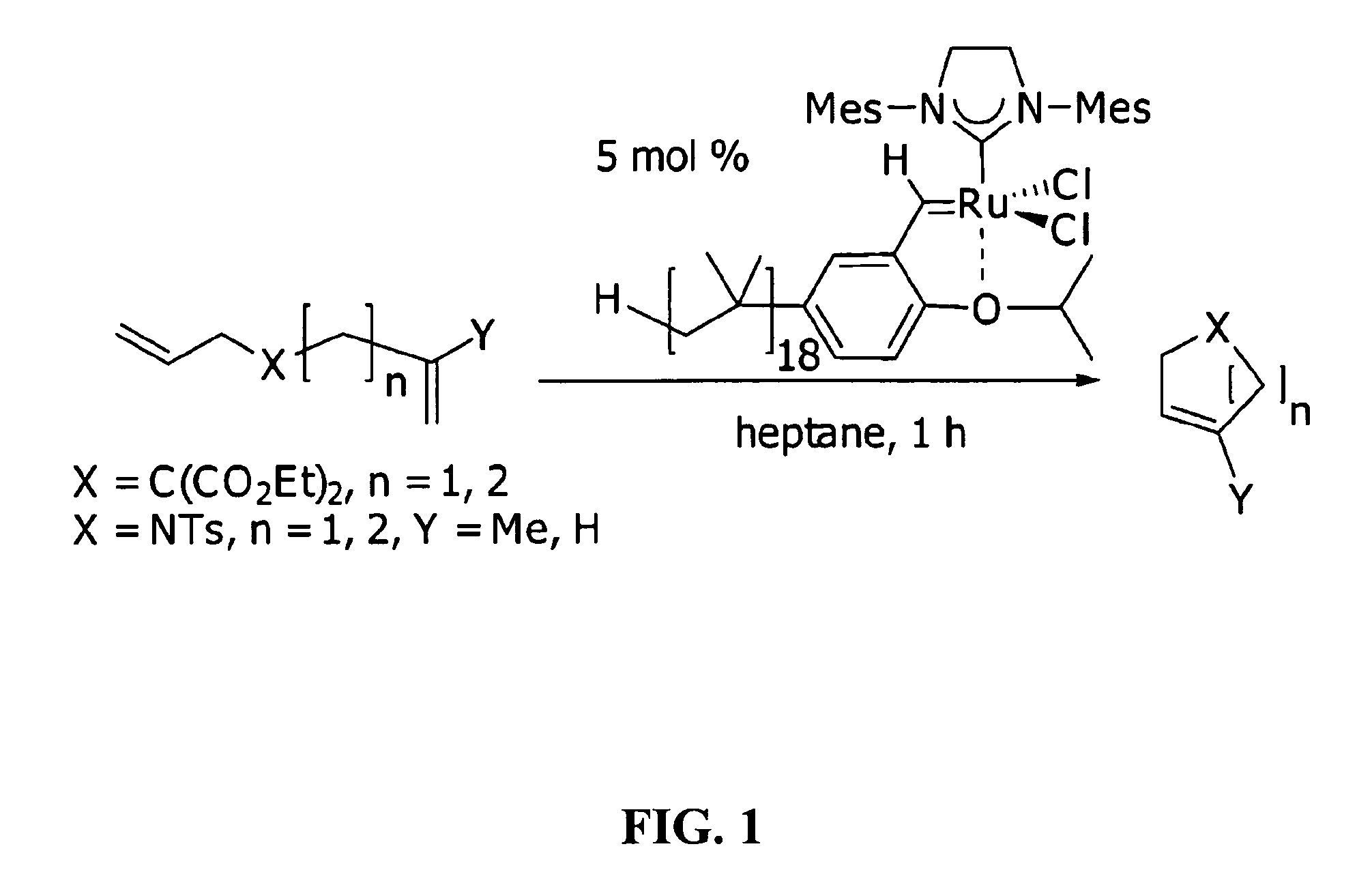
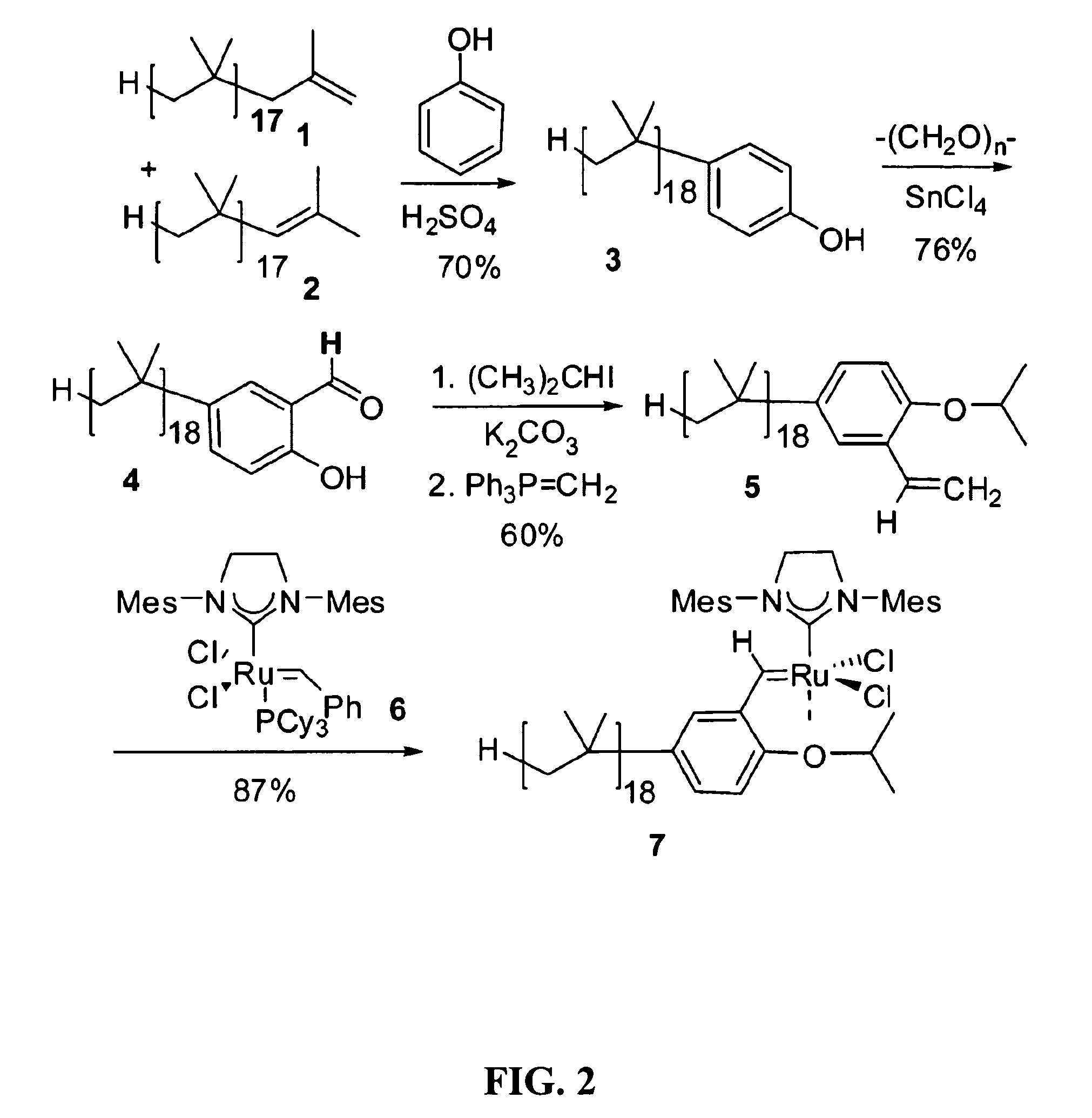
[0027]The instant invention provides a catalysis system having a single nonpolar reaction solvent that is not latently biphasic. The solvent may consist of one or more nonpolar liquid components. Solvents consisting of only one component are inherently monophasic and are thus incapable of being latently biphasic. For those solvents having multiple components, the components remain miscible with each other (i.e. remain monophasic) throughout the entire reaction process (i.e. they do not separate to different phases upon some form of manipulation), from the addition of substrate to the removal of product. This system thus does not necessitate the provision of latent biphasic reaction schemes, which involve rather complex manipulations (e.g. specific temperature or ionic state changes). The inventive reaction scheme allows for the catalyst and substrate to be soluble in the single nonpolar solvent. Surprisingly, the reaction products are easily separated from the nonpolar solvent by vi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com