Encoded solid supports for biological processing and assays using same
a solid support and biological technology, applied in the field of data storage technology to molecular tracking and identification, and to biological, chemical, immunological and biochemical assays, can solve the problems of inability to provide and maintain compounds to support hts, time-consuming analytical methods, and inability to detect and detect the presence of a variety of substances,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment
Event-Detecting Embodiment
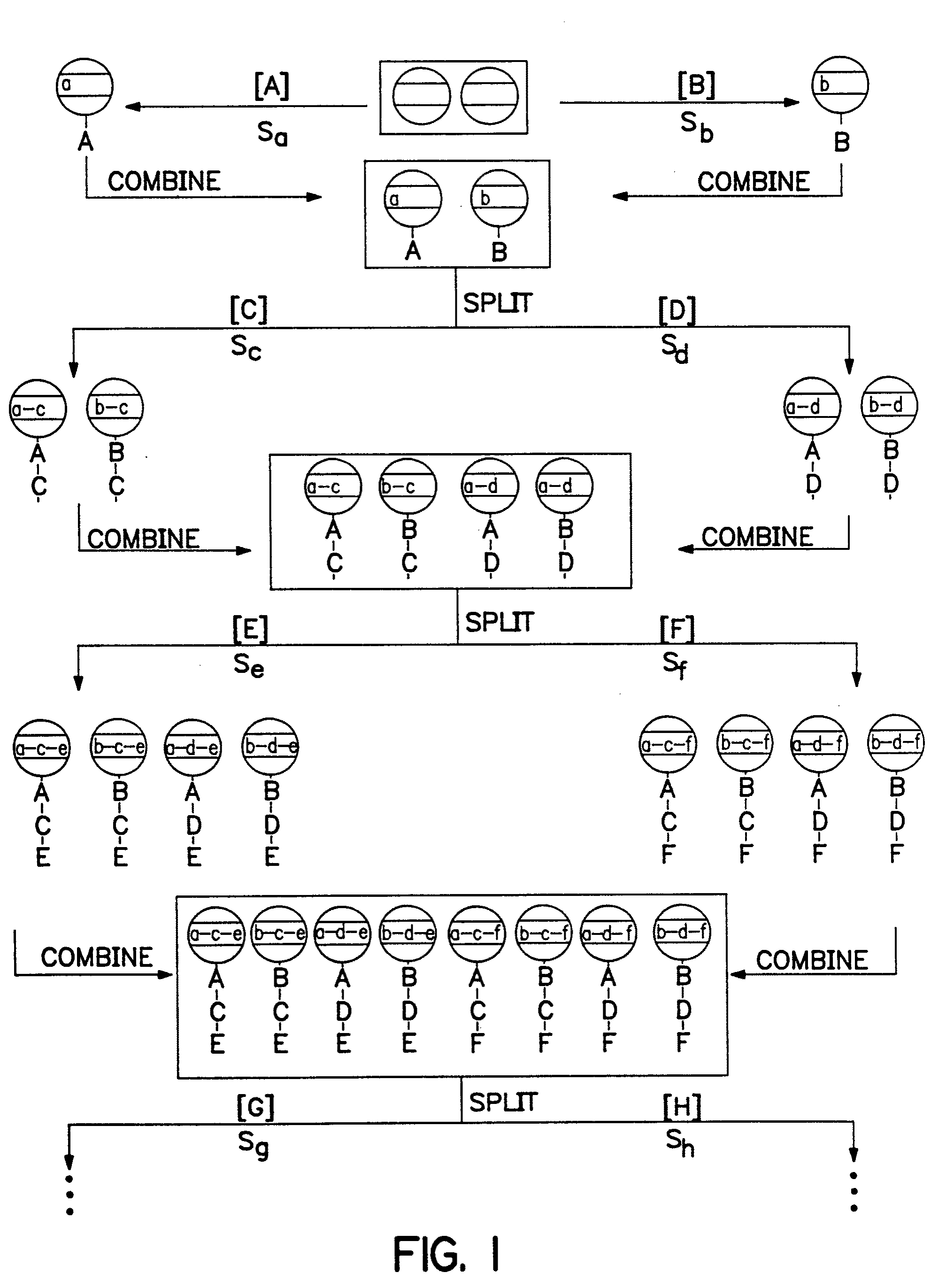
[0256] Another embodiment of the combinations herein utilizes a recording device that can detect the occurrence of a reaction or event or the status of any external parameter, such as pH or temperature, and record a such occurrence or parameter in the memory. Any of the above devices may be modified to permit such detection. For example, the chip with the antifuse memory array with decoder, rectifier components and RF antenna, can be modified by addition of a photodetector and accompanying amplifier components as shown in FIG. 9. The photodetector will be selected so that it is sensitive to the frequencies of expected photoemissions from reactions of interest. To maintain the chip's passive operation, the photodetector circuitry may use voltage supplied by the same RF signal that is used to write other data to memory, so that no detection of photoemission will occur unless RF or other power is applied to provide bias and drain voltage. If an active device i...
example 1
Formulation of a Polystyrene Polymer on Glass and Derivatization of Polystyrene
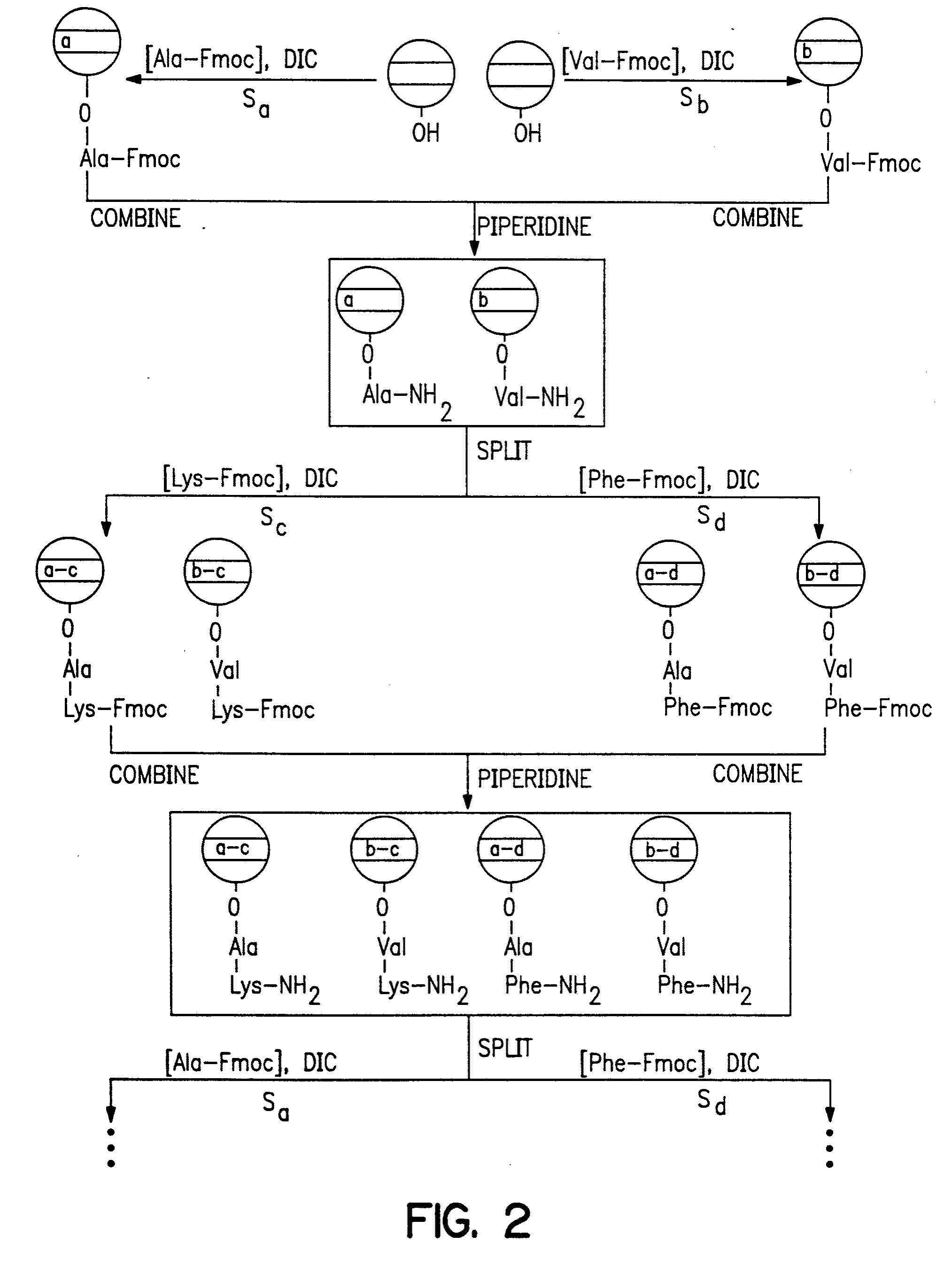
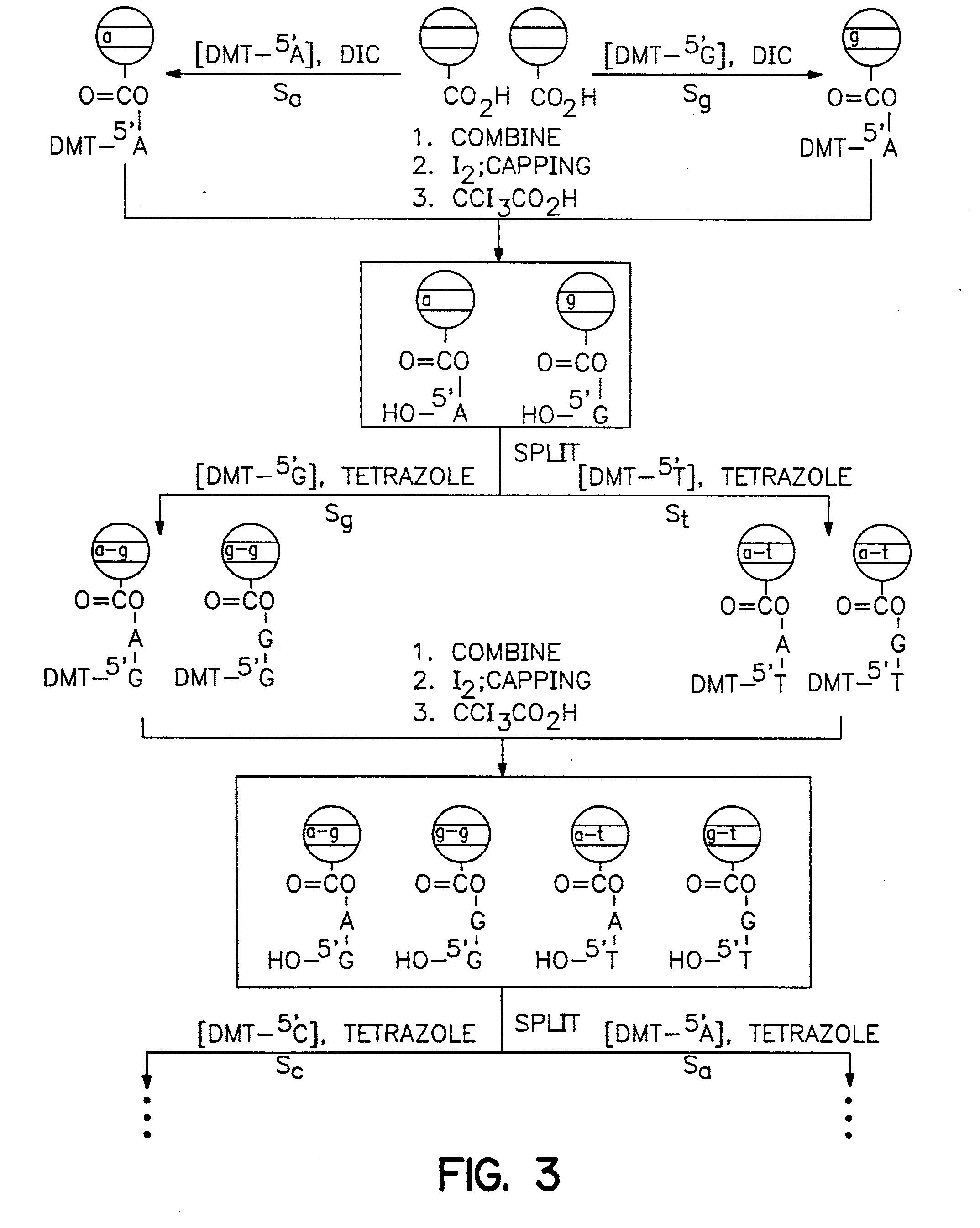
[0447] A glass surface of any conformation [beads for exemplification purposes (1)] that contain a selected memory device that coat the device or that can be used in proximity to the device or subsequently linked to the device is coated with a layer of polystyrene that is derivatized so that it contains a cleavable linker, such as an acid cleavable linker. To effect such coating a bead, for example, is coated with a layer of a solution of styrene, chloromethylated styrene, divinyl benzene, benzoyl peroxide [88 / 10 / 1 / 1 / , molar ratio] and heated at 70° C. for 24 h. The result is a cross-linked chloromethylated polystyrene on glass (2). Treatment of (2) with ammonia [2 M in 1,4-dioxane, overnight] produces aminomethylated coated beads (3). The amino group on (3) is coupled with polyethylene glycol dicarboxymethyl ether (4) [n≈20] under standard conditions [PyBop / DIEA] to yield carboxylic acid derivatized bea...
example 2
Construction of a Matrix with Memory
[0449] A matrix with memory was constructed from (a) and (b) as follows:
[0450] (a) A small (8×1×1 mm) semiconductor memory device [the IPTT-100 purchased from Bio Medic Data Systems, Inc., Maywood, N.J.; see, also U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,422,636, 5,420,579, 5,262,772, 5,252,962, 5,250.962, 5,074,318, and RE 34.936].
[0451] The memory device is a transponder [IPTT-100, Bio Medic Data Systems, Inc., Maywood, N.J.] that includes a remotely addressable memory [EEPROM]. The transponder receives, stores and emits radio frequency signals of different frequencies so that it can be remotely programmed with information regarding synthetic steps and the constituents of linked or proximate molecules or biological particles.
[0452] These devices are designed to operate without a battery, relying on the energy generated by the radio frequency pulses used in the encoding process. Also, it is important to note that additional sensors such as temperature [as in this ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com