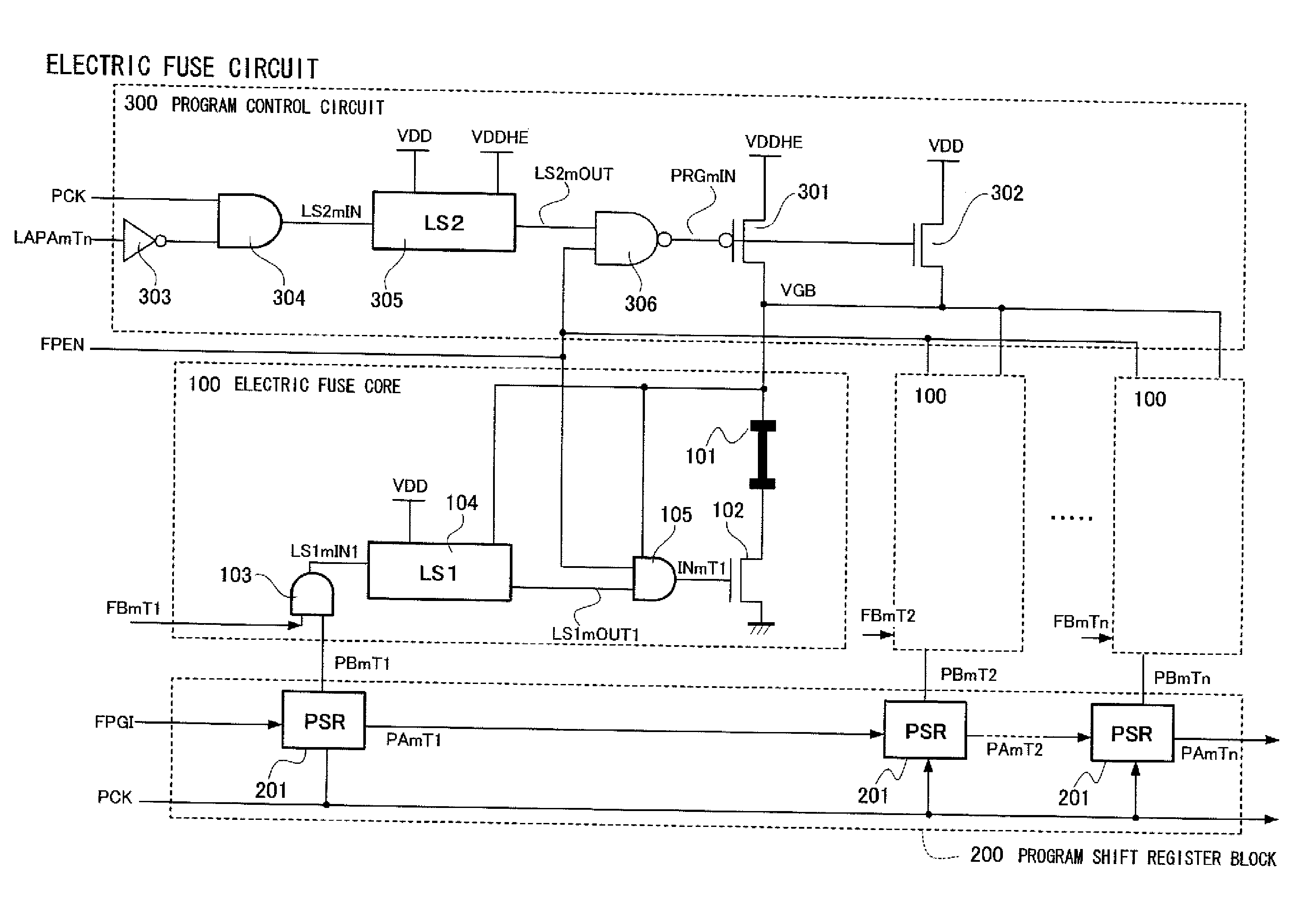
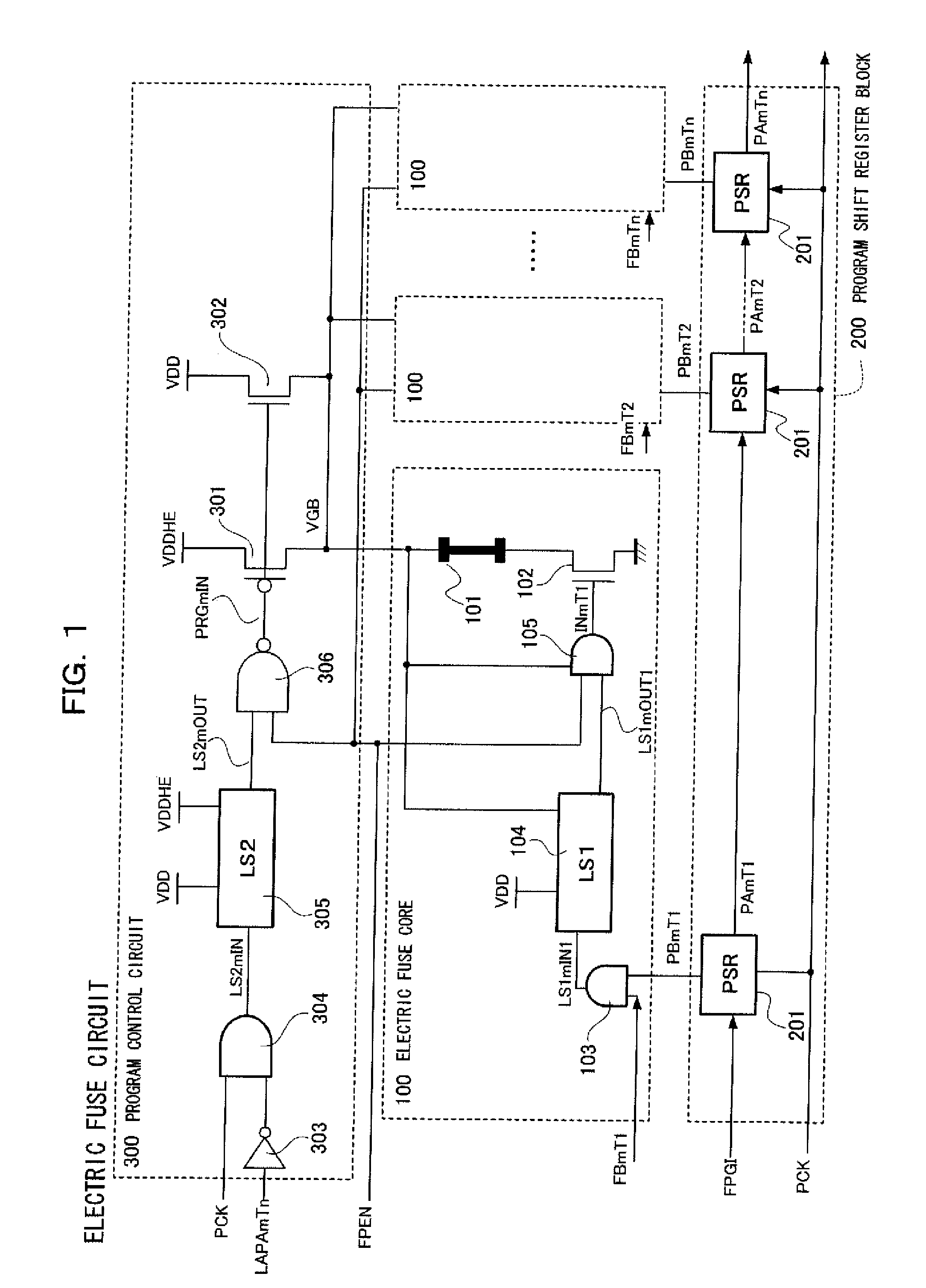
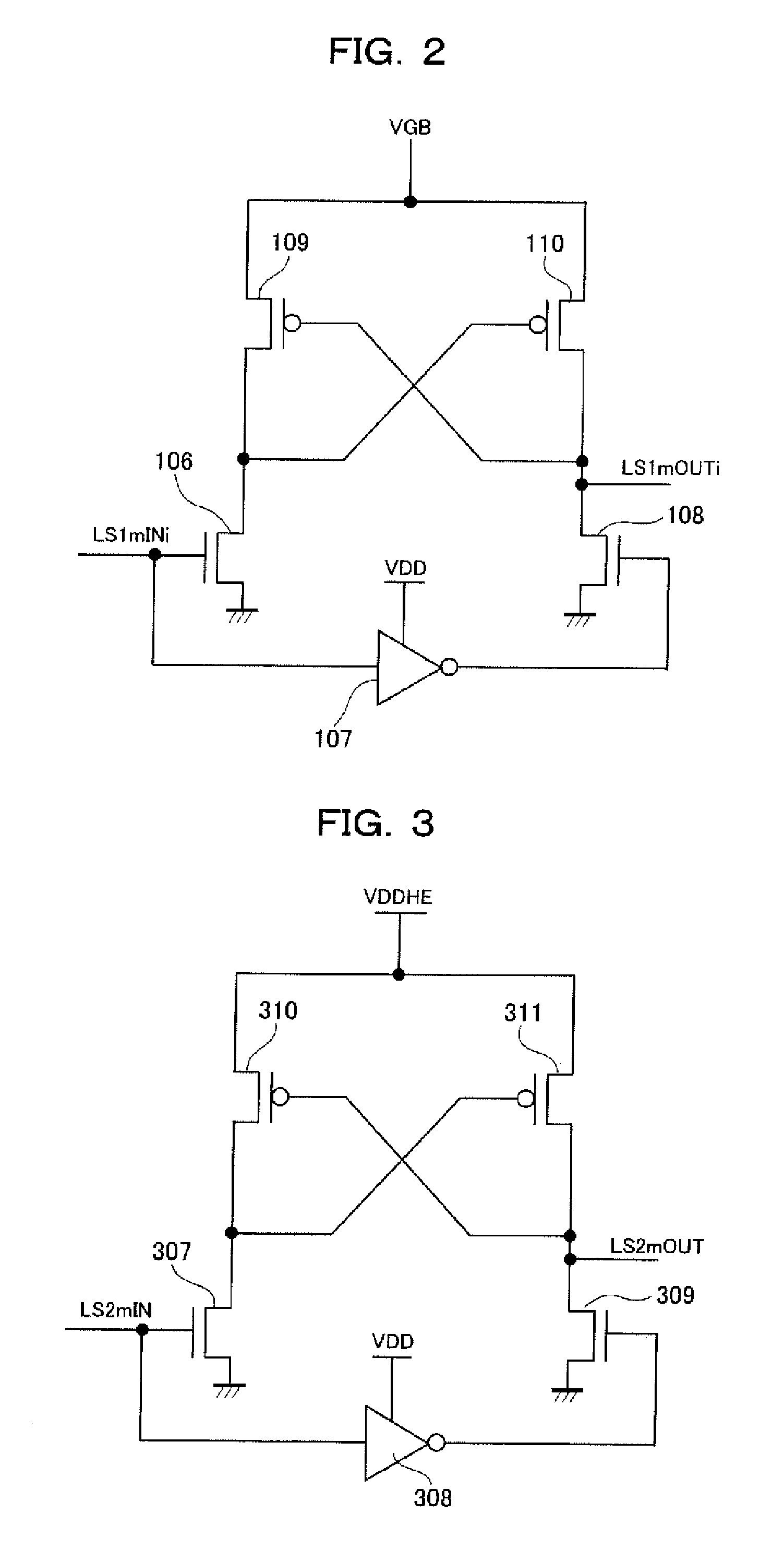
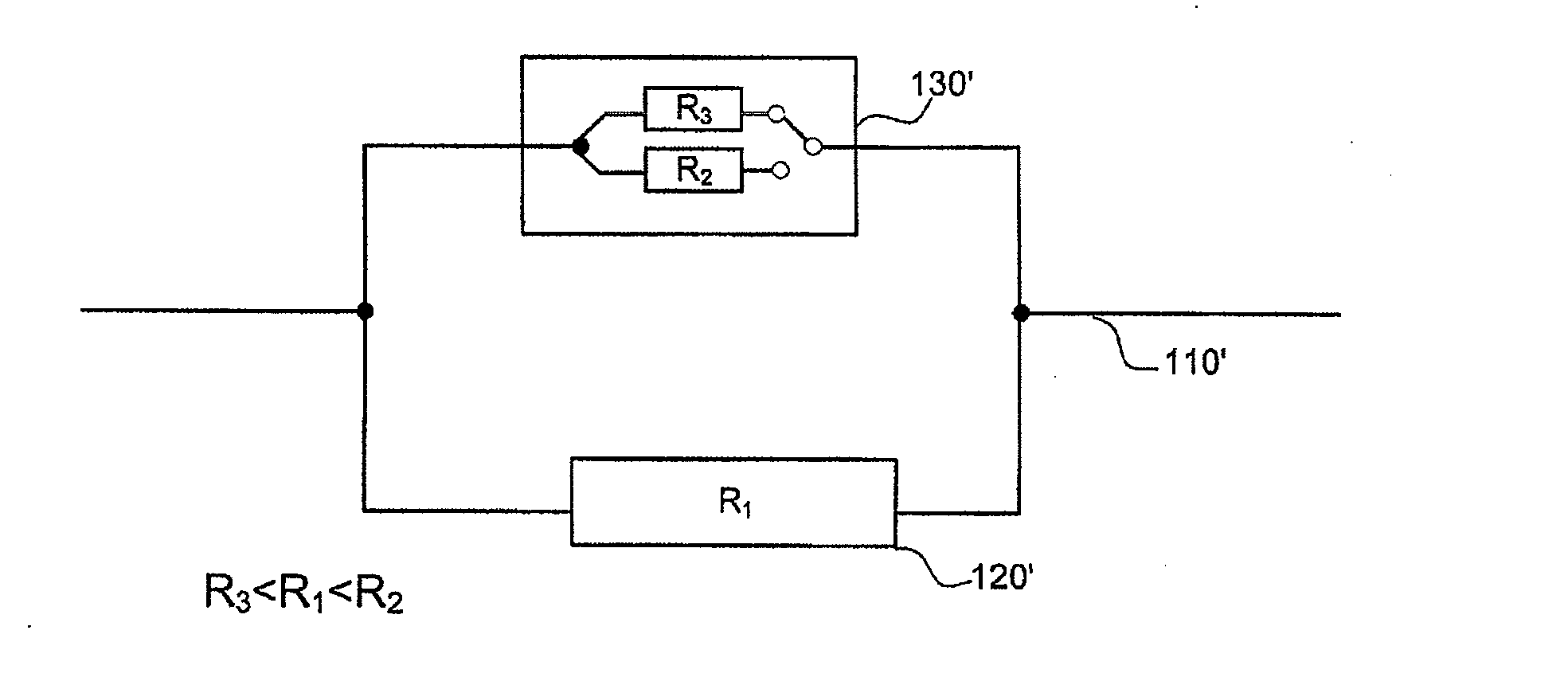
Patents
Literature
324 results about "Electric fuses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
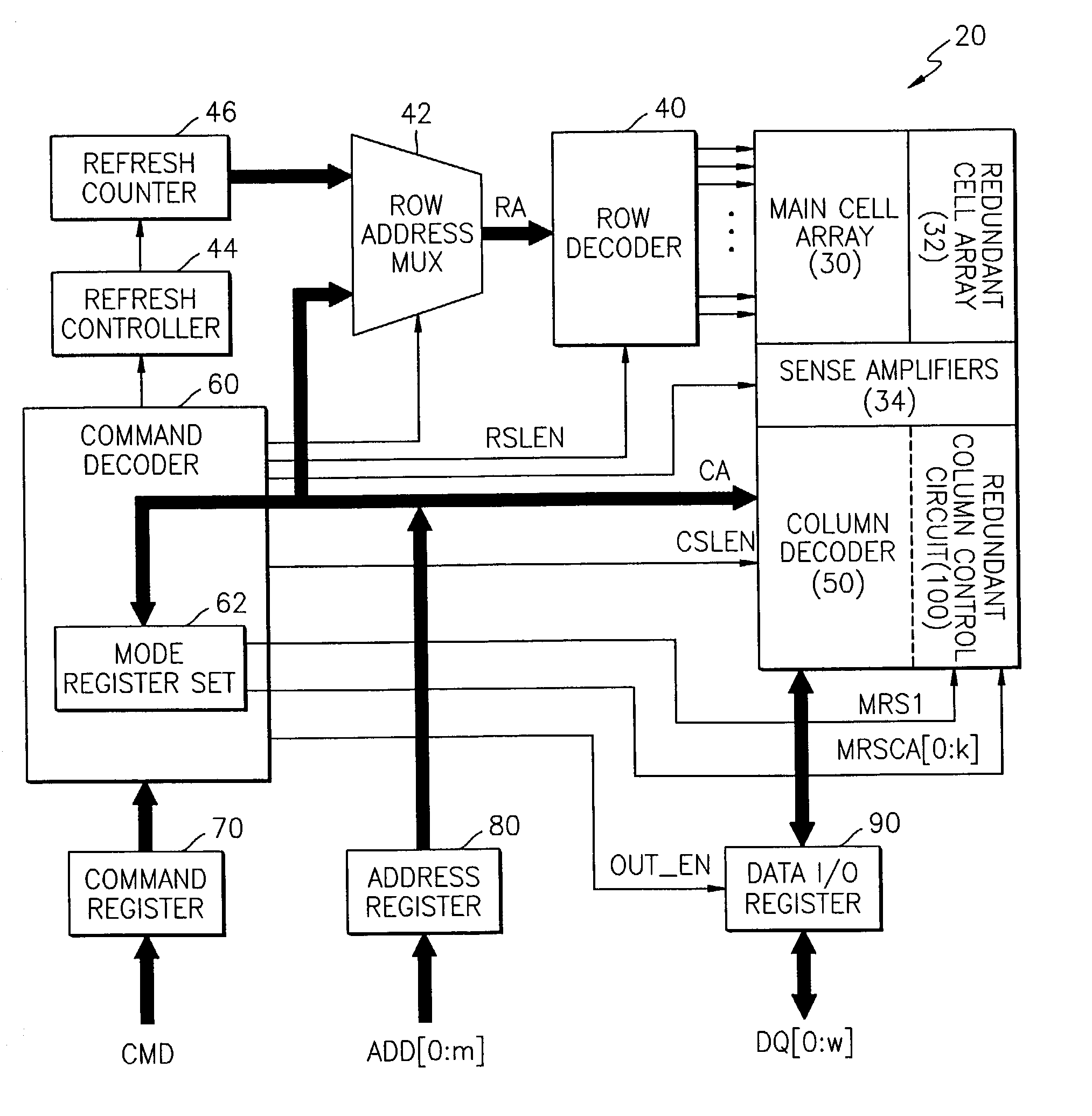
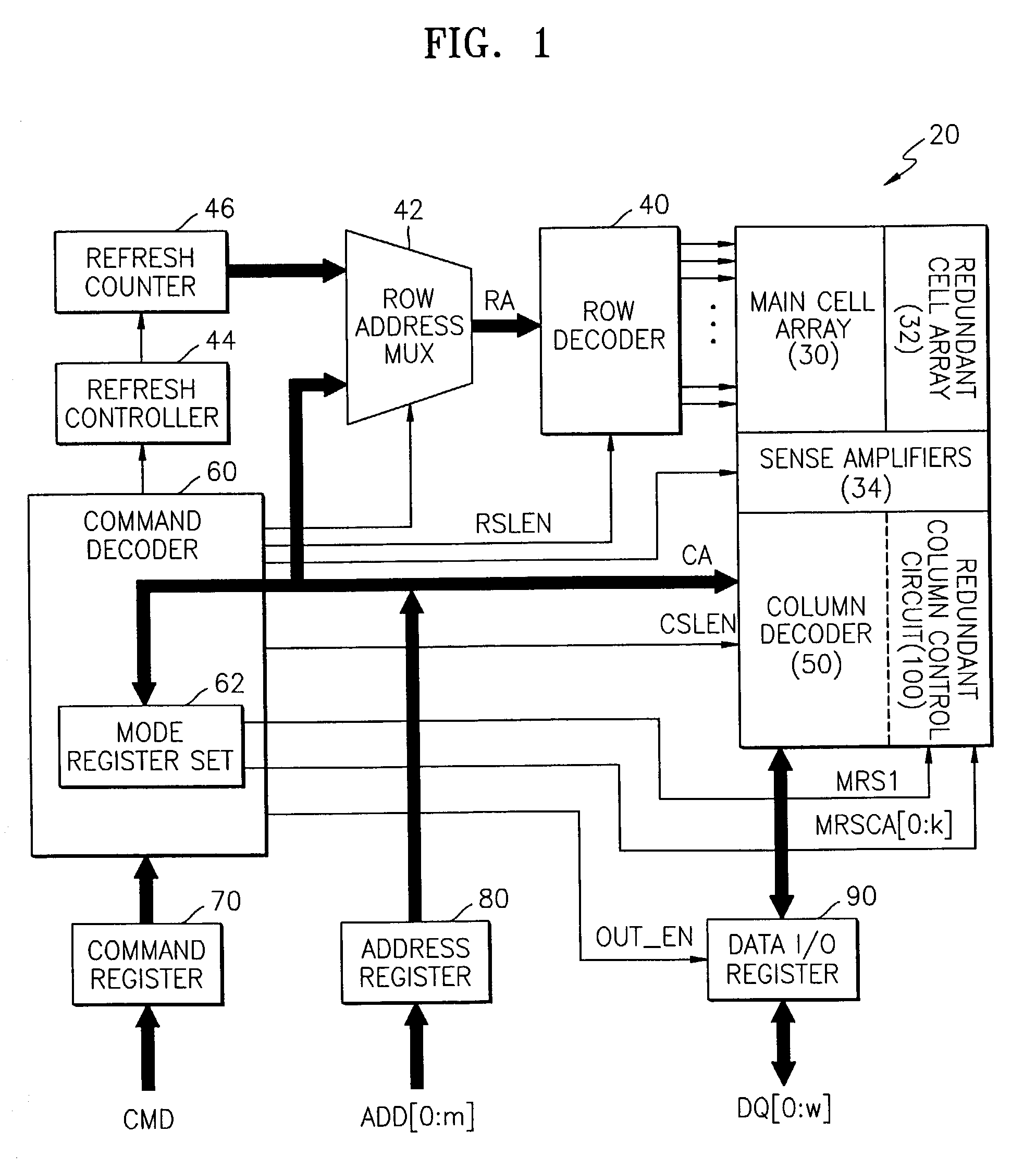
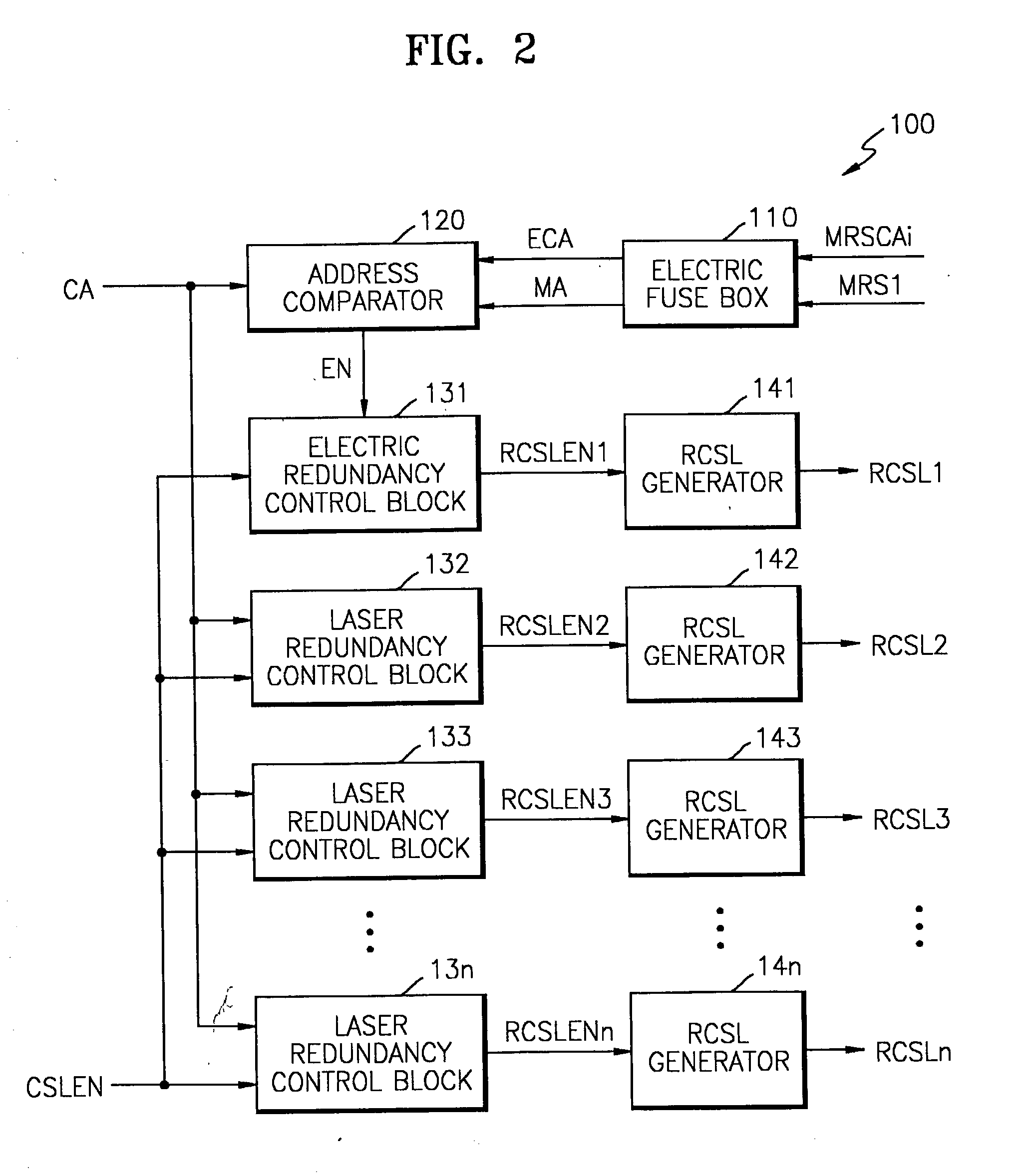
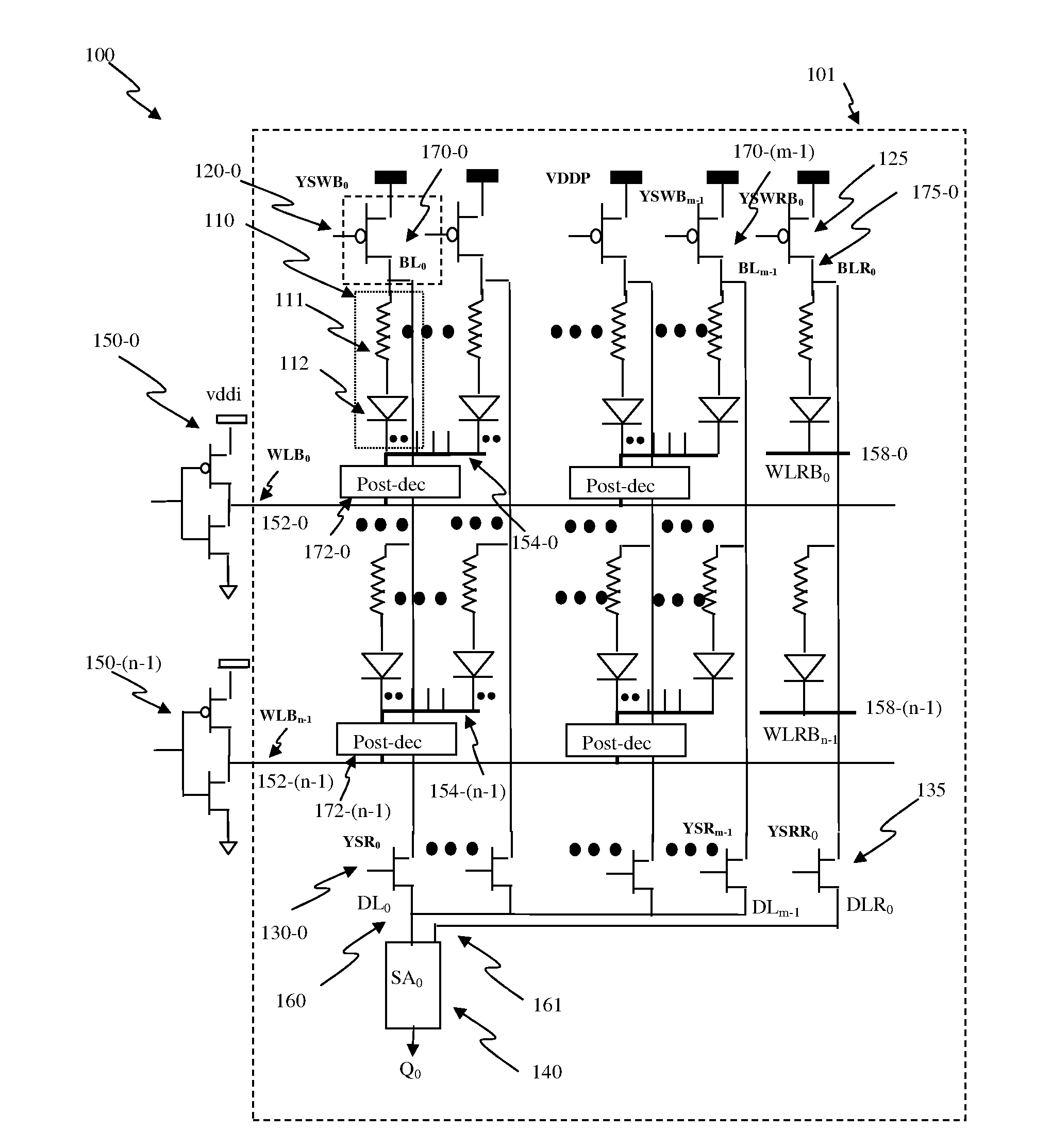
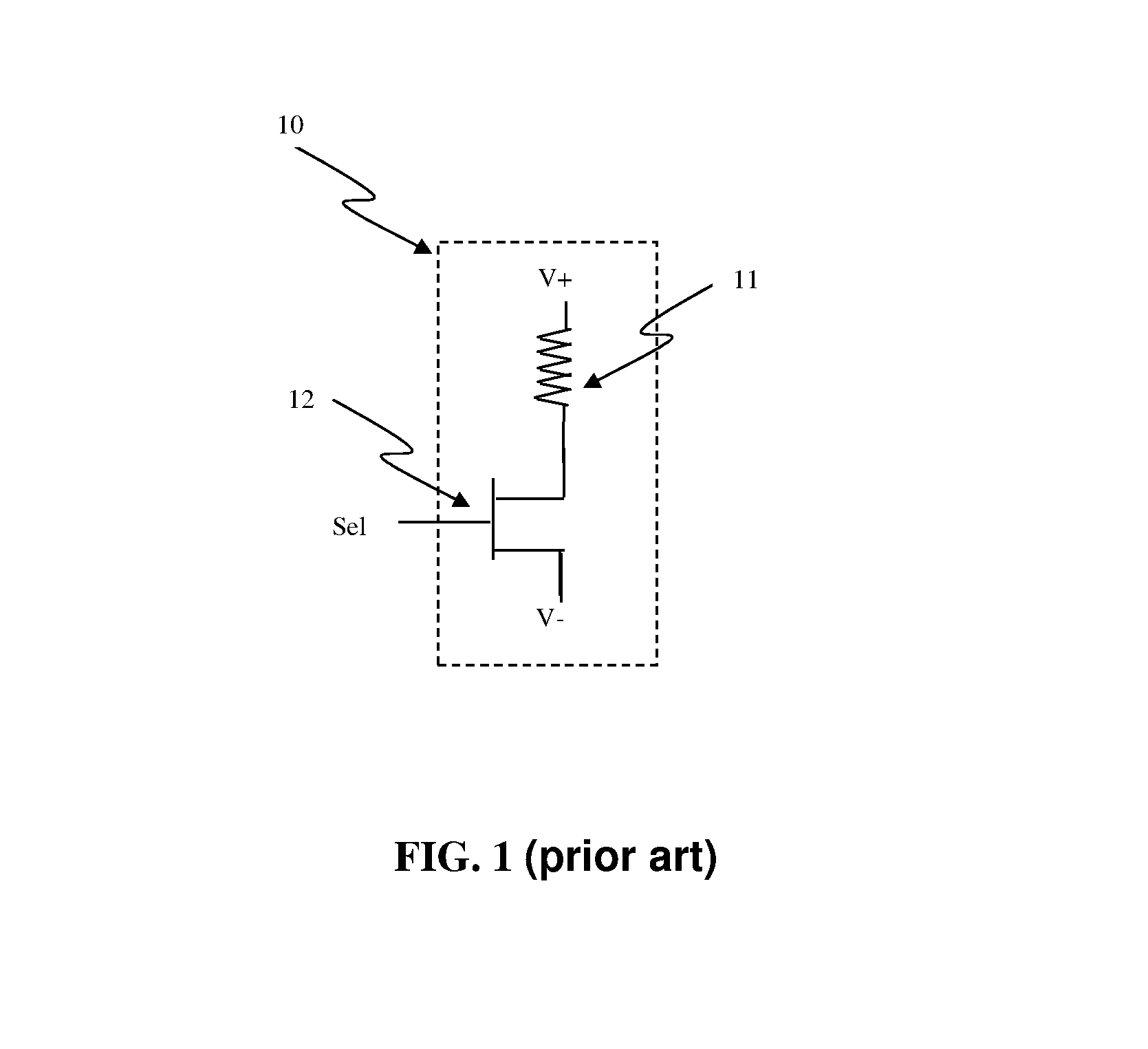
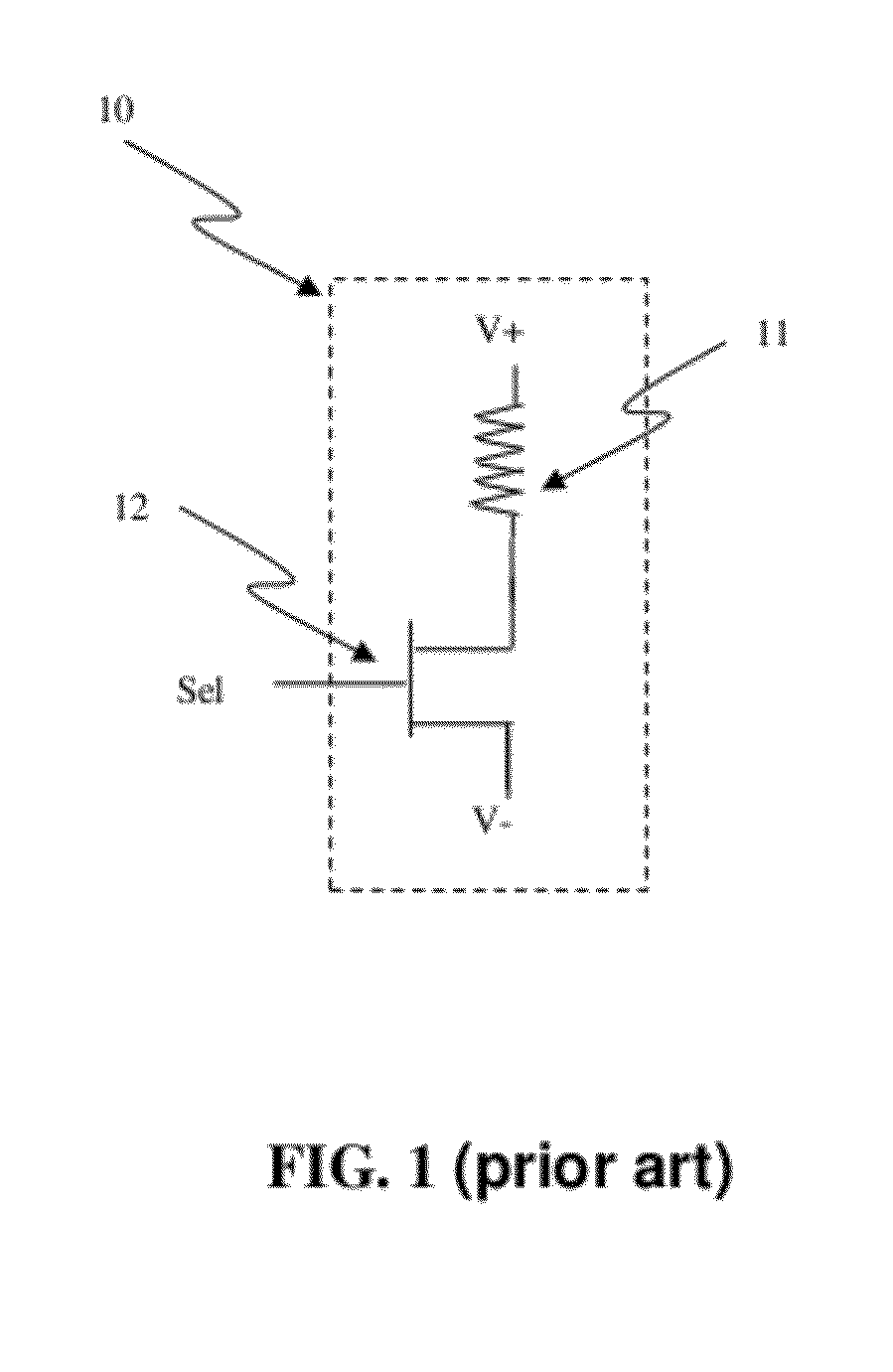
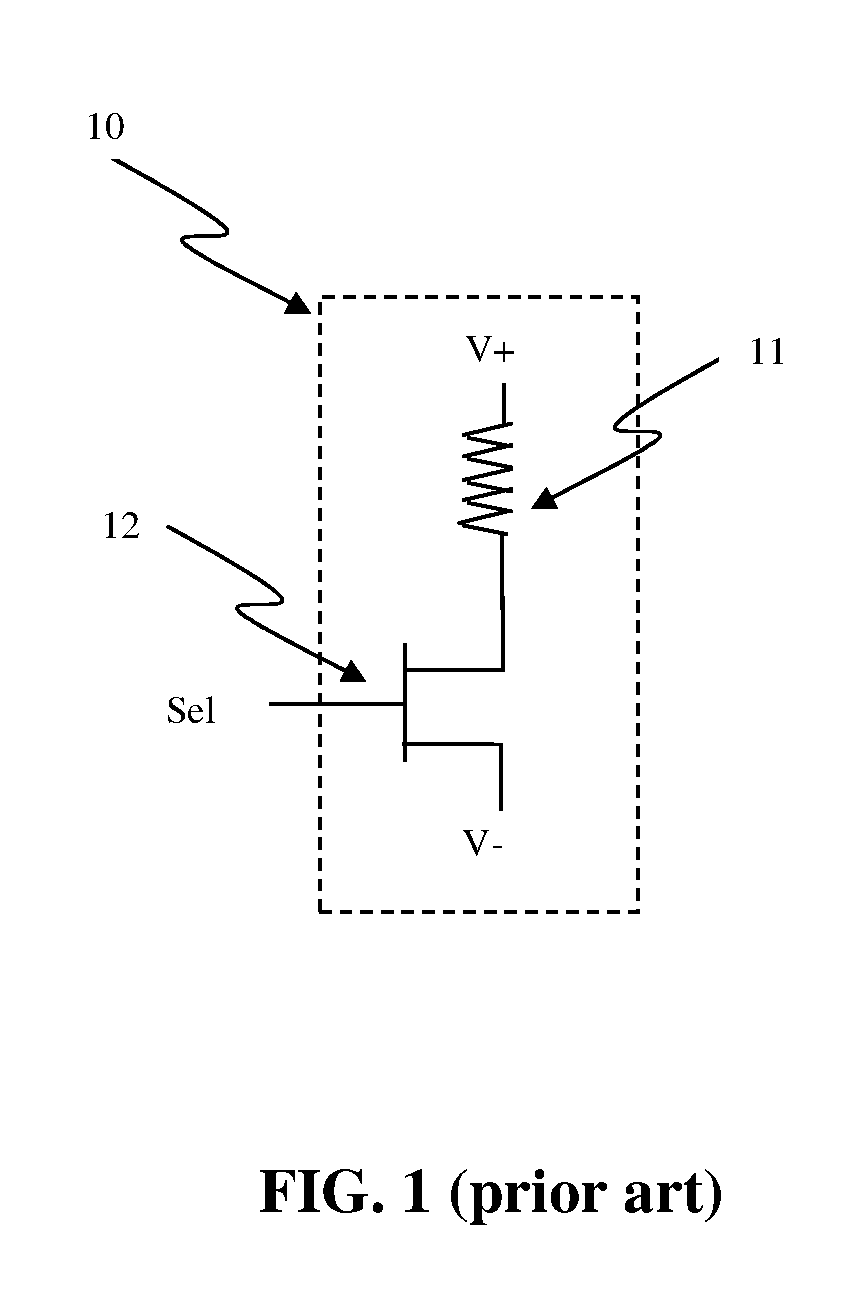
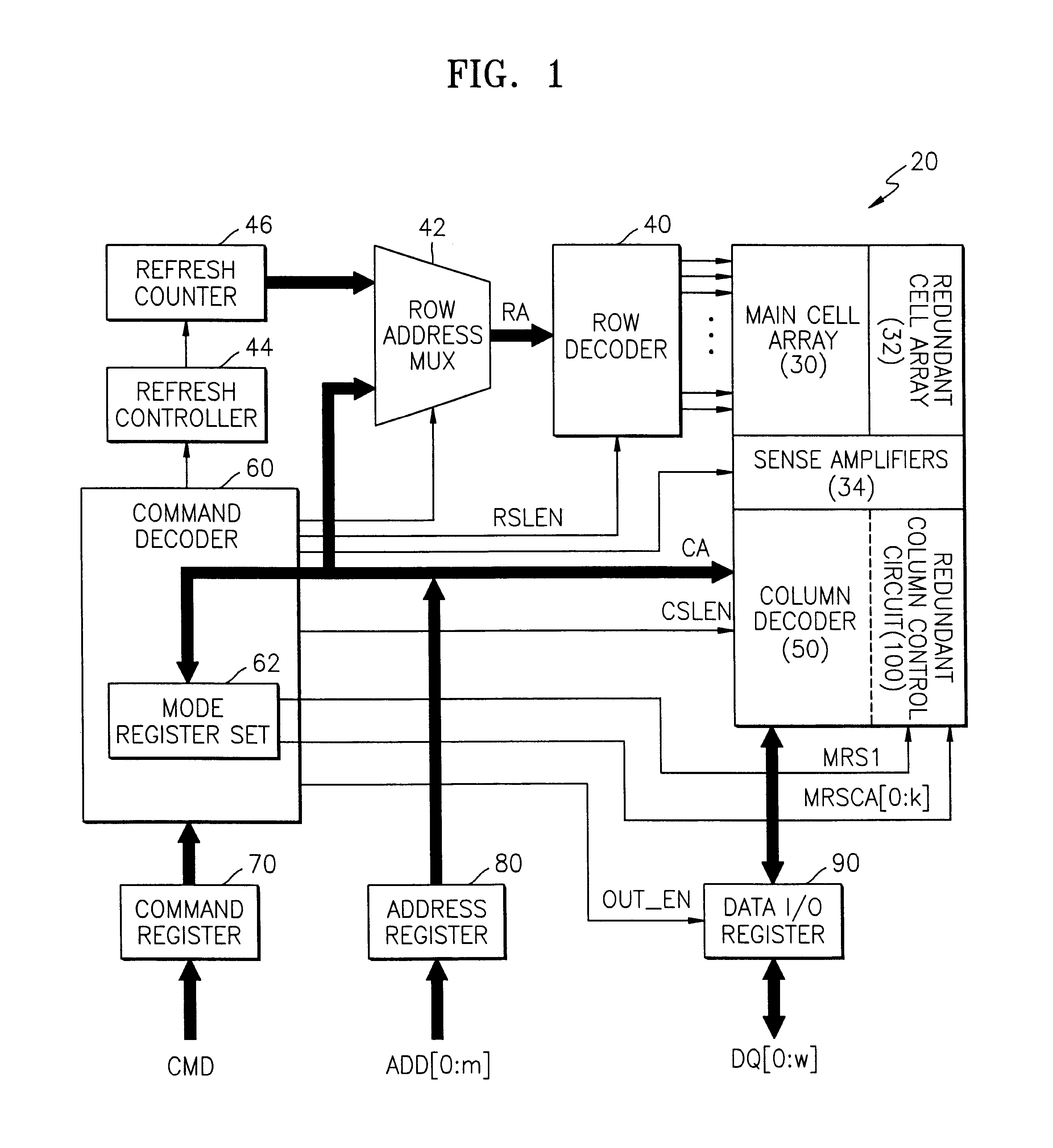
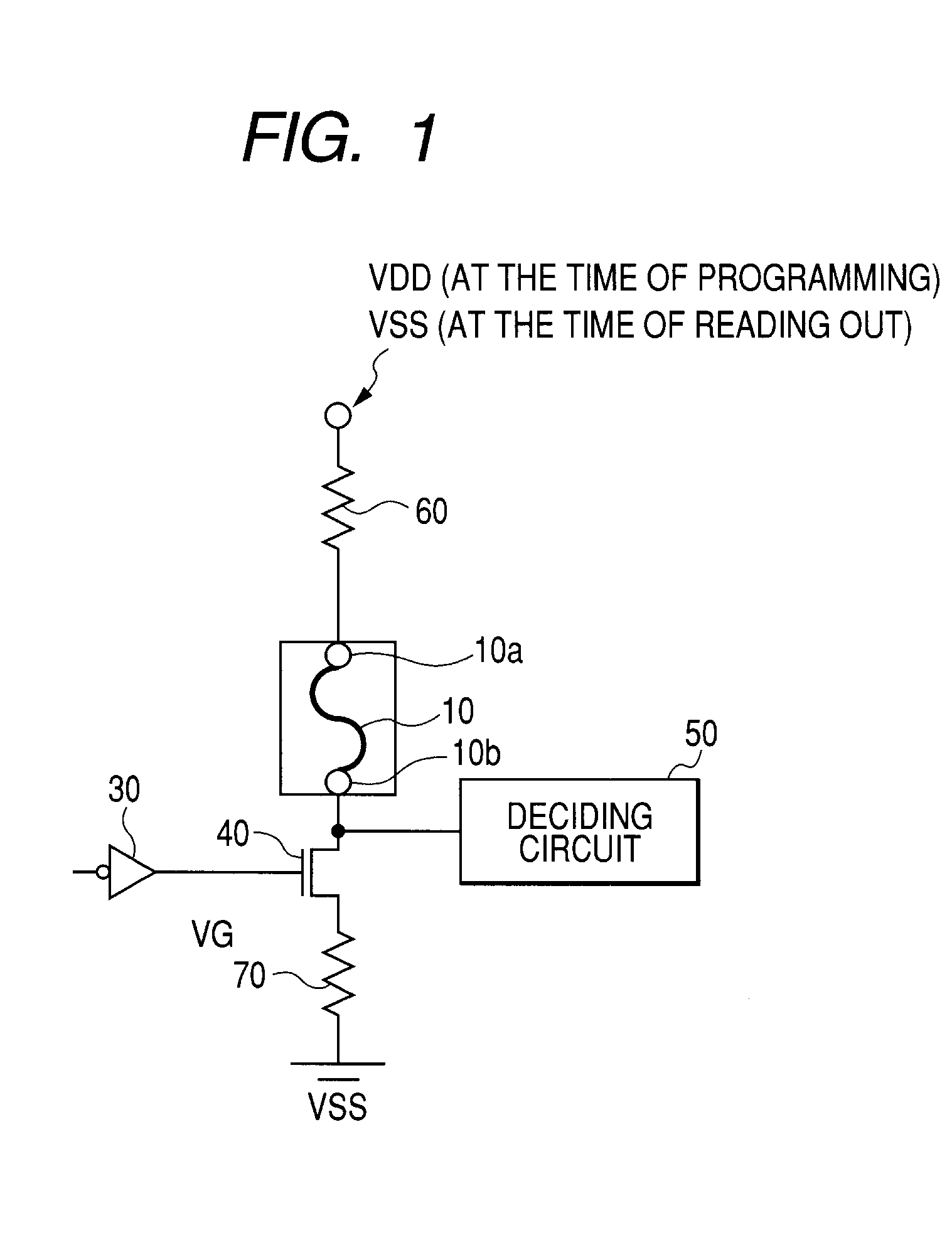
Semiconductor memory device post-repair circuit and method
The ability to repair defective cells in a memory array, by replacing those cells with redundant cells, is improved using a redundant memory line control circuit that employs two types of redundancy programming. Most, or all, redundant memory lines can be programmed while the memory array is in a wafer state by, e.g., cutting laser fuses. But at least one memory line can be programmed subsequent to device packaging ("post repair") using, e.g., commands that cut electric fuses. Preferably, the redundant memory line(s) that are reserved for post repair are selectable among the same redundant memory lines that can be programmed using laser fuses. This allows all redundant memory lines to be available for laser repair, if needed, but also allows a redundant memory line to be selected for post repair after it has been determined that that redundant memory line is defect-free. This increases the likelihood that a device will be repairable, and yet does not unnecessarily waste redundant memory lines by pre-dedicating them to laser or post repair.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
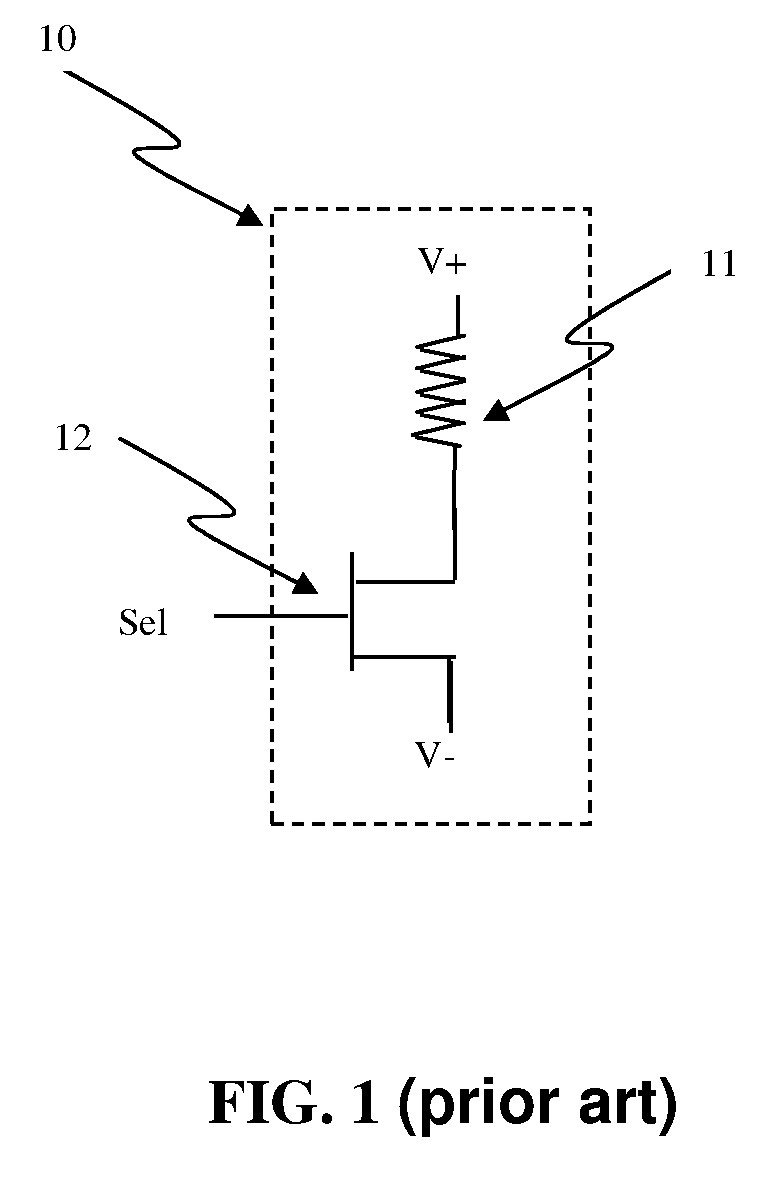
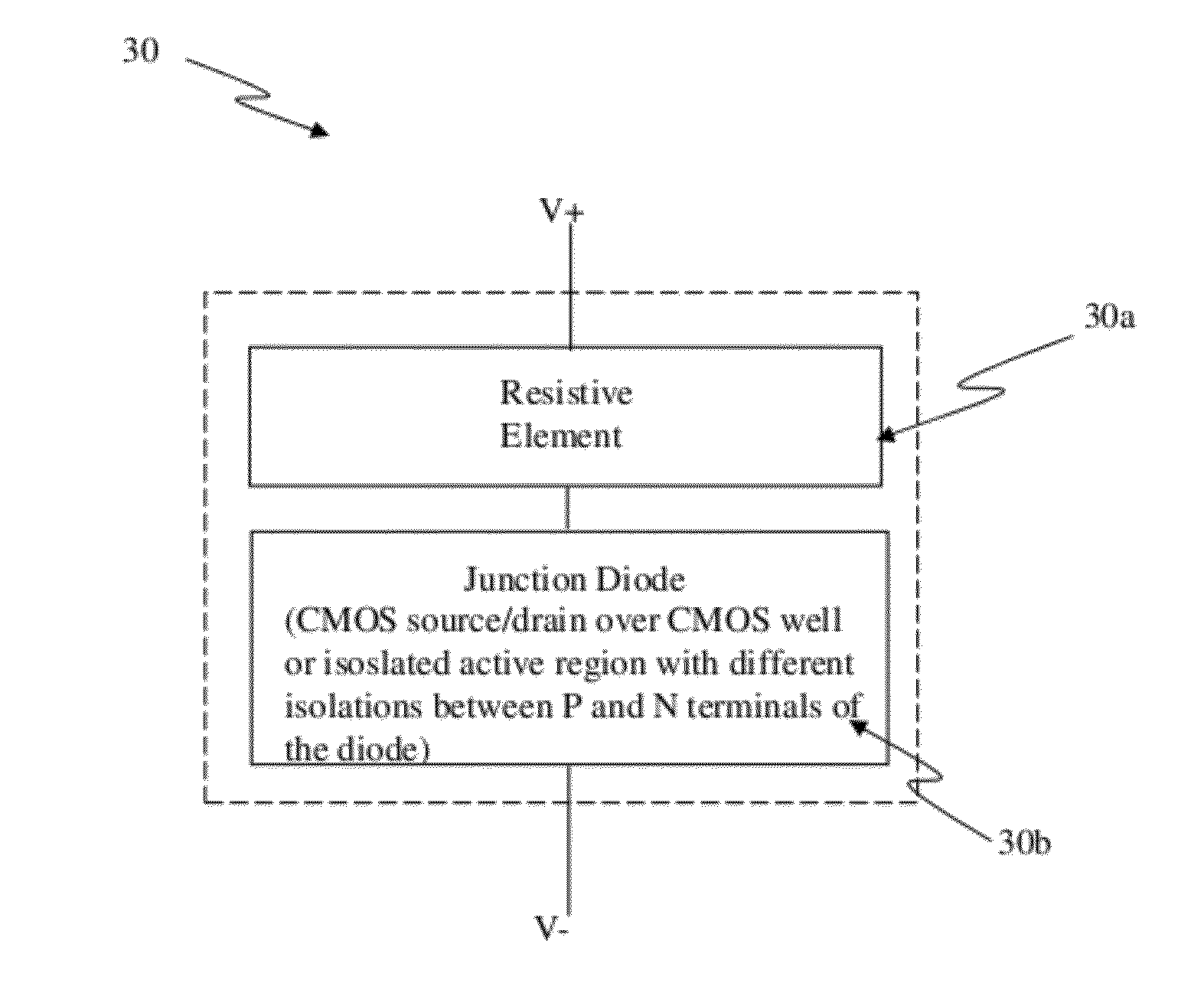
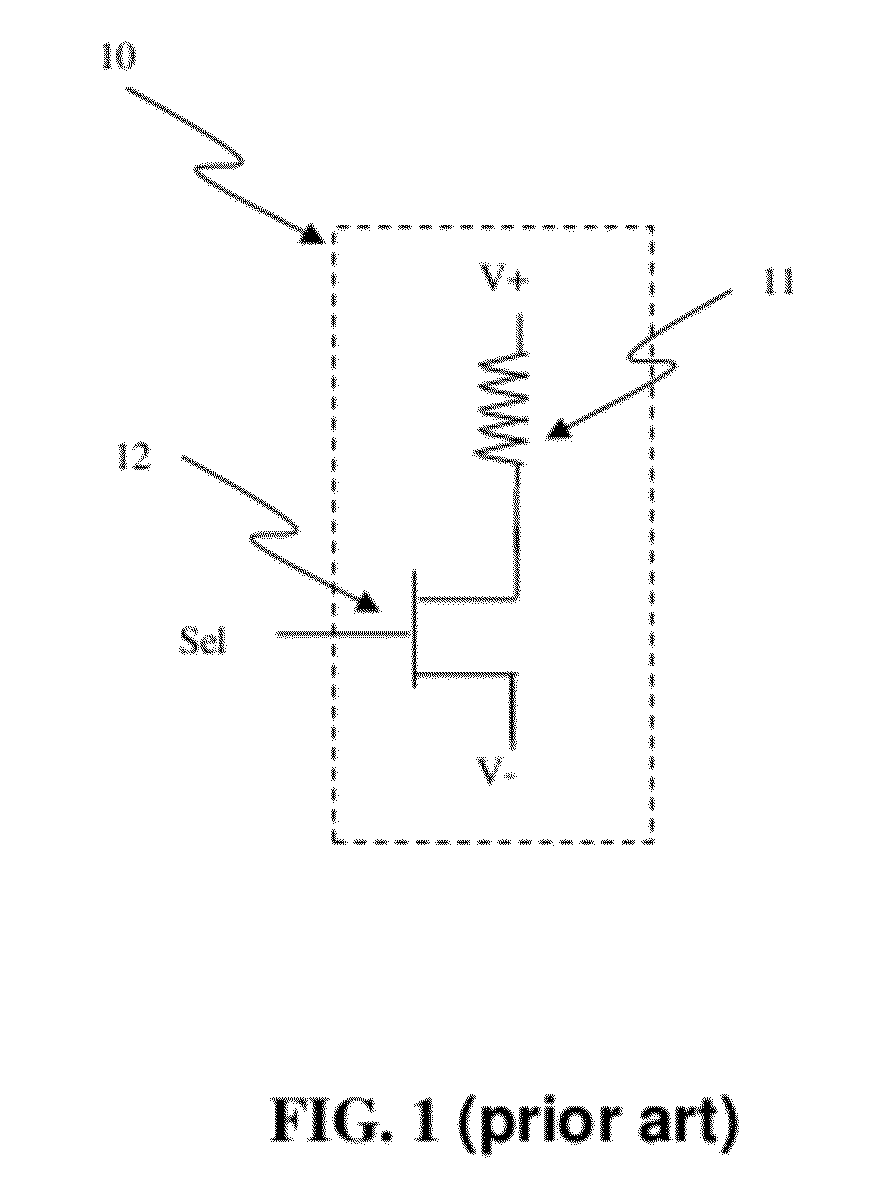
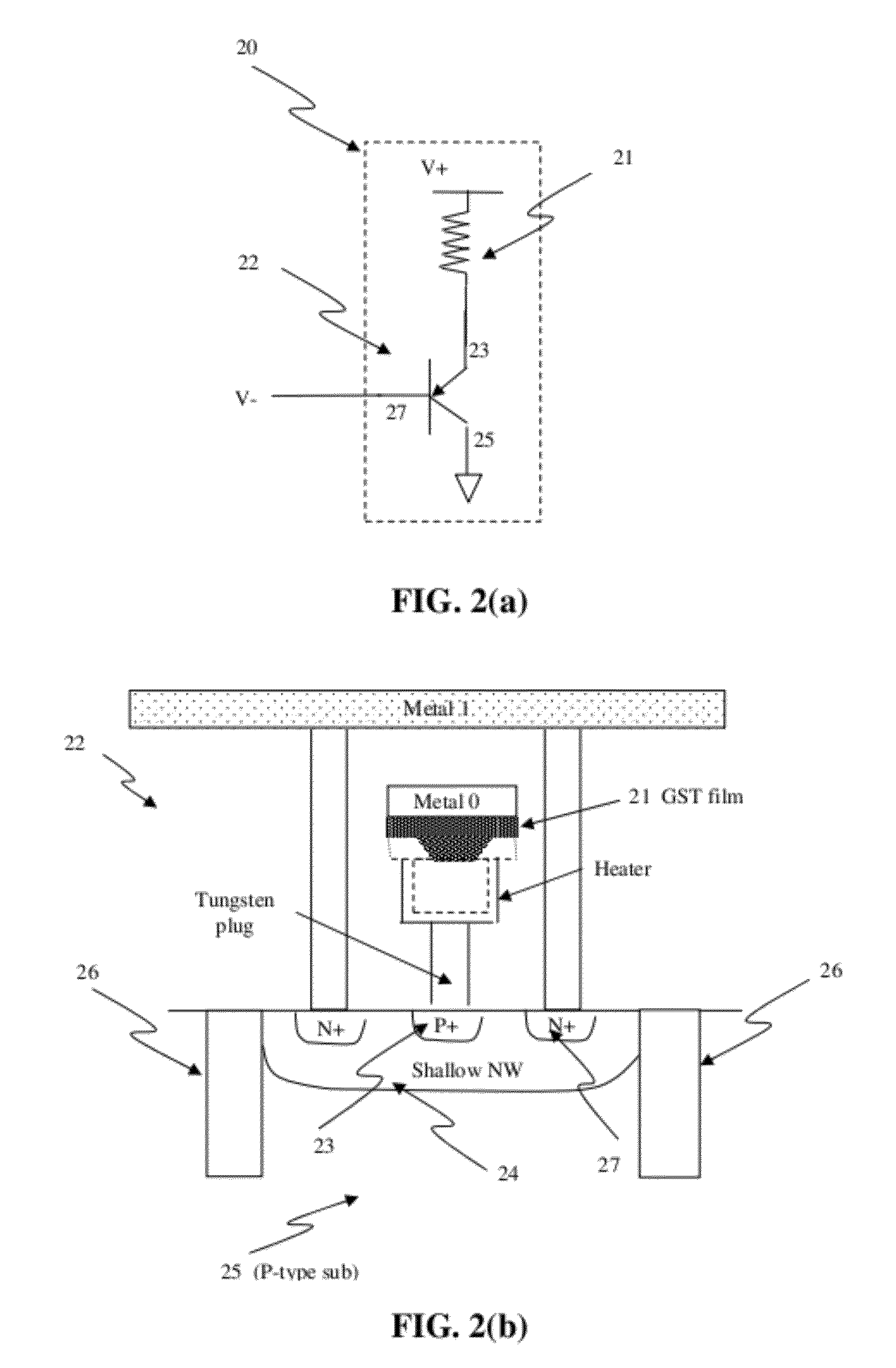
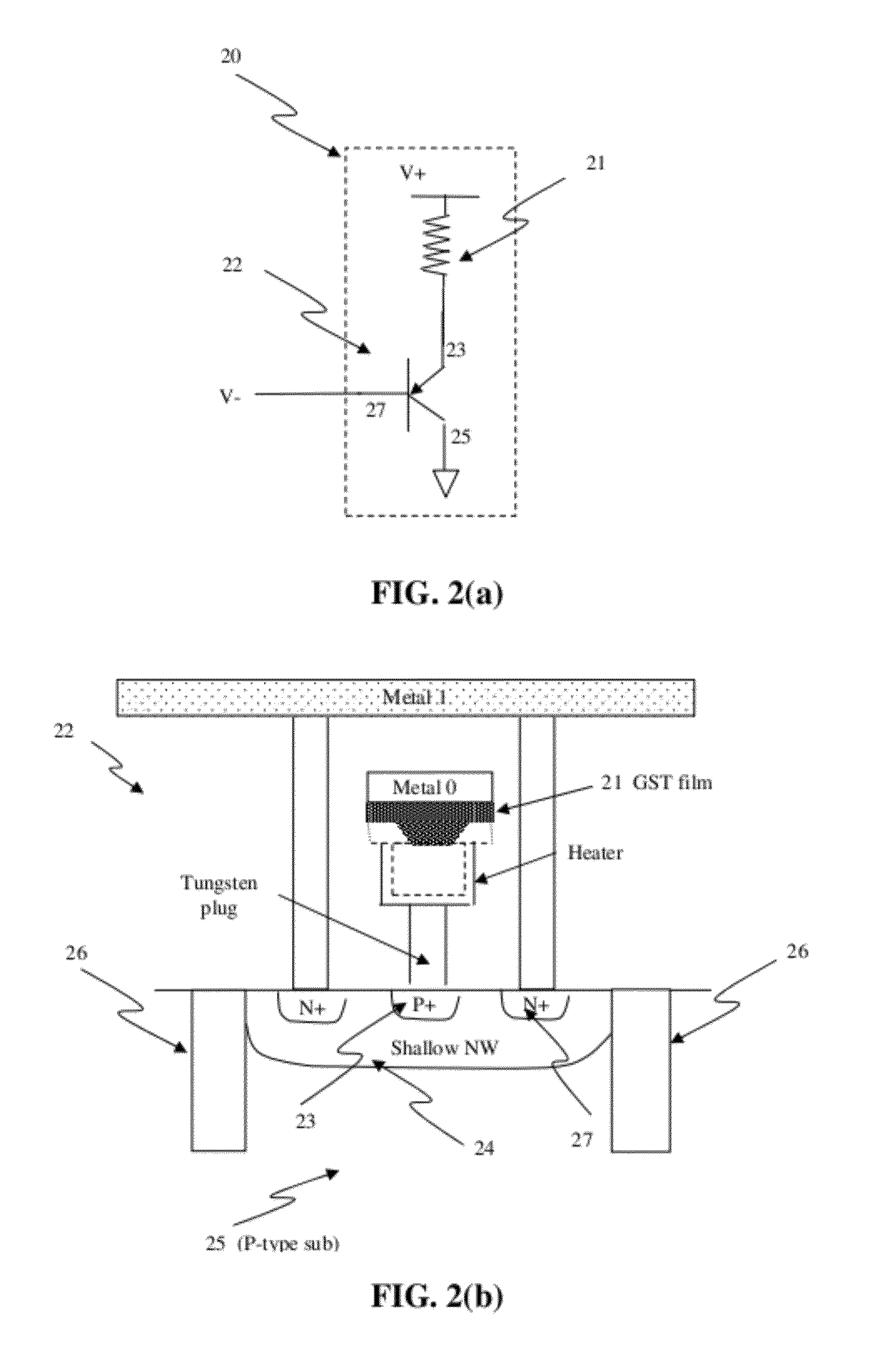
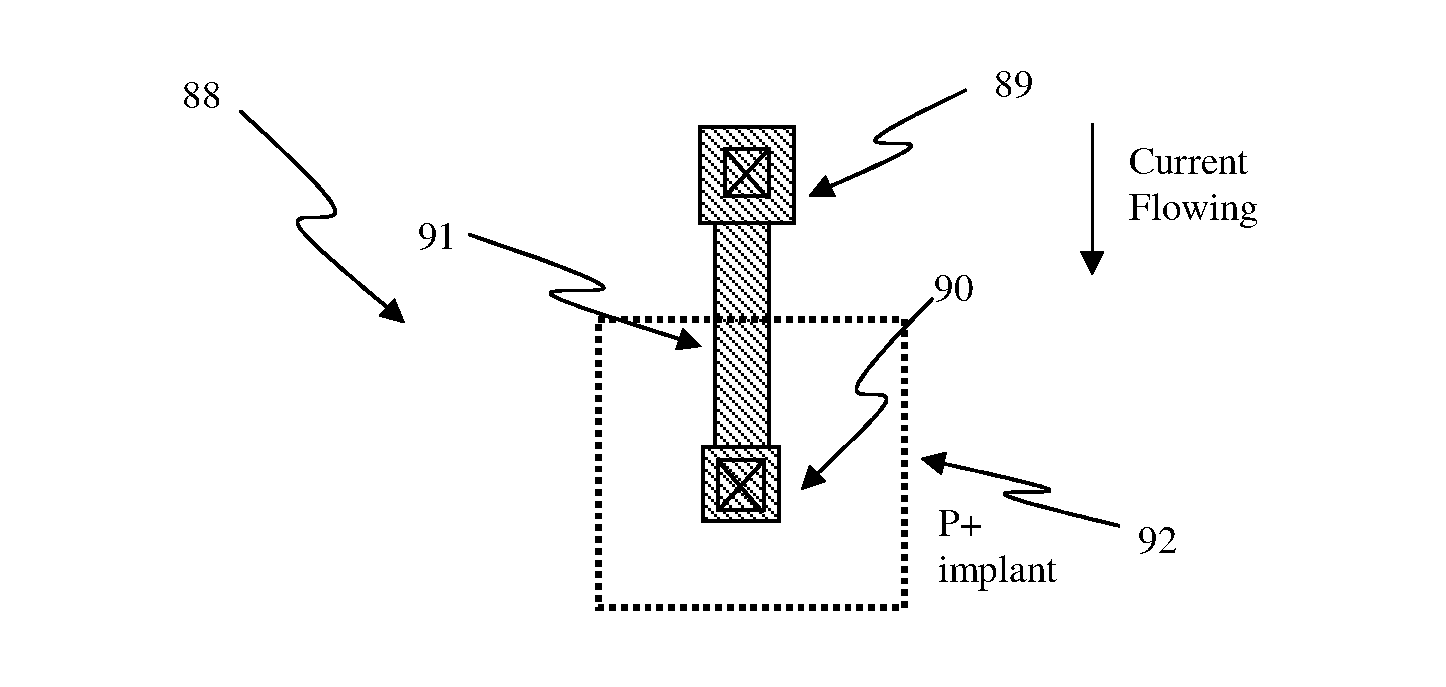
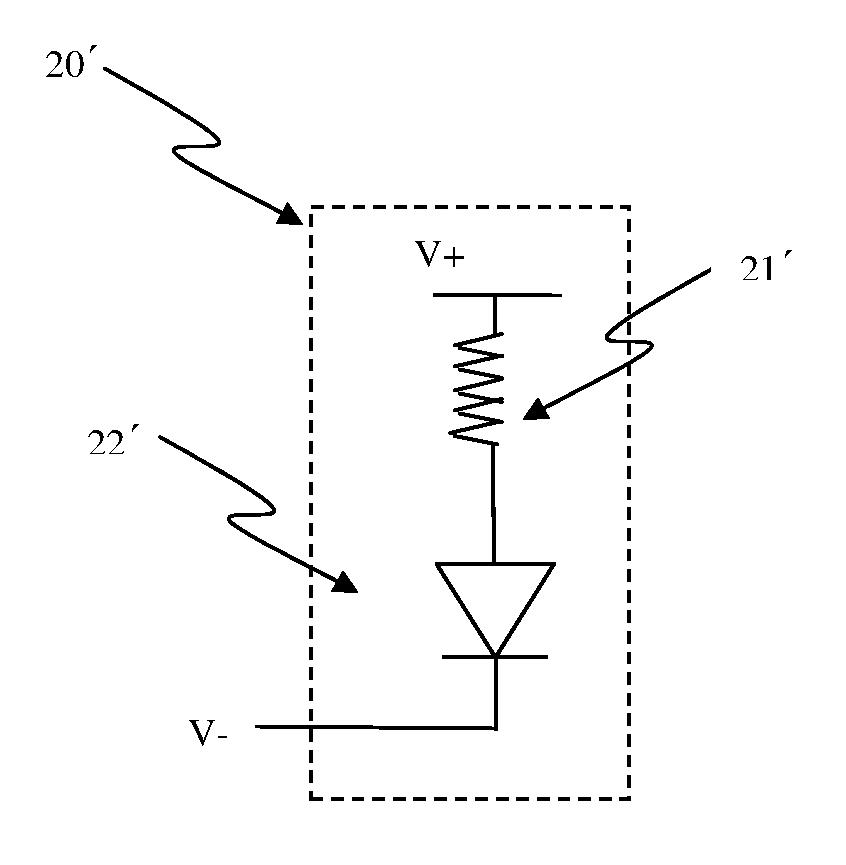
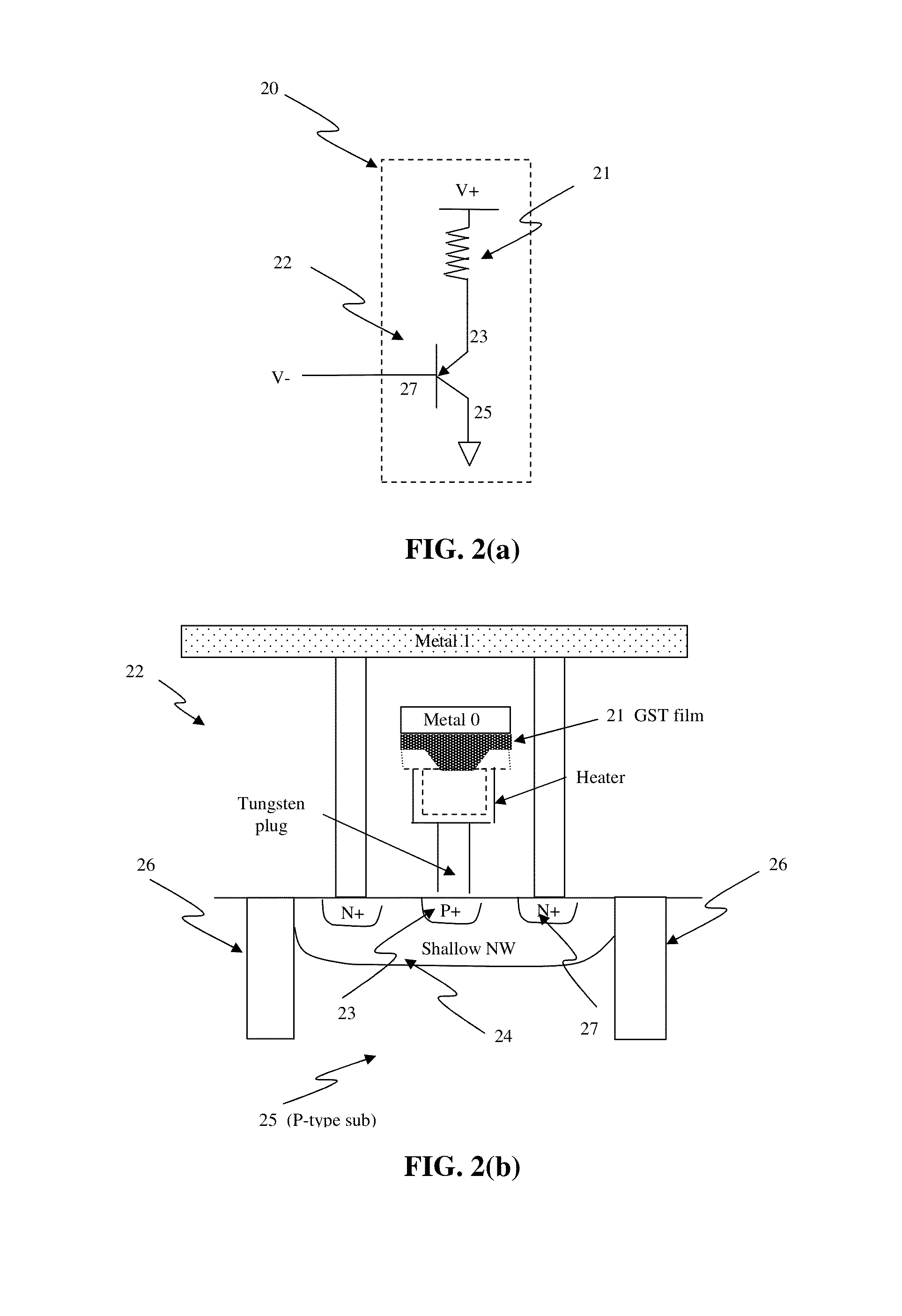
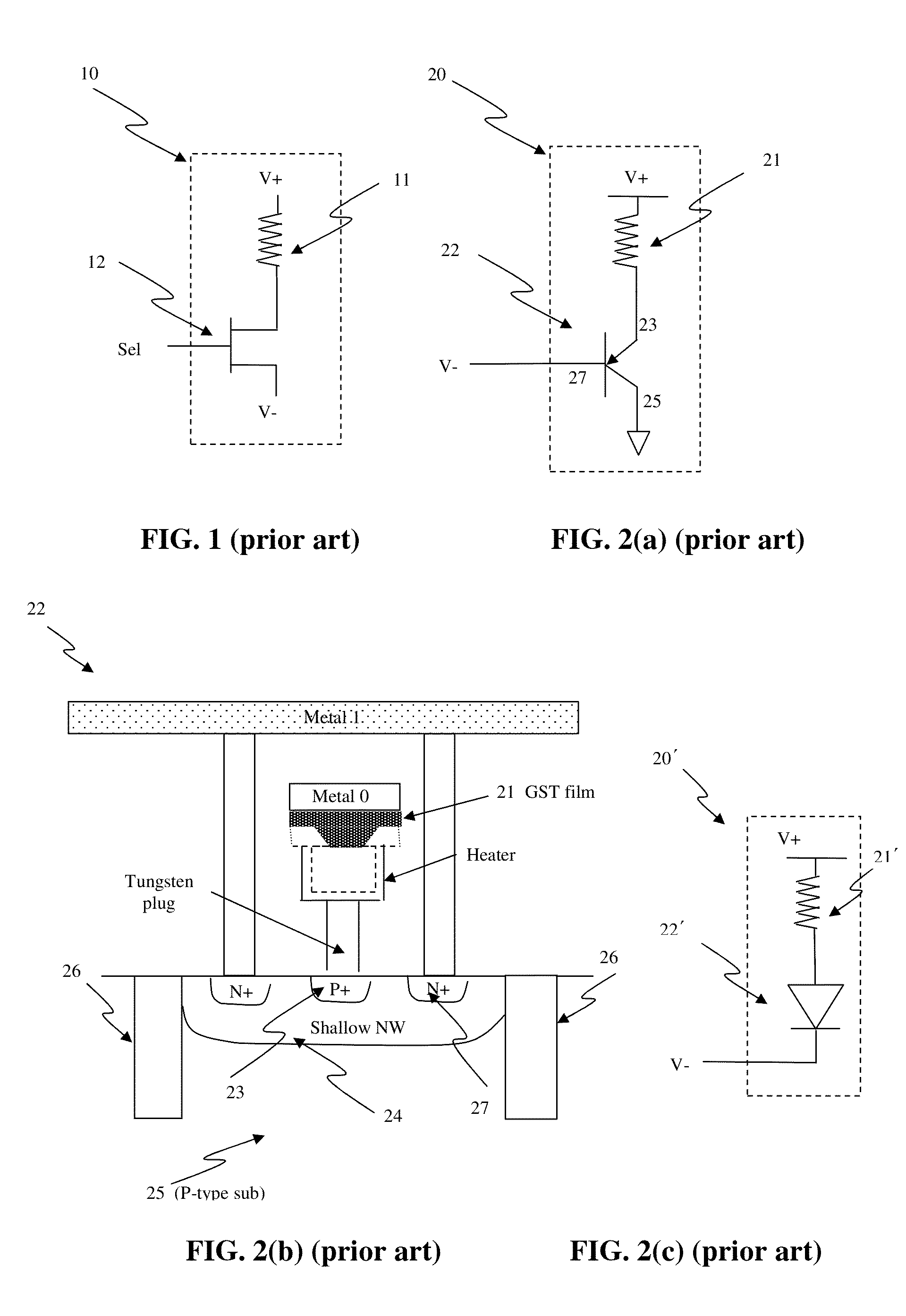
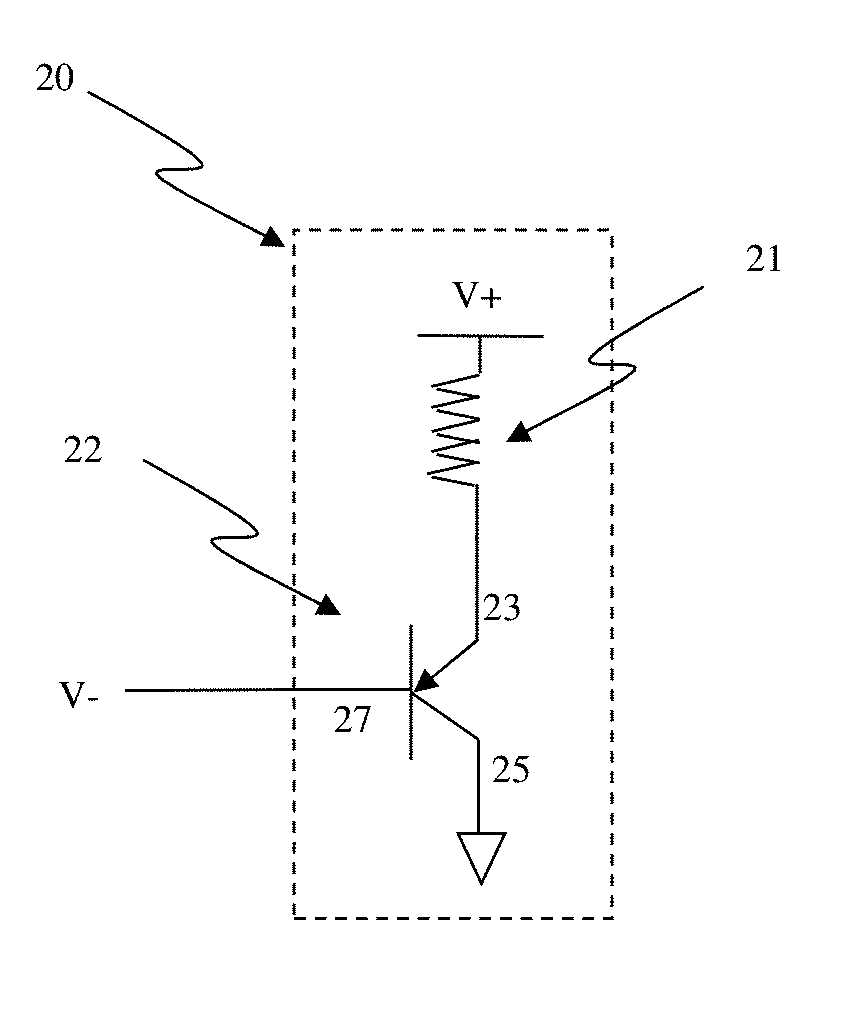
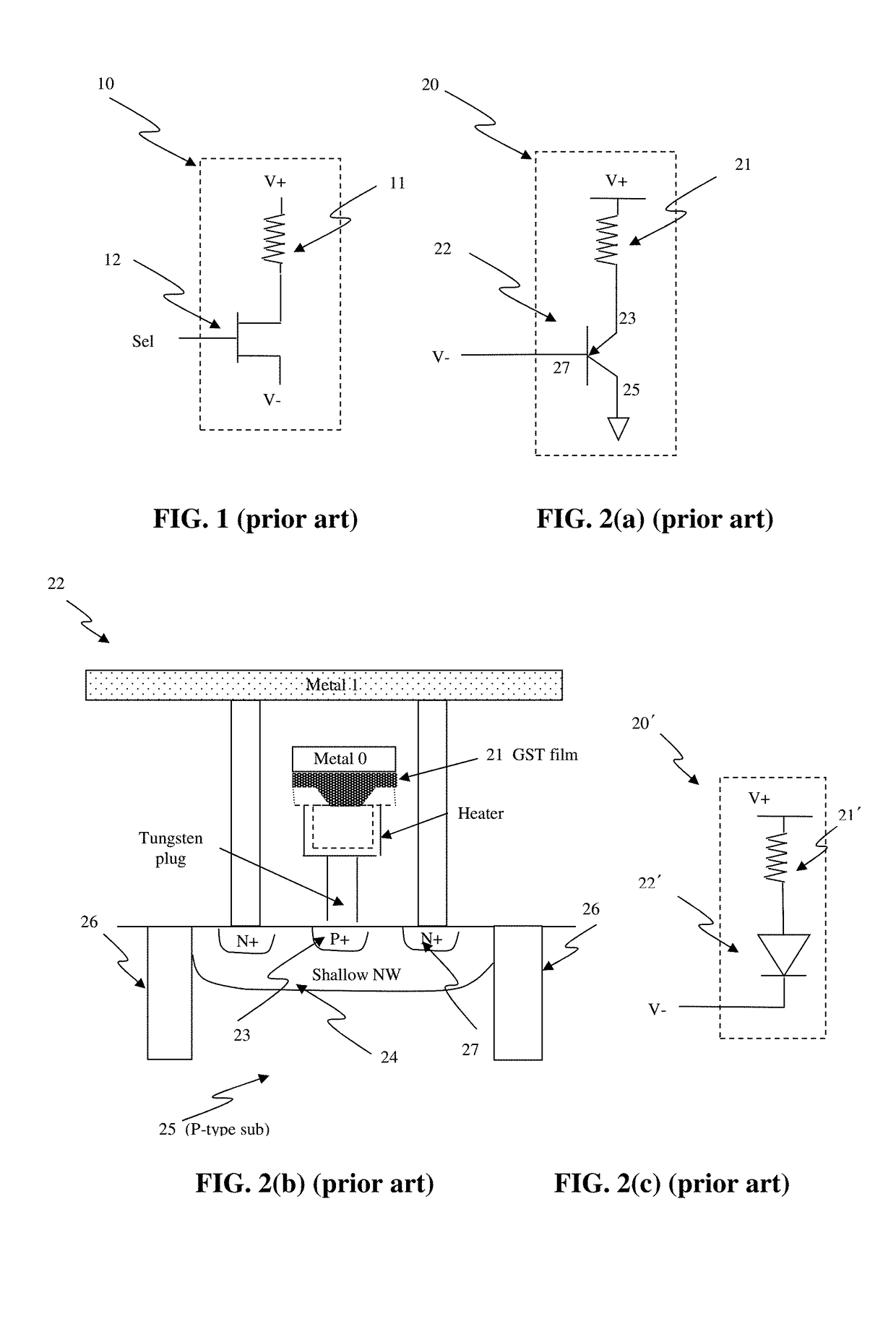
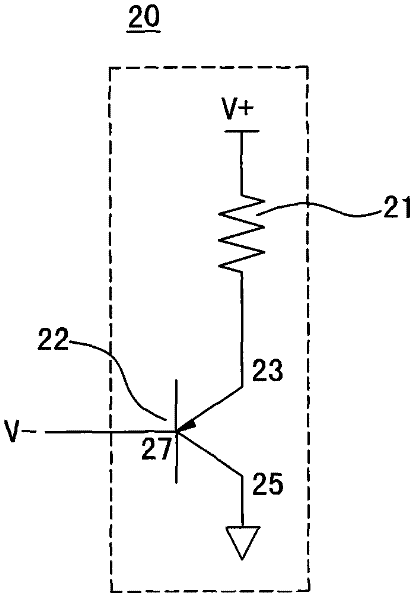
Circuit and system of using a junction diode as program selector for resistive devices
ActiveUS20120044746A1Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic technologies can be used as program selectors for a programmable resistive device, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for proper duration of time, a current flows through a resistive element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal can be connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
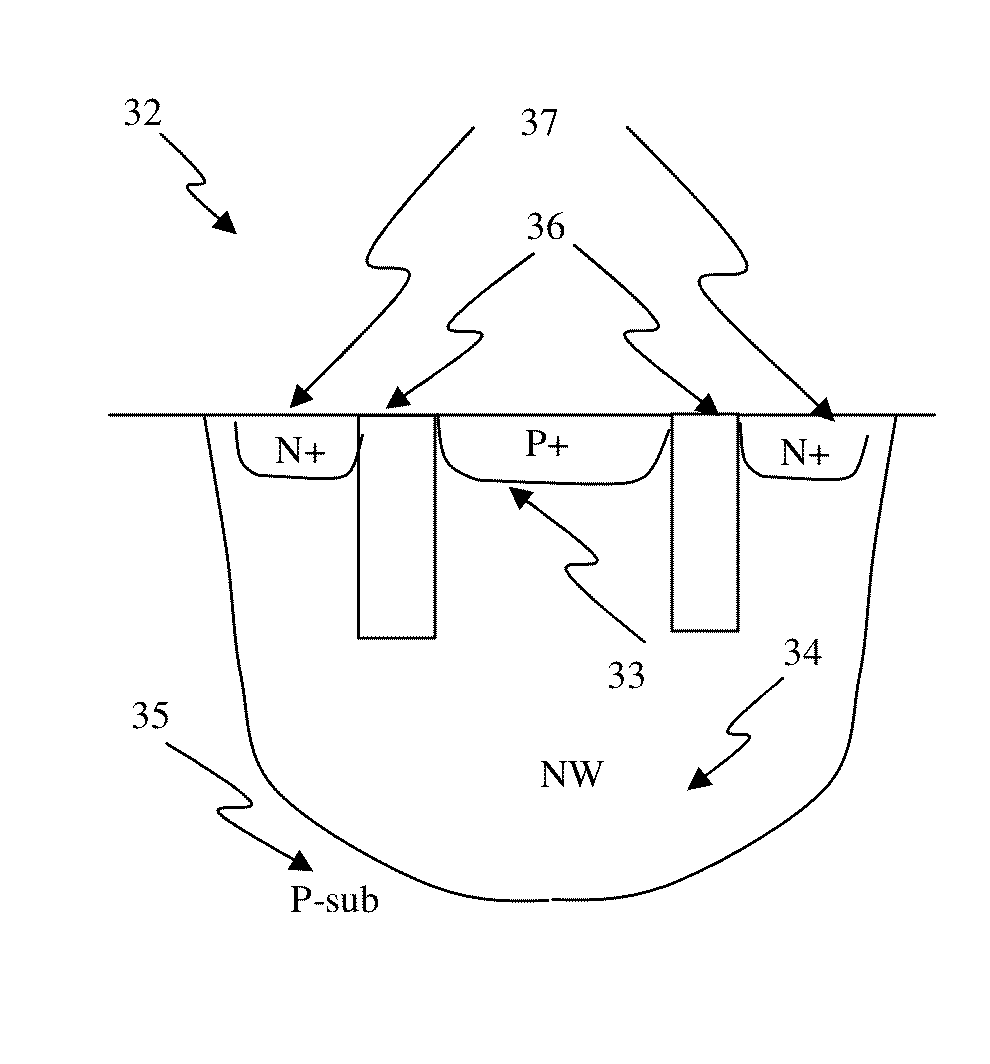
Circuit and System of Using Junction Diode as Program Selector for One-Time Programmable Devices
ActiveUS20120224406A1Small cell sizeLow costMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044739A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal are connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using polysilicon diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044737A1Avoid shortingSave extra spaceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesLow voltageHemt circuits
Polysilicon diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ / N+ implants on a polysilicon as a program selector. By applying a high voltage to an OTP element coupled to the P-terminal of a diode and switching the N-terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through the OTP element may change the resistance state. On the polysilicon diode, the spacing and doping level of a gap between the P- and N-implants can be controlled for different breakdown voltages and leakage currents. The Silicide Block Layer (SBL) can be used to block silicide formation on the top of polysilicon to prevent shorting. If the OTP element is a polysilicon electrical fuse, the fuse element can be merged with the polysilicon diode in one piece to save area.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using a polysilicon diode as program selector for resistive devices in CMOS logic processes
ActiveUS20120044743A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesLow voltageEngineering
Polysilicon diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic technologies can be used as program selectors for a programmable resistive device, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The diode can be constructed by P+ / N+ implants on a polysilicon as a program selector. By applying a high voltage to a resistive element coupled to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for proper time, a current flows through a resistive element may change the resistance state. On the polysilicon diode, the spacing and doping level of a gap between the P+ and N+ implants can be controlled for different breakdown voltages and leakage currents. The Silicide Block Layer (SBL) can be used to block silicide formation on the top of polysilicon to prevent shorting. If the resistive element is a polysilicon electrical fuse, the fuse element can be merged with the polysilicon diode in one piece to save area.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
One-time programmable memories using junction diodes as program selectors
ActiveUS20120044740A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to the diode. The OTP device can be used to construct a two-dimensional OTP memory with the N terminals of the diodes in a row connected as a wordline and the OTP elements in a column connected as a bitline. By applying a high voltage between a selected bitline and a selected wordline to turn on a diode in a selected cell for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The cell data in the OTP memory can also be read by turning on a selected wordline and to couple a selected bitline to a sense amplifier. The wordlines may have high-resistivity local wordlines coupled to low-resistivity global wordlines through conductive contact(s) or via(s).
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
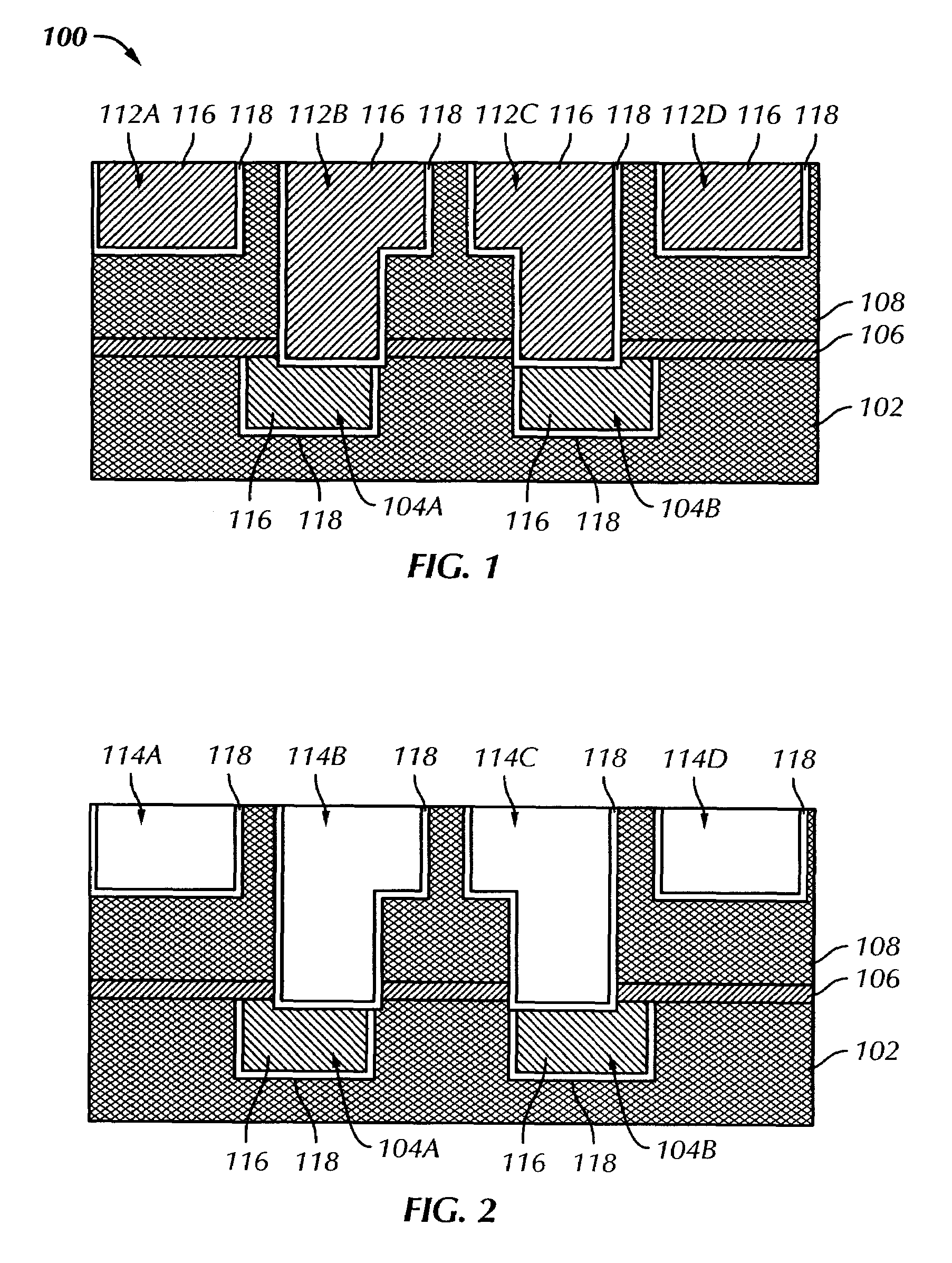
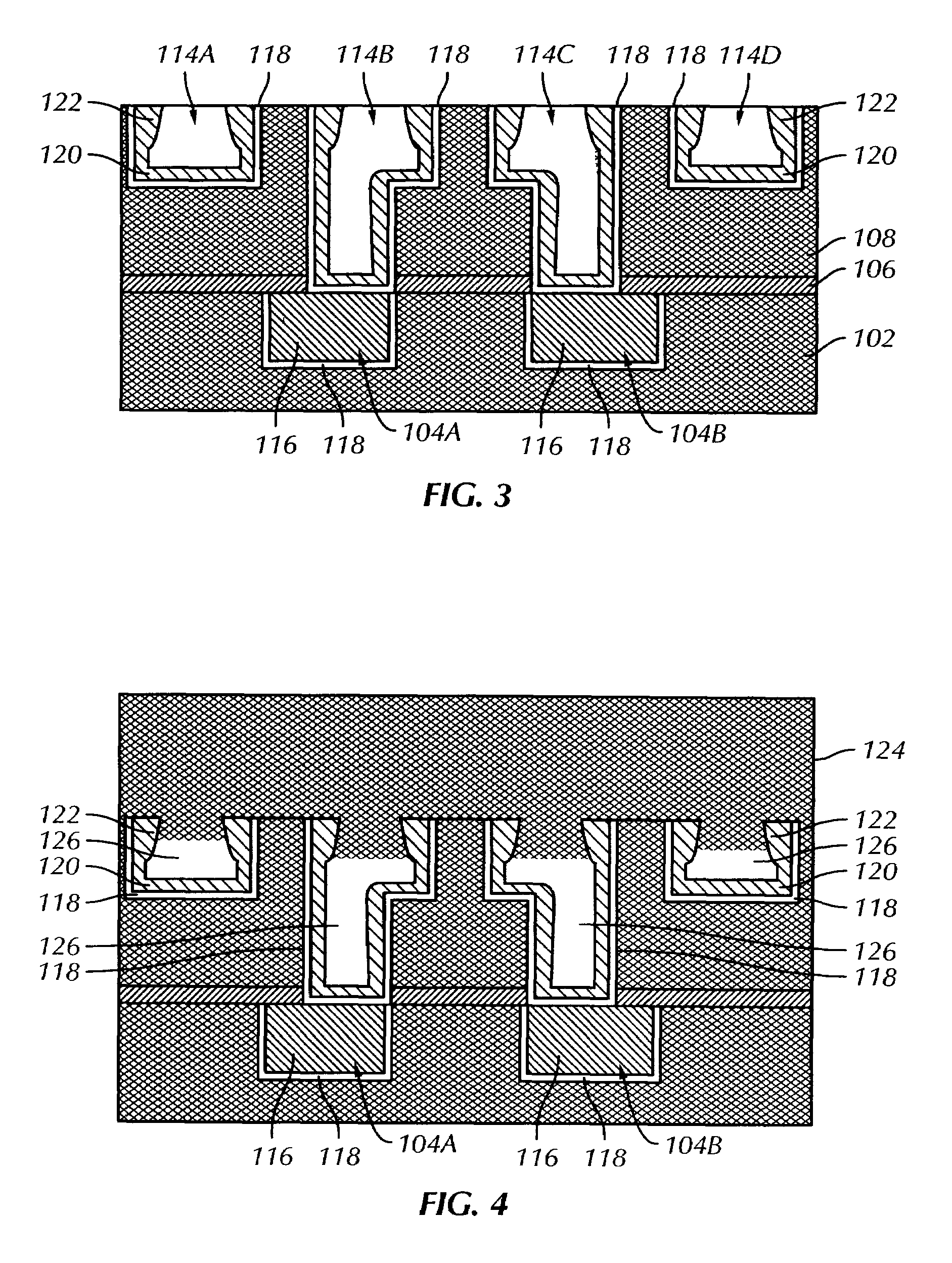
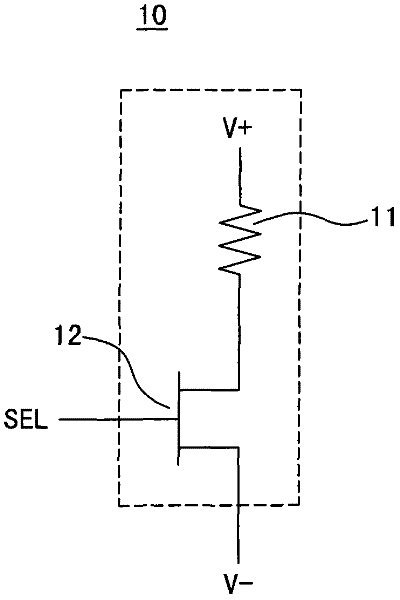
Reversible electric fuse and antifuse structures for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7557424B2Improve electromigration problemsGood reversibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric fusesEngineering
A structure and method of fabricating reversible fuse and antifuse structures for semiconductor devices is provided. In one embodiment, the method includes forming at least one line having a via opening for exposing a portion of a plurality of interconnect features; conformally depositing a first material layer over the via opening; depositing a second material layer over the first material layer, wherein the depositing overhangs a portion of the second material layer on a top portion of the via opening; and depositing a blanket layer of insulating material, where the depositing forms a plurality of fuse elements each having an airgap between the insulating material and the second material layer. The method further includes forming a plurality of electroplates in the insulator material connecting the fuse elements. In another embodiment, the method includes depositing a first and a second material layer on a semiconductor substrate, wherein the second material layer having a higher electrical conductivity than the first material layer; selectively etching the first and second material layer to create at least one constricted region to facilitate electromigration of the second material; wherein the electromigration creates a plurality of micro voids; and forming a plurality of electrical contacts on the second material layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector and mos as read selector for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP cell can have a MOS in series with the OTP element as a read selector. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal-0, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device post-repair circuit and method
The ability to repair defective cells in a memory array, by replacing those cells with redundant cells, is improved using a redundant memory line control circuit that employs two types of redundancy programming. Most, or all, redundant memory lines can be programmed while the memory array is in a wafer state by, e.g., cutting laser fuses. But at least one memory line can be programmed subsequent to device packaging ("post repair") using, e.g., commands that cut electric fuses. Preferably, the redundant memory line(s) that are reserved for post repair are selectable among the same redundant memory lines that can be programmed using laser fuses. This allows all redundant memory lines to be available for laser repair, if needed, but also allows a redundant memory line to be selected for post repair after it has been determined that that redundant memory line is defect-free. This increases the likelihood that a device will be repairable, and yet does not unnecessarily waste redundant memory lines by pre-dedicating them to laser or post repair.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector and MOS as read selector for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP cell can have a MOS in series with the OTP element as a read selector. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal-0, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Method and structure for reliable electrical fuse programming
ActiveUS20150003142A1Small cell sizeLow costMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceAlgorithm
A method of programming electrical fuses reliably is disclosed. If a programming current exceeds a critical current, disruptive mechanisms such as rupture, thermal runaway, decomposition, or melt, can be a dominant programming mechanism such that programming is not be very reliable. Advantageously, by controlled programming where programming current is maintained below the critical current, electromigration can be the sole programming mechanism and, as a result, programming can be deterministic and very reliable. In this method, fuses can be programmed in multiple shots with progressive resistance changes to determine a lower bound that all fuses can be programmed satisfactorily and an upper bound that at least one fuse can be determined failed. If programming within the lower and upper bounds, defects due to programming can be almost zero and, therefore, defects are essentially determined by pre-program defects.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
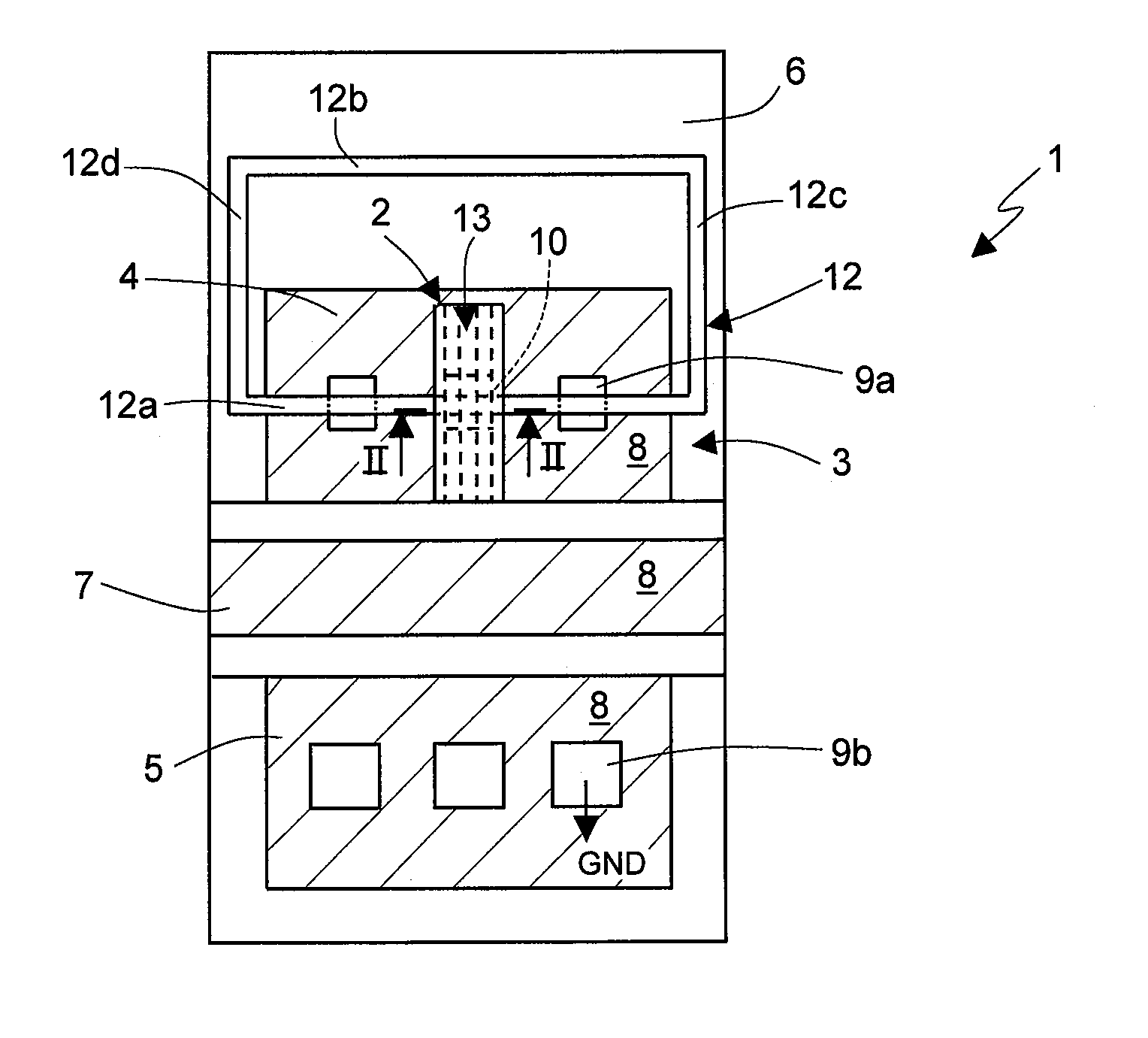
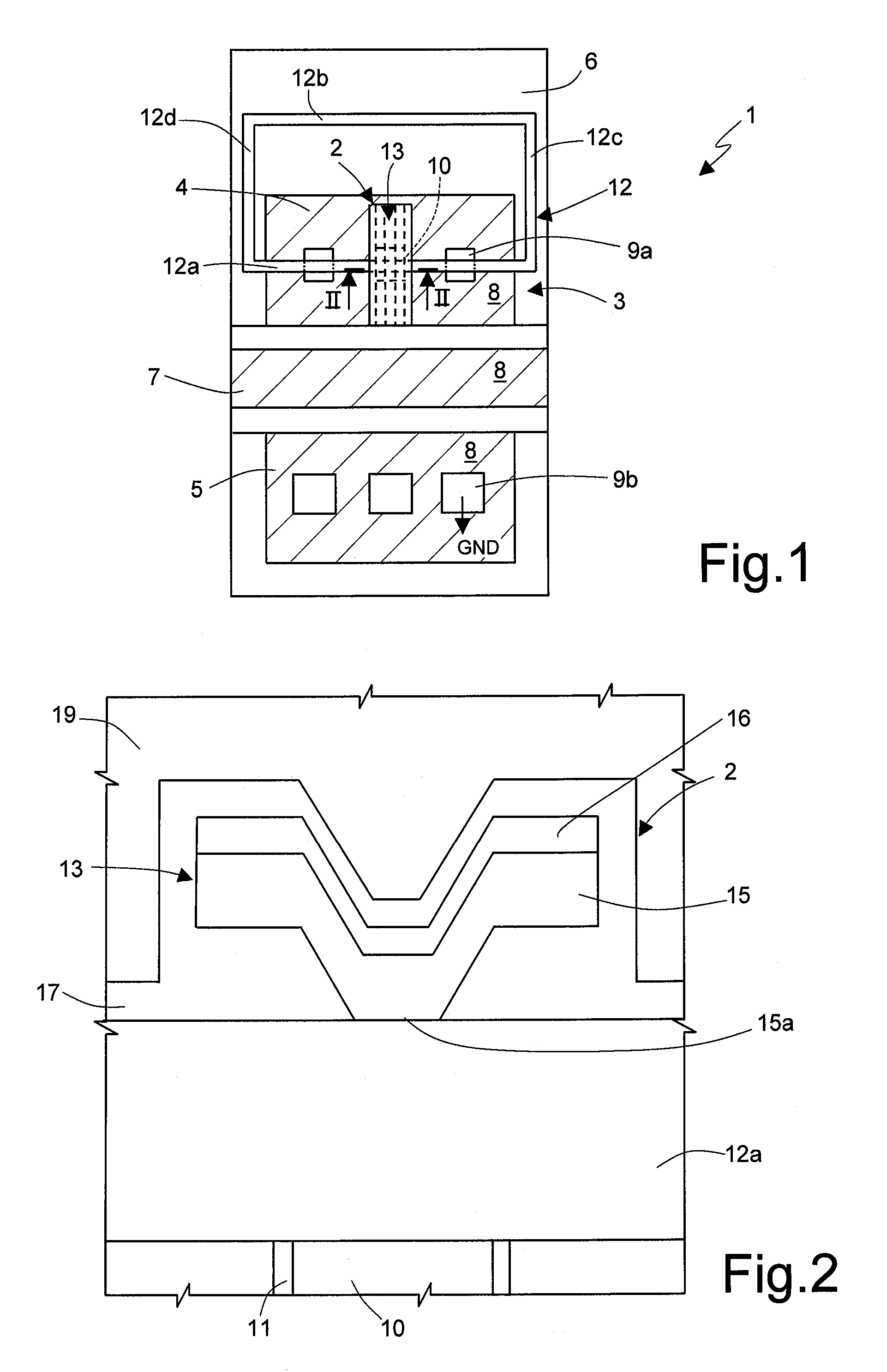
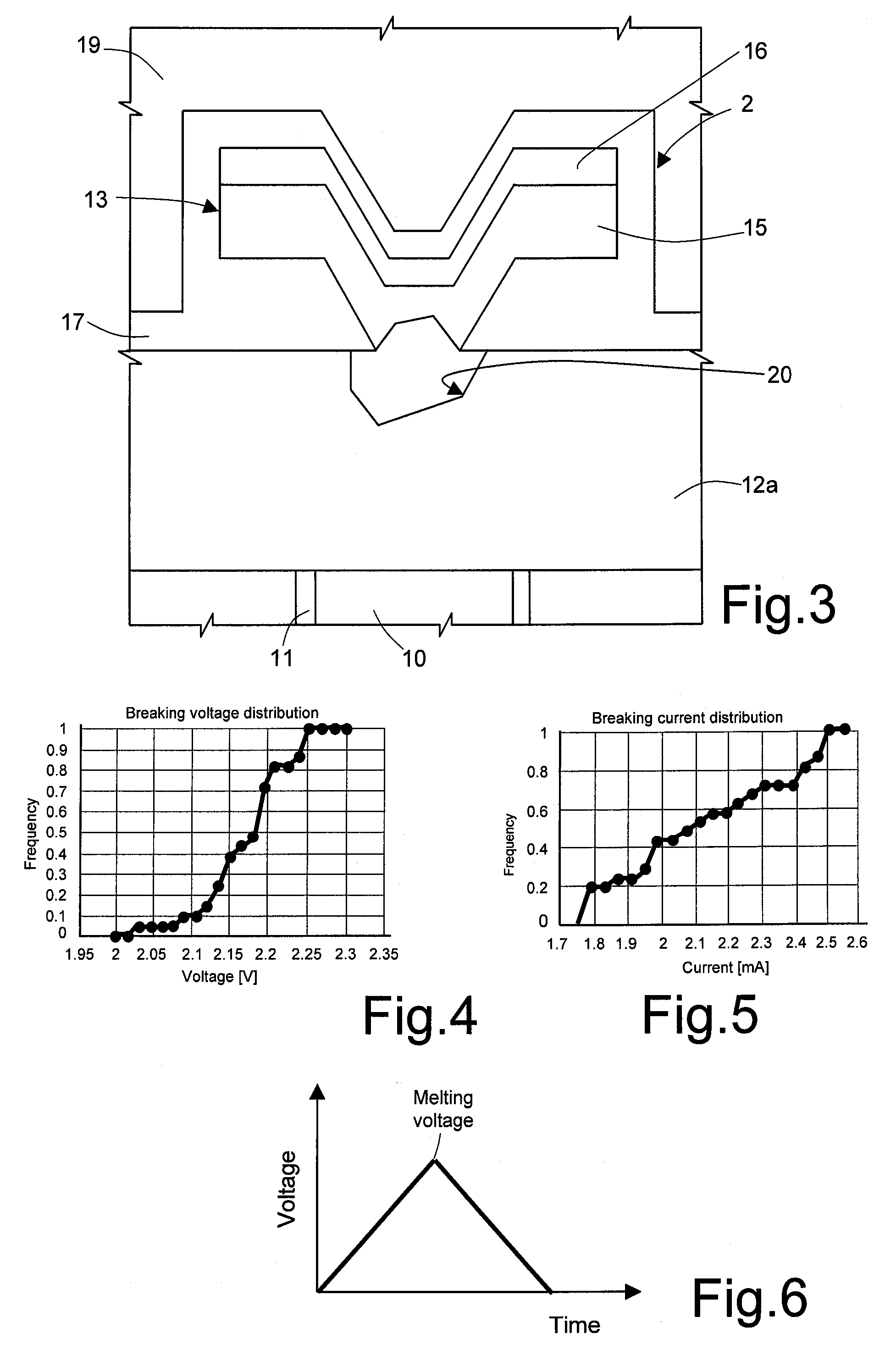
Semiconductor device and a method of increasing a resistance value of an electric fuse
ActiveUS20070210414A1Extension of timeAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric fuses
Provided is a semiconductor device having an electric fuse structure which receives the supply of an electric current to be permitted to be cut without damaging portions around the fuse. An electric fuse is electrically connected between an electronic circuit and a redundant circuit as a spare of the electronic circuit. After these circuits are sealed with a resin, the fuse can be cut by receiving the supply of an electric current from the outside. The electric fuse is formed in a fine layer, and is made of a main wiring and a barrier film. The linear expansion coefficient of each of the main wiring and the barrier film is larger than that of each of the insulator layers. The melting point of each of the main wiring and the barrier film is lower than that of each of the insulator layers.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
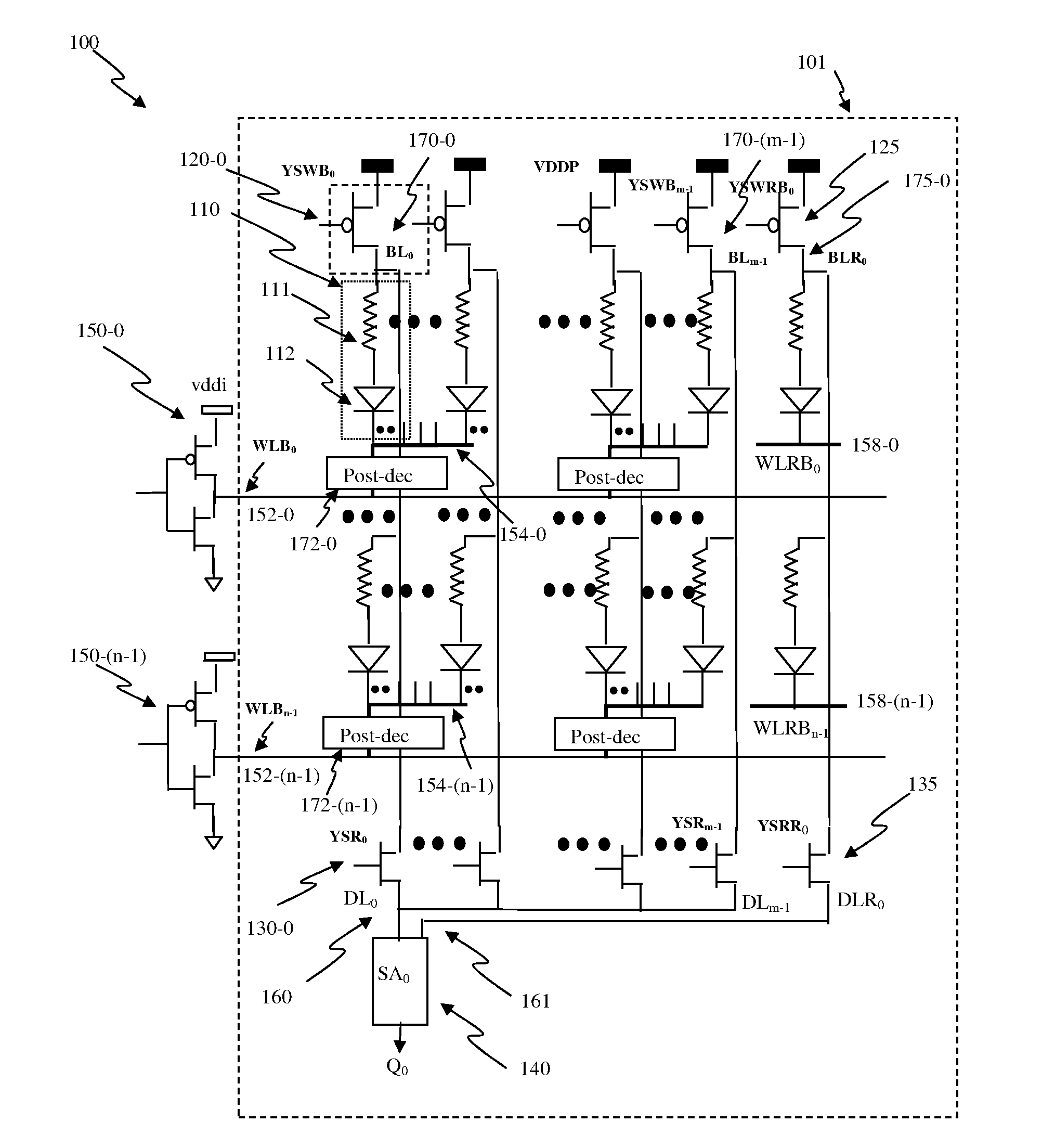
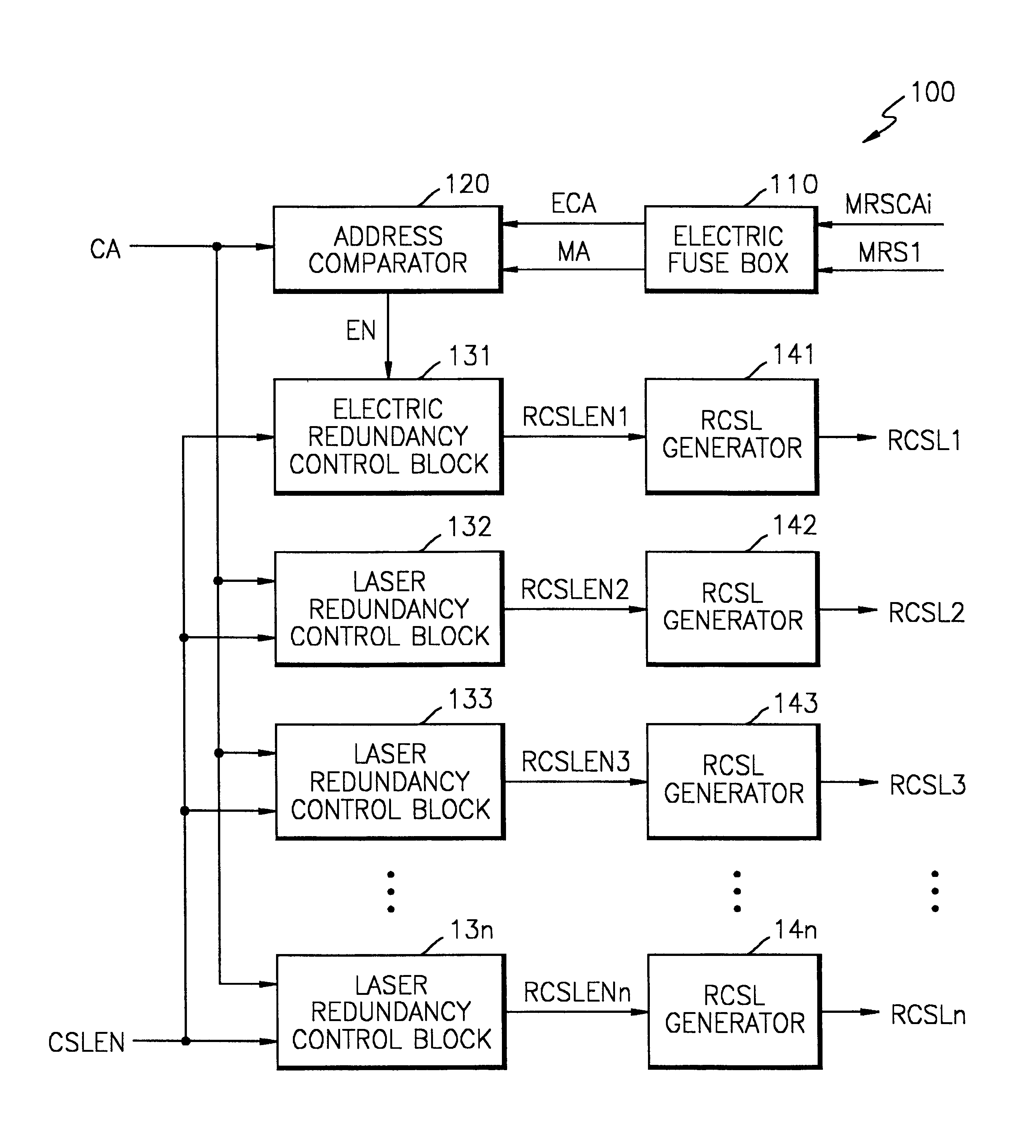
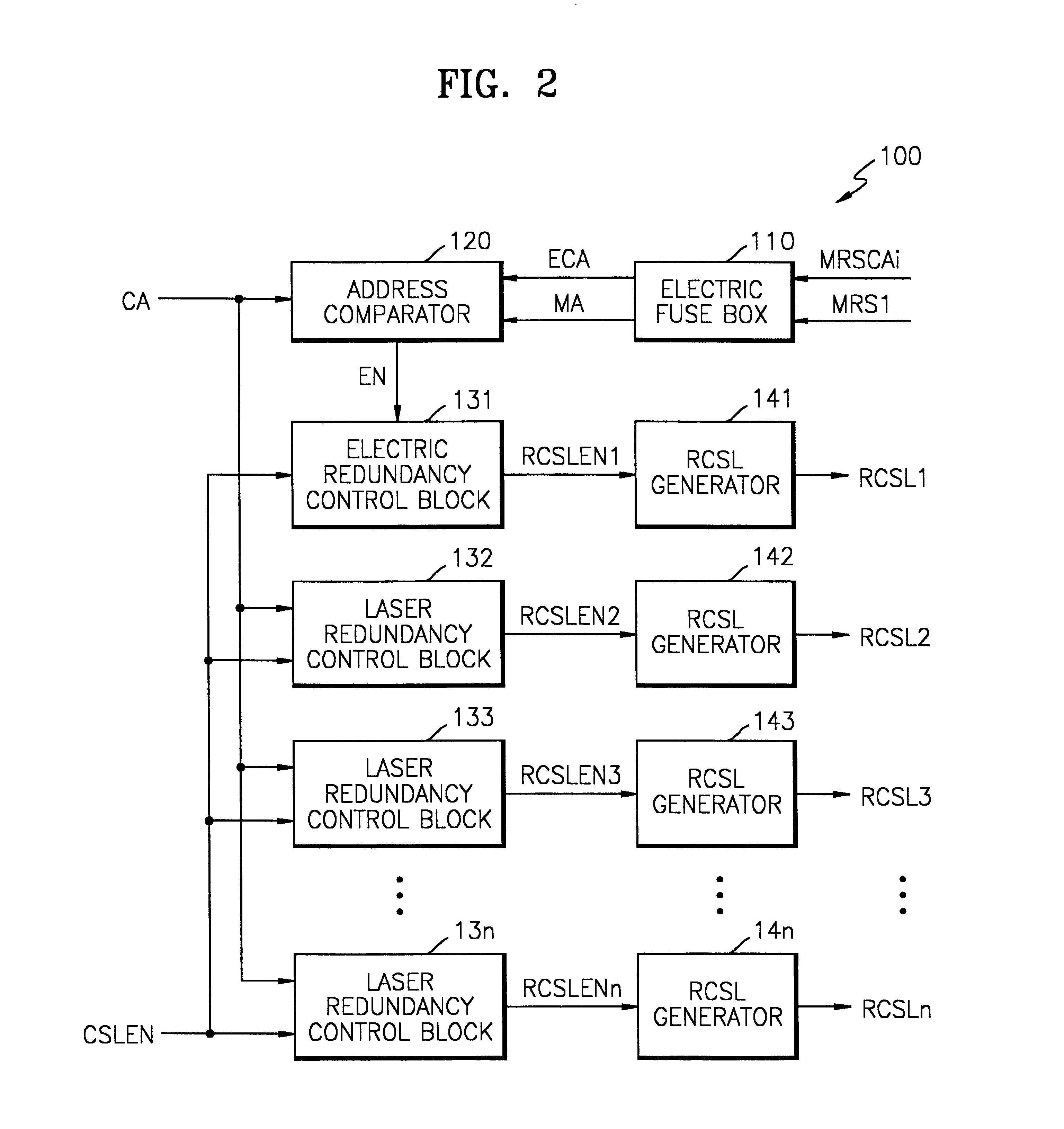
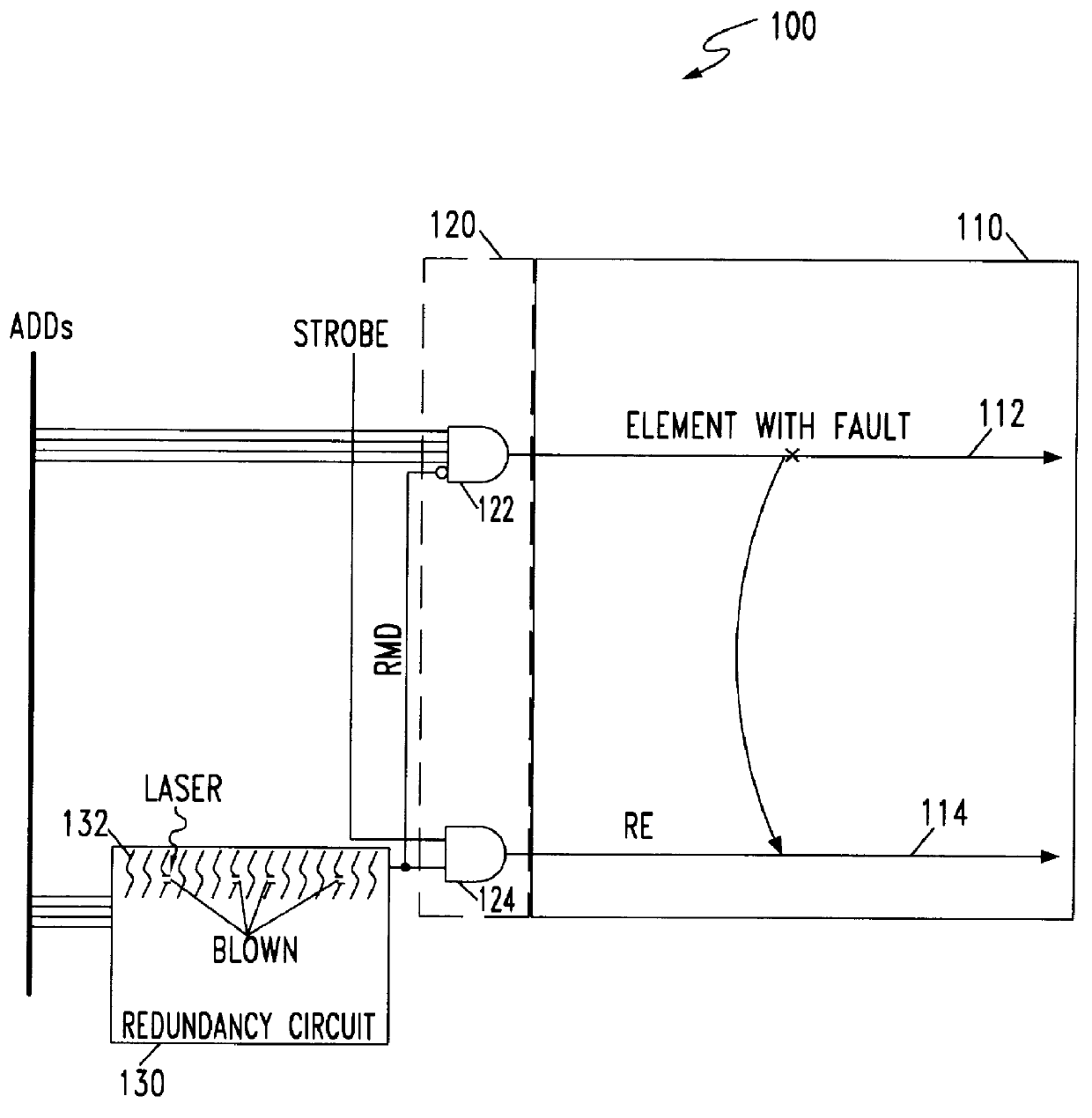
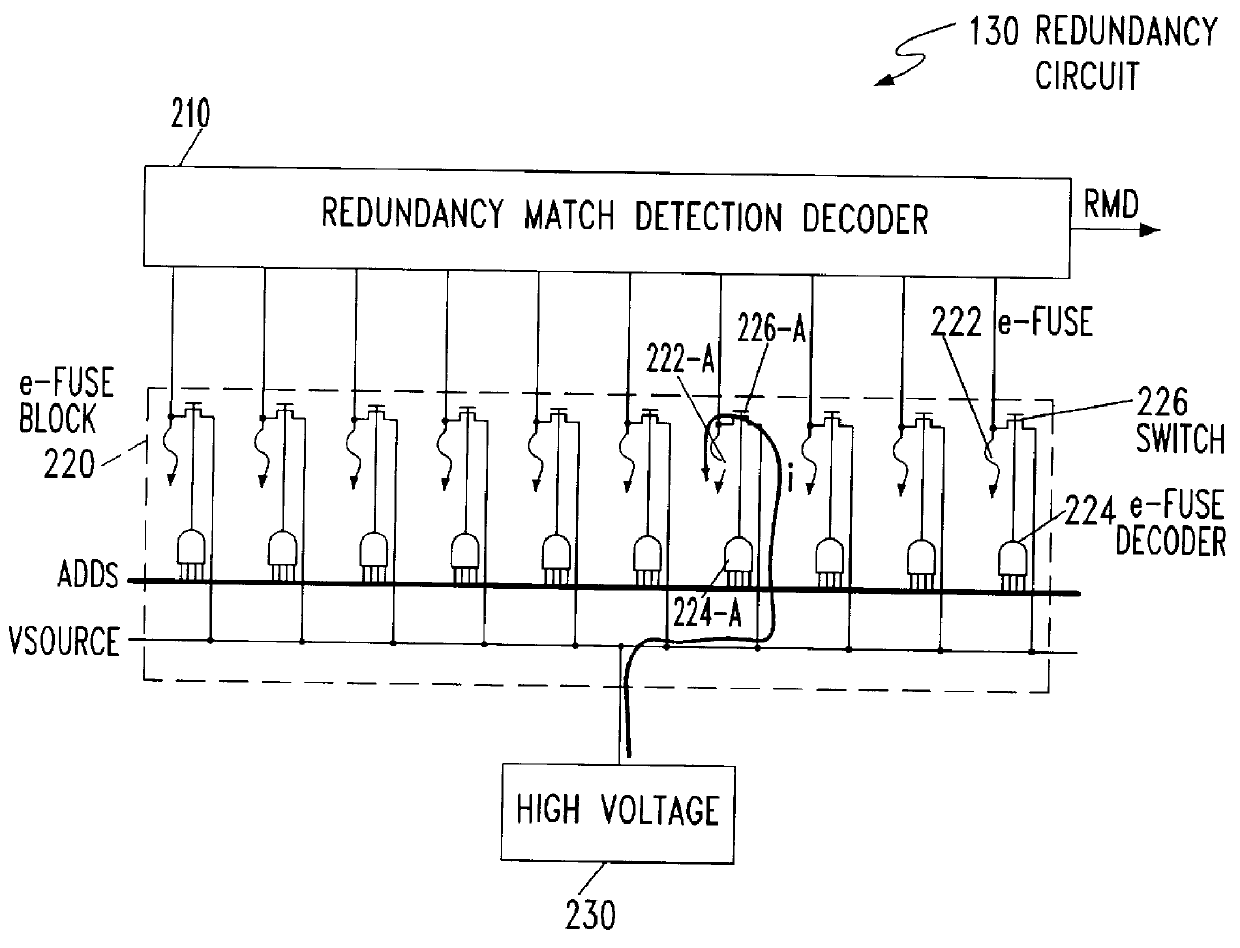
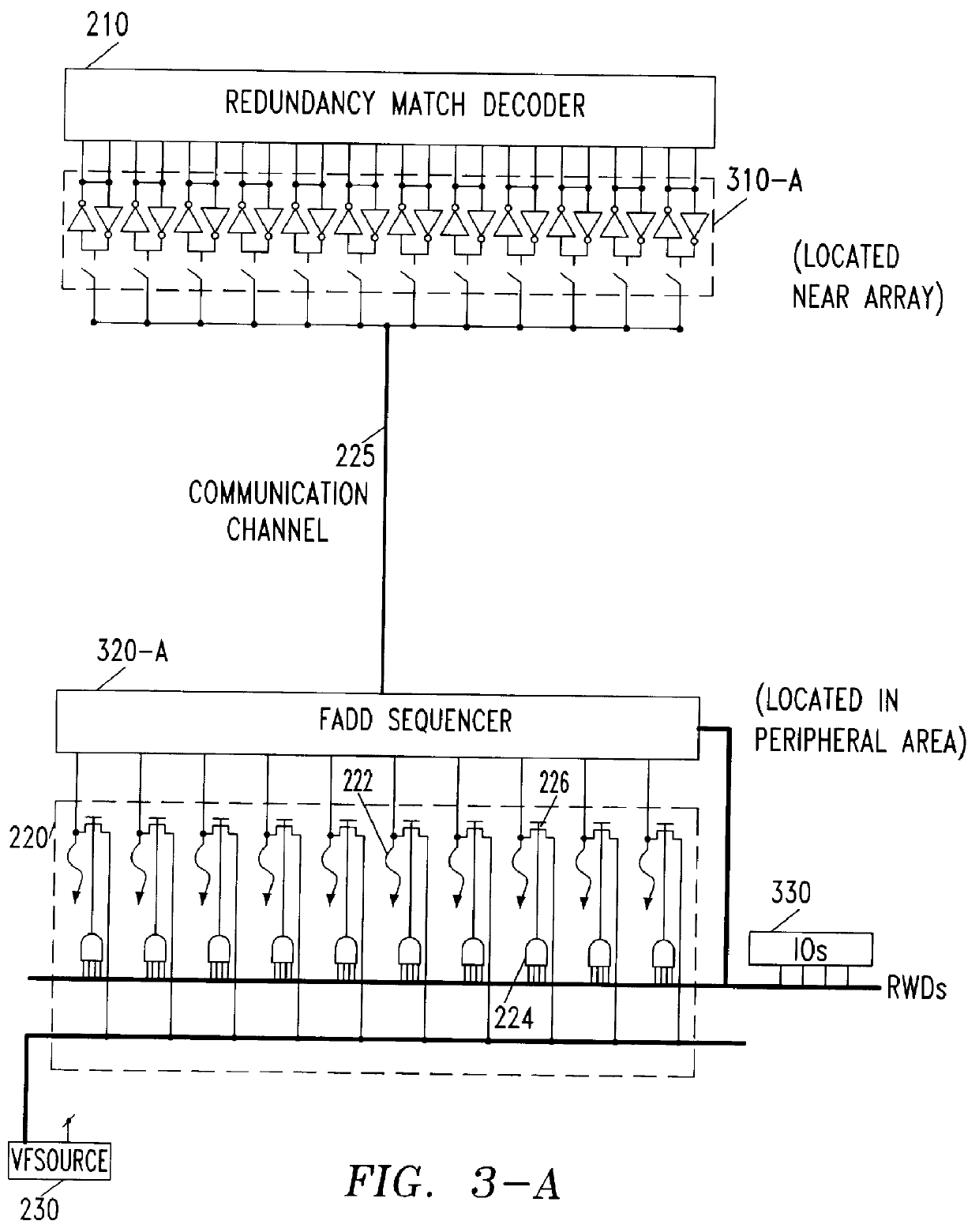
Method for addressing electrical fuses
A memory device that includes a plurality of data storage cells; at least one redundancy data storage cell; a redundancy match detection circuit; and a means for coupling programmable fuses to the redundancy match detection circuit, wherein a defective data storage is replaced by one redundancy data storage when the redundancy match detection detects a pre-determined condition set by said programmable fuse is described. Decoding is accomplished by a data bus selecting the e-fuse to be blown. The data bus is also used for reading the state of the e-fuses to ensure that the e-fuses are correctly blown. Power is effectively applied to the selected e-fuses while sharing the data bus for e-fuse decoding and verification. In order to reduce the number of communication channels between e-fuses and the redundancy match detection circuitry, the transfer operation uses time multiplexing, allowing e-fuse information to be transferred to the redundancy match detection circuitry sequentially. The actual time multiplexing operation for performing the transfer is preferably enabled only after the chip power-up state.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
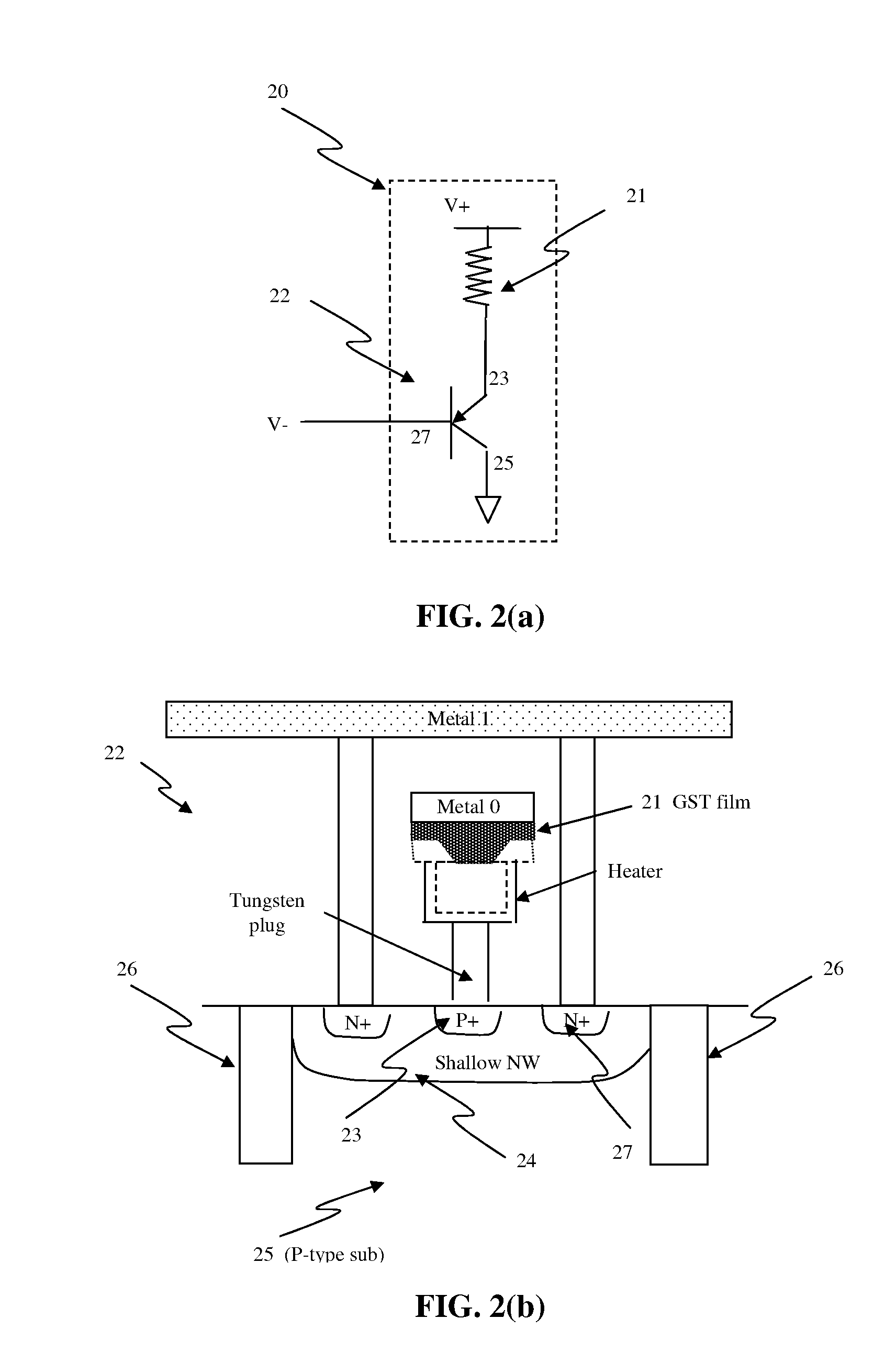
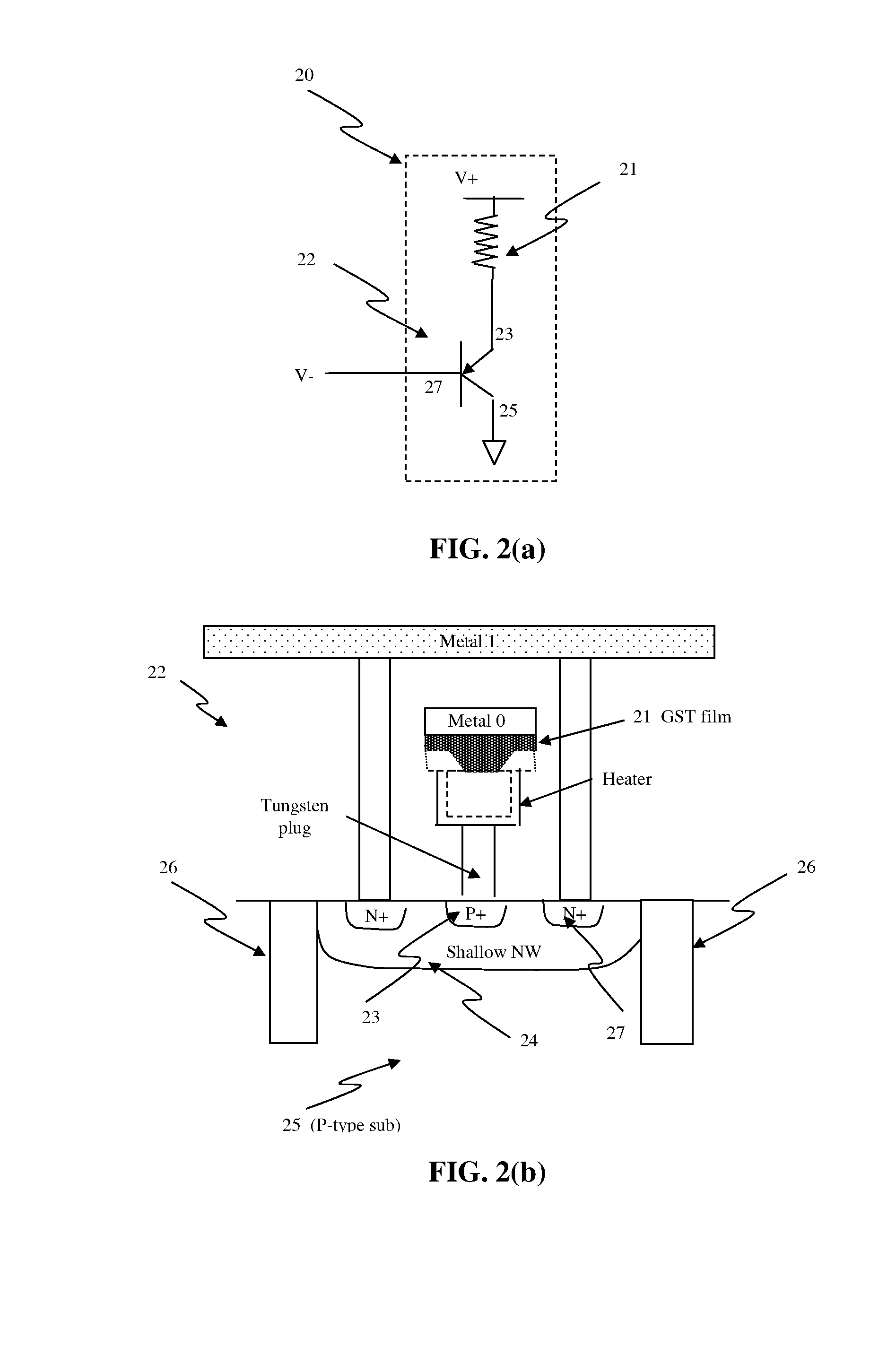
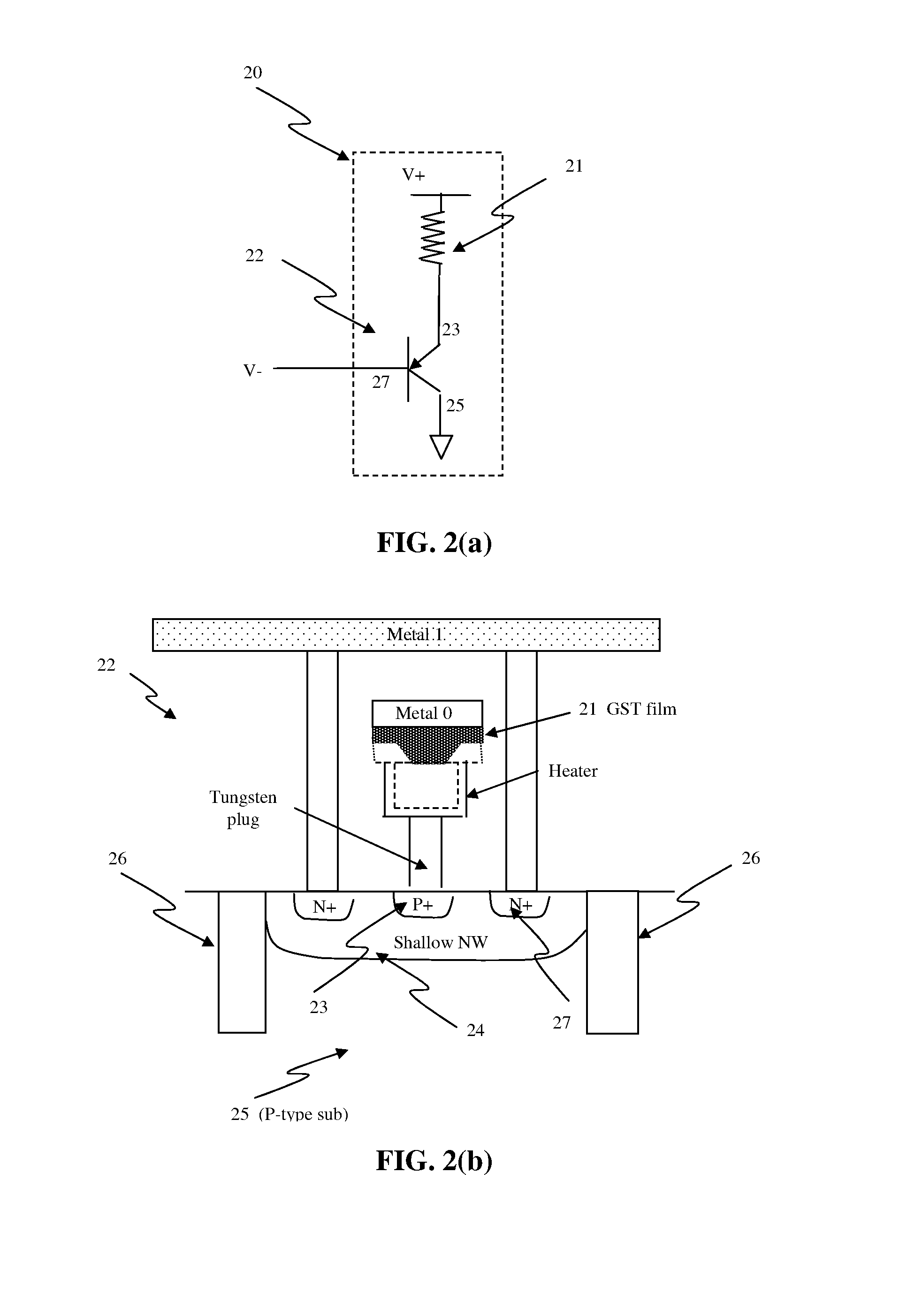
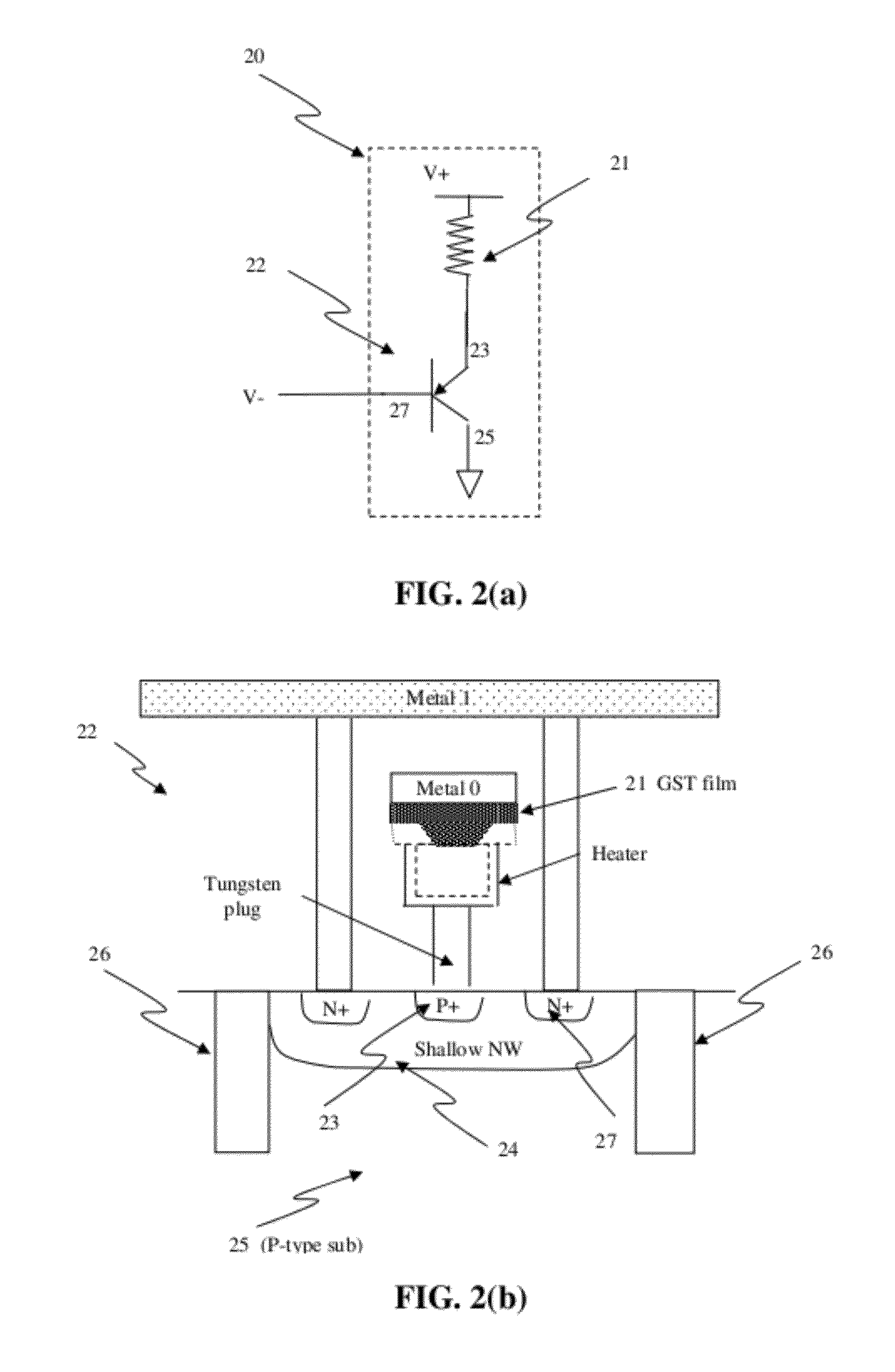
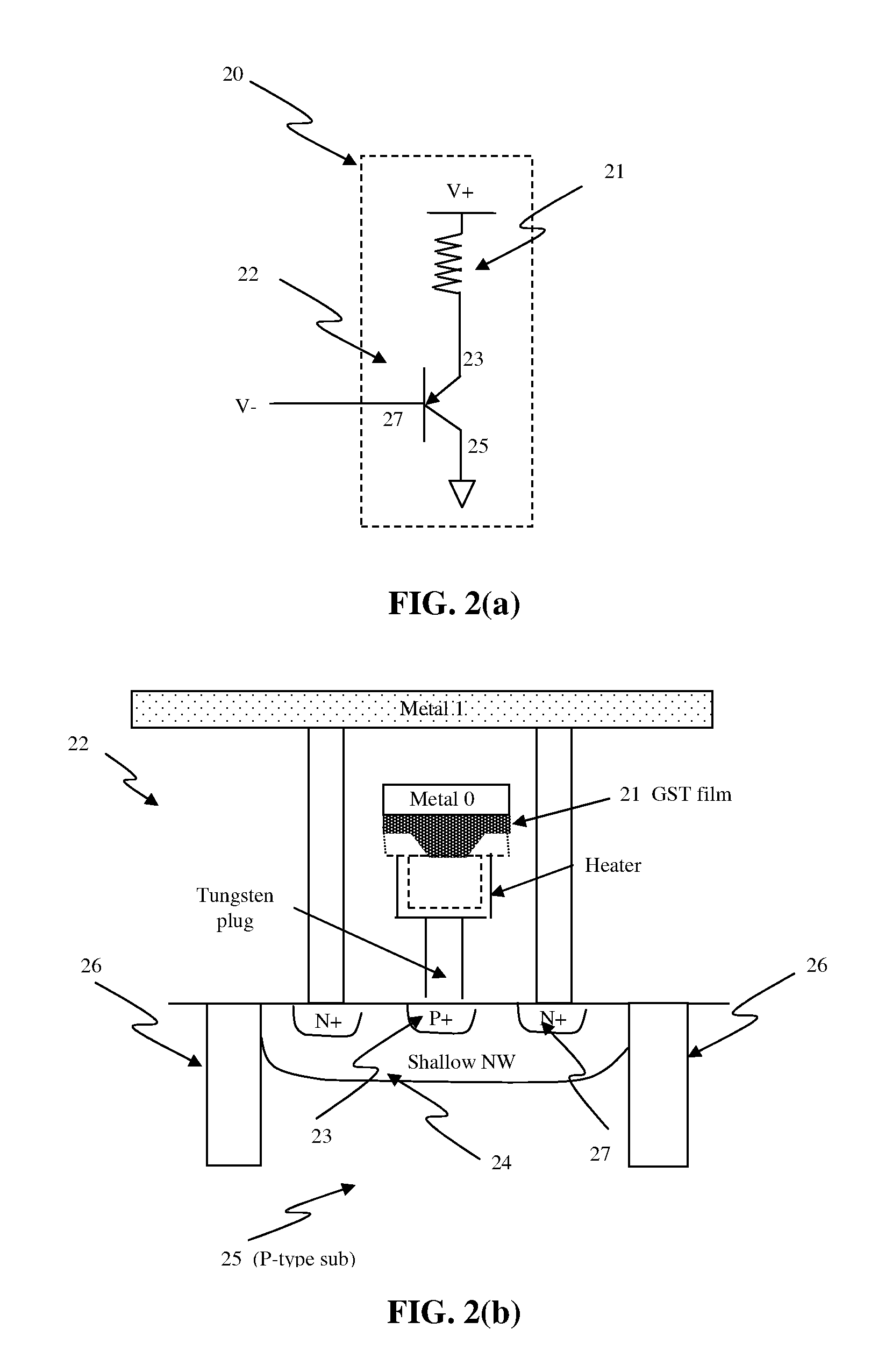
Electrical fuse device based on a phase-change memory element and corresponding programming method
InactiveUS20070189053A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityPhase-change memory
A fuse device has a fuse element provided with a first terminal and a second terminal and an electrically breakable region, which is arranged between the first terminal and the second terminal and is configured to undergo breaking as a result of the supply of a programming electrical quantity, thus electrically separating the first terminal from the second terminal. The electrically breakable region is of a phase-change material, in particular a calcogenic material, for example GST.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
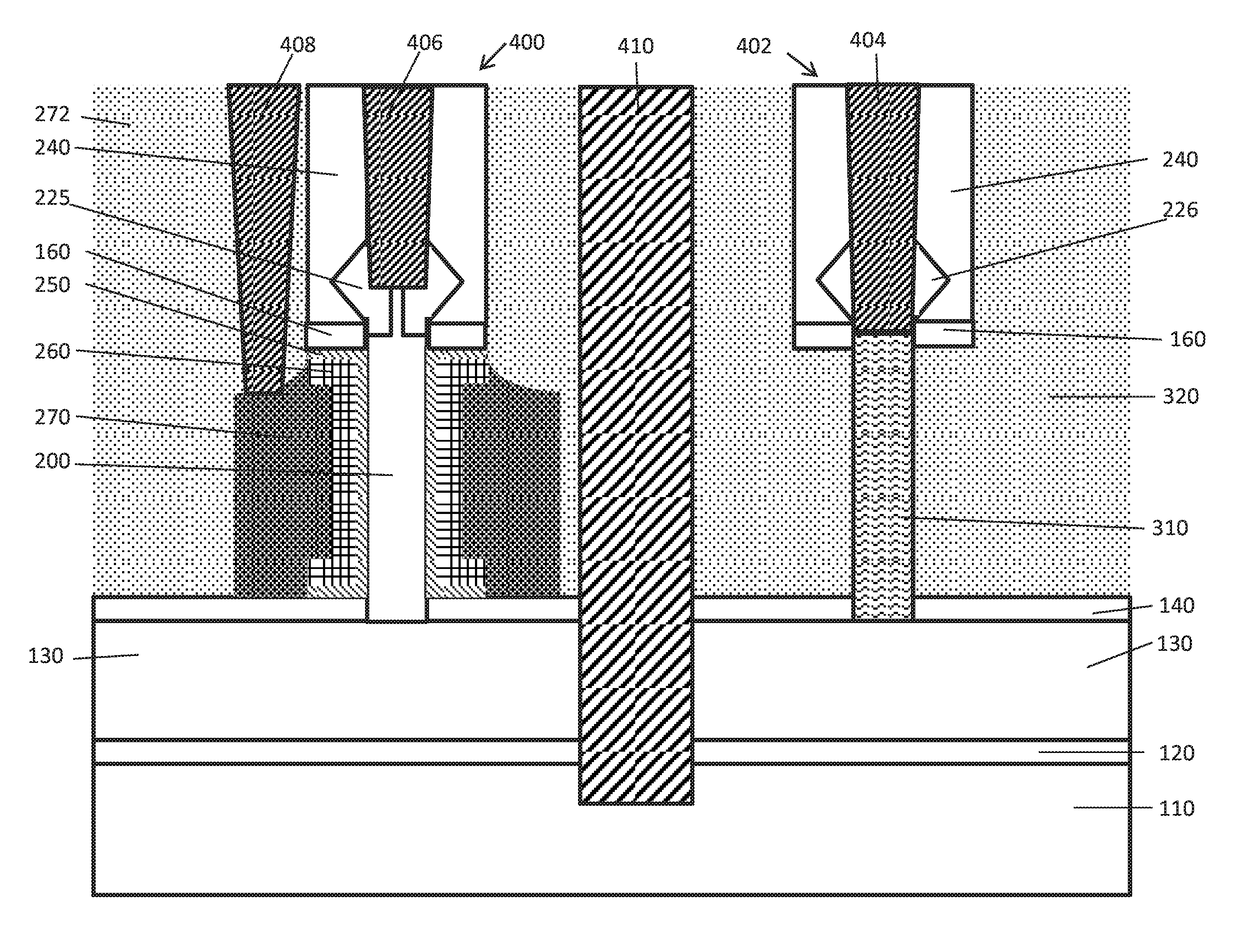
High density programmable e-fuse co-integrated with vertical FETs
A method for integrating vertical transistors and electric fuses includes forming fins through a dielectric layer and a dummy gate stack on a substrate; thinning top portions of the fins by an etch process; epitaxially growing top source / drain regions on thinned portions of the fins in a transistor region and top cathode / anode regions on the thinned portions of the fins in a fuse region; and removing the dummy gate layer and exposing sidewalls of the fins. The fuse region is blocked to form a gate structure in the transistor region. The transistor region is blocked and the fuse region is exposed to conformally deposit a metal on exposed sidewalls of the fins. The metal is annealed to form silicided fins. Portions of the substrate are separated to form bottom source / drain regions for vertical transistors in the transistor region and bottom cathode / anode regions for fuses in the fuse region.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
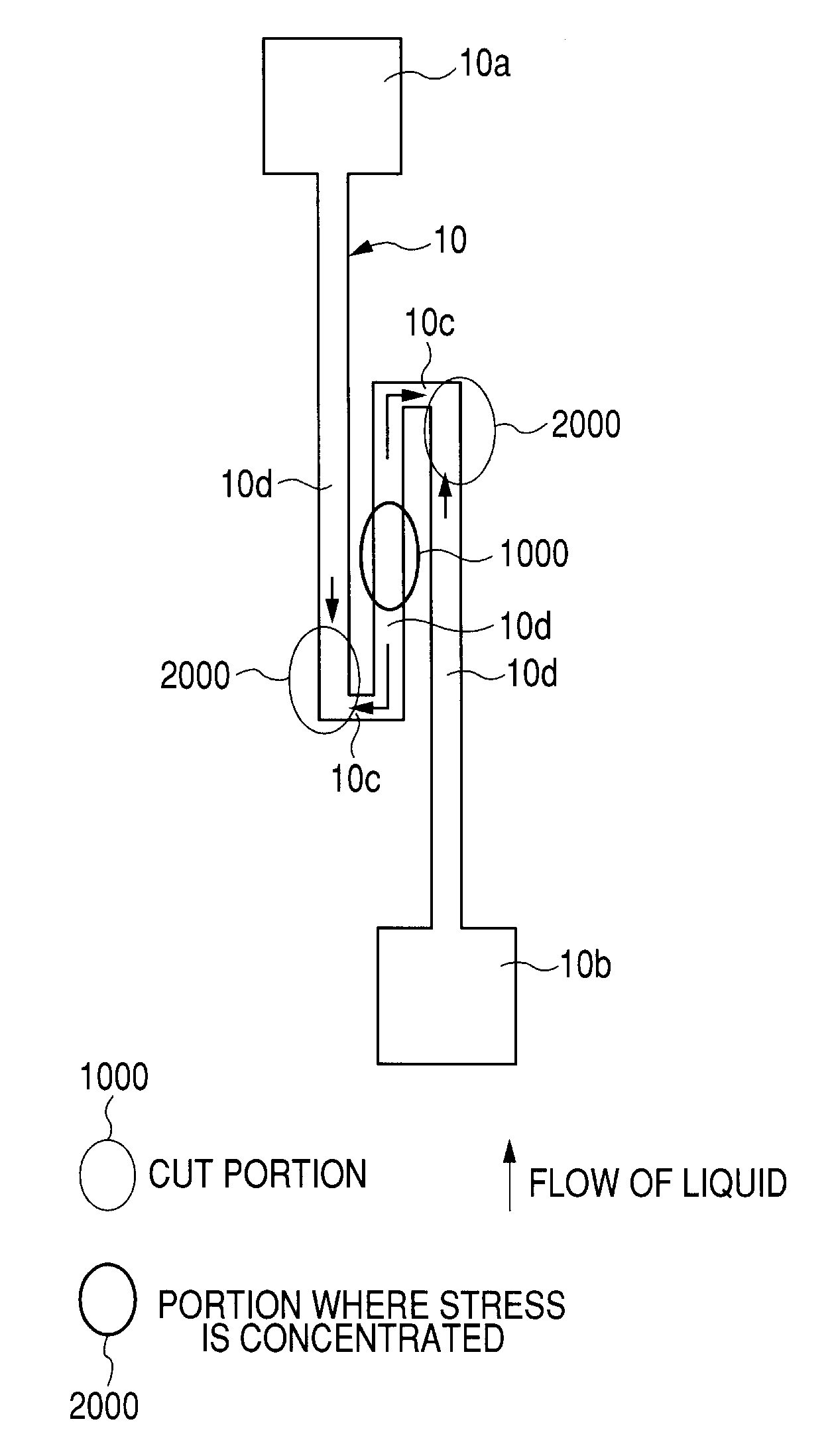
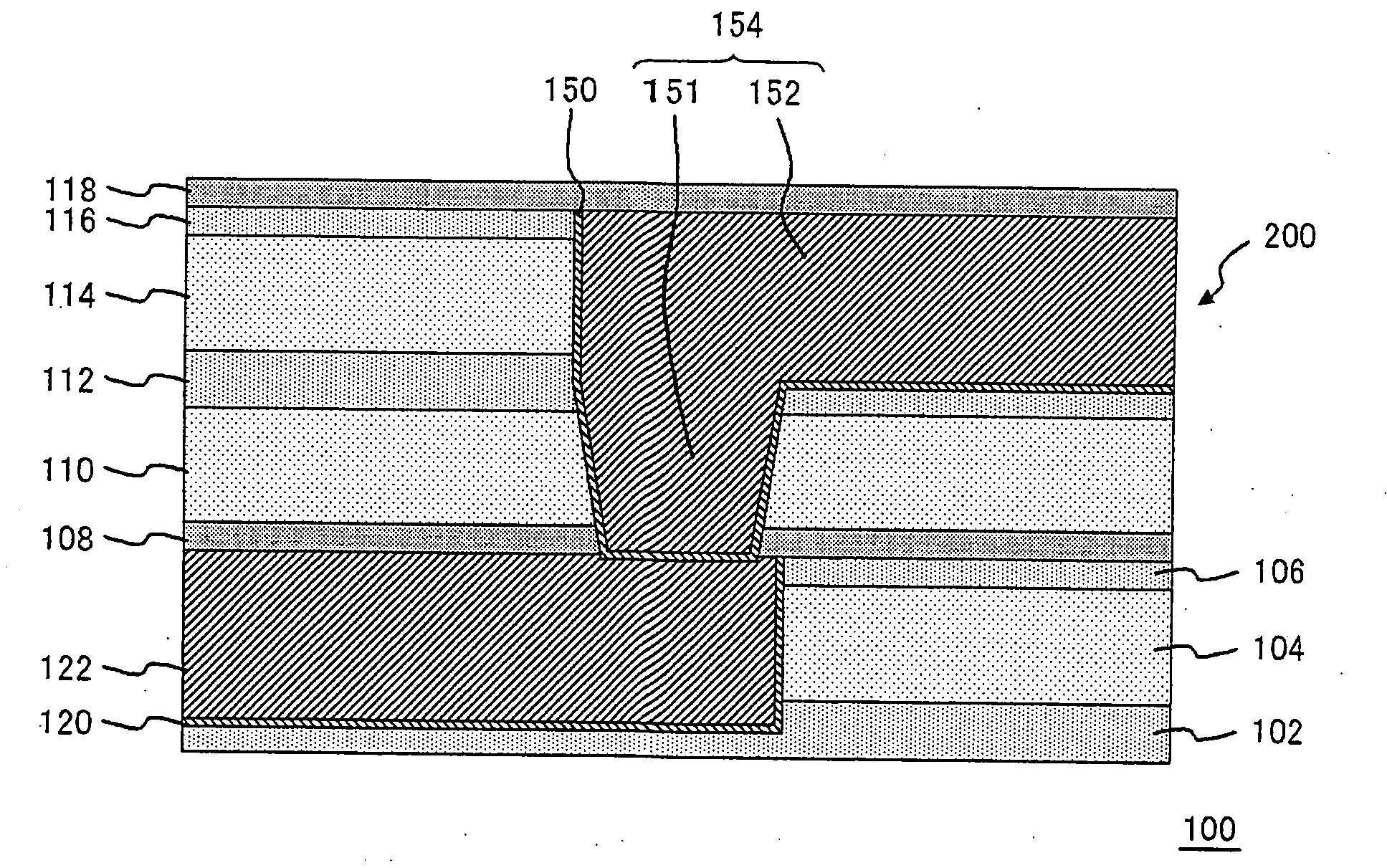
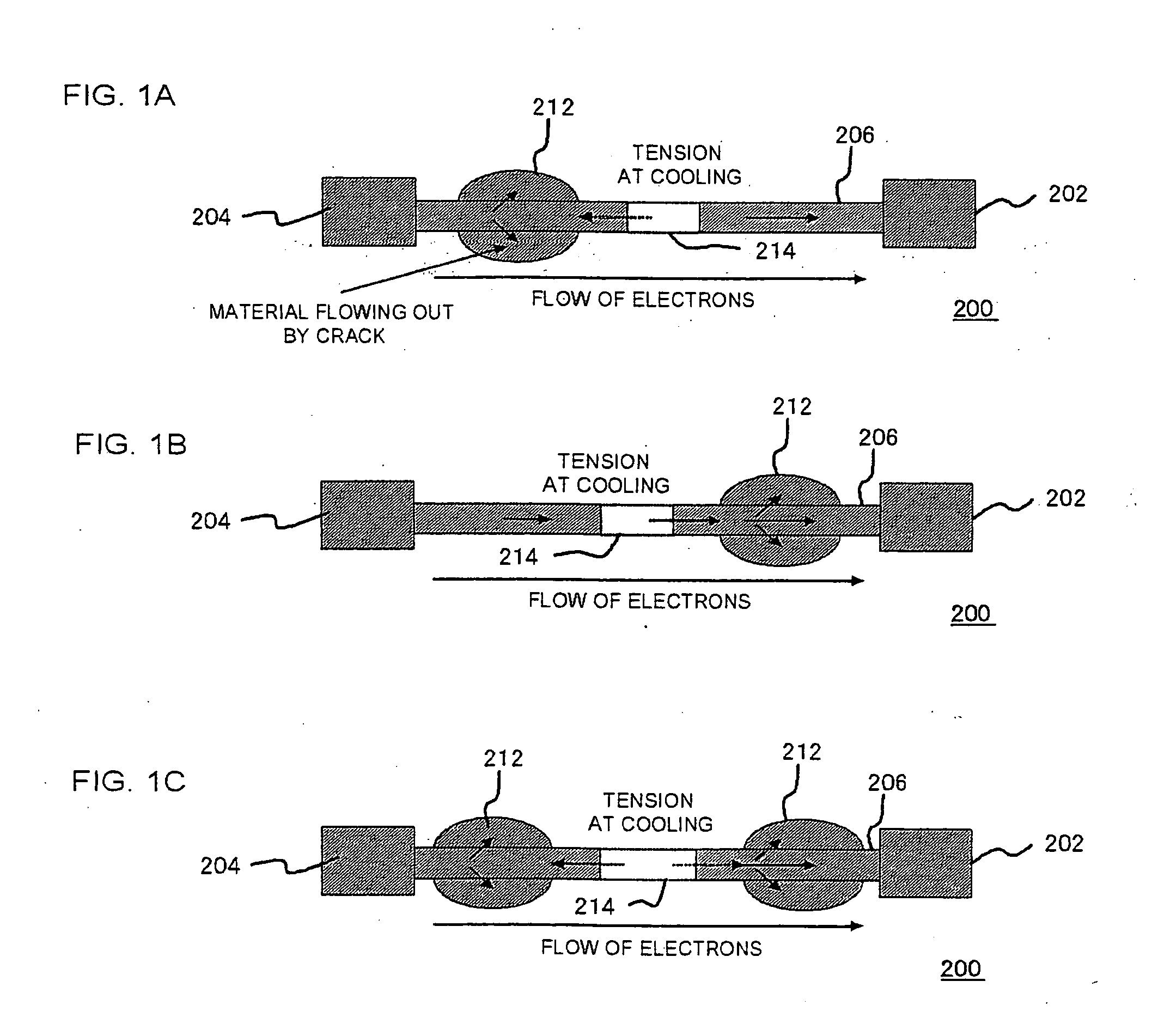
Semiconductor device and method for cutting electric fuse
ActiveUS20070262414A1Improve the situationBalance is lostSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric fusesEngineering
A semiconductor device includes an electric fuse formed on a semiconductor substrate and composed of an electric conductor. The electric fuse includes an upper layer interconnect, a via coupled to the upper interconnect and a lower layer interconnect coupled to the via, which are formed in different layers, respectively, in a condition before cutting the electric fuse, and wherein the electric fuse includes a flowing-out region formed of the electric conductor being flowed toward outside from the second interconnect and a void region formed between the first interconnect and the via or in the via, in a condition after cutting the electric fuse.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
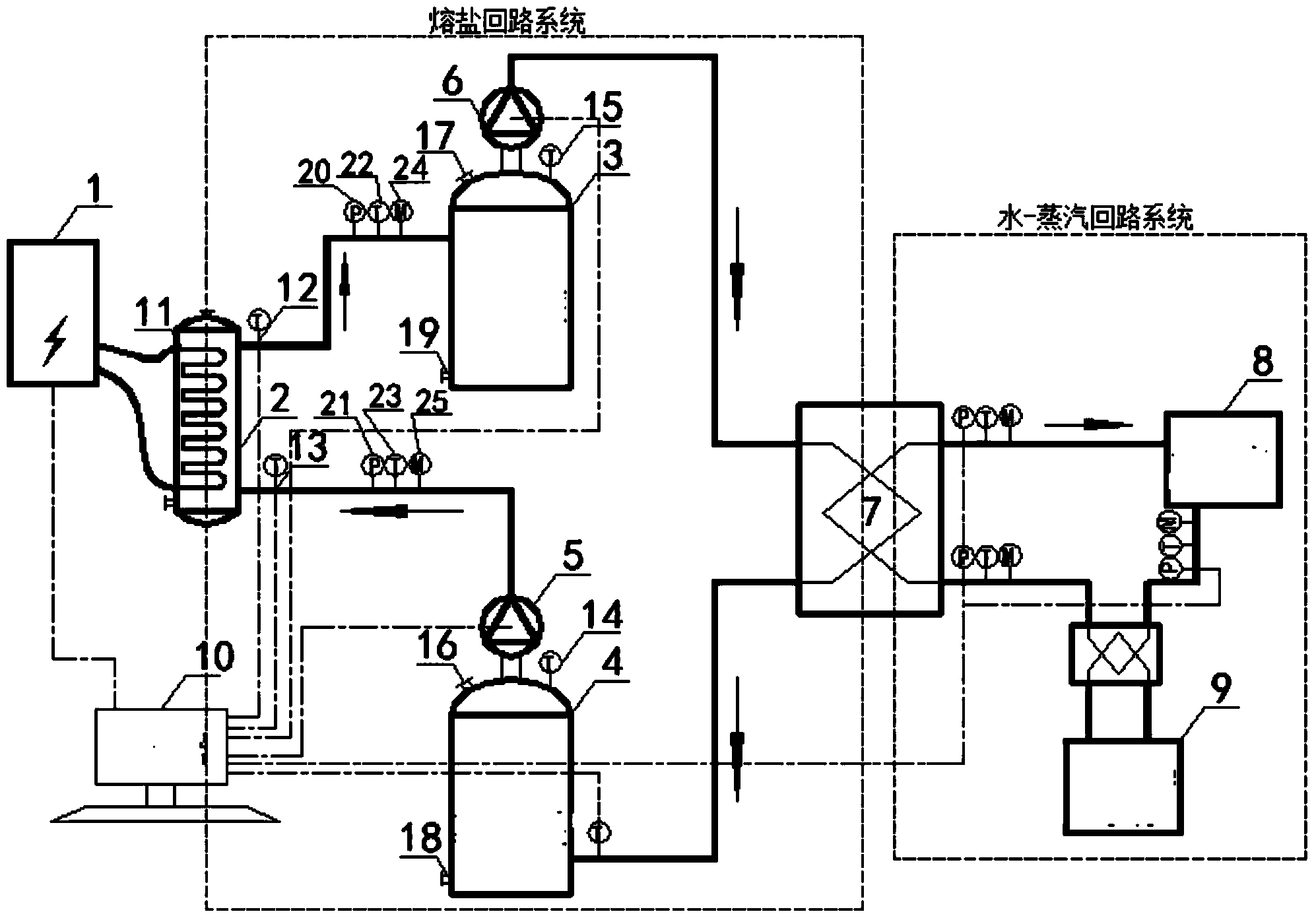
Independent fused salt heat storage power plant
InactiveCN103868389ASmall footprintImprove utilization efficiencyHeat storage plantsEngineeringHeat energy
An independent fused salt heat storage power plant belongs to the technical field of energy storage, and comprises a power supply, an electric fused salt heater, a high-temperature hot salt tank, a low-temperature cold salt tank, a fused salt pump, a fused salt circuit system, a brine heat exchanger, a conventional power generation island, a water-steam circuit system and an intelligent control system. When unstable or redundant electric energy such as photovoltaic power, wind power and off-peak power is stored, the electric energy is converted into high-temperature heat energy to be stored in the high-temperature fused salt through heating the high-temperature fused salt by the electric fused salt heater. When electricity utilization is needed, high-temperature heat energy stored in the high-temperature fused salt can heat water to generate water steam to drive a steam turbine to generate power to realize the energy release. In addition, a large-scale high-temperature thermal storage power plant built in cities can also be combined with city heat supply to construct a large-scale high-temperature heat storage and combined heat and power supply station.
Owner:中投亿星新能源投资有限公司
Otp memory with high data security
ActiveUS20180005703A1Reduce cell size and costLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesThermal runawayDecomposition
A method of programming electrical fuses reliably is disclosed. If a programming current exceeds a critical current, disruptive mechanisms such as rupture, thermal runaway, decomposition, or melt, can be a dominant programming mechanism such that programming is not be very reliable. Advantageously, by controlled programming where programming current is maintained below the critical current, electromigration can be the sole programming mechanism and, as a result, programming can be deterministic and very reliable. In this method, fuses can be programmed in multiple shots with progressive resistance changes to determine a lower bound that all fuses can be programmed satisfactorily and an upper bound that at least one fuse can be determined failed. If programming within the lower and upper bounds, defects due to programming can be almost zero and, therefore, defects are essentially determined by pre-program defects.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Reversible electric fuse and antifuse structures for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20080157269A1Improve electromigration problemsGood reversibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialElectric fuses
A structure and method of fabricating reversible fuse and antifuse structures for semiconductor devices is provided. In one embodiment, the method includes forming at least one line having a via opening for exposing a portion of a plurality of interconnect features; conformally depositing a first material layer over the via opening; depositing a second material layer over the first material layer, wherein the depositing overhangs a portion of the second material layer on a top portion of the via opening; and depositing a blanket layer of insulating material, where the depositing forms a plurality of fuse elements each having an airgap between the insulating material and the second material layer. The method further includes forming a plurality of electroplates in the insulator material connecting the fuse elements. In another embodiment, the method includes depositing a first and a second material layer on a semiconductor substrate, wherein the second material layer having a higher electrical conductivity than the first material layer; selectively etching the first and second material layer to create at least one constricted region to facilitate electromigration of the second material; wherein the electromigration creates a plurality of micro voids; and forming a plurality of electrical contacts on the second material layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
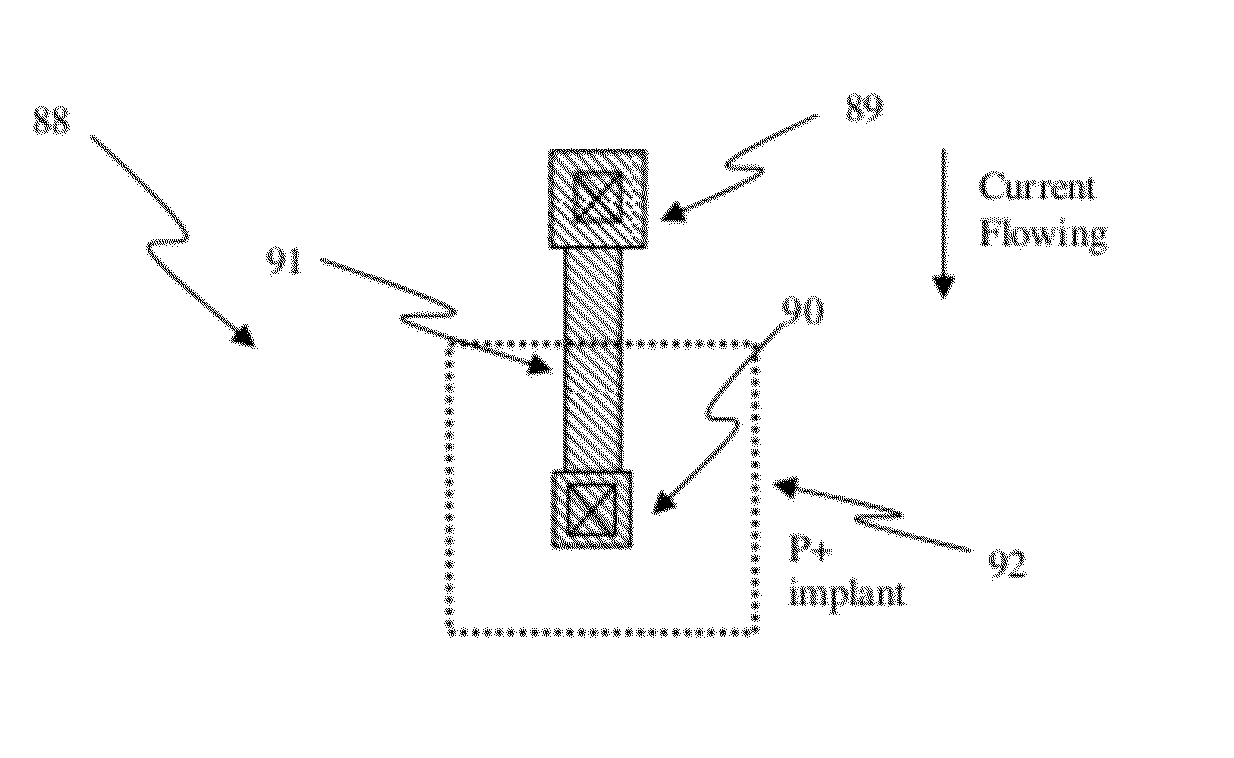
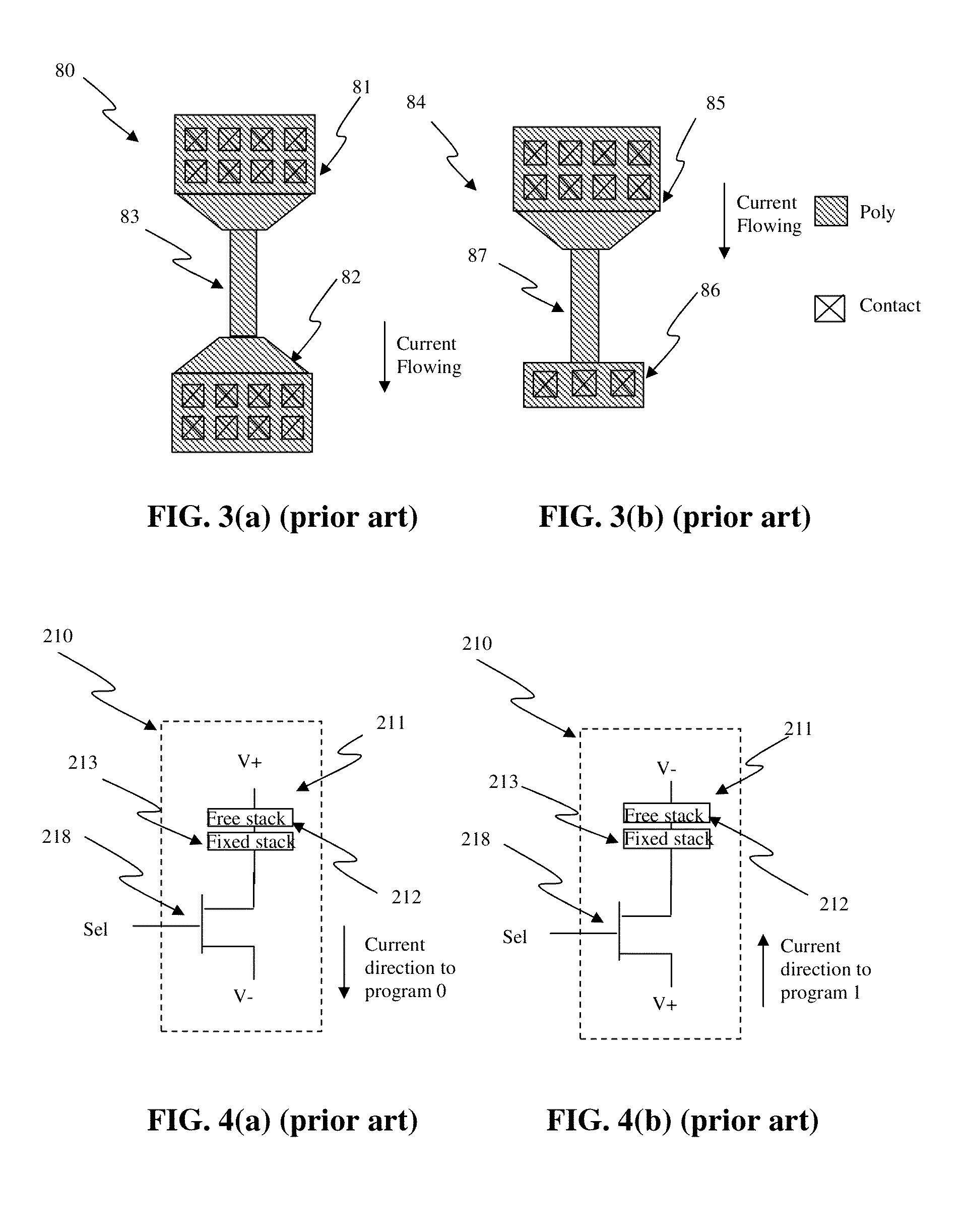
One-time programmable memor, electric system, electric fuse memory and method
The present invention discloses a one-time programmable memory, an electric system, an electric fuse memory, a programmable resistance assembly memory and a method thereof, wherein the programmable resistance assembly memory comprising a plurality of programmable resistance memory units, the programmable resistance assembly is coupled to a first power supply voltage line; and a diode comprising at least a first active zone and a second active zone, wherein the first active zone is provided with a first type of doping, the second active zone is provided with a second type of doping, the first active zone provides a first end of the diode, the second active zone provides a second end of the diode, the first active zone and the second active zone are all located in a same hole, the first active zone is coupled to the programmable resistance assembly, and the second active zone is coupled to a second power supply voltage line. The first and second active zones are manufactured from the source electrode or the drain electrode of a complementary metal oxide semiconductor CMOS assembly, and the programmable resistance assembly is programmed through applying a voltage to the first and second power supply lines.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070052063A1Prone to feverEasy to cutSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialElectric fuses
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
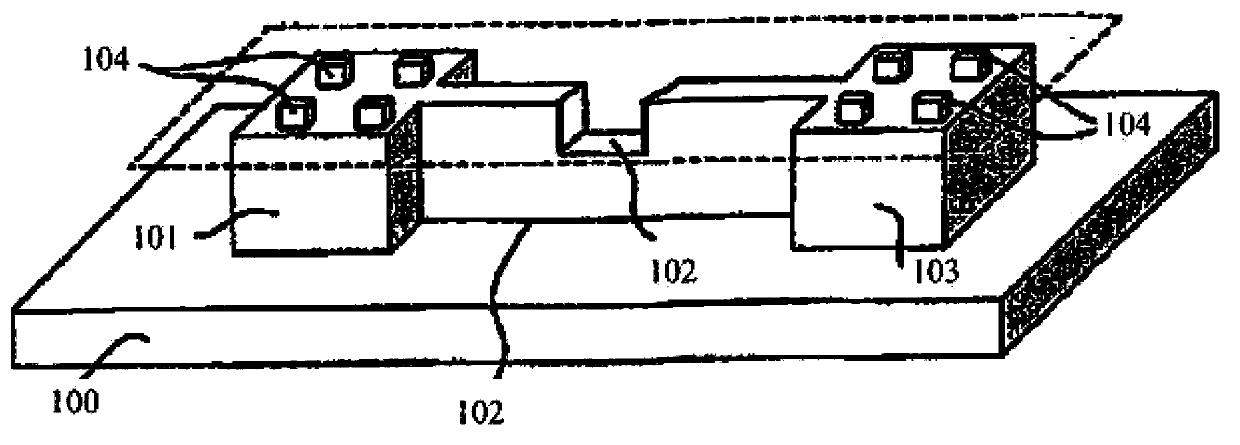
Electric-fuse structures and formation methods thereof, and semiconductor devices and formation methods thereof
ActiveCN104183542AEasy to formNovel electric fuse structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNanowireElectric fuses
The embodiment of the invention provides a plurality of kinds of electric-fuse structures and formation methods thereof, and semiconductor devices and formation methods thereof, e.g., doping is carried out in a nanowire or a fin part so that an electric-fuse structure is formed and while a full-surrounding gate transistor or a fin-type field effect transistor is formed, a corresponding electric-fuse structure is formed at the same time and thus diversity of the electric-fuse structures and the semiconductor devices is realized. And when a step of forming the electric-fuse structure parasitizes in a step of forming the full-surrounding gate transistor or the fin-type field effect transistor, no extra process step is added so that production cost is low.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
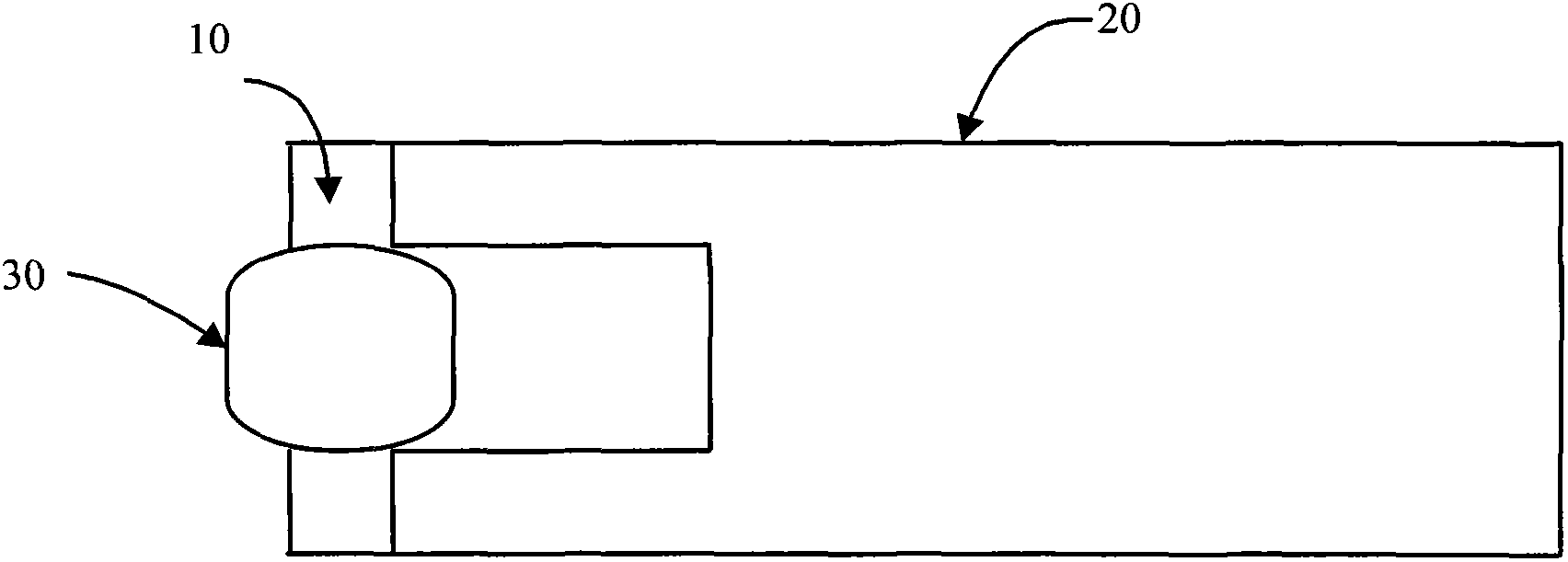
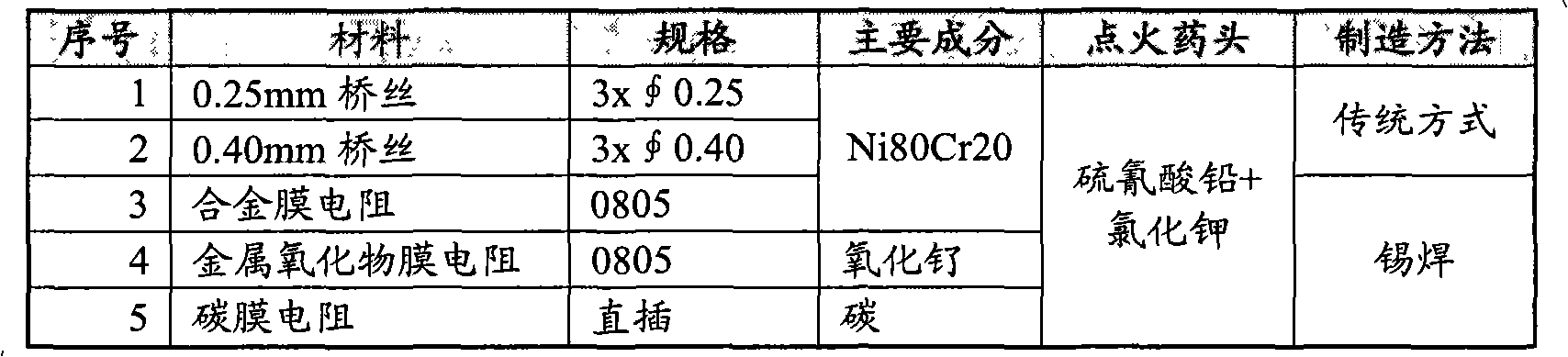
Electric fuse ignition device, electric detonator comprising electric fuse ignition device, electronic detonator comprising electric fuse ignition device, and manufacturing methods for electric detonator and electronic detonator
InactiveCN102878877AEasy to manufactureSimple preparation processBlastingAmmunition fuzesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The invention provides an electric fuse ignition device. The electric fuse ignition device comprises a film resistor and an ignition explosive head wrapping the film resistor, wherein a power supply device can supply energy to the film resistor so that the film resistor generates enough joule heat and heats the ignition explosive head to a set temperature; and therefore, the ignition explosive head is lighted. The invention also provides an electric detonator comprising the electric fuse ignition device and an electronic detonator comprising the electric fuse ignition device. The invention also provides manufacturing methods for the electric detonator and the electronic detonator. According to the electric fuse ignition device provided by the invention, the film resistor is easy to manufacture, low in cost, high in yield, not easy to break and high in resistance precision, so that the electric detonator comprising the electric fuse ignition device and the electronic detonator comprising the electric fuse ignition device also have the advantages that the manufacturing is simple, the cost is low, the yield is high, the misfire rate is low, and the explosion precision is high. The manufacturing methods for the electric detonator and the electronic detonator are high in assembly automation degree, precise, reliable, high in yield and low in cost.
Owner:XINJIANG CHUANGANDA ELECTRONICS TECH DEV
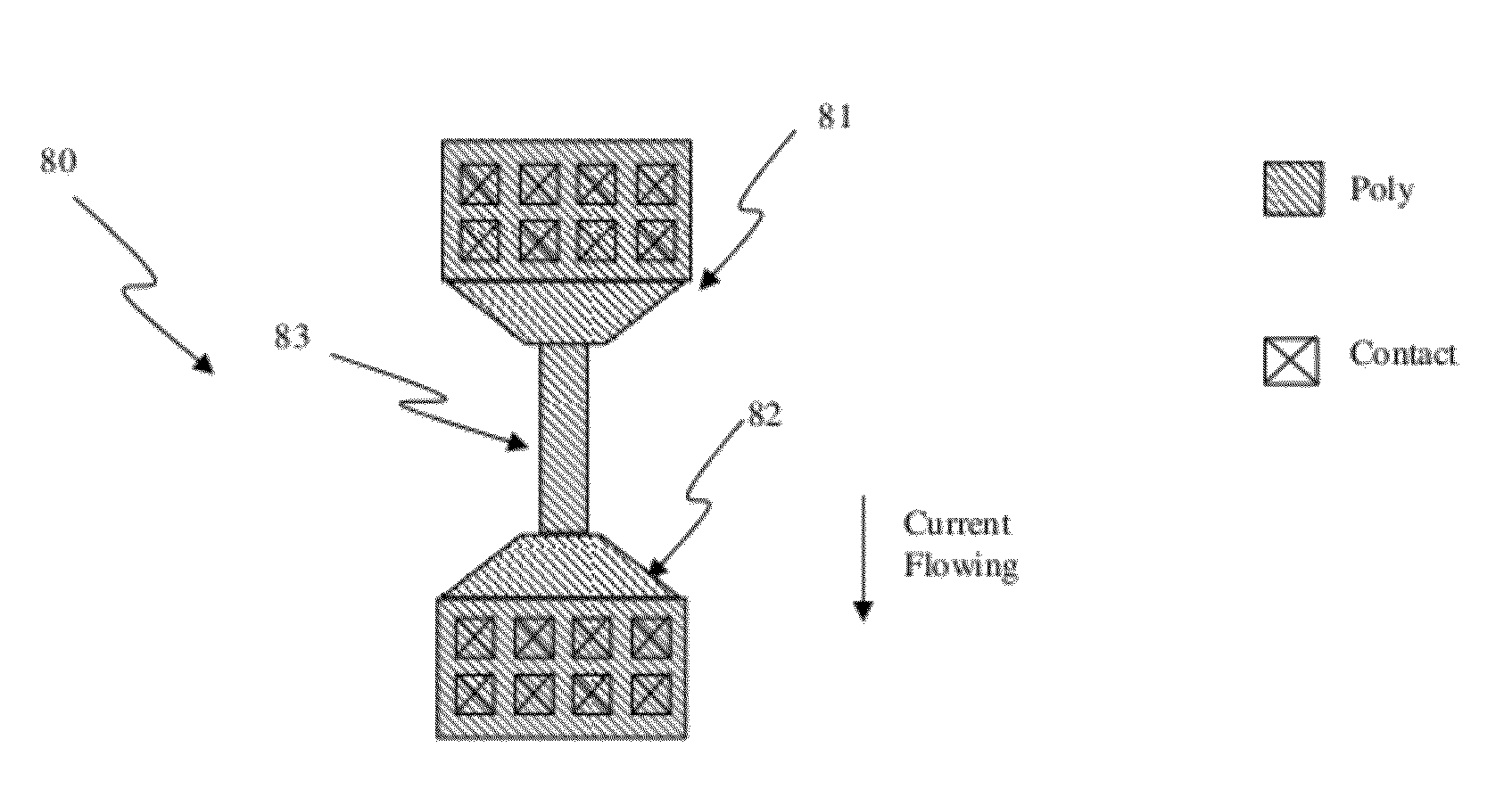
Multicrystalline silicon compounds electric fuse silk part
ActiveCN101170099AIncreased median resistanceInhibit zone overheatingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor materials
A polycide electric fuse device includes an underlay, and a semiconductor material layer arranged on the underlay. The semiconductor material layer includes an outgoing area with the same doping sorts on two ends and a middle undoped area or a middle area with the doping content lower than two ends of the outgoing area. The middle area is provided with one or a plurality of blowing areas. A metal silicide layer is arranged on the semiconductor material layer. The invention will control the blowing within the undoped or less doped middle area. After blowing, resistance medium value increases and distribution range narrows down. The invention also can prohibit the area overheating caused by current in blowing.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
CMOS image sensor including tunable read amplifier
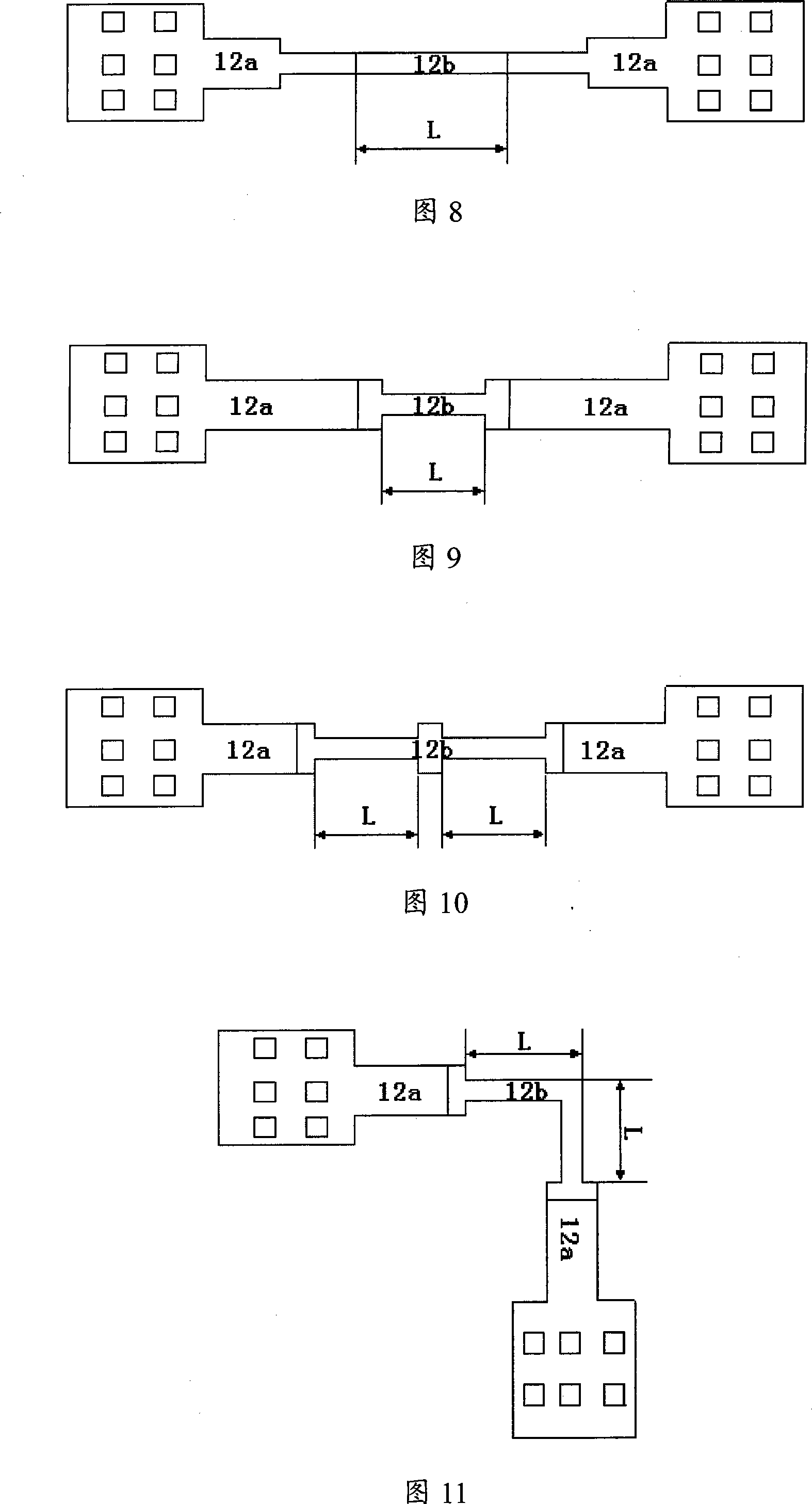
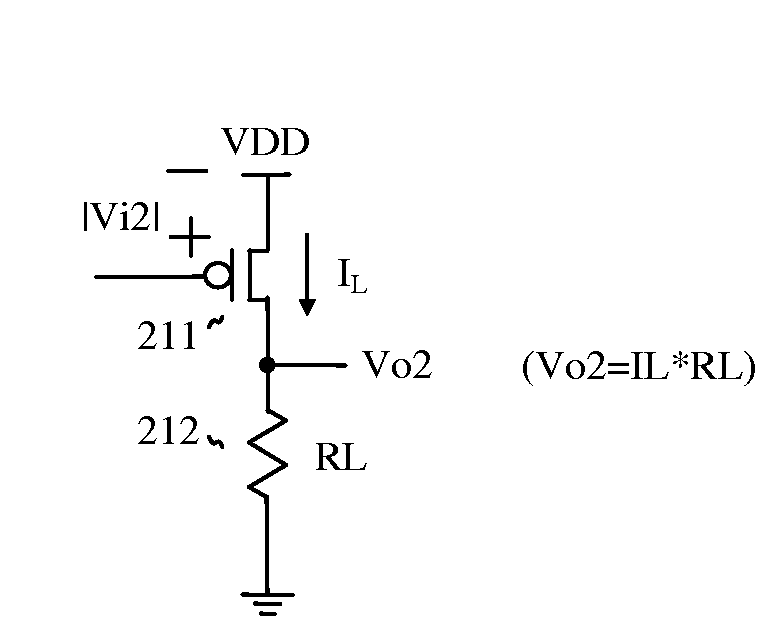
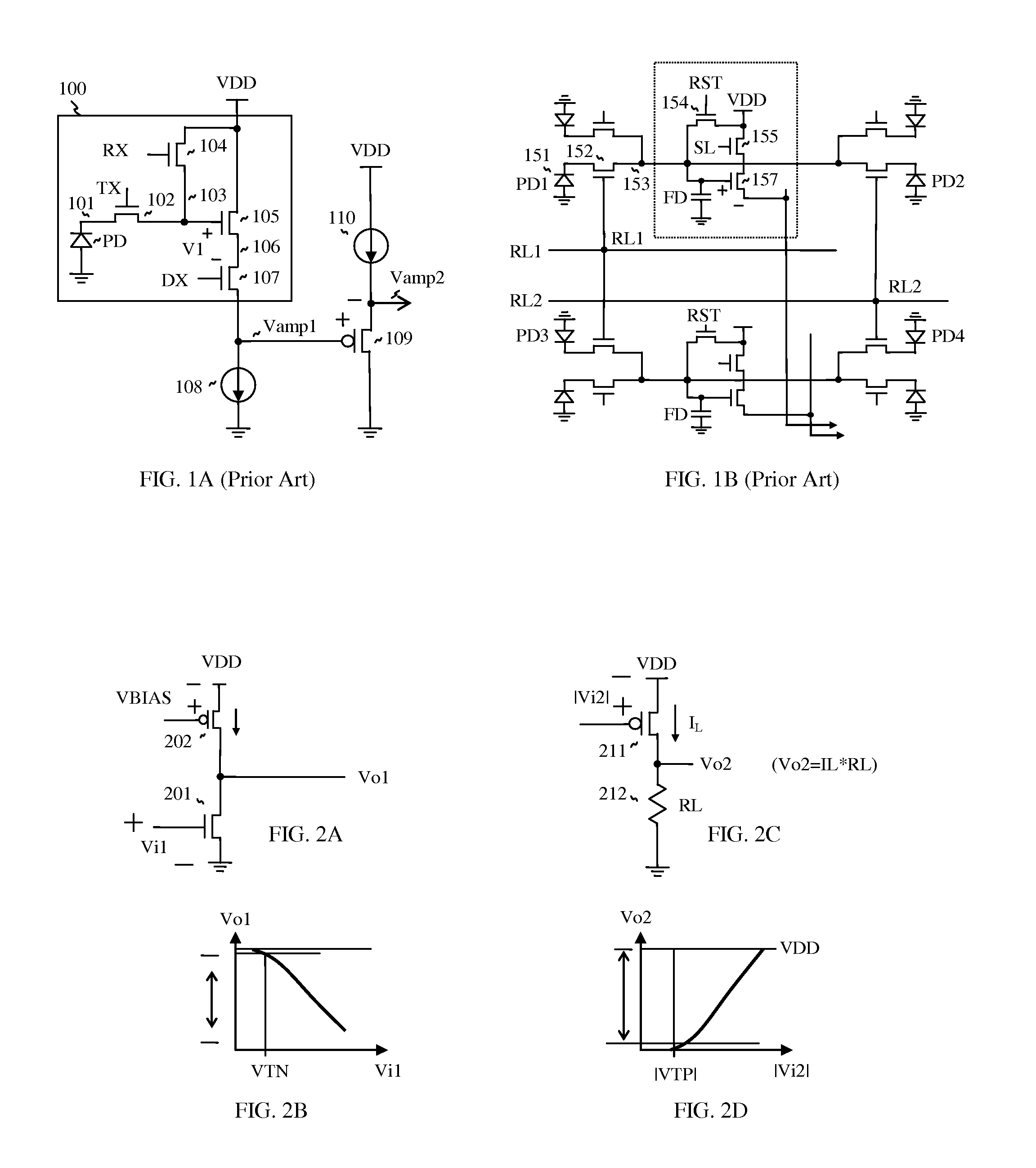
InactiveUS20100013042A1Improve production yieldGain of the amps can be optimizedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
CMOS image sensor is realized, wherein a pre-amp amplifies the voltage of a photo detector, and a main amp amplifies the output of the pre-amp. And the pre-amp is adjustable for receiving the output of the photo detector, and also the main amp is adjustable for optimizing the output swing. With the adjustable amps, low sensitivity photo detector can be amplified more, and high sensitivity photo detector can be amplified less, which enables to adjust the gain of each amp from the low-sensitive to high-sensitive photo detector. The information for adjusting the amps is stored in the latches of the chip, wherein include laser-blown fuses or electric fuses. In doing so, the photo detector can be stacked over the access device. In particular, photo detector is repairable, wherein failed photo detector is replaced with non-failed photo detector.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
Electric fuse circuit available as one time programable memory
ActiveUS20080186789A1Reduce areaInexpensiveRead-only memoriesHeating/cooling contact switchesElectric fusesElectrical current
A first transistor is connected in series with one end of a fuse element. A second transistor is connected in series with the other end of the fuse element. A current flows through the fuse element when both the first and second transistors are turned on.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for protecting an electric line
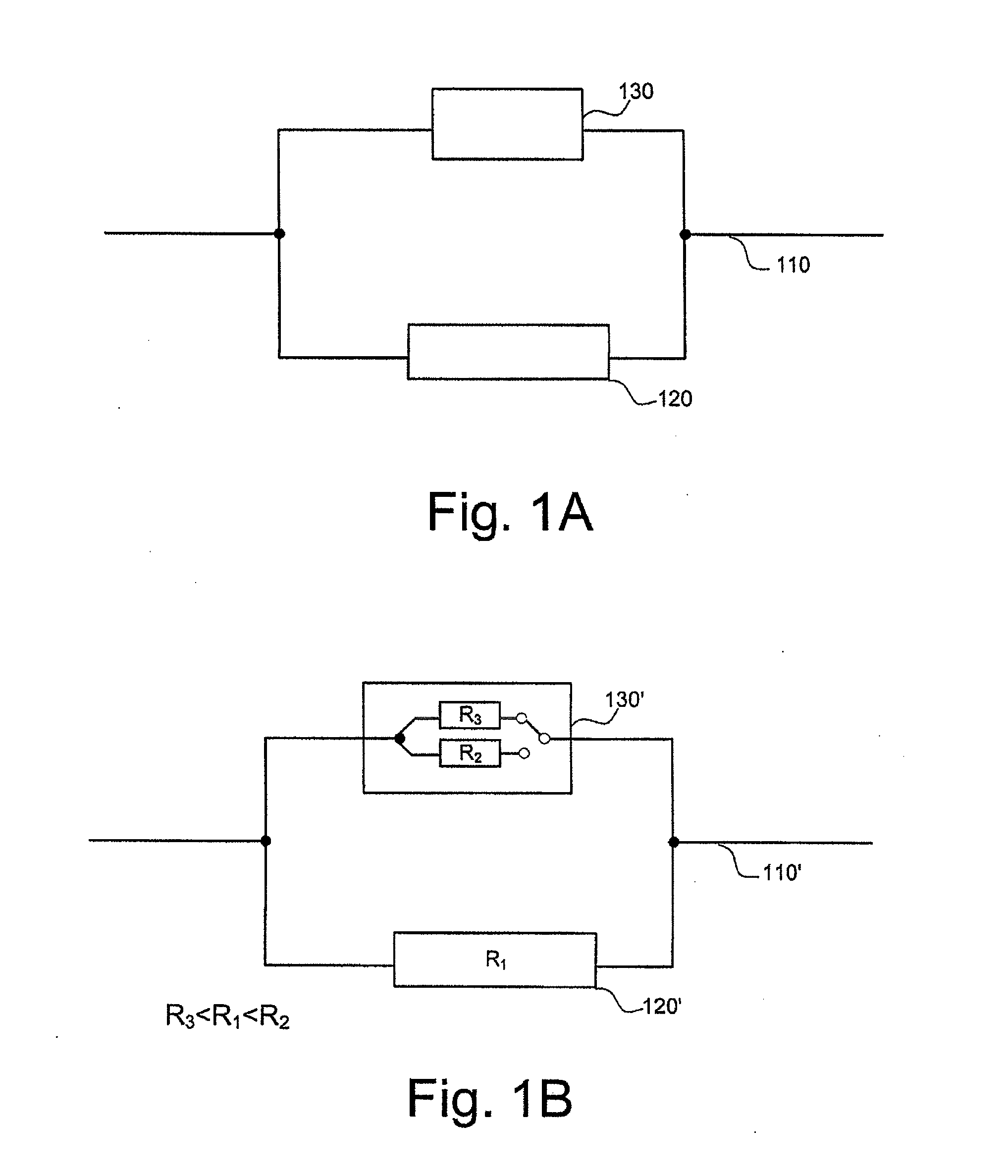
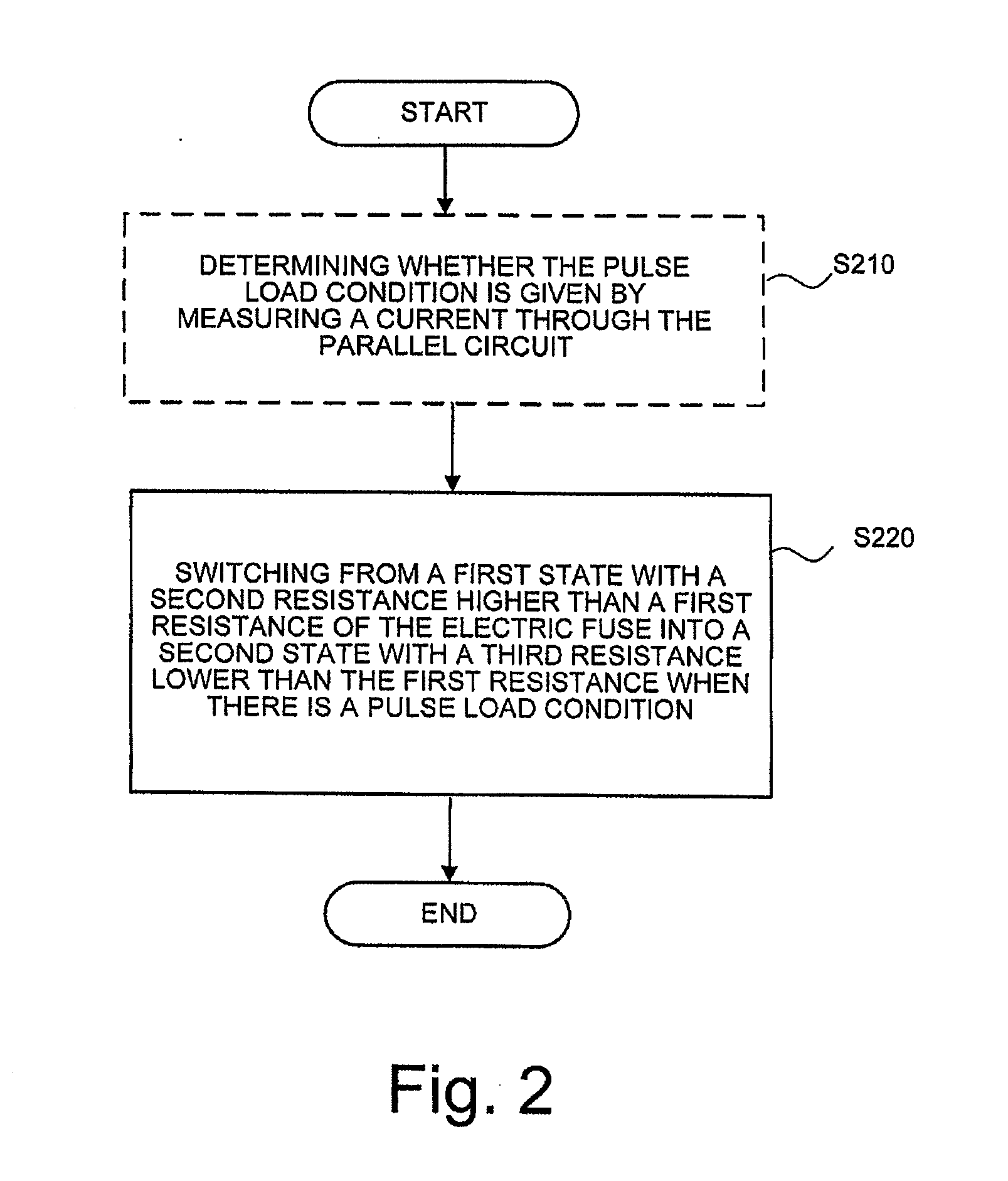
ActiveUS20110096448A1Batteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsPulse loadElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for protecting an electric line in a vehicle, it being possible to adapt the apparatus to the properties of the electric line to be protected. The apparatus for protecting an electric line comprises an electric fuse and a controllable switching element, the controllable switching element and the electric fuse being formed as a parallel circuit, and the parallel circuit being connectable in series to the electric line, the electric fuse being disposed in a first branch of the parallel circuit, which has a first resistance, and the controllable switching element being disposed in a second branch of the parallel circuit, and the controllable switching element being configured to accommodate at least two states, a first state with a second resistance higher than the first resistance, and a second state with a third resistance lower than the first resistance, and to switch into the second state when there is a pulse load condition.
Owner:LISA DRAXLMAIER GMBH
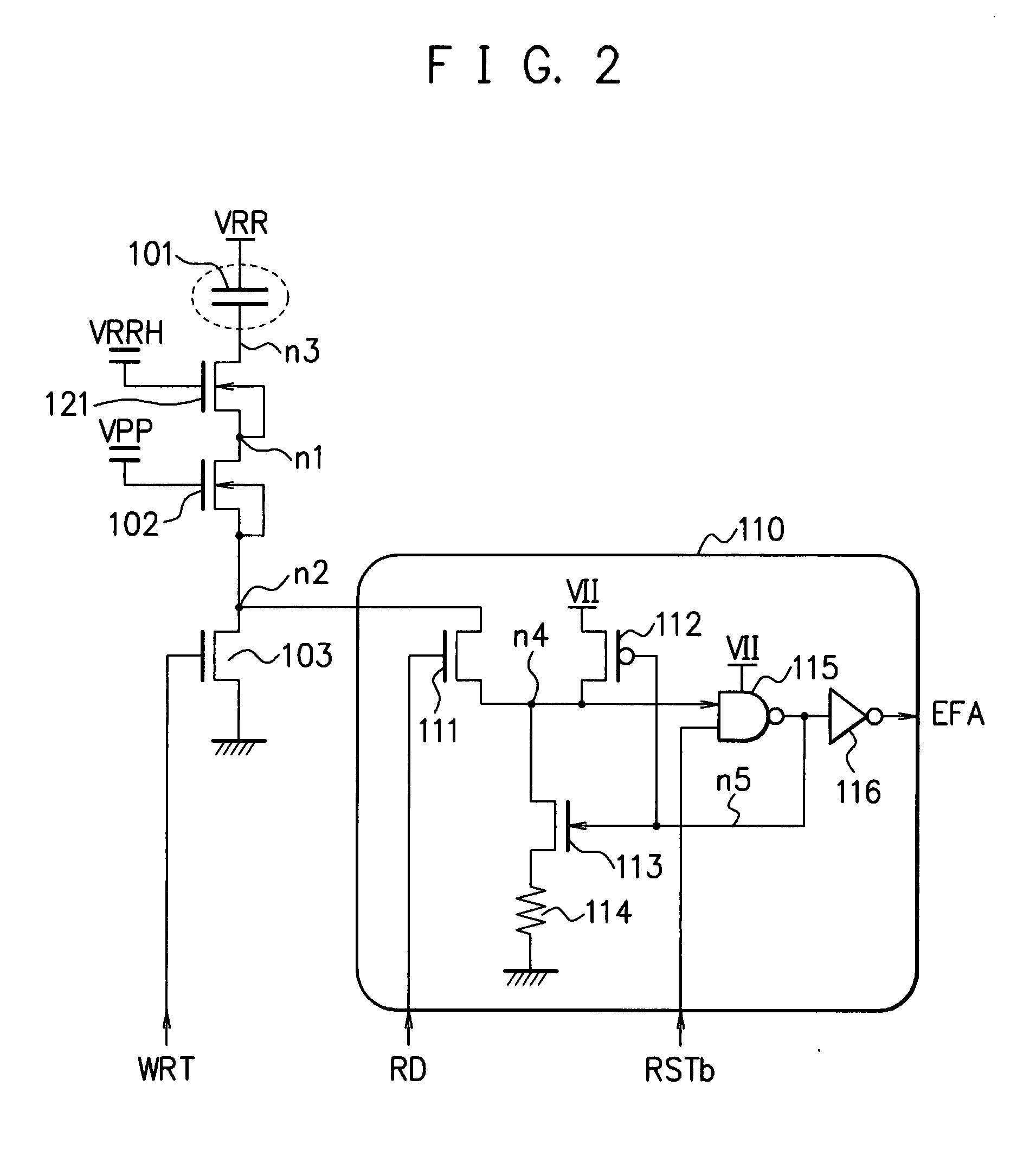
Electric fuse circuit and electronic component
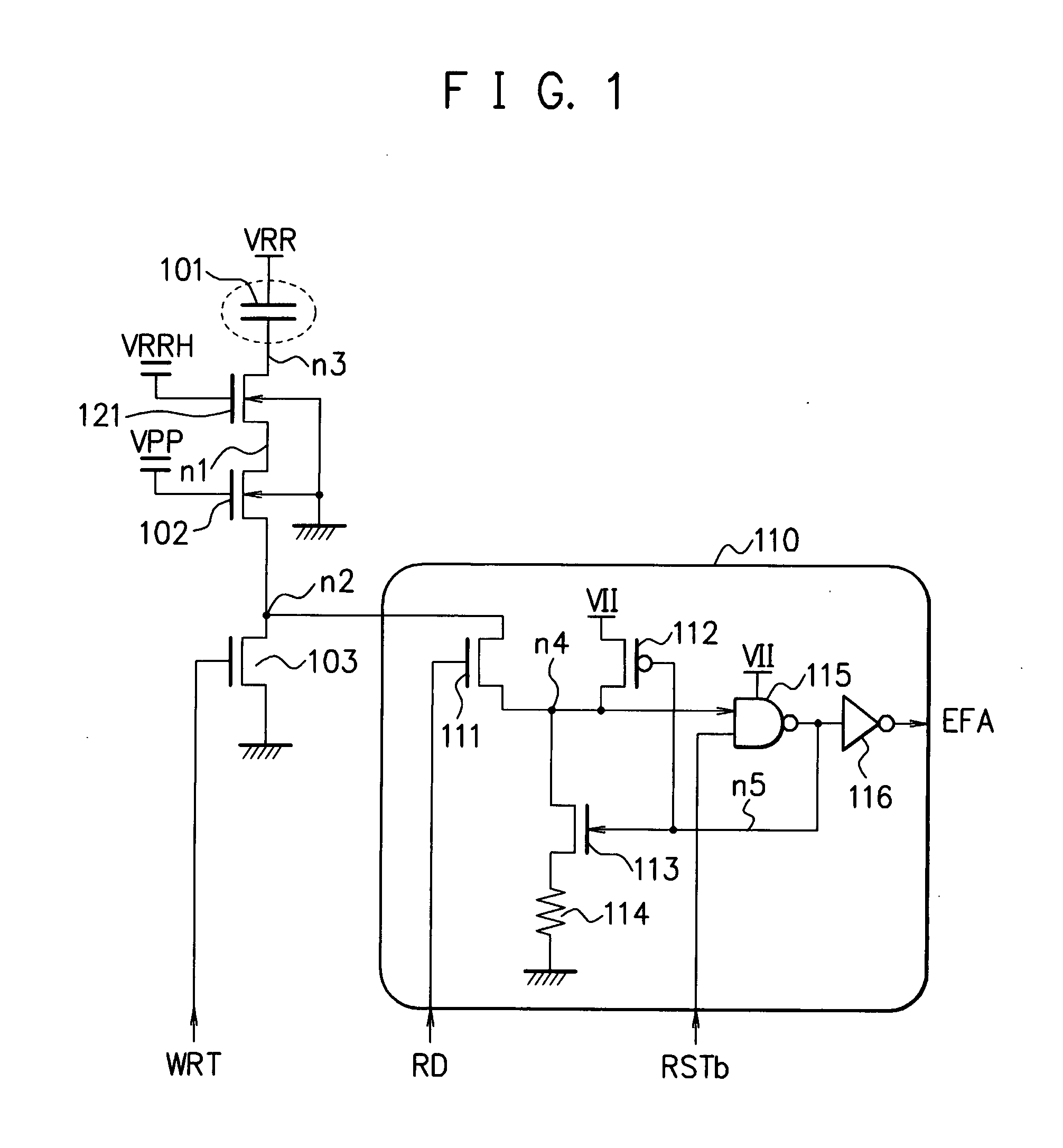
InactiveUS20080042234A1Improve reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric fusesEngineering
An electric fuse circuit is provided which has a capacitor that forms an electric fuse; a write circuit for breaking an insulating film of the capacitor, by applying a voltage to a terminal of the capacitor in response to a write signal; and at least two transistors, including a first transistor and a second transistor, which are connected in series between the capacitor and the write circuit.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Electric apparatus with electric terminals and fused structures
InactiveUS6707688B2Increased capacity and power ratingEasy to installElectrically conductive connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityService personnel
Electric apparatus having distinct electric terminals has an input power terminal of electrically insulating material, including a base of electric insulating material having a first electric terminal base portion and a second electric base portion spaced from that first electric base portion, and a barrier wall of insulating material on that base acting as an isolator between the first and second electric terminals on these base portions, and preferably also as a standoff for a protective cover. A plurality of electric fuse holders in that or other electric apparatus may be mounted in mutually spaced relationship, and a heat sink including a frame around that plurality of mutually spaced electric fuse holders is in heat-transfer relationship with these electric fuse holders, and includes a cross-piece between each adjacent pair of the mutually spaced electric fuse holders. A flame-resistant designation card for that or other apparatus has a first data-bearing section, a second data-bearing section, a first folding crease between such first and second data-bearing sections, a shorter third section adjacent that second data-bearing section, and a second folding crease between the shorter third section and the second data-bearing section. Fuse condition designation flags are rendered better visible by service personnel and fuse rating designation pins are better organized. Ground wire terminals are safeguarded against rotation and loosening.
Owner:TELECT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com