Electrical fuse device based on a phase-change memory element and corresponding programming method
a technology of phase-change memory and electrical fuse device, which is applied in the direction of digital storage, semiconductor devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high programming voltage, large oxide thickness of modern integrated circuit, and inability to make their use totally satisfactory within modern integrated devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
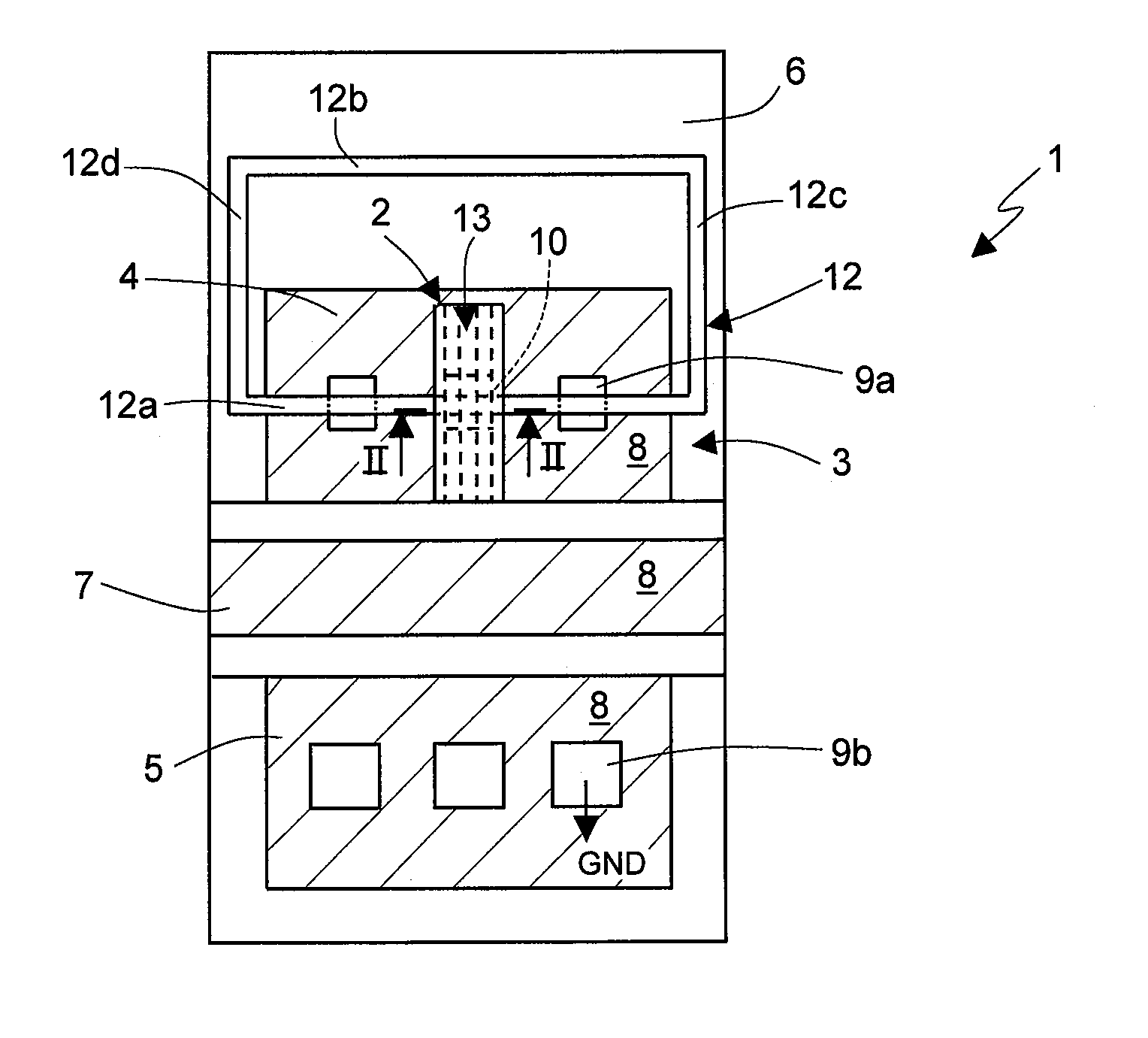
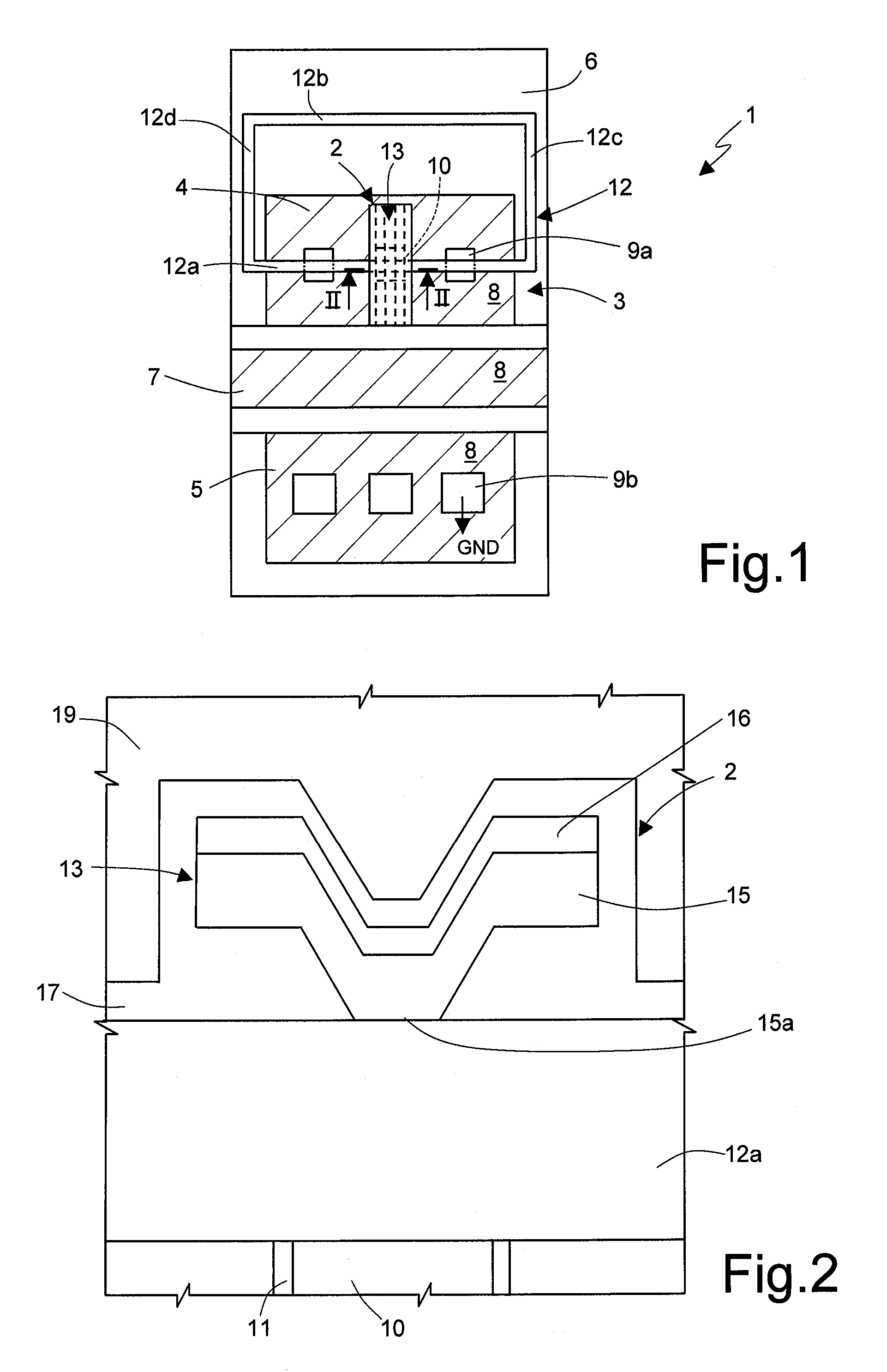
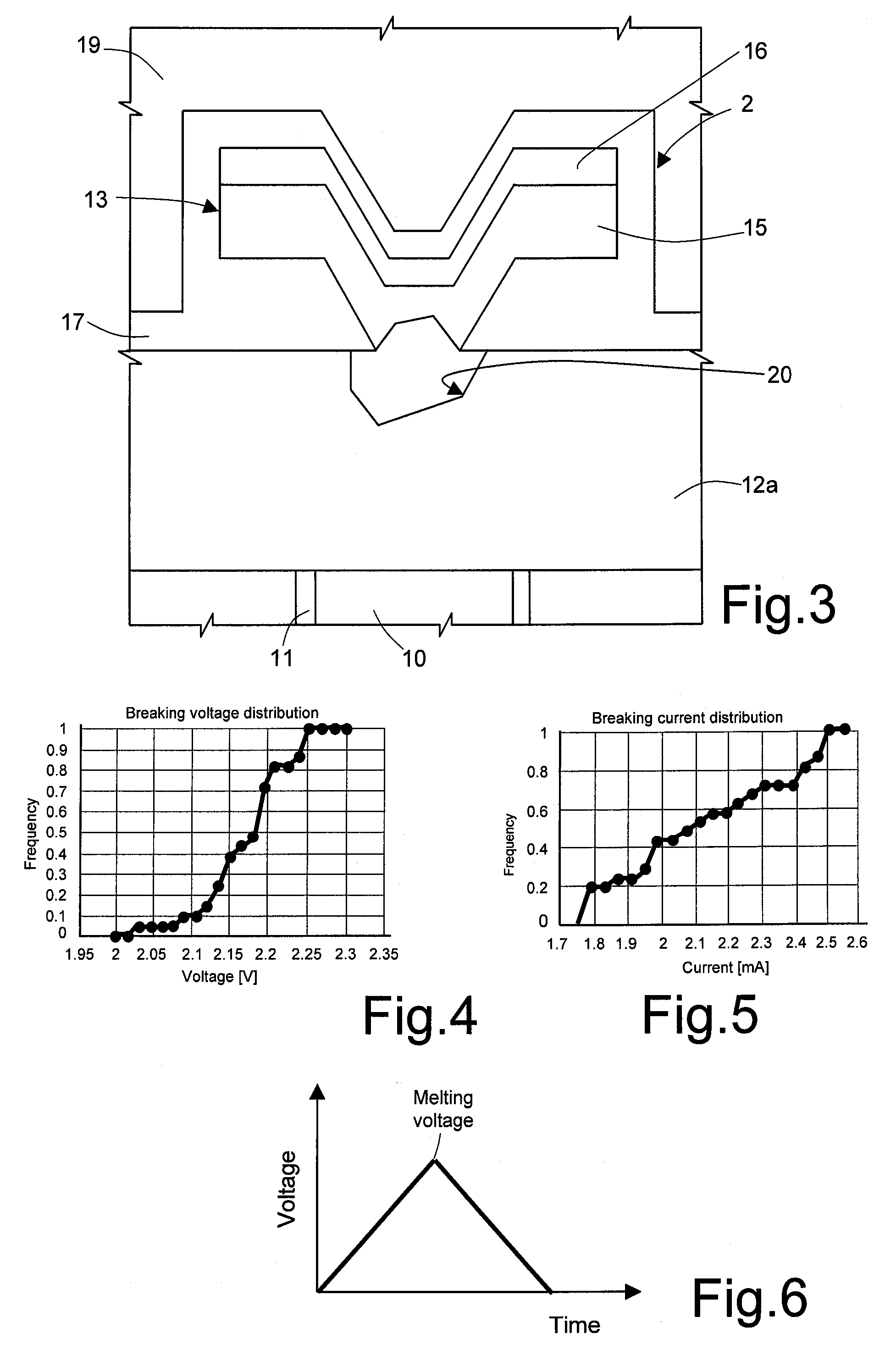
[0031] In detail, and as illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2, a fuse device 1 according to the present invention, comprises a fuse element 2 (as will be clarified hereinafter, based on a phase-change memory element), and a selector element 3, which is electrically connected to the fuse element 2 and is configured to enable programming of the fuse element 2. In particular, by way of example, the selector element 3 illustrated in FIG. 1 is an N-channel MOSFET of a planar type. It is clear, however, that other selector elements could be used in an altogether equivalent way, for example any FET (vertical MOSFET, JFET, FinFET, etc.), or else a BJT or a BiFET. Furthermore, FIG. 1 and the following figures illustrate a phase-change memory element having a microtrench architecture. Once again, it is clear that other structures could be used in an altogether equivalent way, for example of the wall or tubular type.
[0032] In detail, the selector element 3 is provided with: a first current-conduction ...
second embodiment
[0043] A second embodiment, illustrated in FIGS. 9 and 10, envisages again the use of a selector element 3 of the planar N-channel MOSFET type, but in this case the bottom electrode 10 of the fuse element 2 is connected to the source region 5 of the selector element 3.
[0044] In detail, the selector element 3 has an active area 22, having P-type conductivity, made within the substrate 6 (having a P-doping) and isolated by means of isolation trenches 23, for example using the Shallow-Trench Isolation (STI) technique. The drain region 4 and the source region 5 are provided within the active area 22; in detail, the drain region 4 comprises a first drain strip 4a and a second drain strip 4b, which extend in a first direction x parallel to one another, and the source region 5 comprises a source strip extending in the first direction x between the drain strips 4a, 4b. In addition, electrical contacts 24 (illustrated in FIG. 9) contact the drain strips 4a, 4b. The gate region 7 is constitut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com