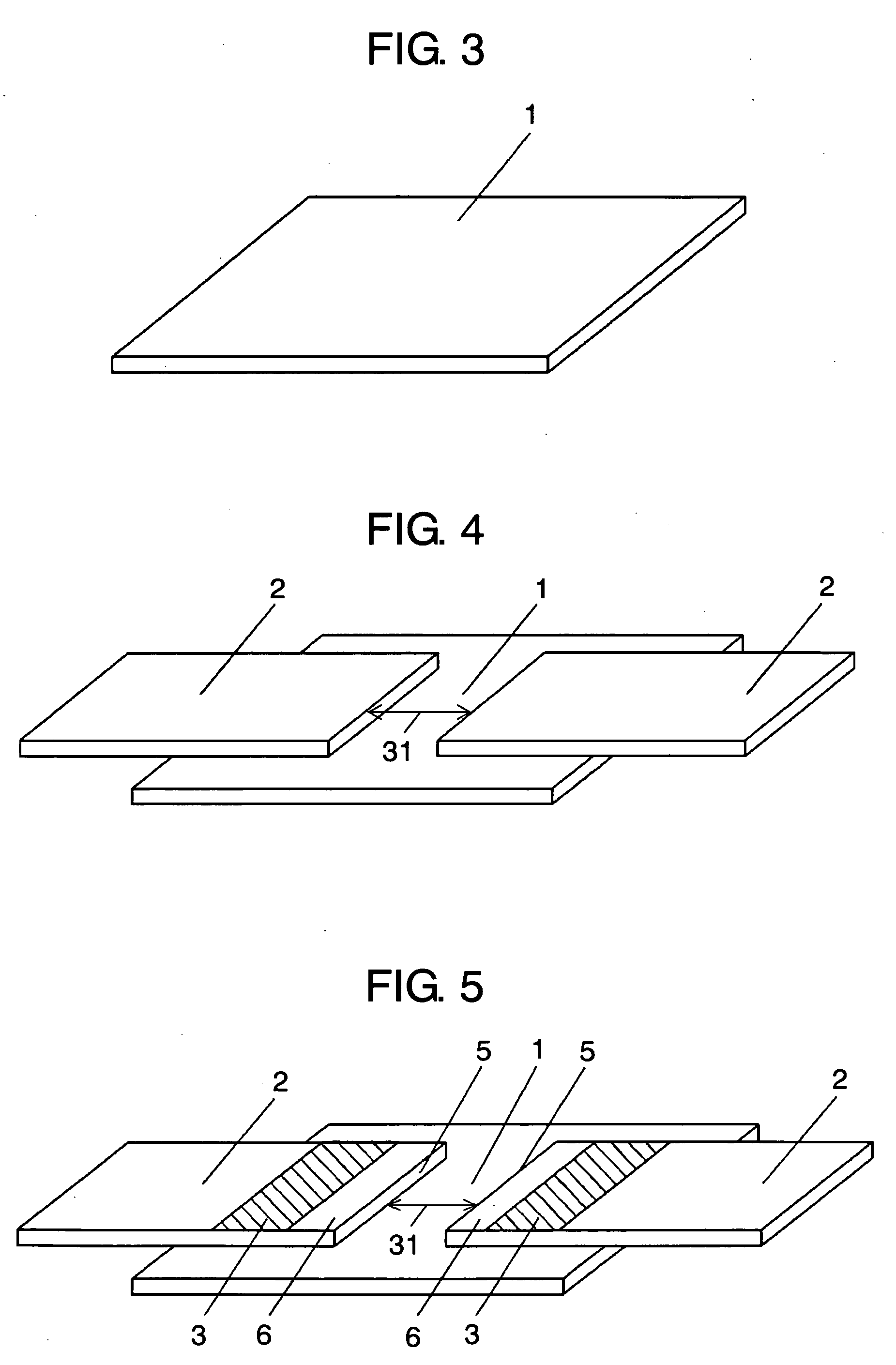
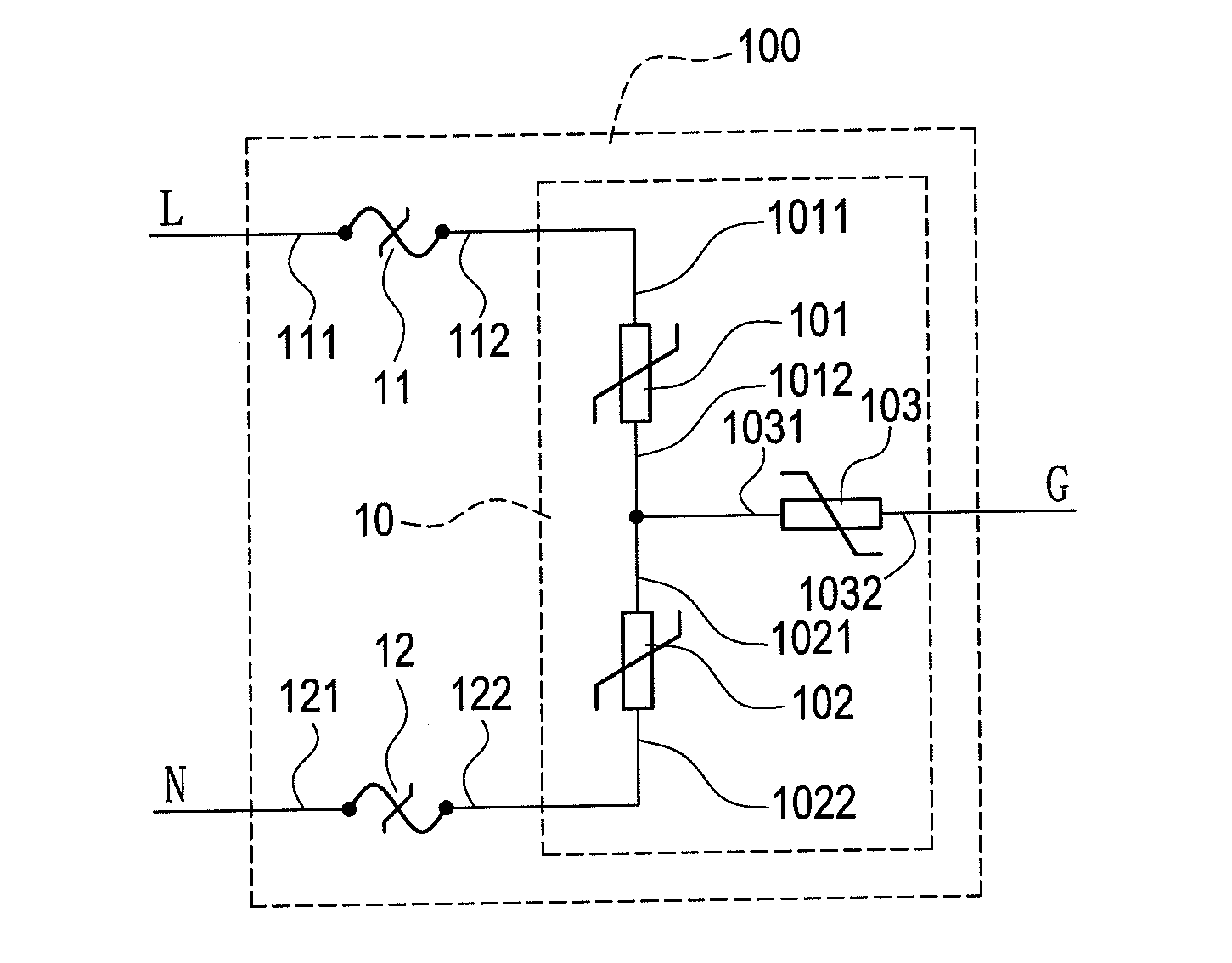
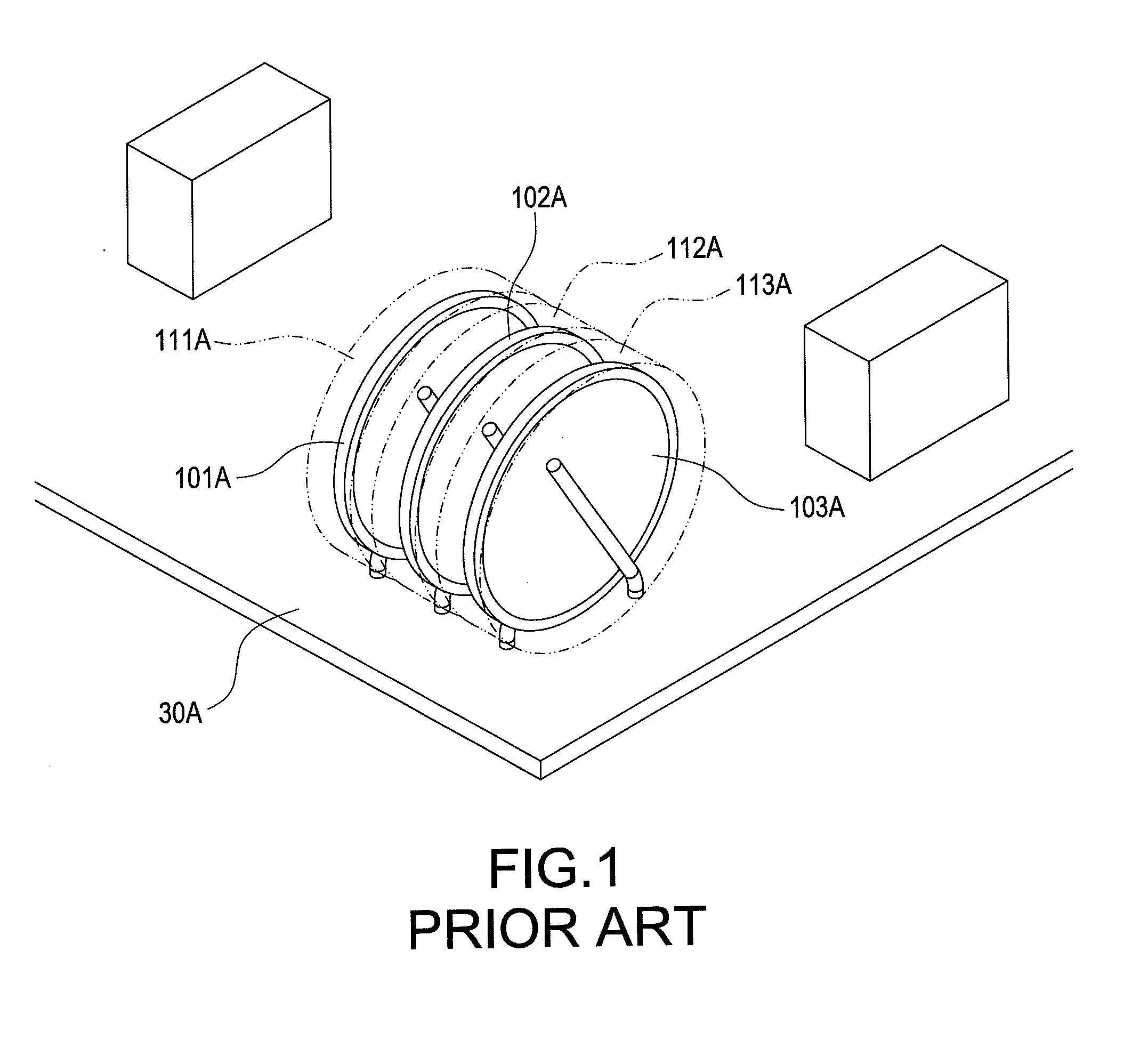
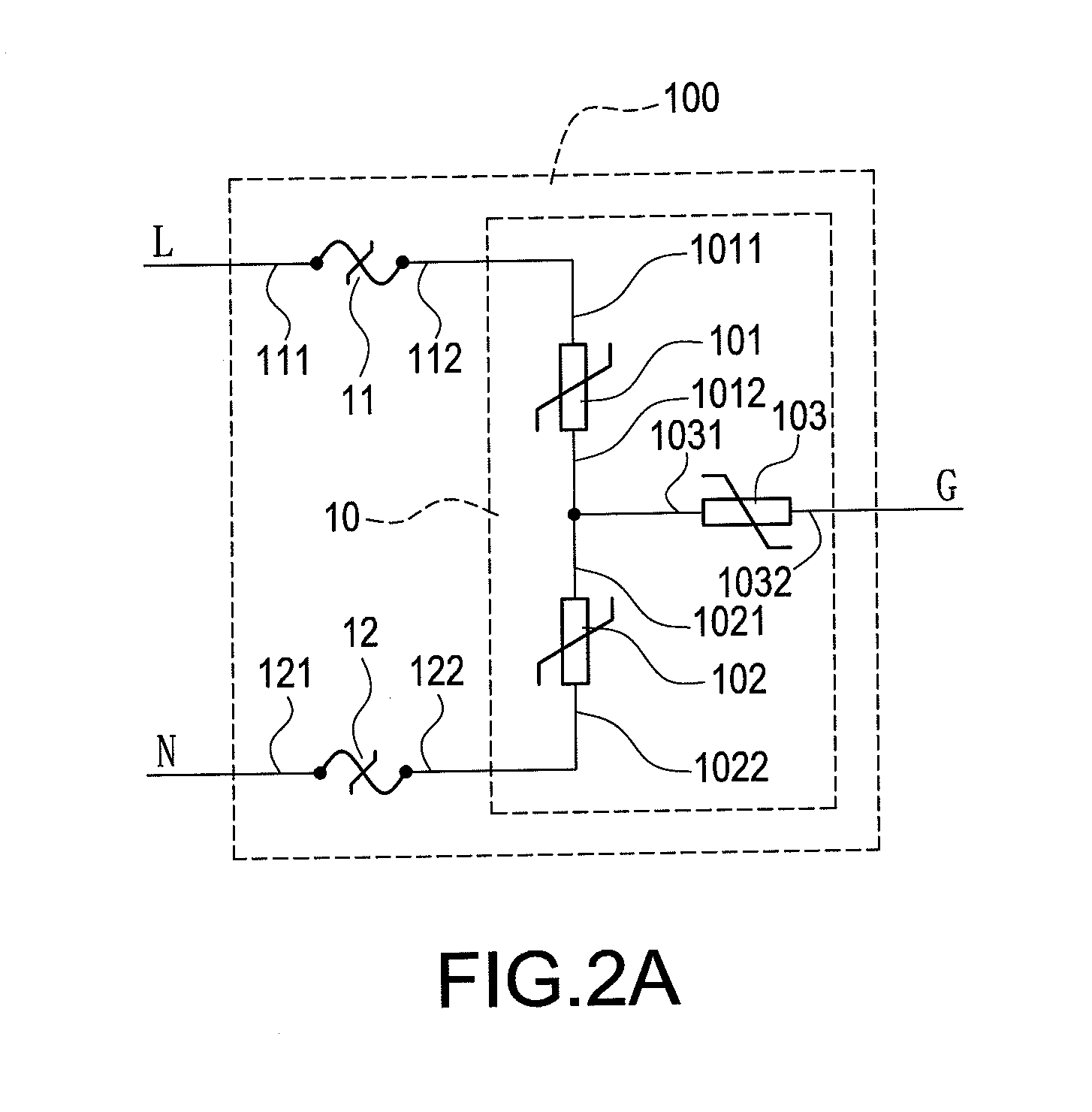
Patents
Literature
3978 results about "Fuse cutout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
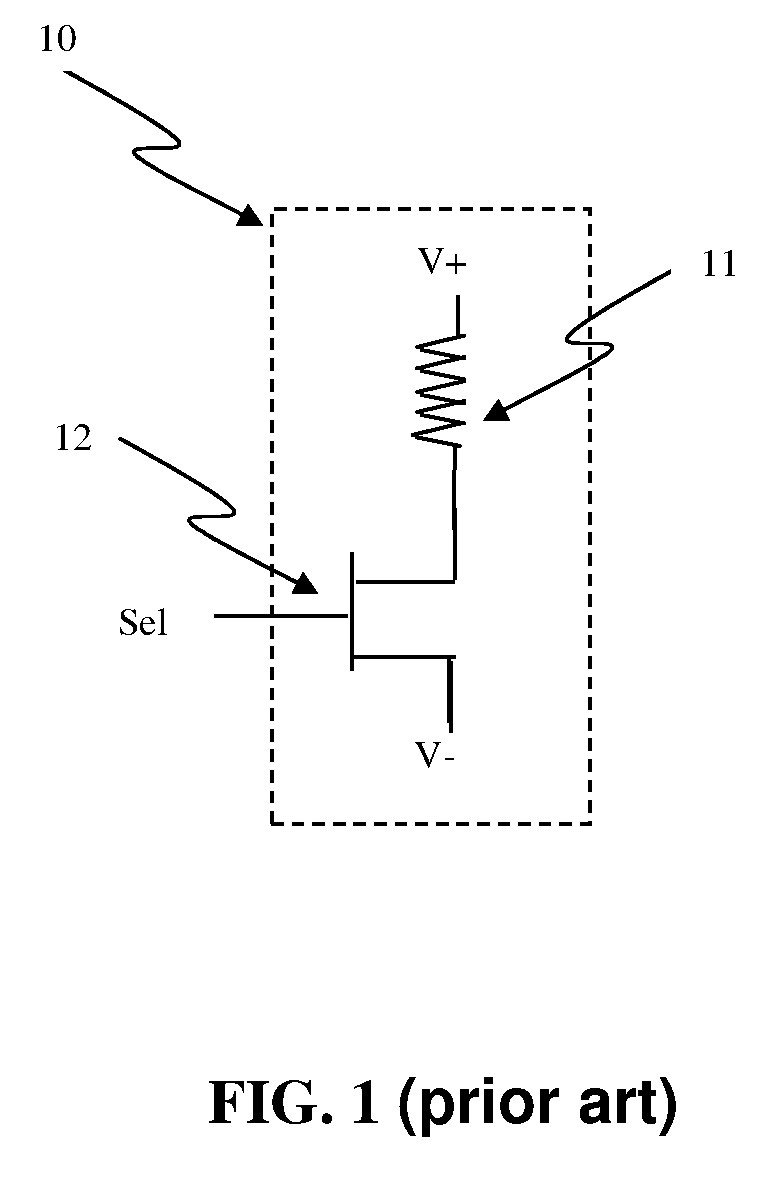
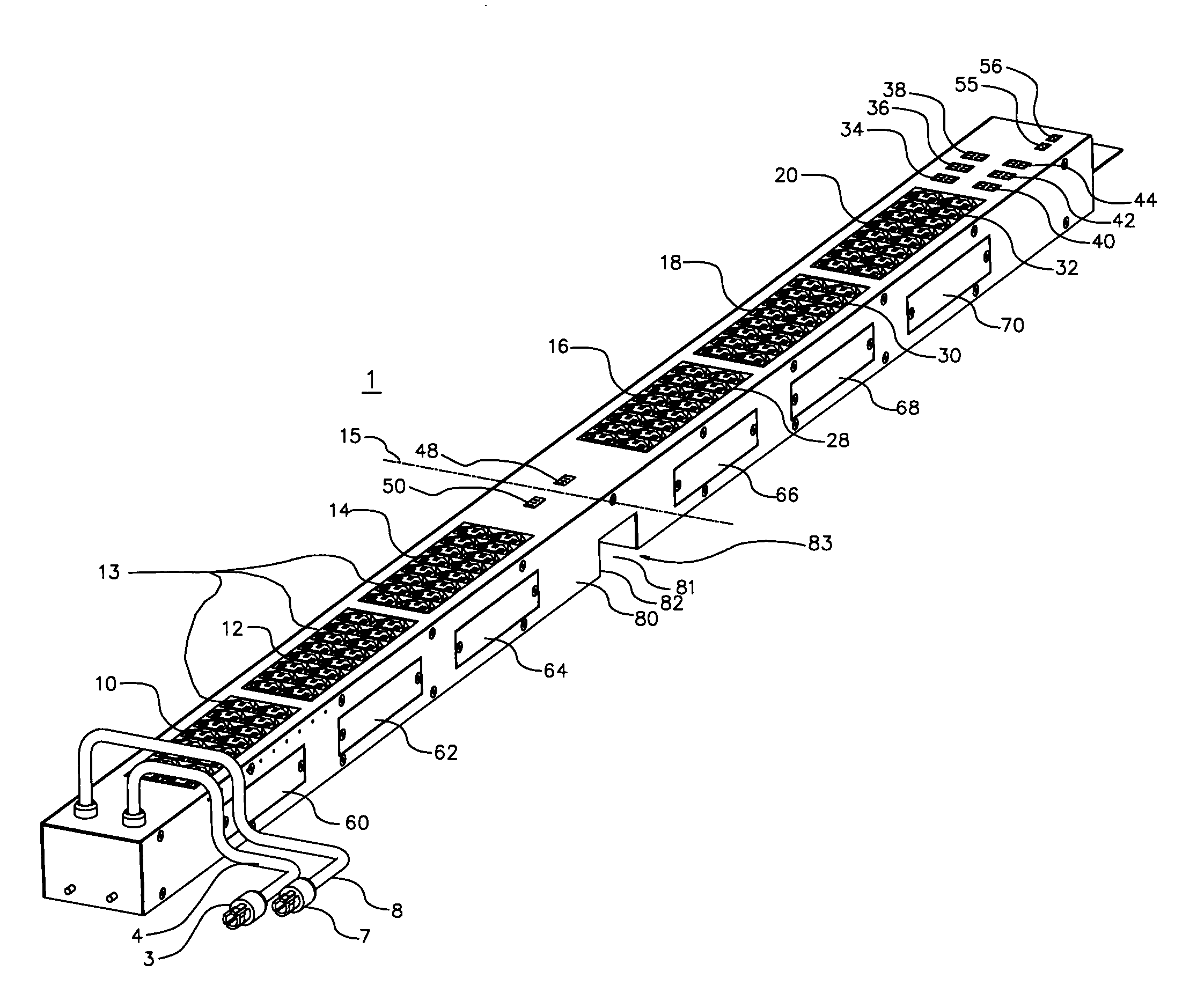
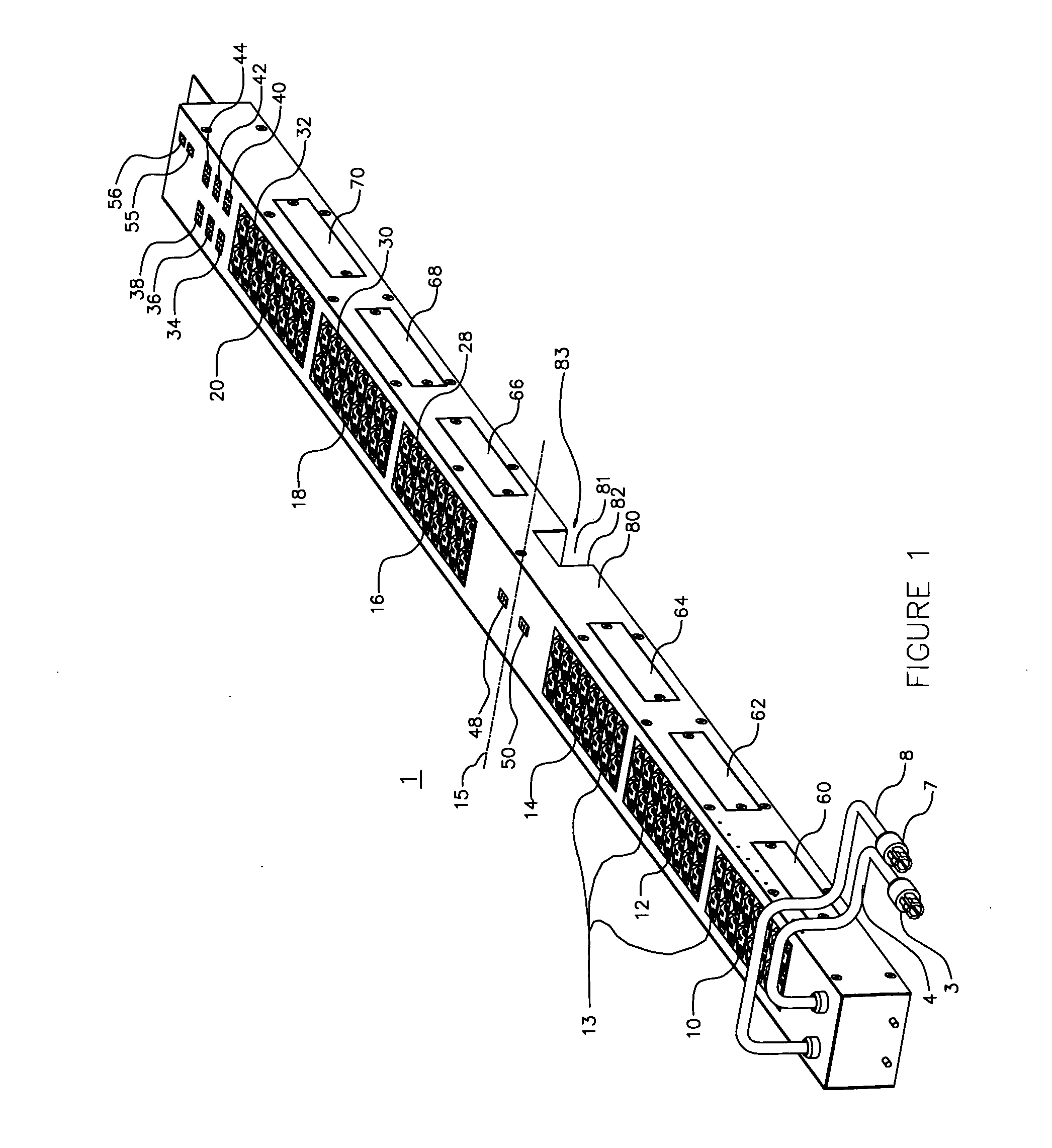
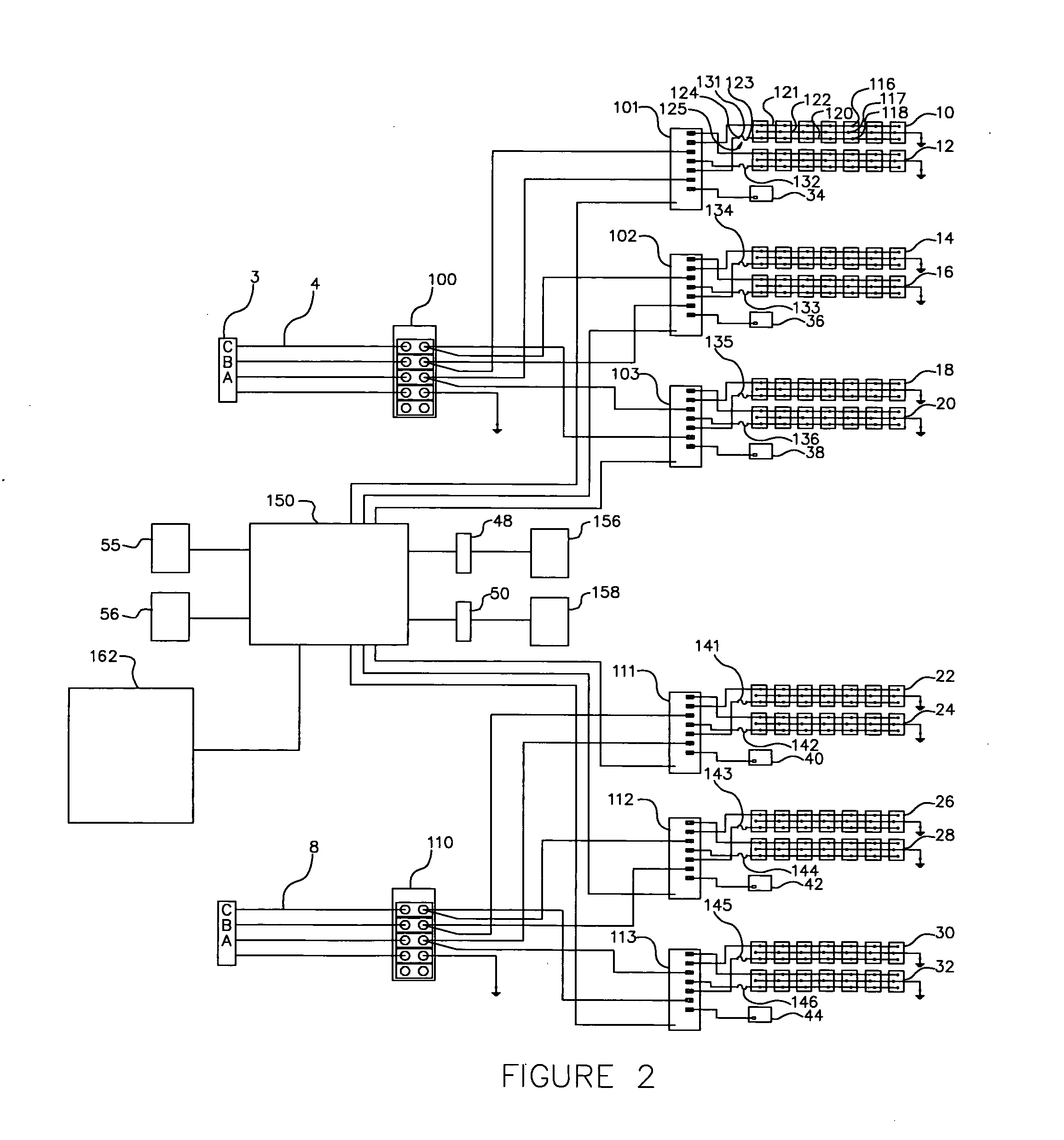
In electrical distribution, a fuse cutout or cut-out fuse is a combination of a fuse and a switch, used in primary overhead feeder lines and taps to protect distribution transformers from current surges and overloads. An overcurrent caused by a fault in the transformer or customer circuit will cause the fuse to melt, disconnecting the transformer from the line. It can also be opened manually by utility linemen standing on the ground and using a long insulating stick called a "hot stick".
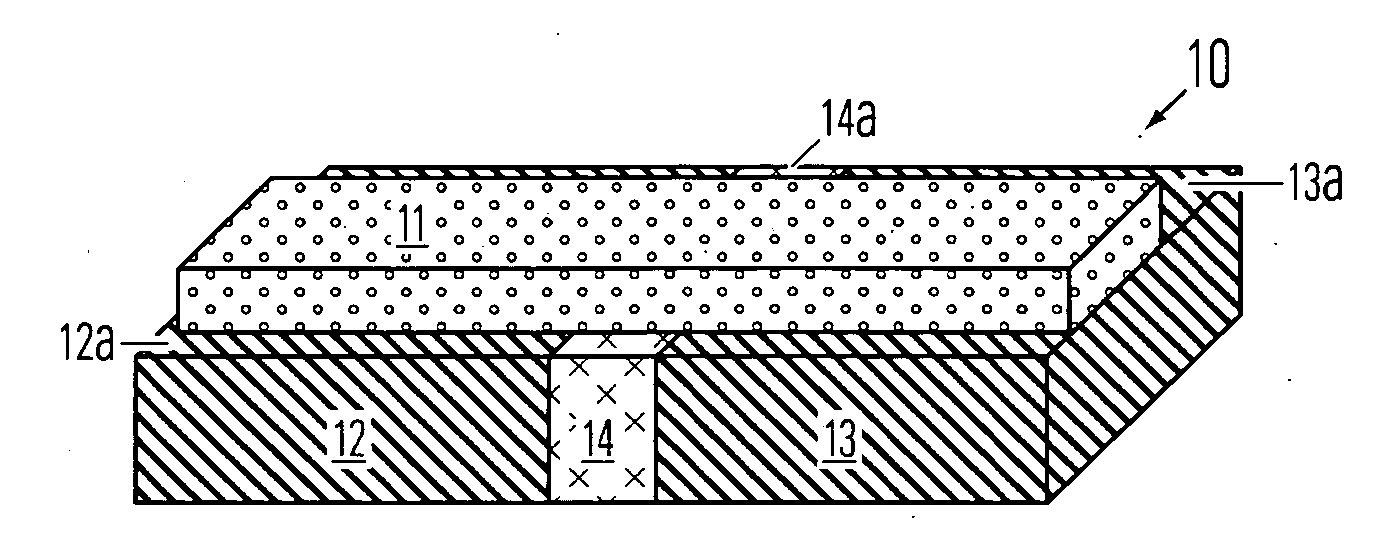
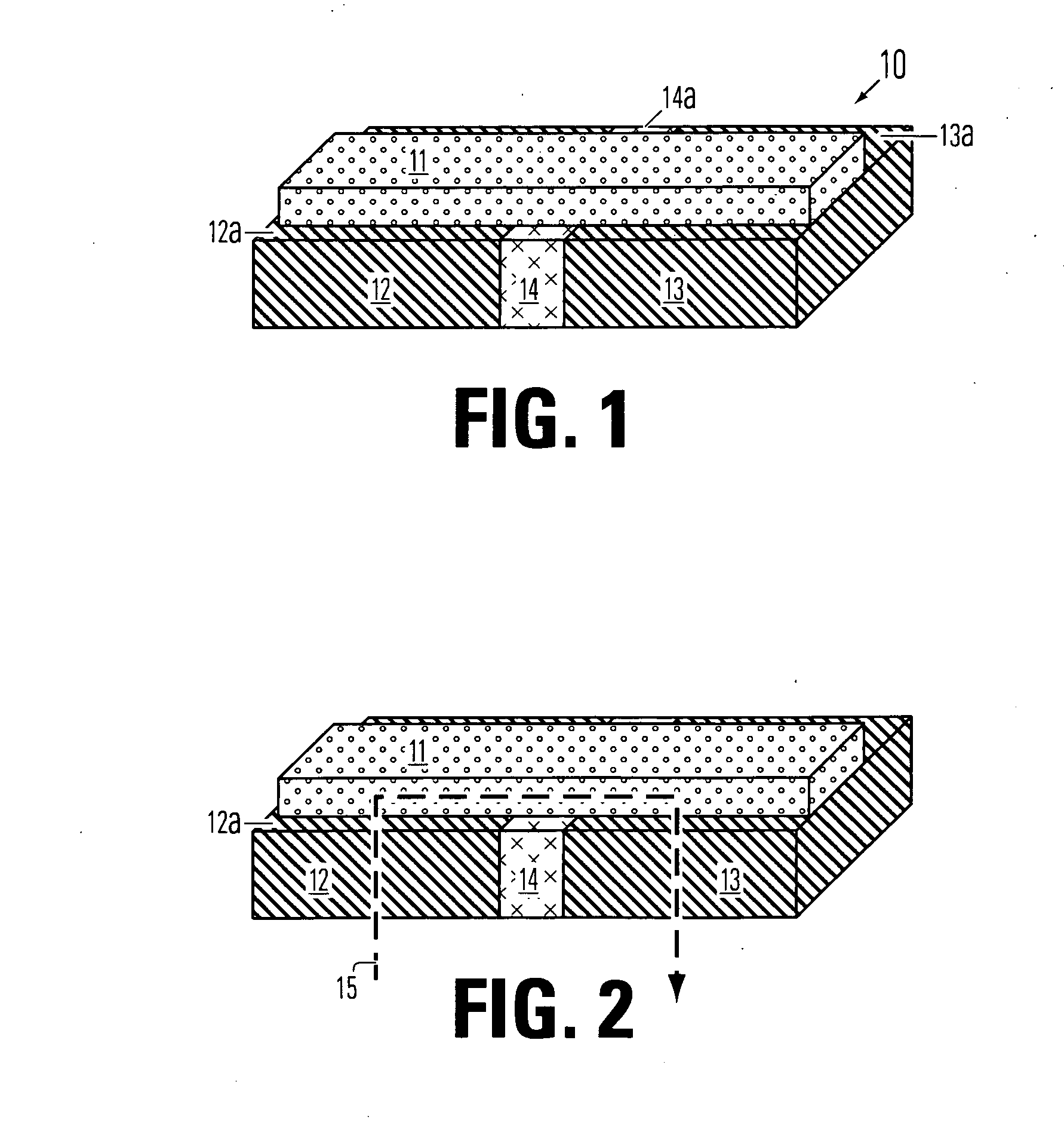
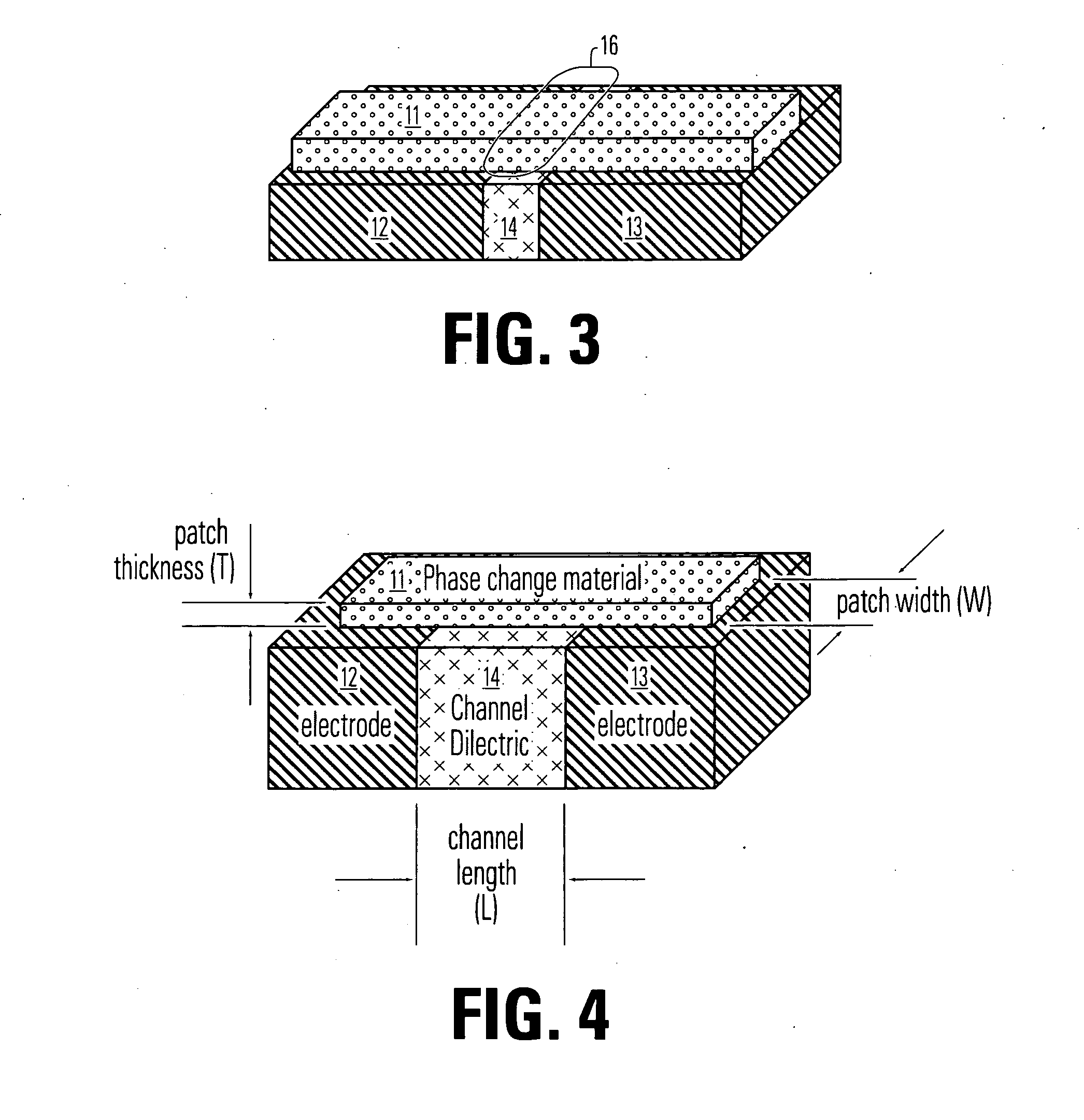
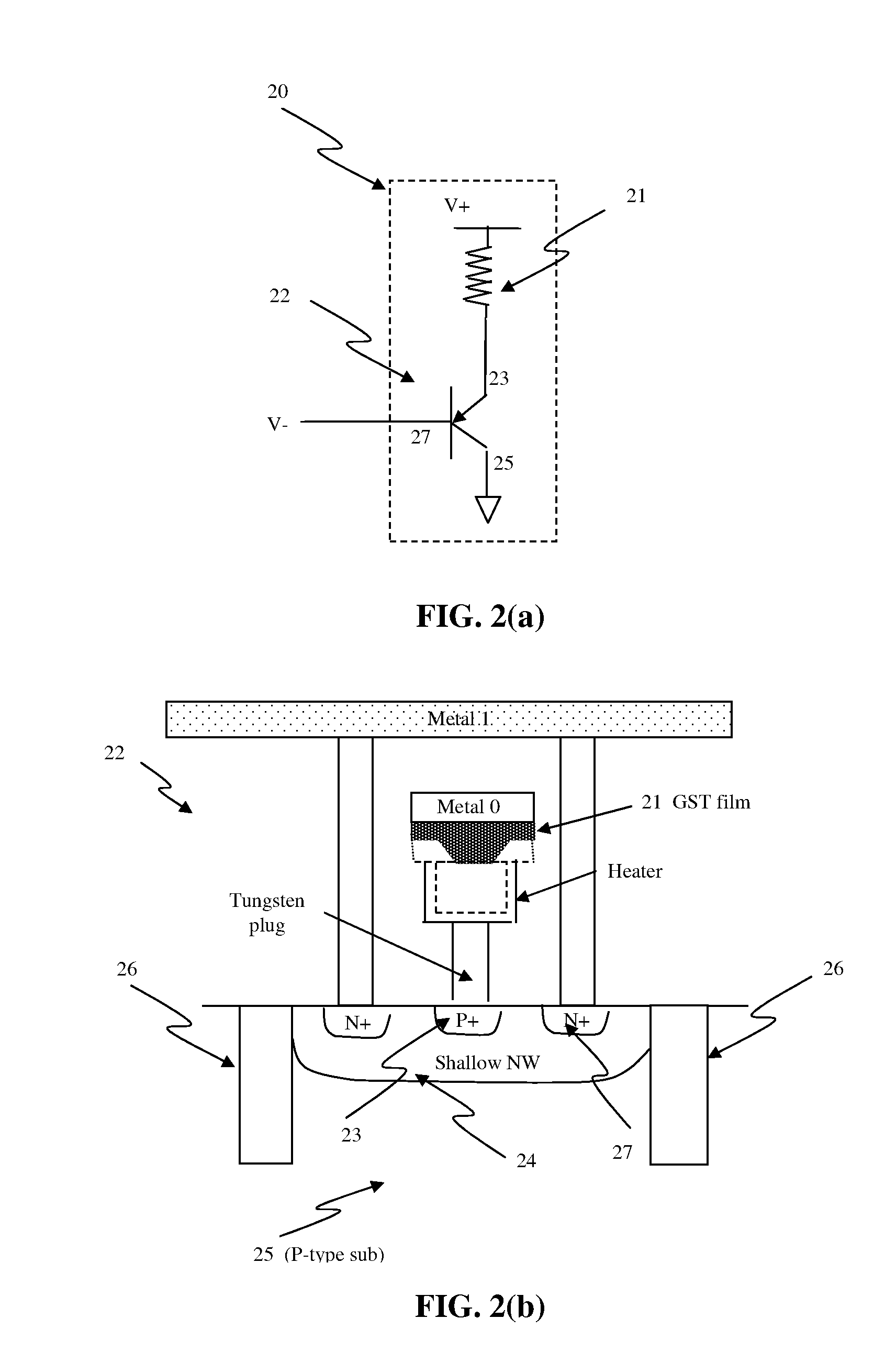
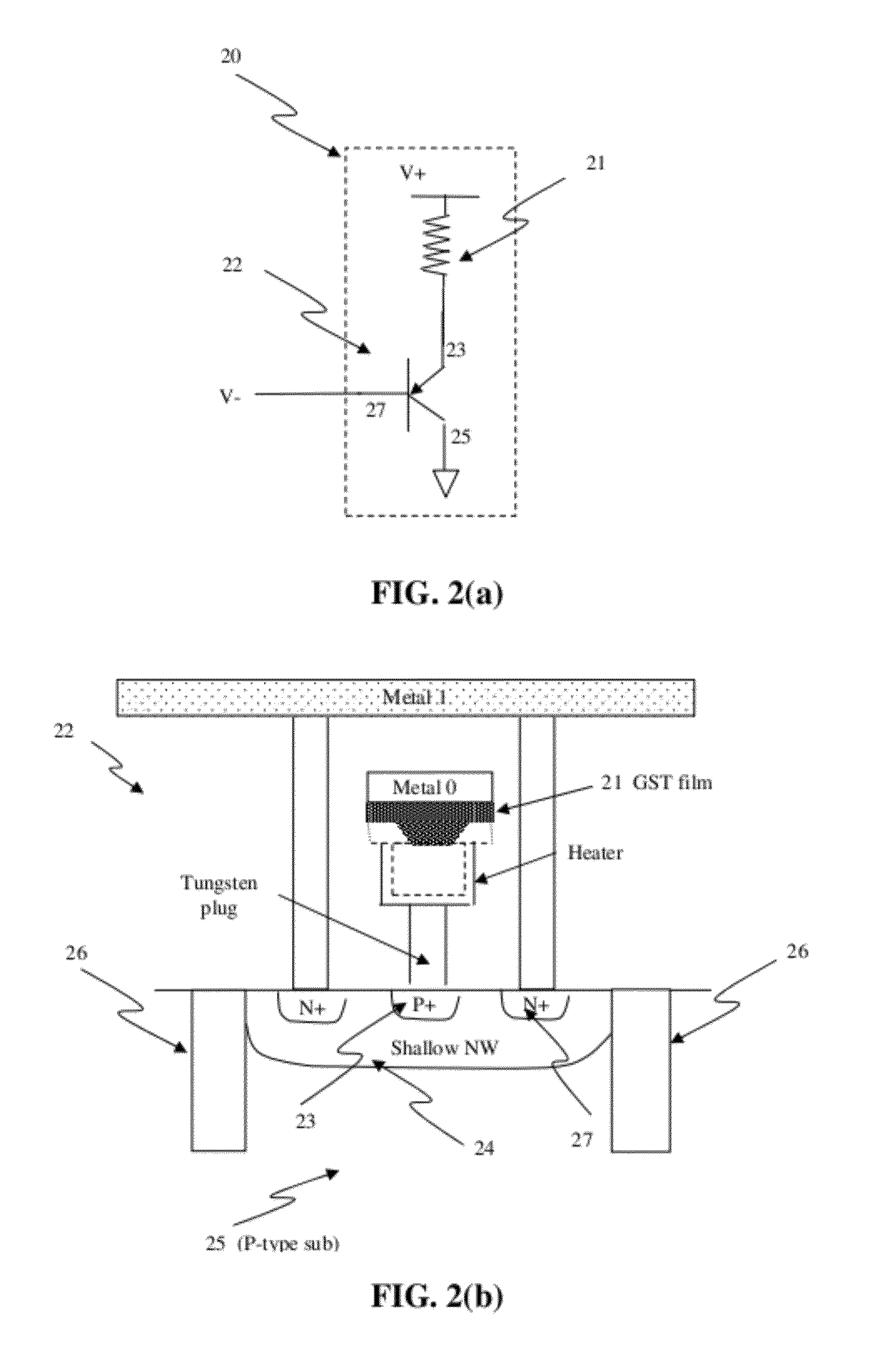
Thin film fuse phase change RAM and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060284279A1Simple structureReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesDigital storageEngineeringPhase change
A memory device comprising a first electrode having a top side, a second electrode having a top side and an insulating member between the first electrode and the second electrode. The insulating member has a thickness between the first and second electrodes near the top side of the first electrode and the top side of the second electrode. A bridge of memory material crosses the insulating member, and defines an inter-electrode path between the first and second electrodes across the insulating member. An array of such memory cells is provided. In the array, a plurality of electrode members and insulating members therebetween comprise an electrode layer on an integrated circuit. The bridges of memory material have sub-lithographic dimensions.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
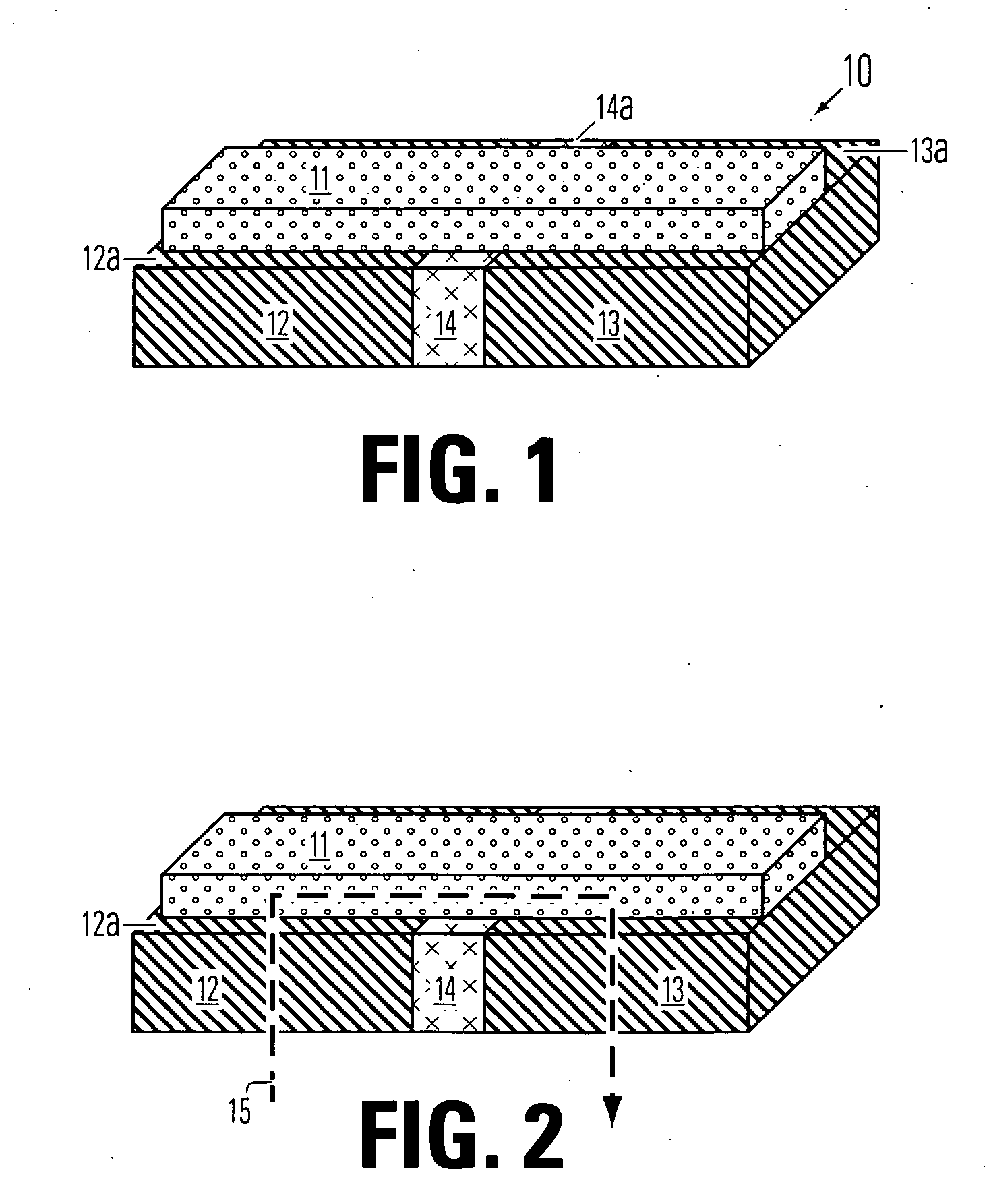
Manufacturing methods for thin film fuse phase change ram
InactiveUS20060286709A1Simple structureReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryOptoelectronics
A method for manufacturing a memory device comprises forming an electrode layer on a substrate which comprises circuitry made using front-end-of-line procedures. The electrode layer includes a first electrode and a second electrode, and an insulating member between the first and second electrodes for each phase change memory cell to be formed. A bridge of memory material is formed on the top surface of the electrode layer across the insulating member for each memory cell to be formed. An access structure over the electrode layer is made by forming a patterned conductive layer over said bridge, and forming a contact between said first electrode and said patterned conductive layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
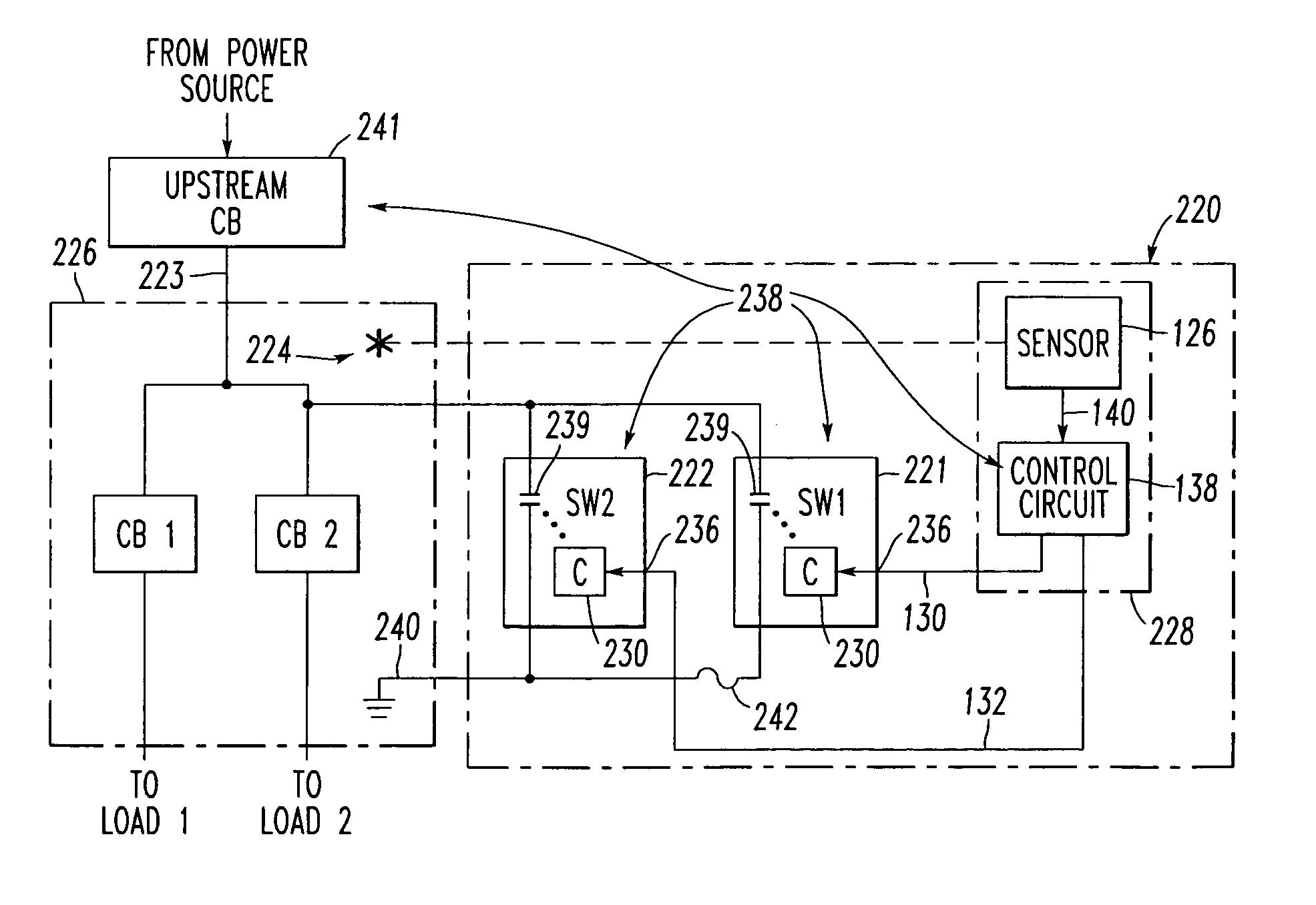
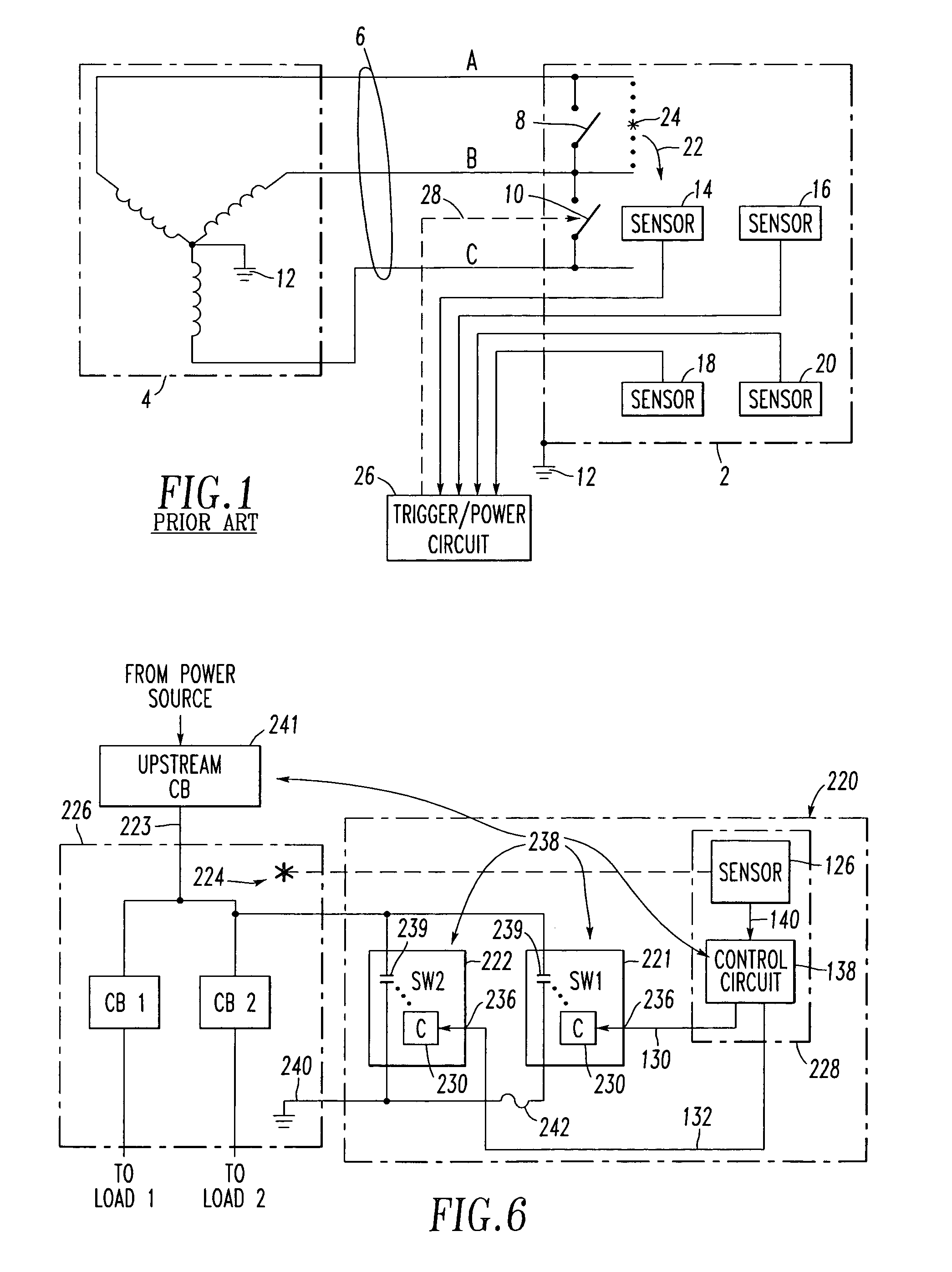
System for eliminating arcing faults and power distribution system employing the same
ActiveUS7145757B2Emergency protective arrangement detailsElectric switchesElectricityDistribution system
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
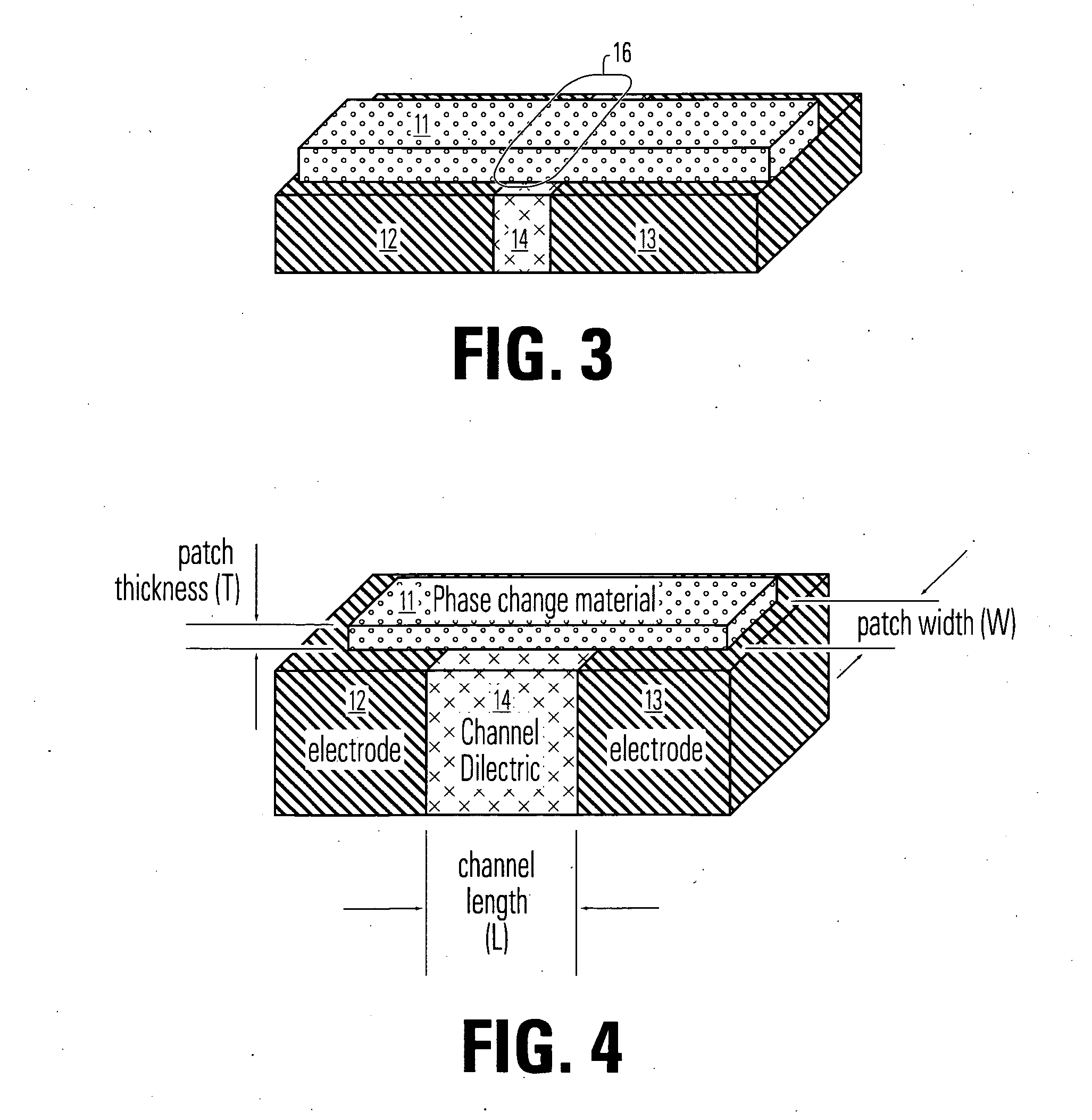
Thin film fuse phase change cell with thermal isolation layer and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060284214A1Simple structureReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesDigital storageThermal isolationEngineering
A memory device comprising a first electrode having a top side, a second electrode having a top side and an insulating member between the first electrode and the second electrode. The insulating member has a thickness between the first and second electrodes near the top side of the first electrode and the top side of the second electrode. A bridge of memory material crosses the insulating member, and defines an inter-electrode path between the first and second electrodes across the insulating member. An array of such memory cells is provided. The bridge comprises an active layer of memory material on the first side having at least two solid phases and a blanket of thermal insulating material overlying the memory material having thermal conductivity less than that of an overlying electrically insulating layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Self-aligned manufacturing method, and manufacturing method for thin film fuse phase change ram
ActiveUS20070173063A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storagePhase-change memoryEngineering
A method for manufacturing a self aligned narrow structure over a wider structure based on mask trimming. A method for manufacturing a memory device comprises forming an electrode layer on a substrate which comprises circuitry made using front-end-of-line procedures. The electrode layer includes a first electrode and a second electrode, and an insulating member between the first and second electrodes for each phase change memory cell to be formed. A patch of memory material is formed on the top surface of the electrode layer across the insulating member for each memory cell to be formed. The patch and the first and second electrodes are formed using a self-aligned process based on mask trimming.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
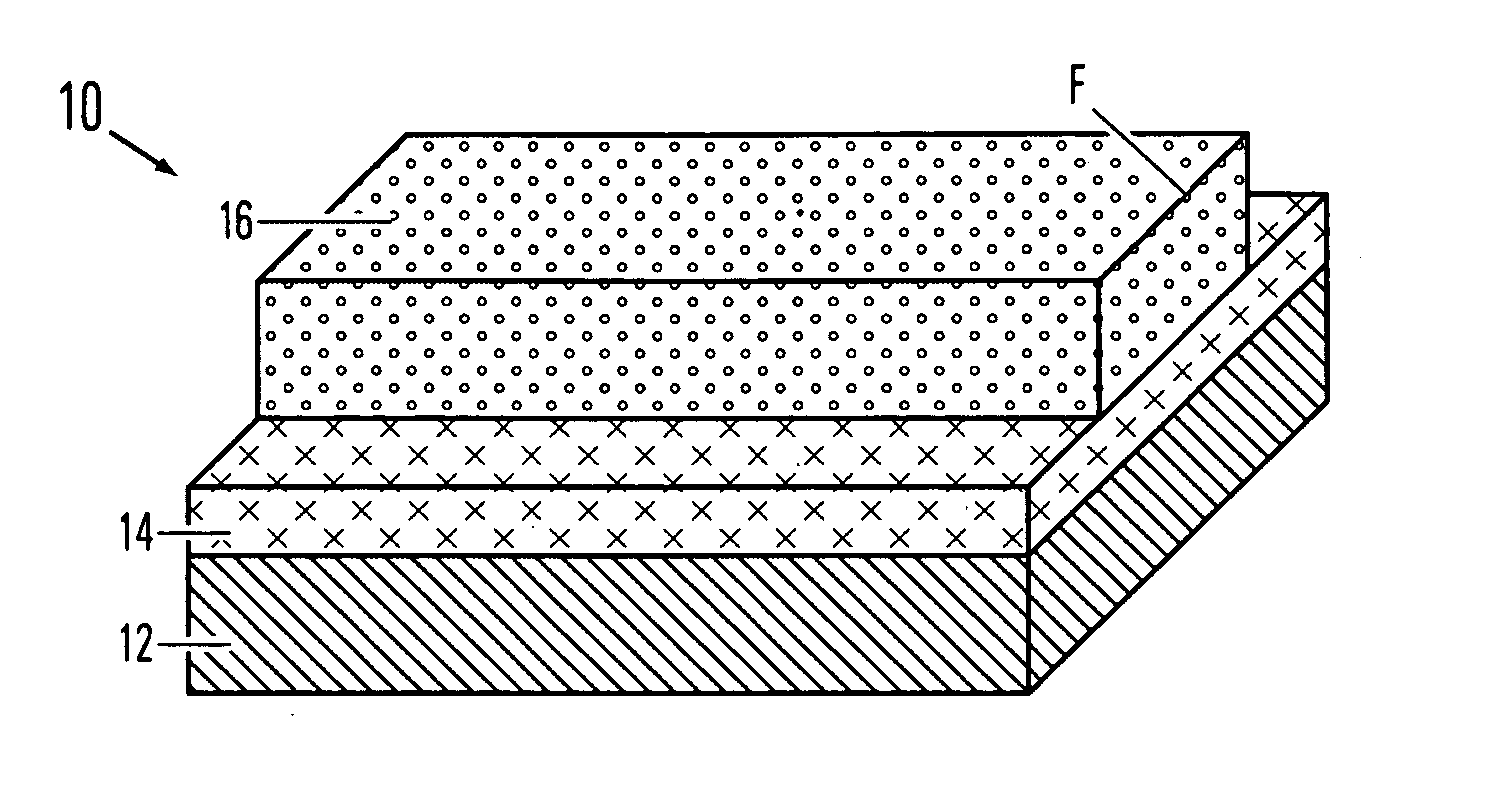
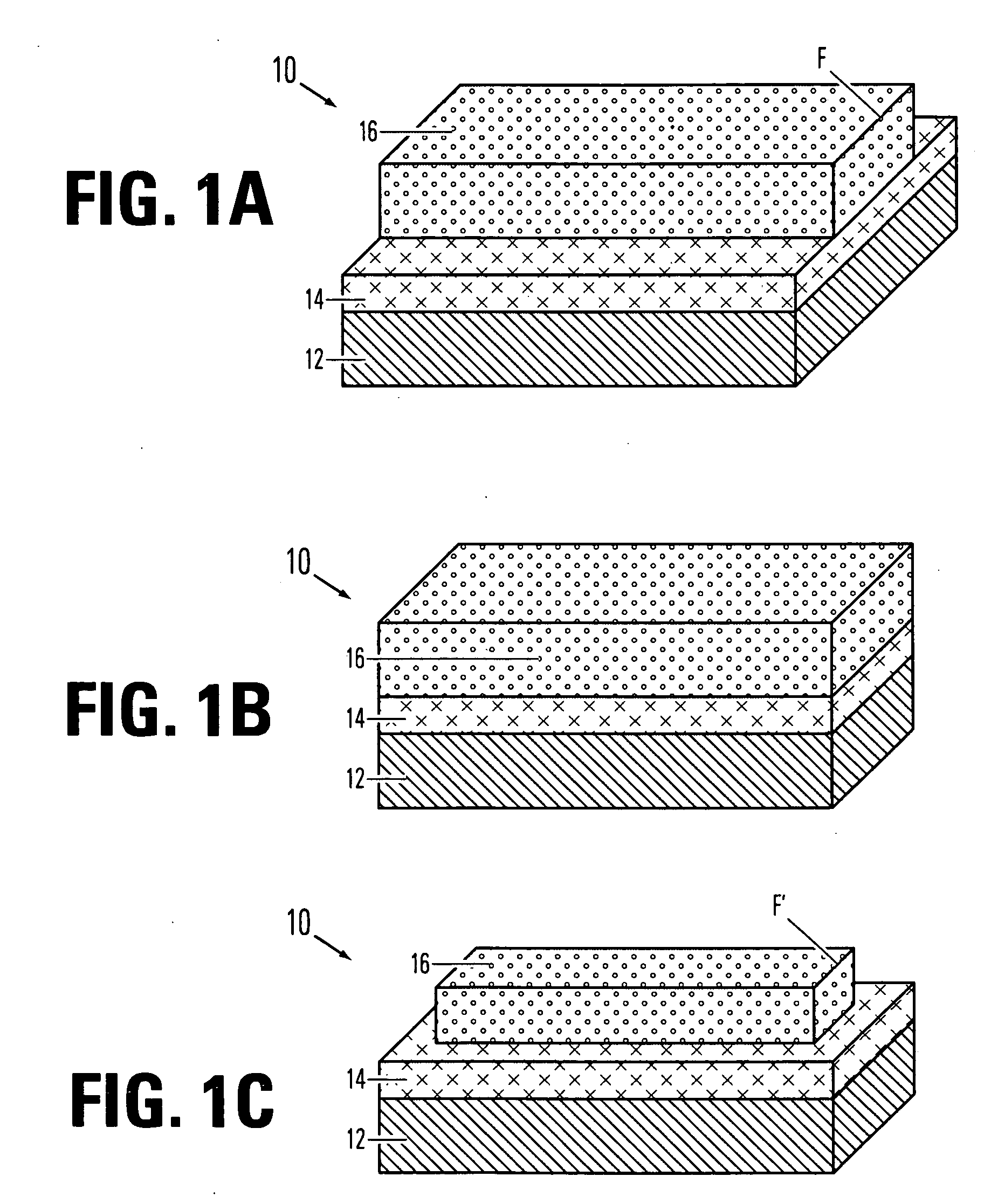
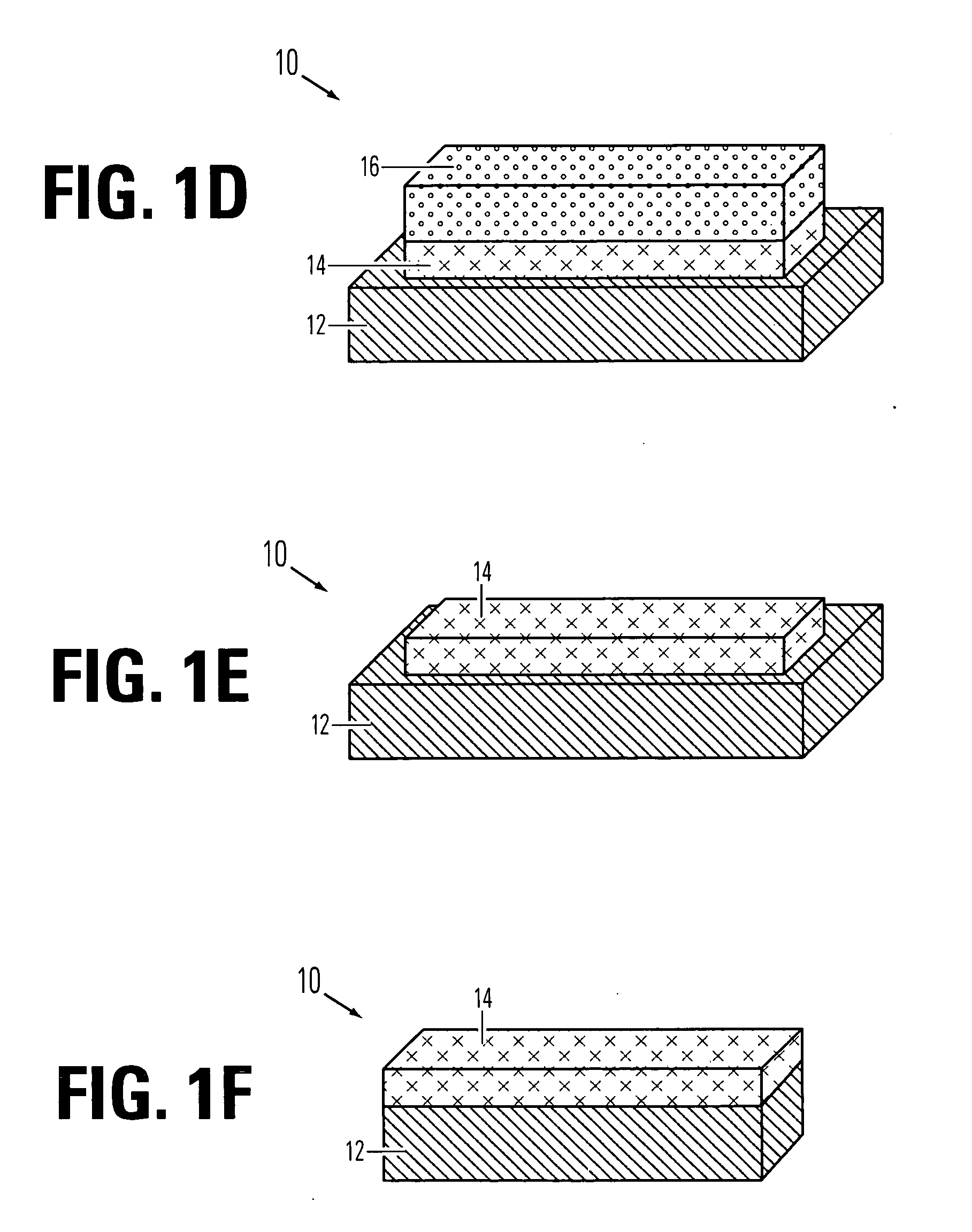
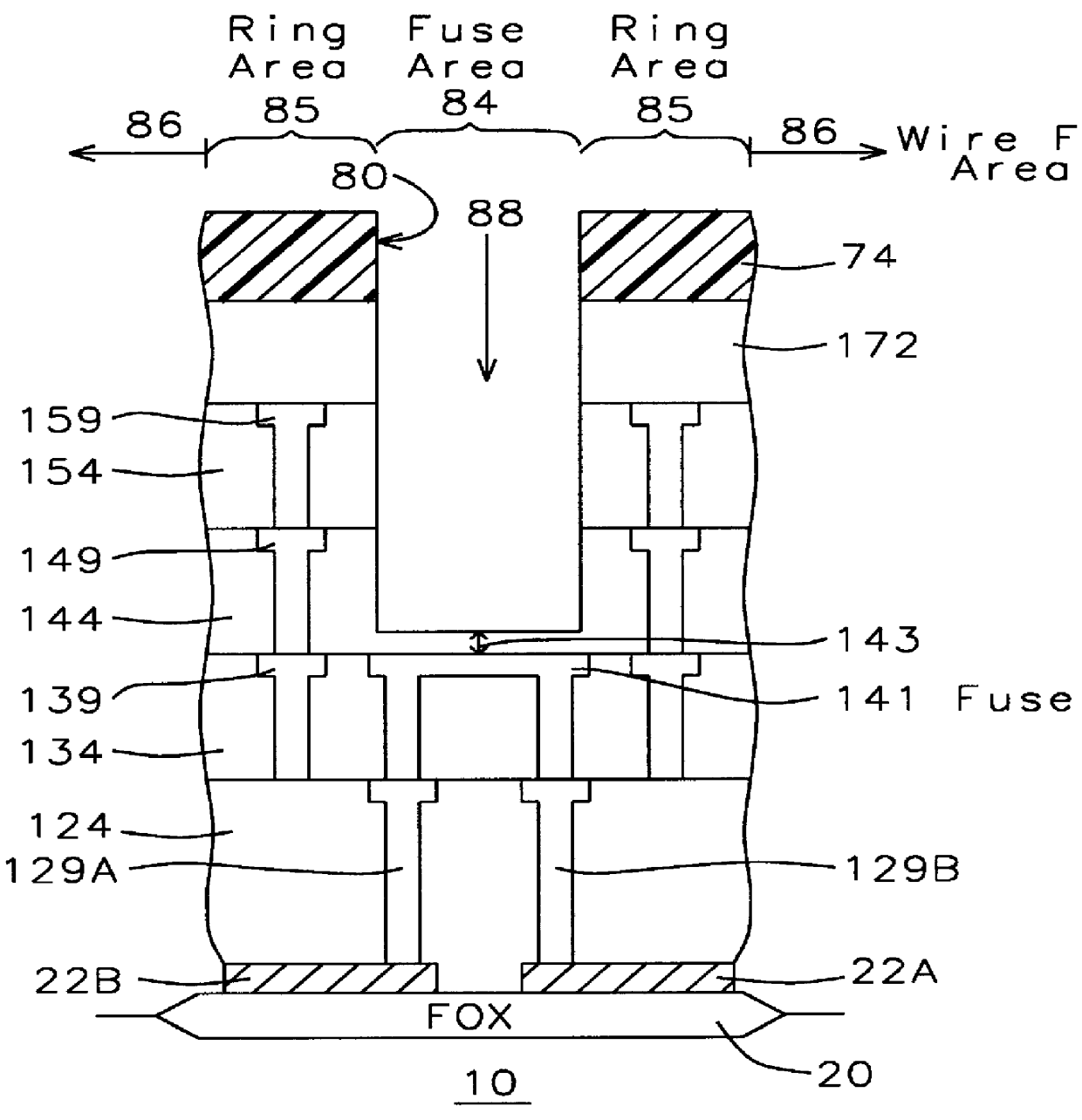
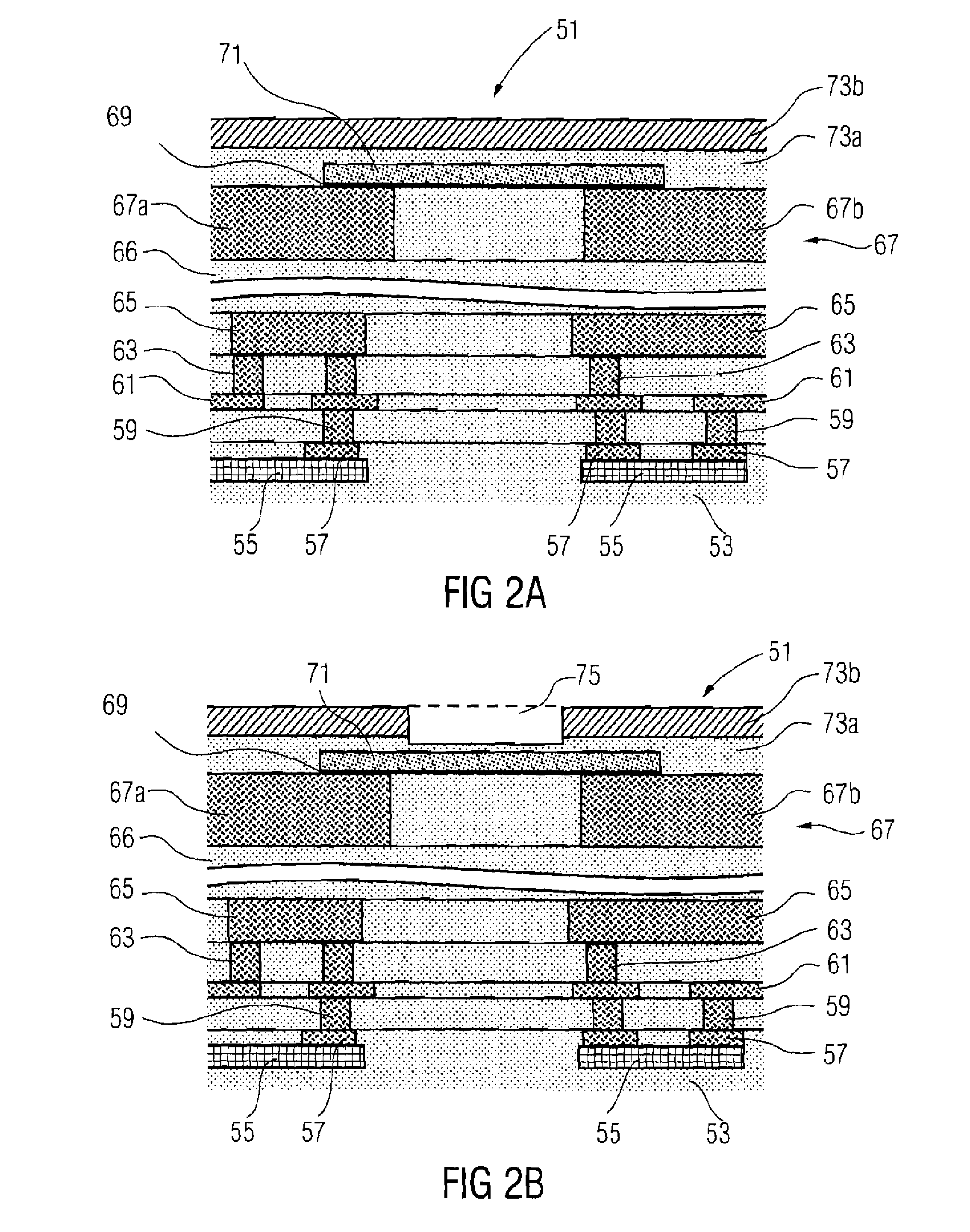
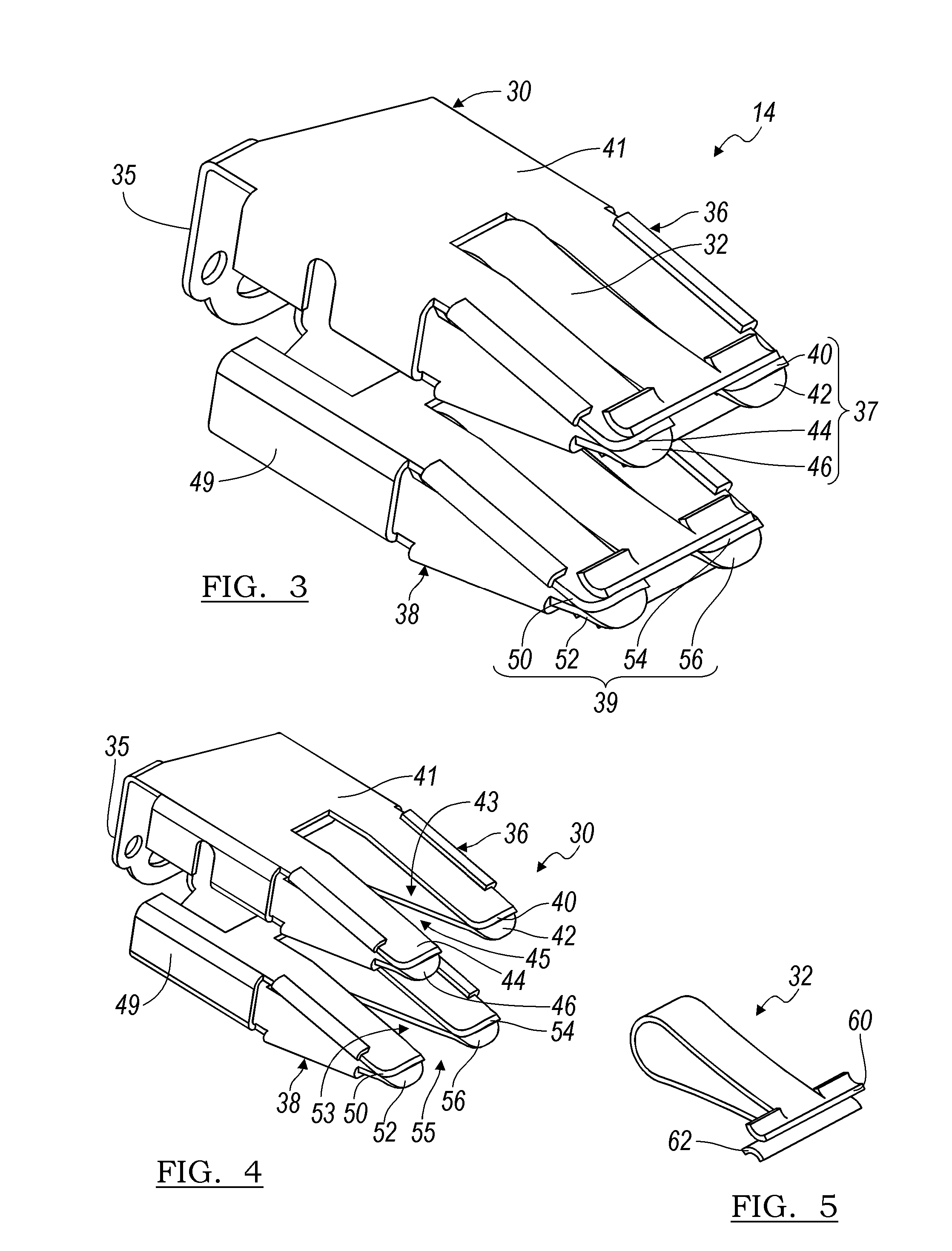
Fabrication of metal fuse design for redundancy technology having a guard ring
InactiveUS6100118ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionEngineering
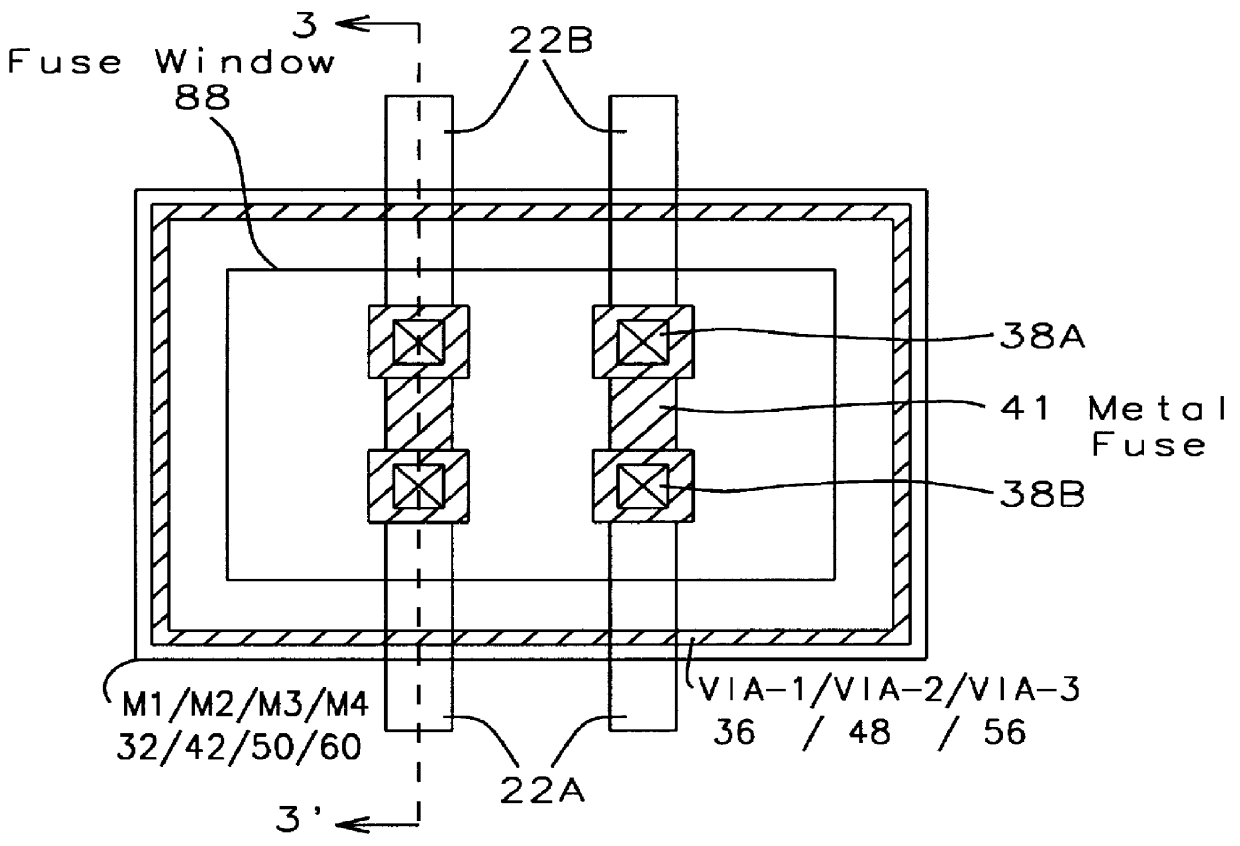
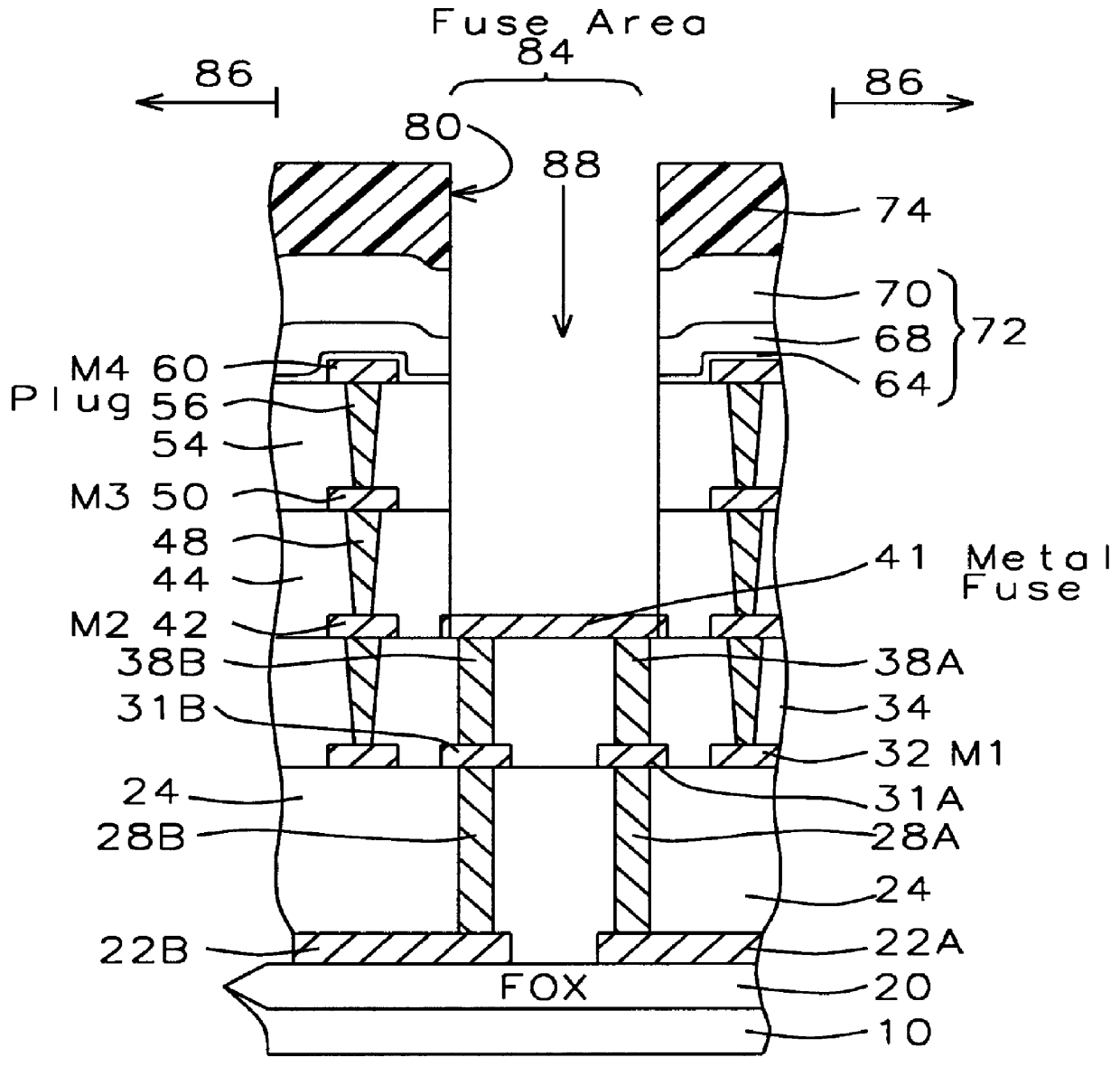
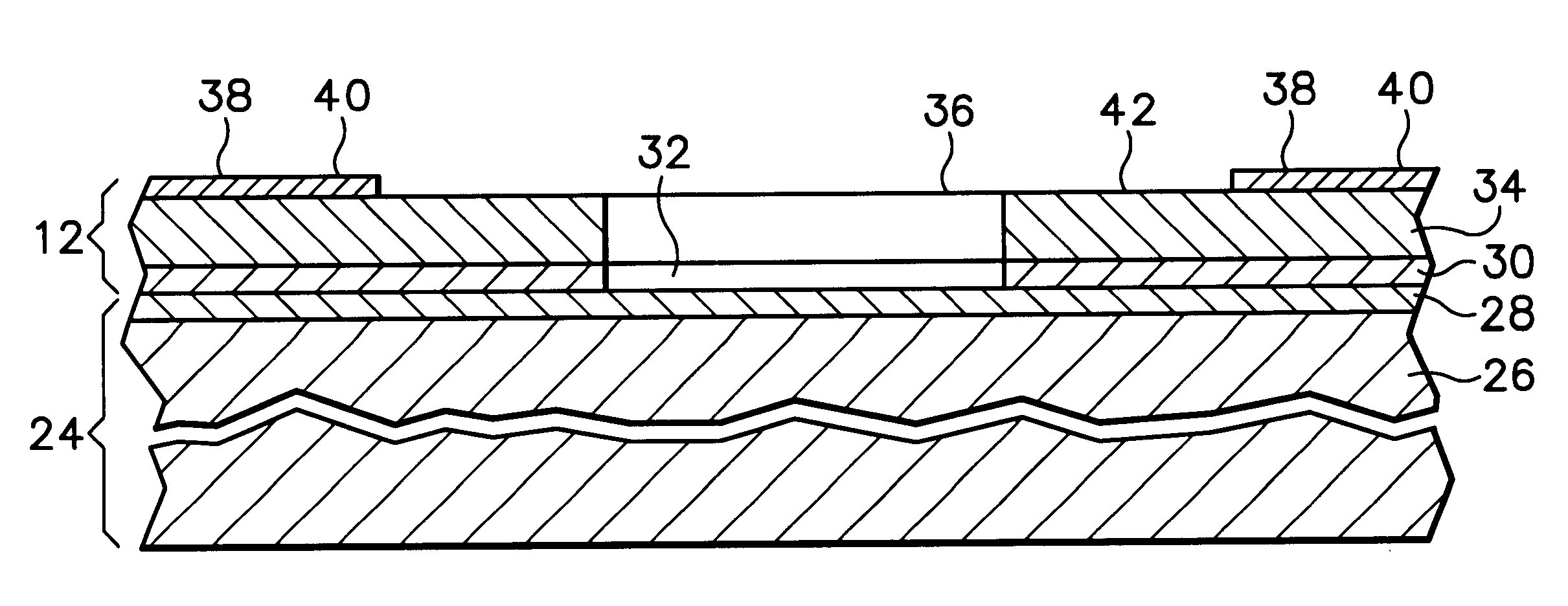
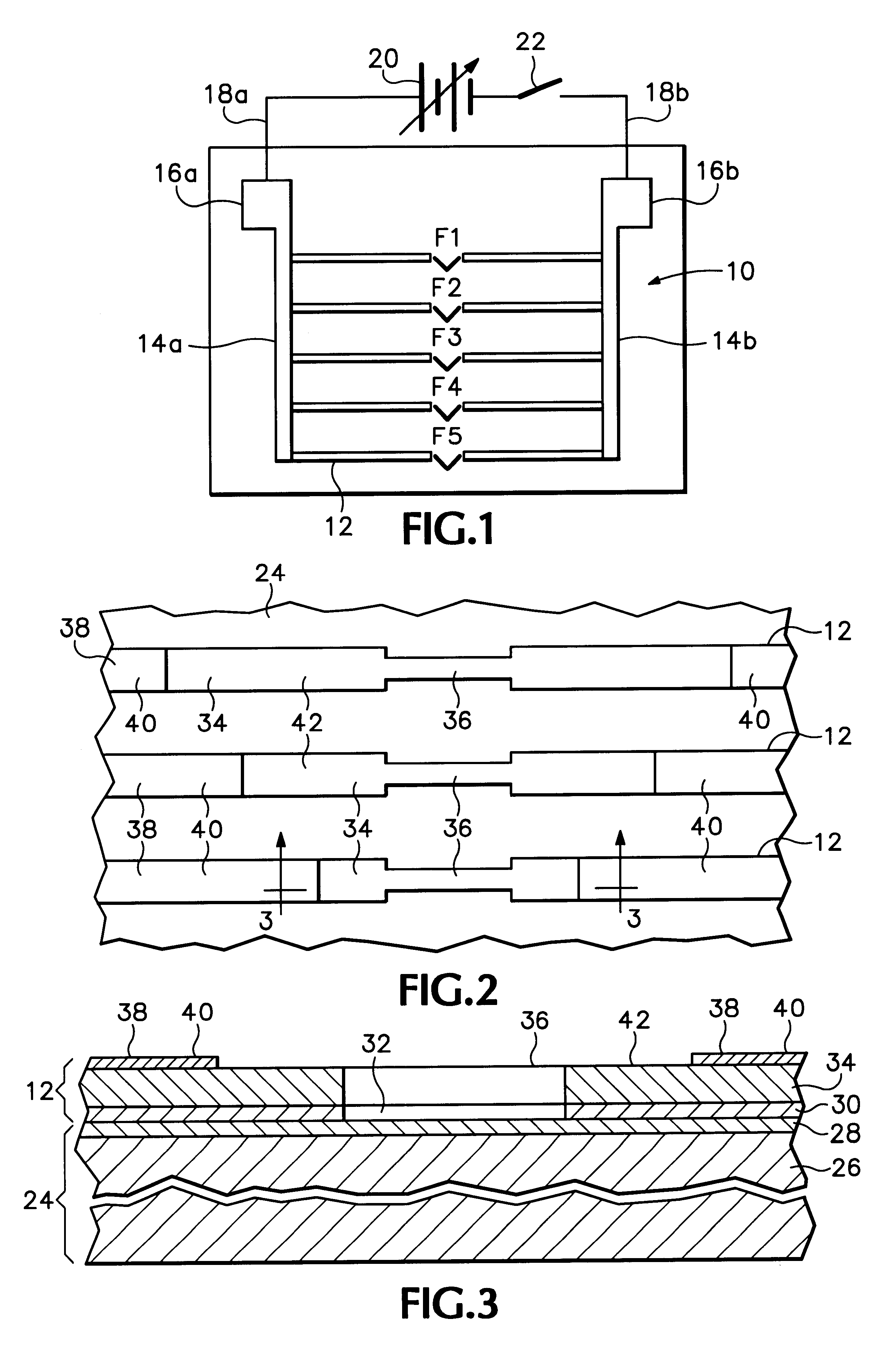
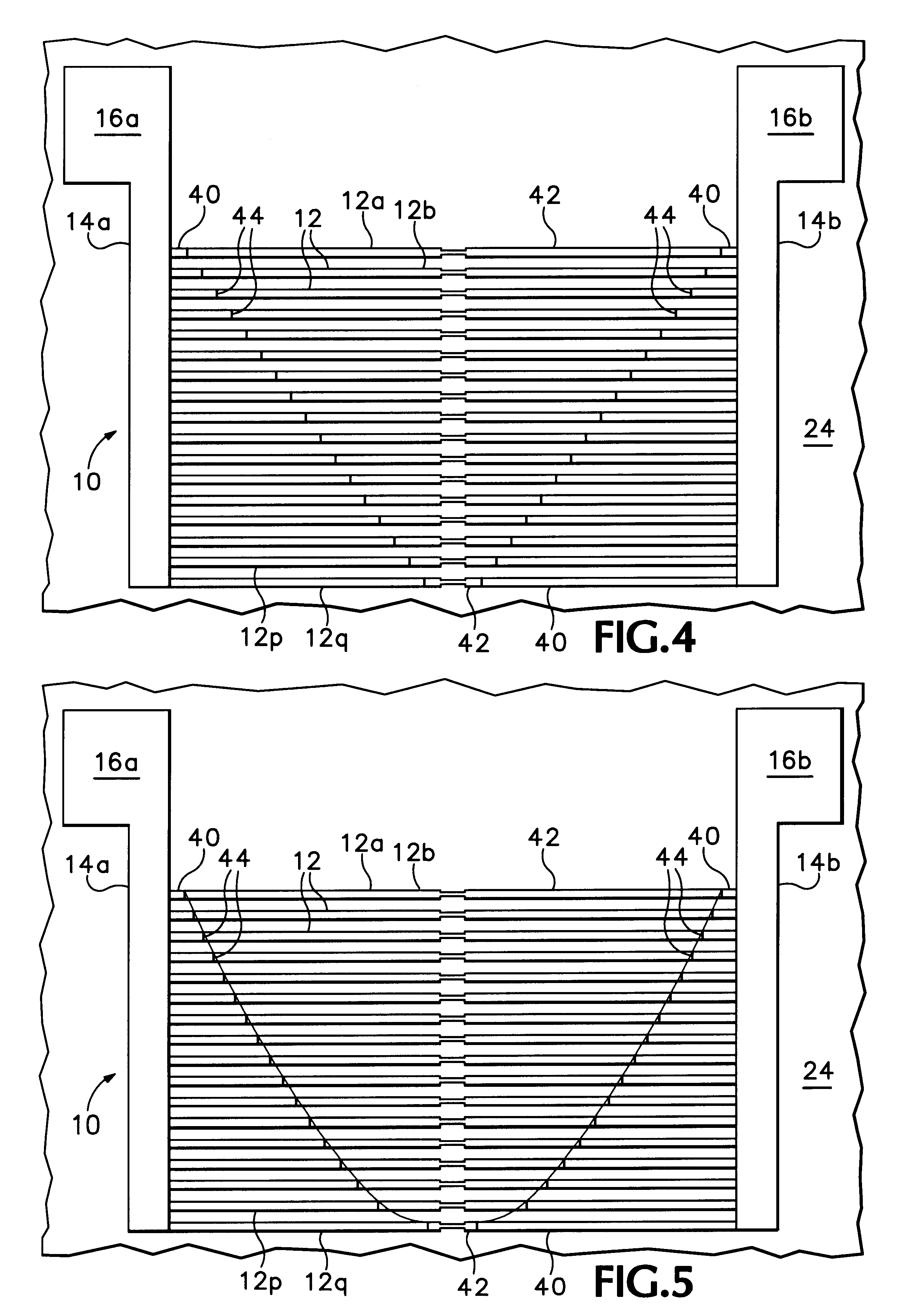
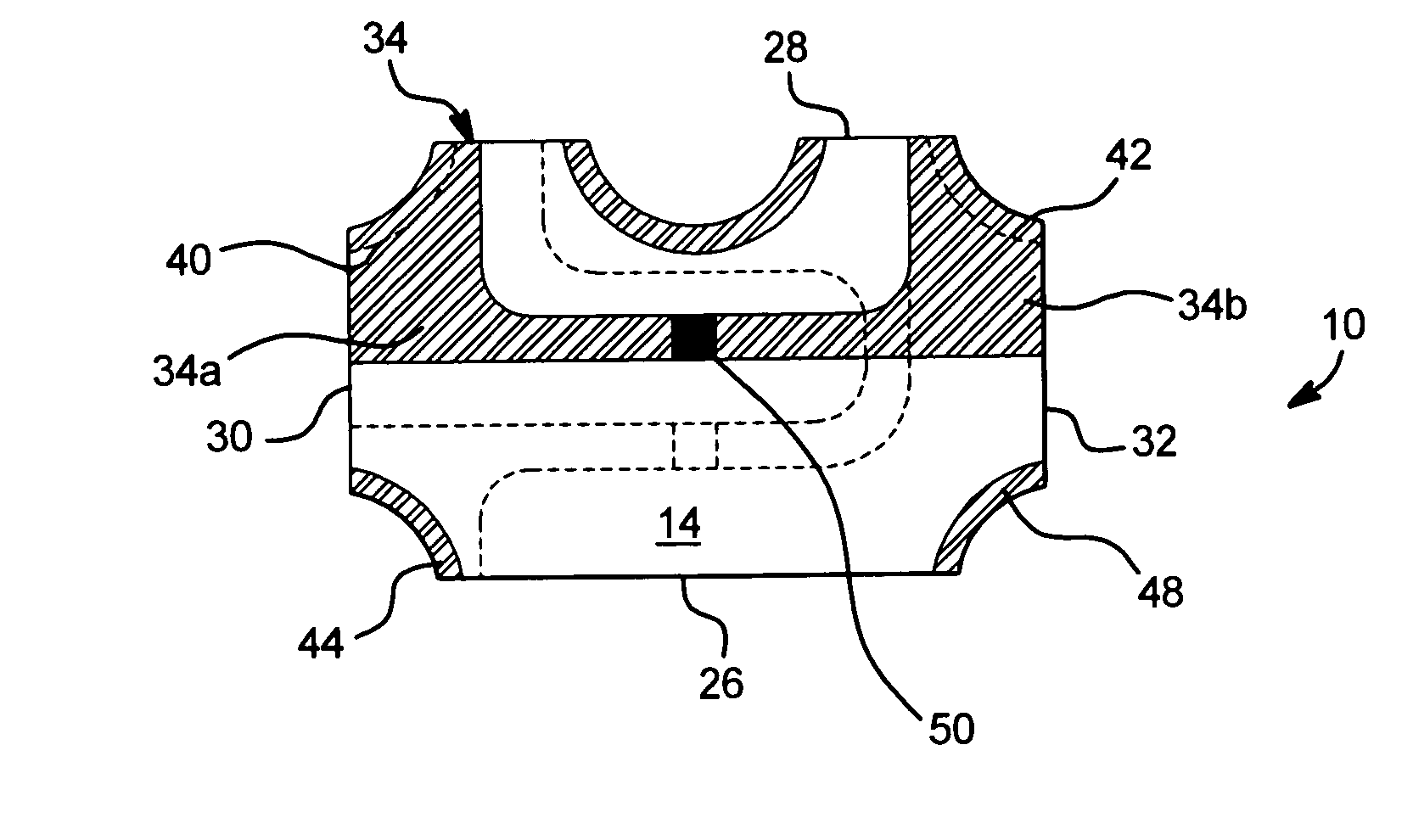
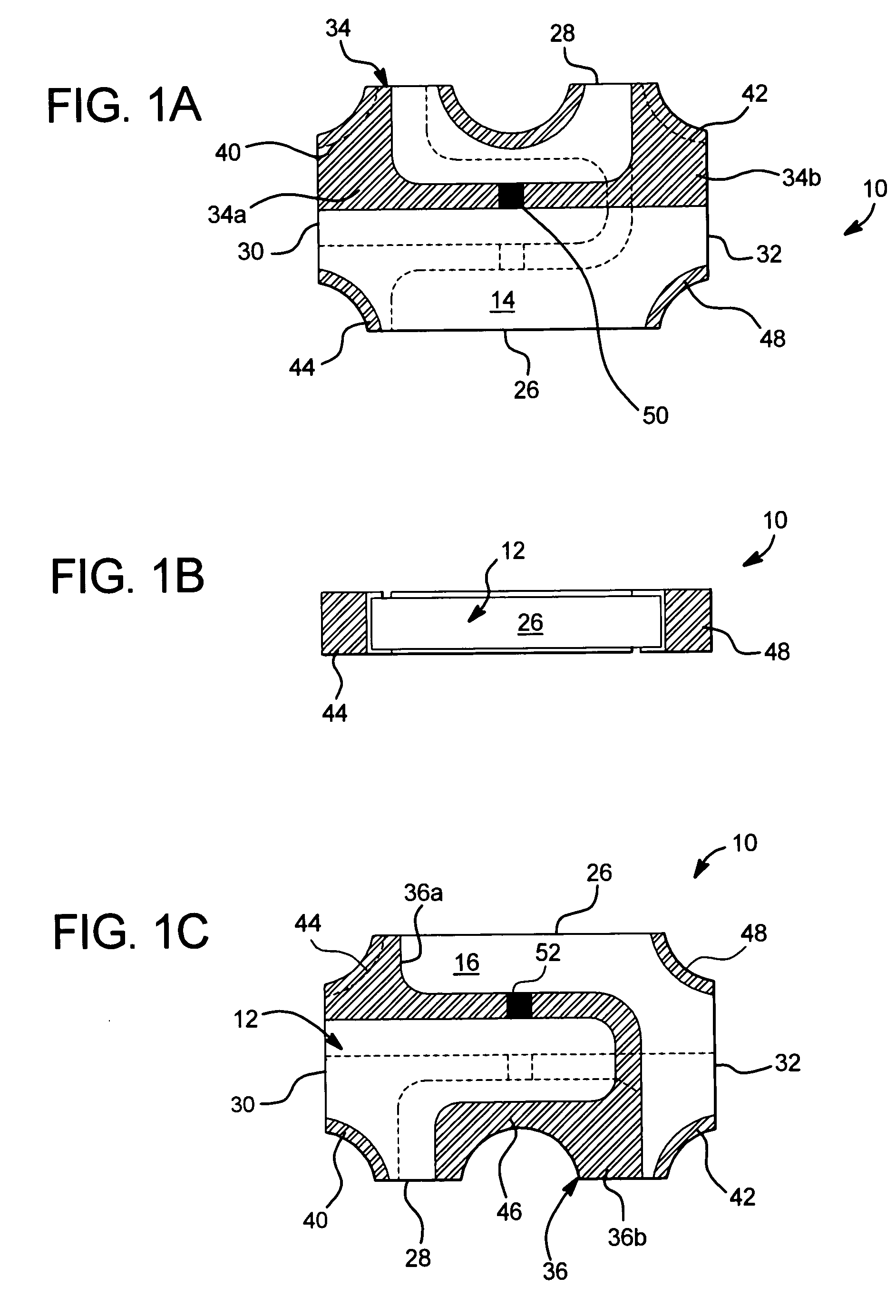
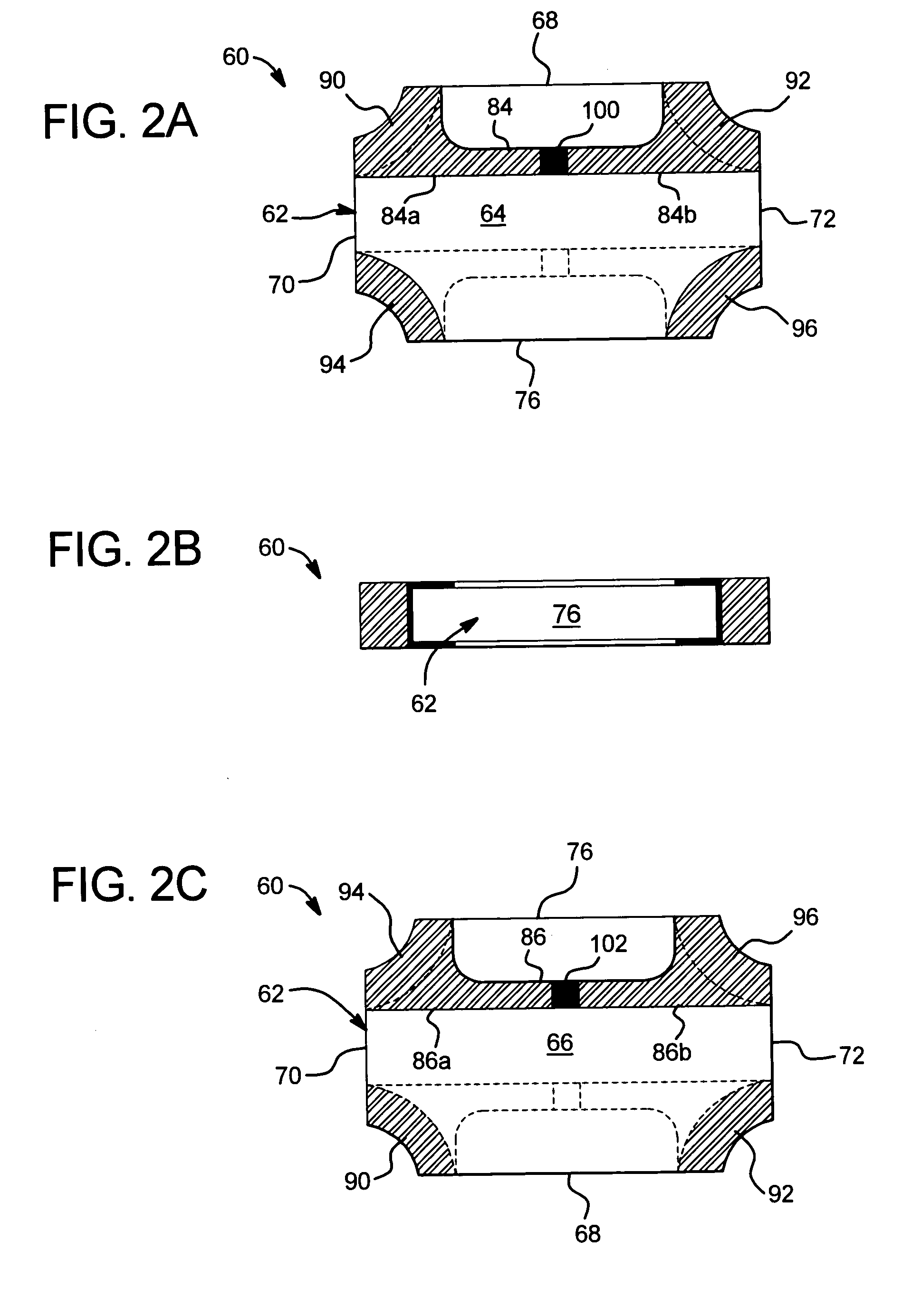
A method of fabricating a metal guard ring (e.g., 139 149 159) around for a metal fuse 141 and fuse opening 88. The metal fuse 41 is formed from a second metal layer (M2) (or M3 or M4, etc.) and is connected to an underlying polysilicon layer 22 by fuse interconnections 129A 129B. The method comprises: a) forming a first polysilicon line 22A and a second polysilicon line 22B over at least the fuse area 84 insulated (e.g., 20) from a substrate 10; b) forming one or more levels of fuse interconnects (129A 129B) electrically connected to the first polysilicon line 22A and the second polysilicon line 22B; the fuse interconnects 129A 129B passing through vias in one or more insulating layers 24 34; c) simultaneously forming a metal fuse 141 connecting the polysilicon interconnects 129A 129B over the fuse area 84 and forming a first guard ring 139 around a fuse area 84; d) forming an dielectric layer 144 over the metal fuse 141 and the first guard ring 139; e) forming a guard ring around the fuse areas 84; the guard ring composed of a plurality of metal wiring layers 149 159 formed on and through vias in a plurality of dielectric layers 144 154; and f) forming a fuse opening 88 through at least a portion of the plurality of dielectric layers 144 154 172 in the fuse area.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
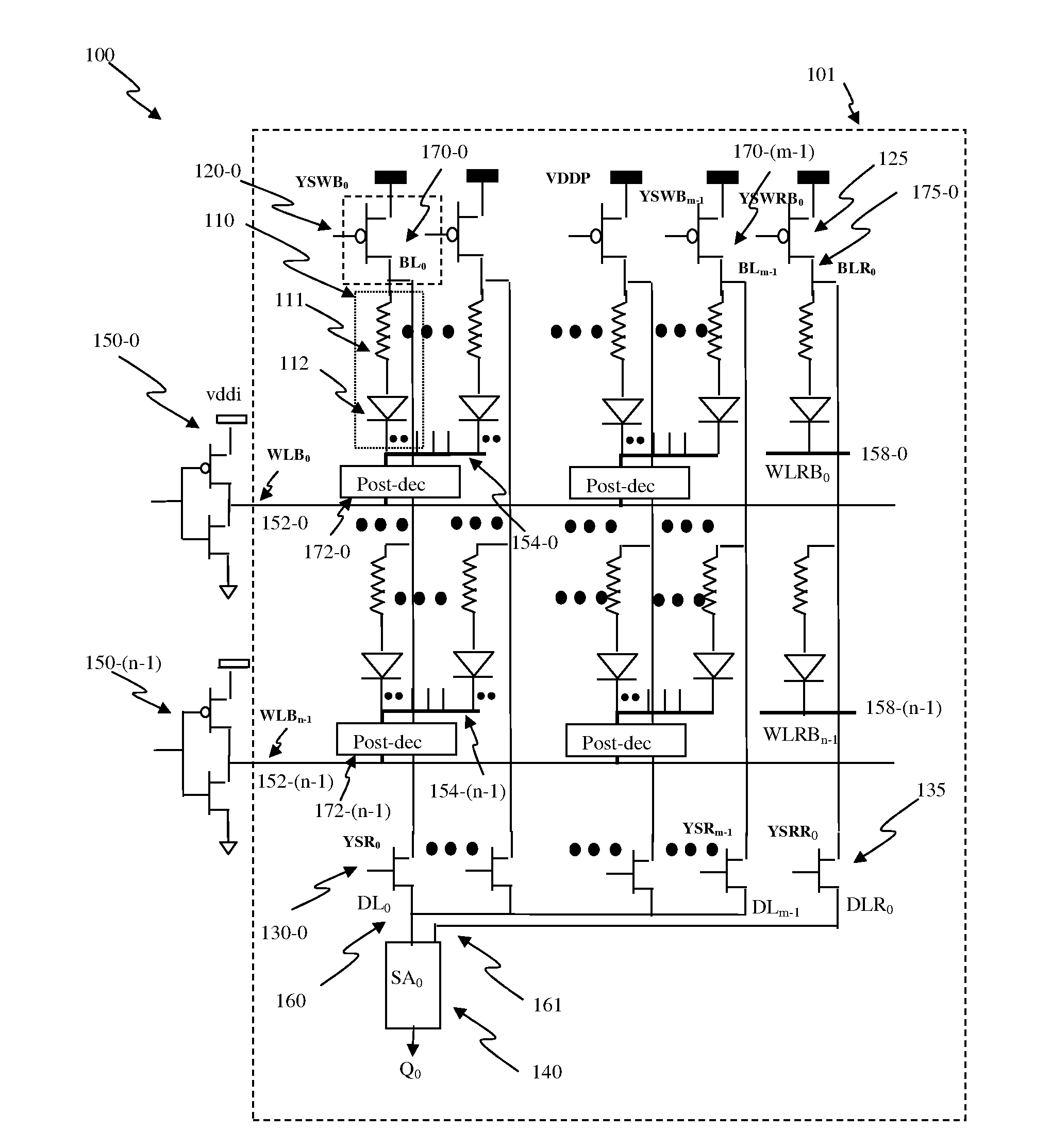
Addressable fuse array for circuits and mechanical devices
InactiveUS6501107B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
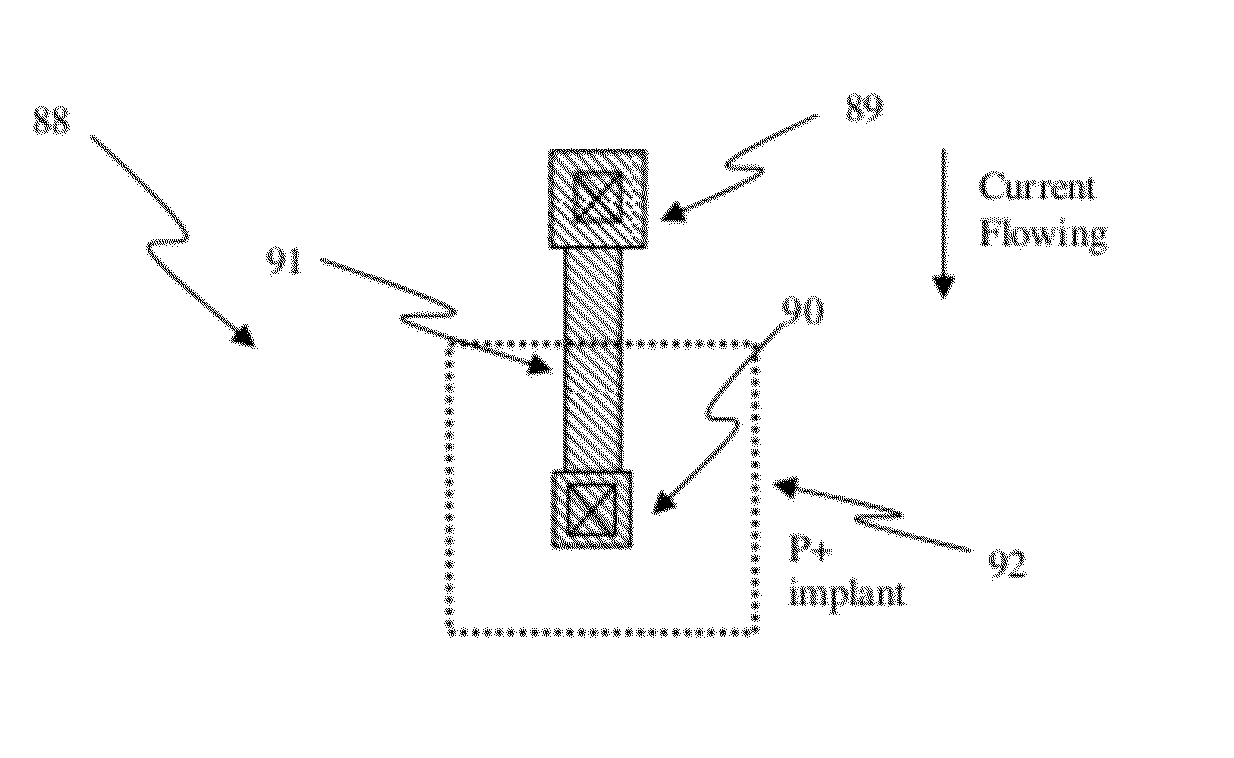
A fuse array having a plurality of fusible links that can be addressed by two electrodes is disclosed. The fuse array includes two conductive strips having the plurality of fusible links located therebetween and electrically coupled to the conductive strips. The fusible links have different electrical resistance and each fusible link includes a fuse portion. A voltage potential applied across the conductive strips induces current flow through the fusible links in accordance with Ohm's law and ohmic heating occurs at the fuse portion in proportion to the square of the current. The voltage is increased to cause sufficient ohmic heating to occur in the most conductive fusible link (the fusible link having the lowest electrical resistance) so that the fuse portion in that fusible link fuses. Because the fusible links are connected in parallel to the conductive strips, an equivalent resistance of the plurality of fusible links increases and the current flow diminishes so that no further fuse portions are fused at the selected voltage level. Thereafter, the voltage level may be increased to fuse the most conductive fusible link remaining that is not fused. The fuse array may be incorporated into a circuit as a resistor that can be tuned to circuit requirements or as a physical structure in MEMS devices wherein the fuse array may be tuned to change physical properties of the MEMS device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dual fuse link thin film fuse
A surface mount fuse having a plurality of fusible links is provided. The links are located on opposite sides of an insulative substrate or one otherwise thermally insulated or decoupled from one another. The fuse links entered to terminals that can be asymmetrically secured to the substrate to discourage improper mounting. The fuse protects multiple different circuits or loads having a same common or grounded line.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Fuse Structure and Method for Manufacturing Same
ActiveUS20080067627A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A fuse structure includes a substrate, a fuse conductive trace disposed closer to a first chip surface than to a second chip surface facing away from the first chip surface, a metallization layer on the substrate disposed on a side of the fuse conductive trace facing away from the first chip surface, and a planar barrier multilayer assembly disposed between the fuse conductive trace and the metallization layer and including multiple barrier layers of different materials, wherein the fuse conductive trace, the metallization layer and the barrier multilayer assembly are arranged such that when cutting the fuse conductive trace and the barrier multilayer assembly, a first area of the metallization layer is electrically isolated from a second area of the metallization layer.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Circuit and system of using a junction diode as program selector for resistive devices
ActiveUS20120044746A1Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic technologies can be used as program selectors for a programmable resistive device, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for proper duration of time, a current flows through a resistive element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal can be connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044739A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal are connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
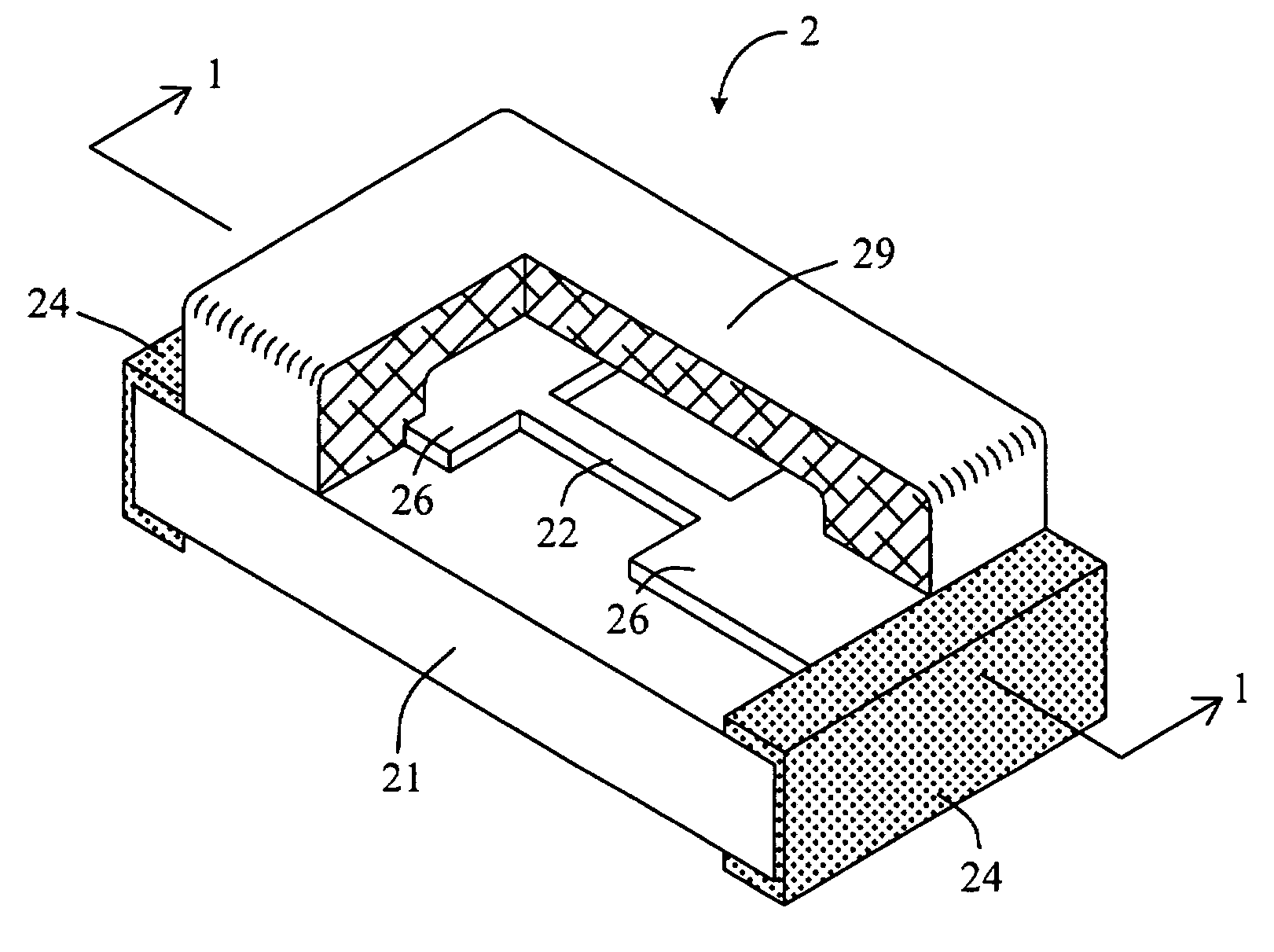
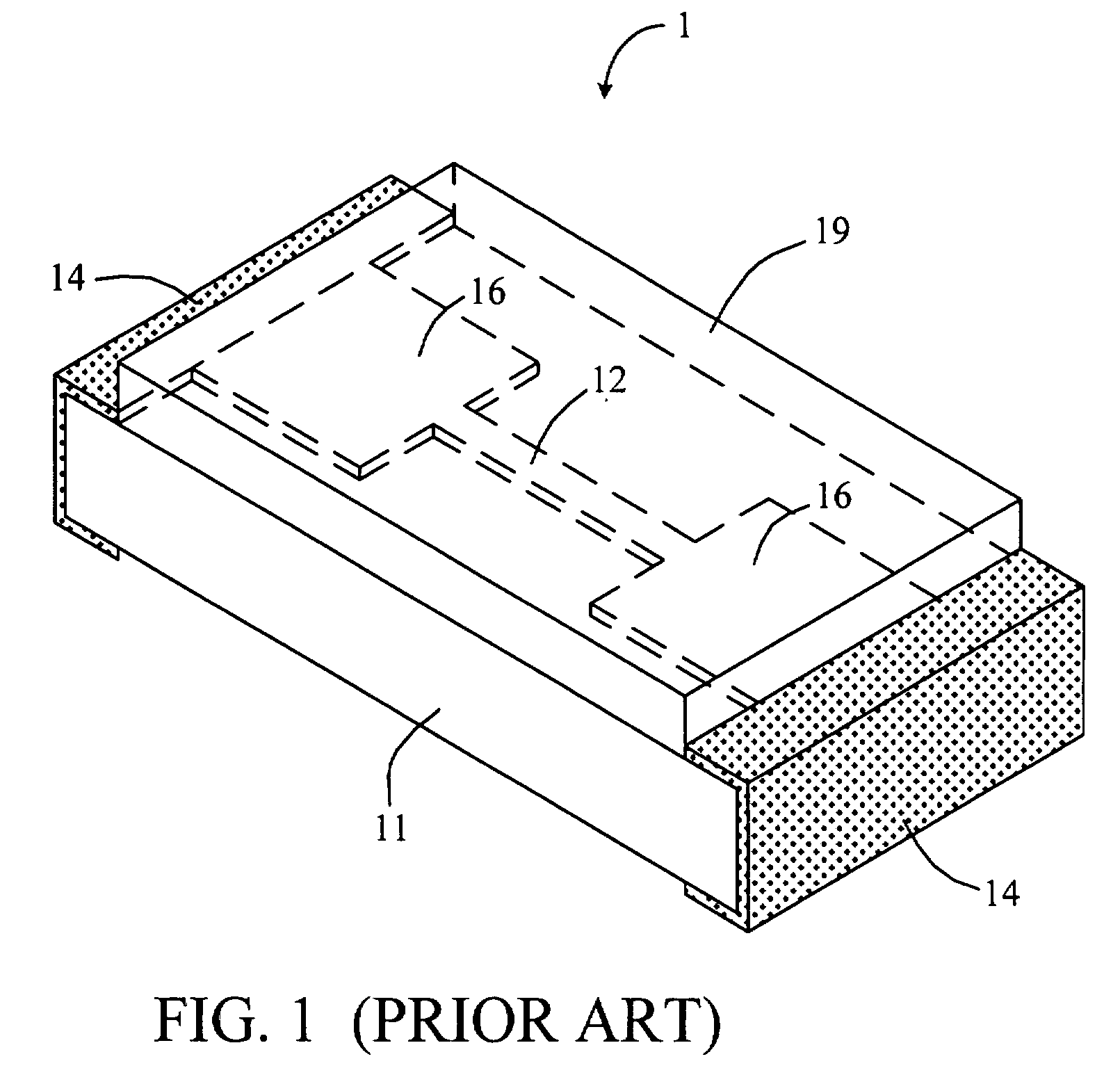
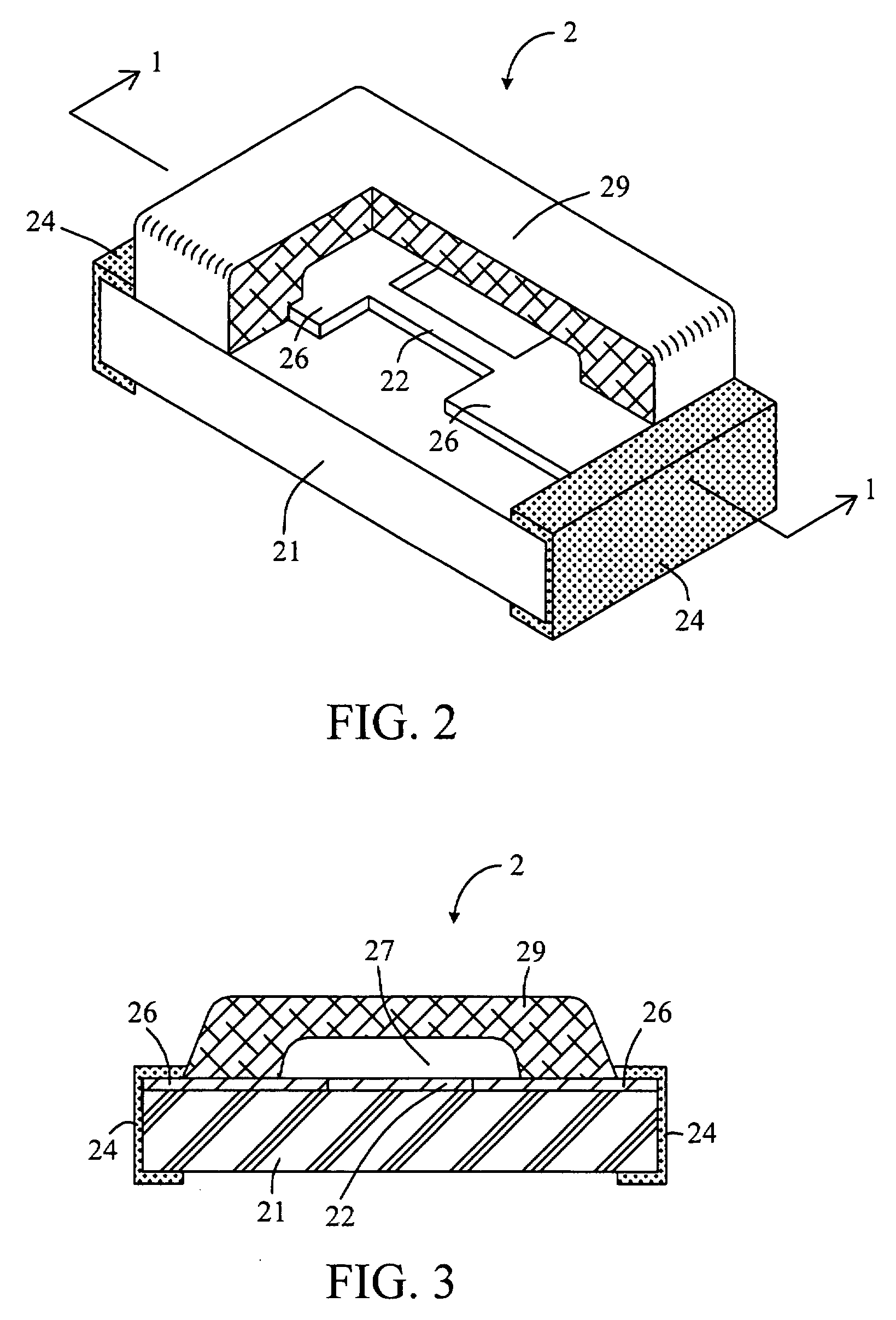
Chip-type fuse and method of manufacturing the same
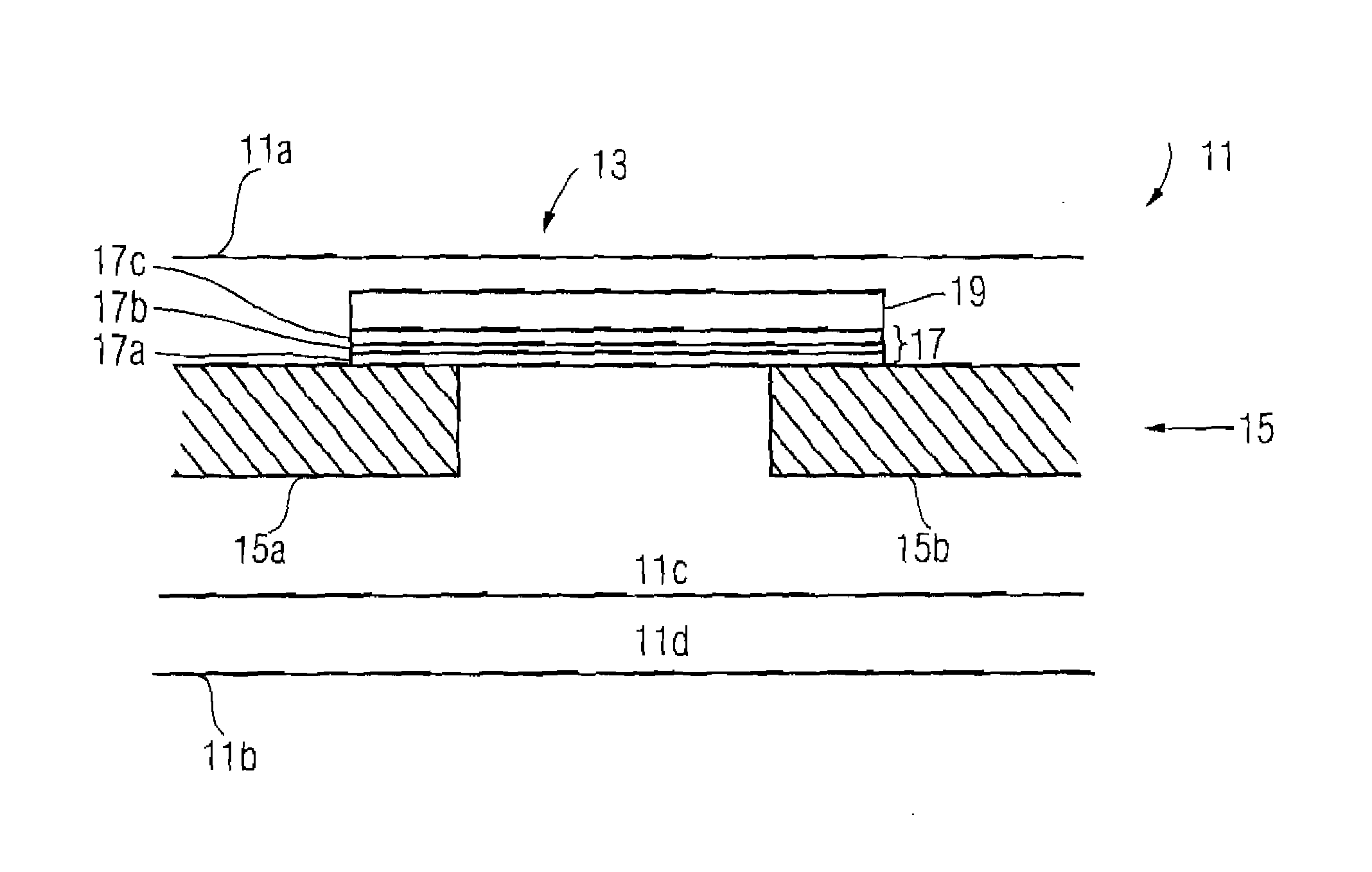
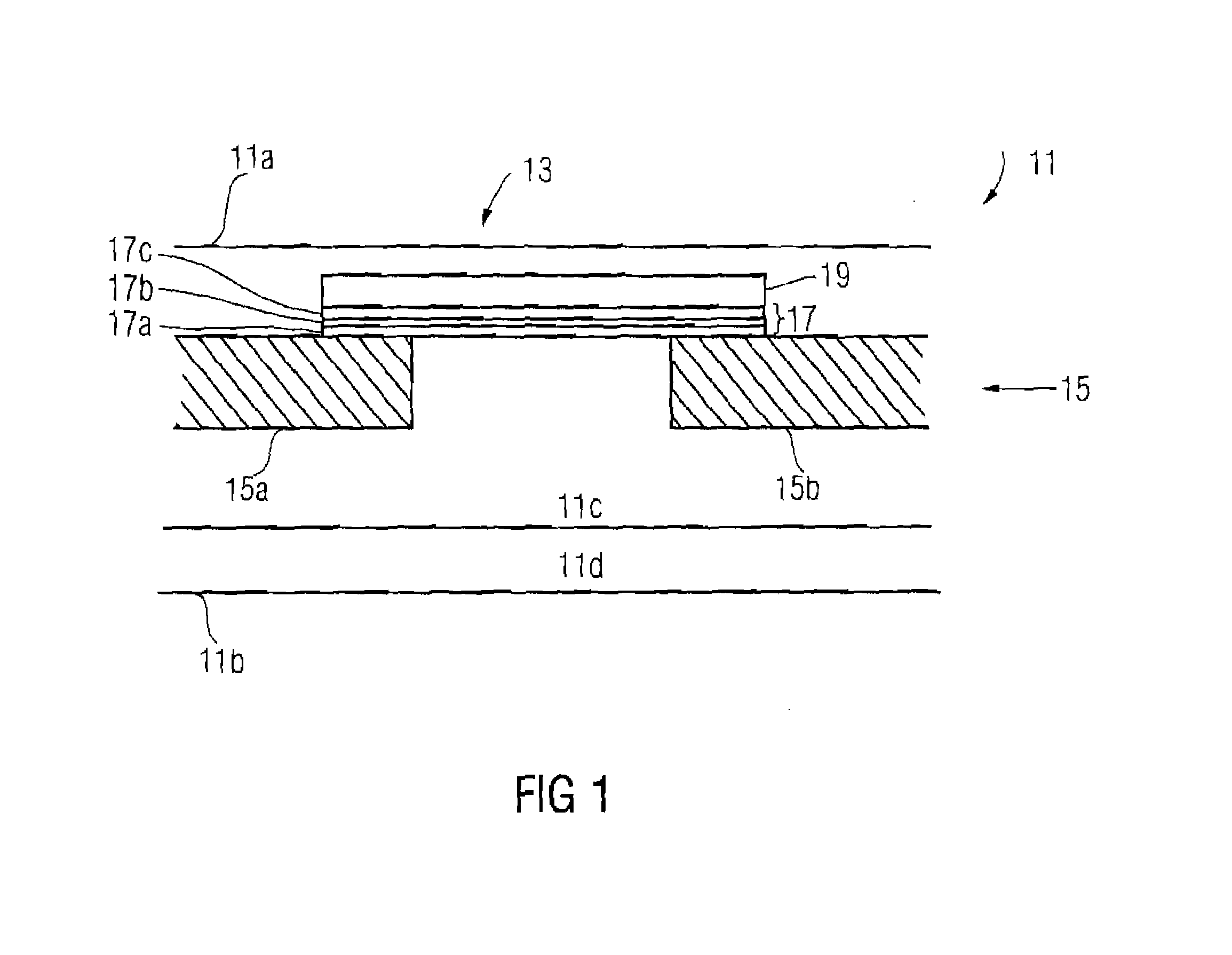
InactiveUS20080191832A1Ensure long-term reliabilityLow costFuse device manufactureElectrical and Electronics engineeringFuse cutout
A chip-type fuse is based on an electrically insulating substrate and fusible element is disposed thereon. A protective layer is formed over the fusible element and adheres to the substrate around the fusible element so as to define a cavity between the protective layer and the fusible element. The cavity isolates the protective layer from direct contact with the fusible element so that the protective layer will not be melted or breached by the excessive heat and arc generated by the fusible element under overload condition. Further, the cavity can be hermetically sealed to enclose a gas of pressure less than one atmosphere. A thermally insulating layer and an arc suppressive layer may be incorporated to reduce the response time and arc intensity of the chip-type fuse respectively under overload condition. The method of manufacturing chip-type fuse, particularly the method of forming fusible element and cavity, is described too.
Owner:BESDON TECH CORP
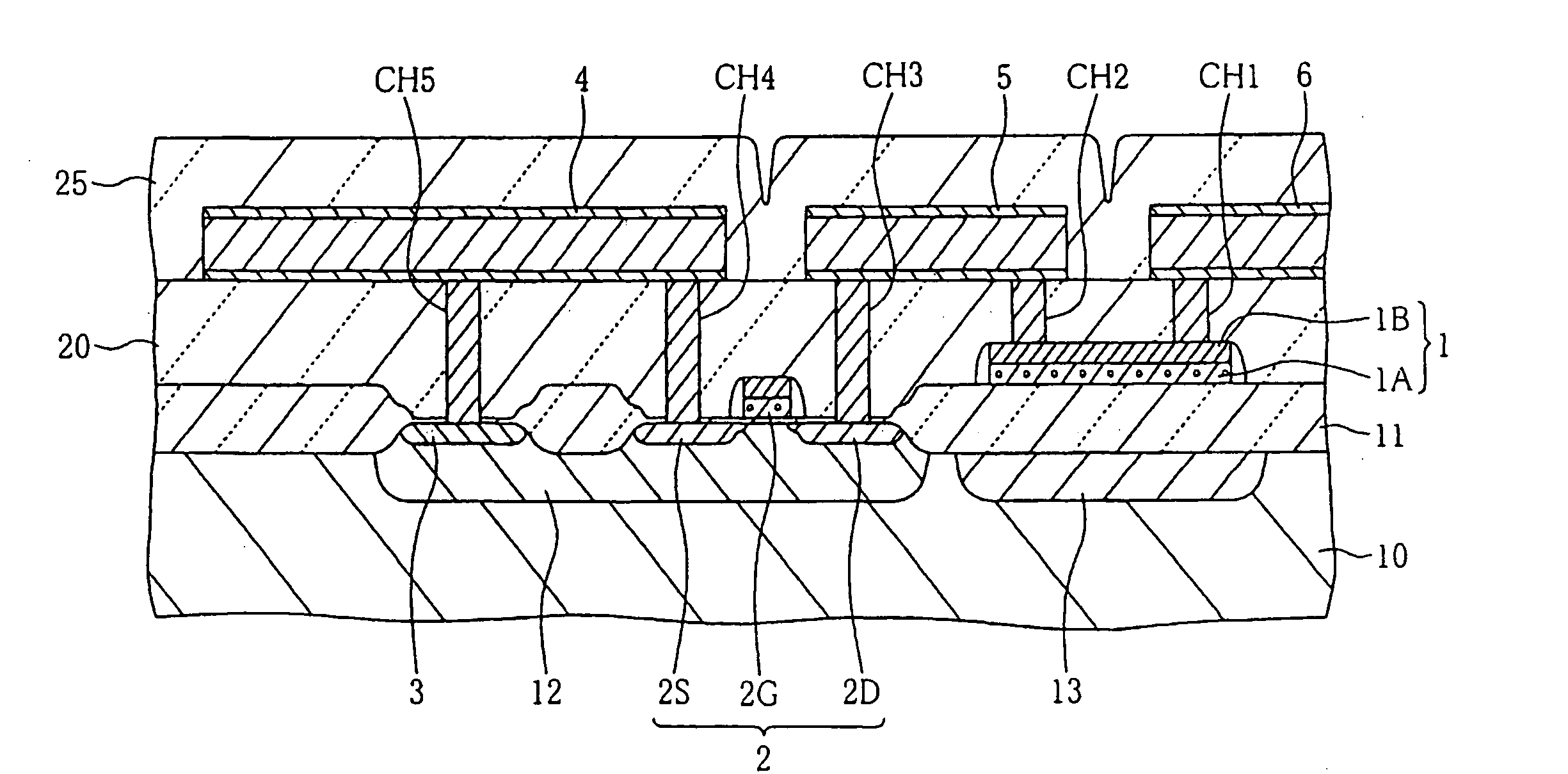
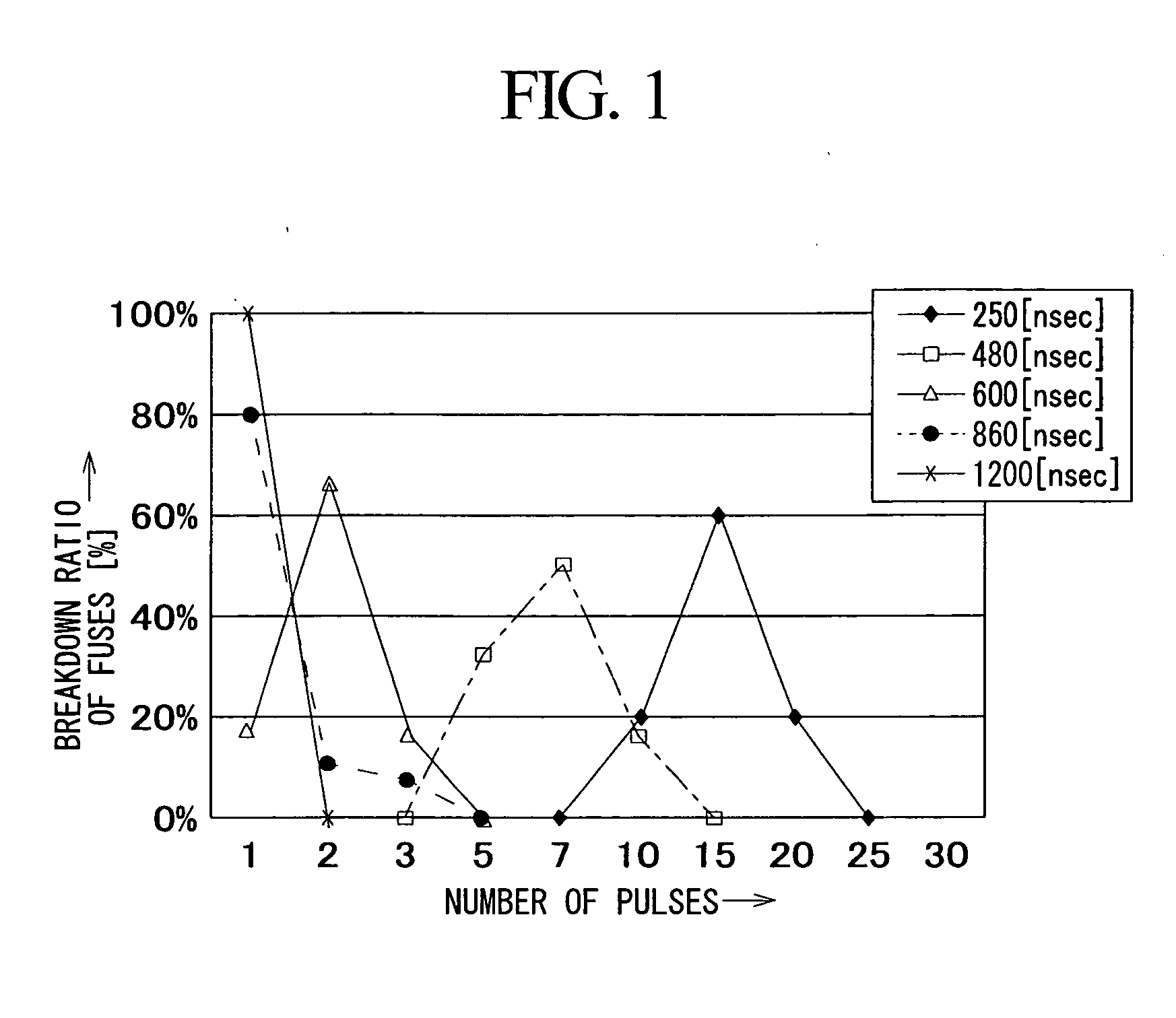
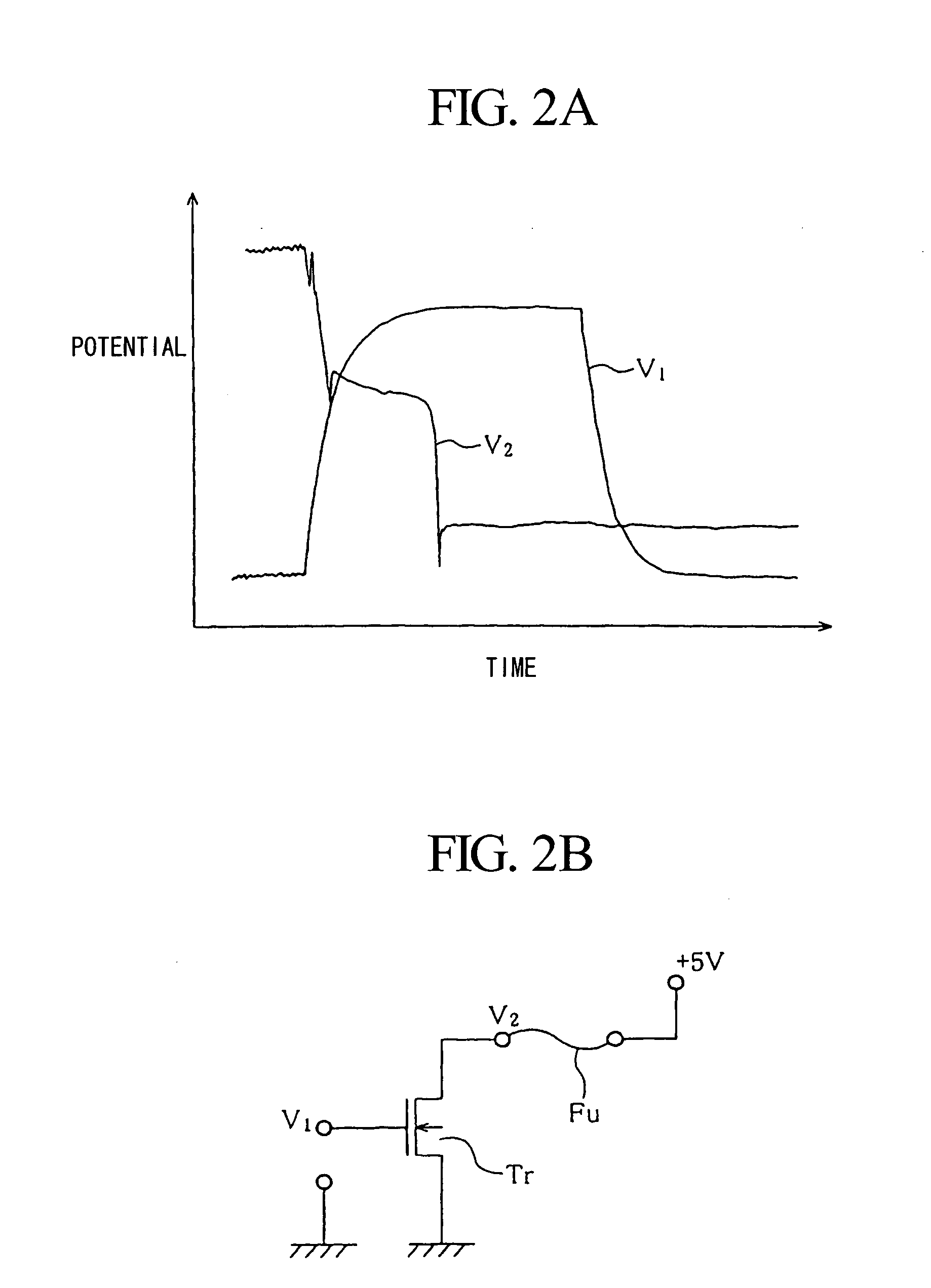
Fuse breakdown method adapted to semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070007621A1Increase distanceInhibit degassingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEvaporation
A plurality of pulses each having relatively low energy are consecutively applied to a subject fuse to cause breakdown, wherein the total energy of pulses is set in light of a prescribed breakdown threshold, which is calculated in advance. The subject fuse has a pair of terminals and an interconnection portion that is narrowly constricted in the middle so as to realize fuse breakdown with ease. A pulse generator generates pulses, which are repeatedly applied to the subject fuse by way of a transistor; then, it stops generating pulses upon detection of fuse breakdown. Side wall spacers are formed on side walls of fuses, which are processed in a tapered shape so as to reduce thermal stress applied to coating insulating films. In addition, pulse energy is appropriately determined so as to cause electro-migration in the subject fuse, which is thus increased in resistance without causing instantaneous meltdown or evaporation.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
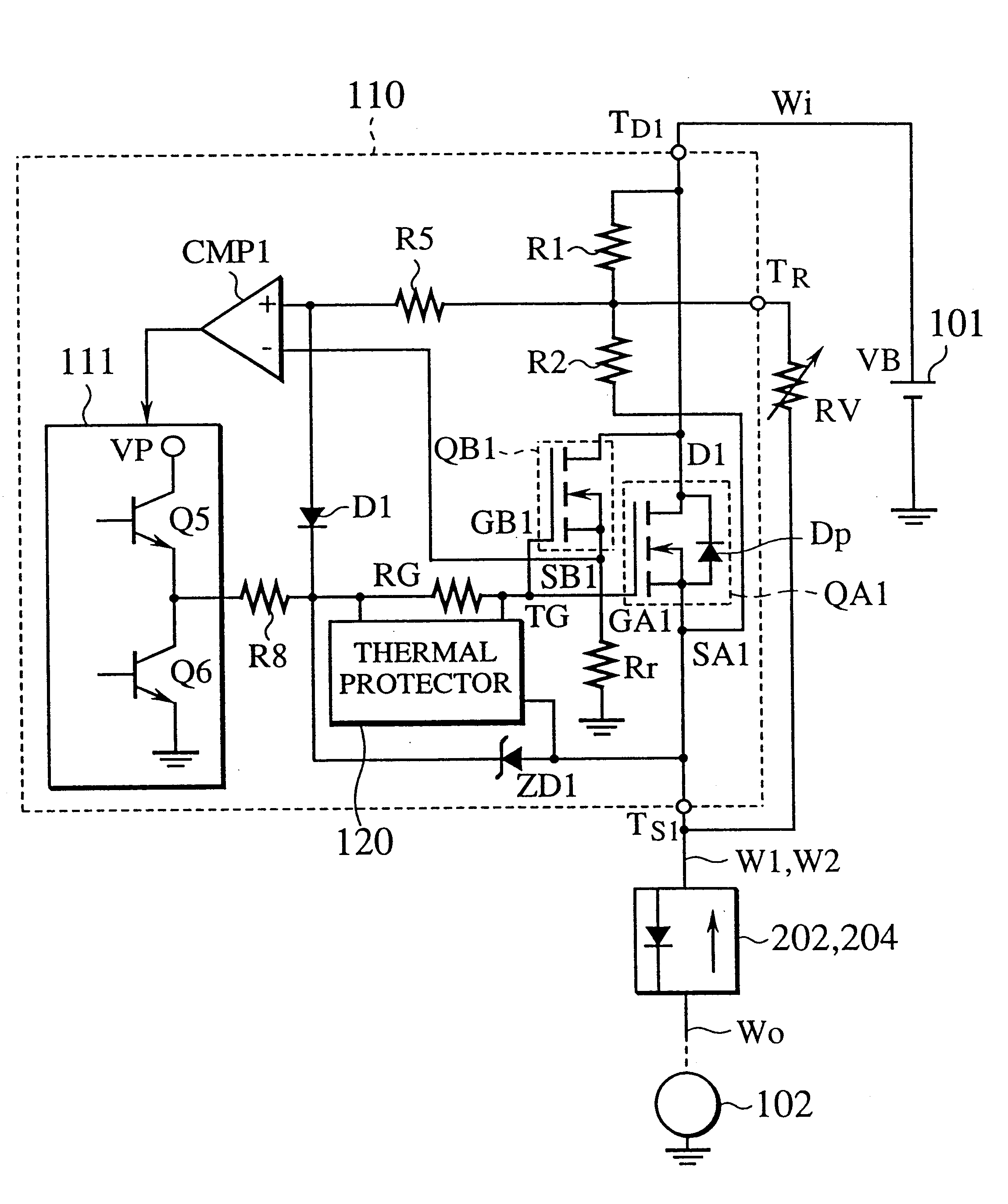
Power supply system having semiconductor active fuse
InactiveUS6269011B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSemiconductorDiode
The power supply system of the present invention includes m first semiconductor active fuses arranged in parallel with each other in a forward direction, a first wire having m branches, each branch is connected to one of m input terminals of the m first semiconductor active fuses, m intermediate wires, each of intermediate wires is connected to one of the first end of the m input terminals of the m first semiconductor active fuses, m second semiconductor active fuses arranged in parallel with each other in a reverse direction, each of the second embodiment active fuses having an output terminal connected to one of the second end of the m intermediate wires, and a second wire having m branches, each branch is connected to one of m input terminals of the m second semiconductor active fuses. Each of the reverse configured m second semiconductor active fuses can conduct the main current forwardly through parasitic diode inherently embodied in the structure. Employing this structure, the present invention provides a power supply system with high reliability.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Fuse, battery pack using the fuse, and method of manufacturing the fuse
InactiveUS20050001710A1Fuse device manufactureHeating/cooling contact switchesEngineeringBattery pack
A fuse has a pair of lead terminals disposed on a substrate, an intermediate layers for welding formed on the surface of at least one of the lead terminals, and a fuse element. The fuse element is welded to the pair of lead terminals through the intermediate layer so as to span the same. Further, the intermediate layer is formed on at least one of the lead terminals except a face thereof opposing each other. Owing to this configuration, after the fuse has melted down, the melted fuse element is prevented from being spread out into the space between the opposing faces of the lead terminals and insulation therebetween is secured.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Modular lightning surge protection apparatus
InactiveUS20140092514A1Emergency protective arrangement detailsOvervoltage protection resistorsElectricityElectric power system
A modular lightning surge protection apparatus is applied to a single-phase three-wire power system with a line, a neutral, and a ground. The modular lightning surge protection apparatus includes a substrate, a surge protection unit, a first temperature fuse, and a second temperature fuse. The surge protection unit has a first surge protection element, a second surge protection element, and a third surge protection element to form a wye connection or a delta connection structure. Furthermore, the surge protection unit, the first temperature fuse, and the second temperature fuse are electrically connected on the substrate to form a small-scale modular circuit integration structure.
Owner:CERAMATE TECH CO LTD
Self testing ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with end of life (EOL) indicator, secondary power supply for EOL and self test circuitry, and device for opening line hot when EOL occurs
ActiveUS20070279814A1Increase surface temperatureProtective switch detailsSwitch operated by earth fault currentsDiode bridgePrinted circuit board
A self test (ST) ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) provides a half wave rectifier for powering circuitry for determining and annunciating end of life (EOL) of the GFCI regardless of a shorted diode bridge or opening of a printed circuit board (PCB) trace. A fuse resistor is provided to open before an open PCB trace can occur. A microprocessor-controlled heat-conducting circuit is provided adjacent to a thermal fuse to controllably open the thermal fuse and remove power from face receptacle contacts and load terminals when EOL occurs.
Owner:HUBBELL INC
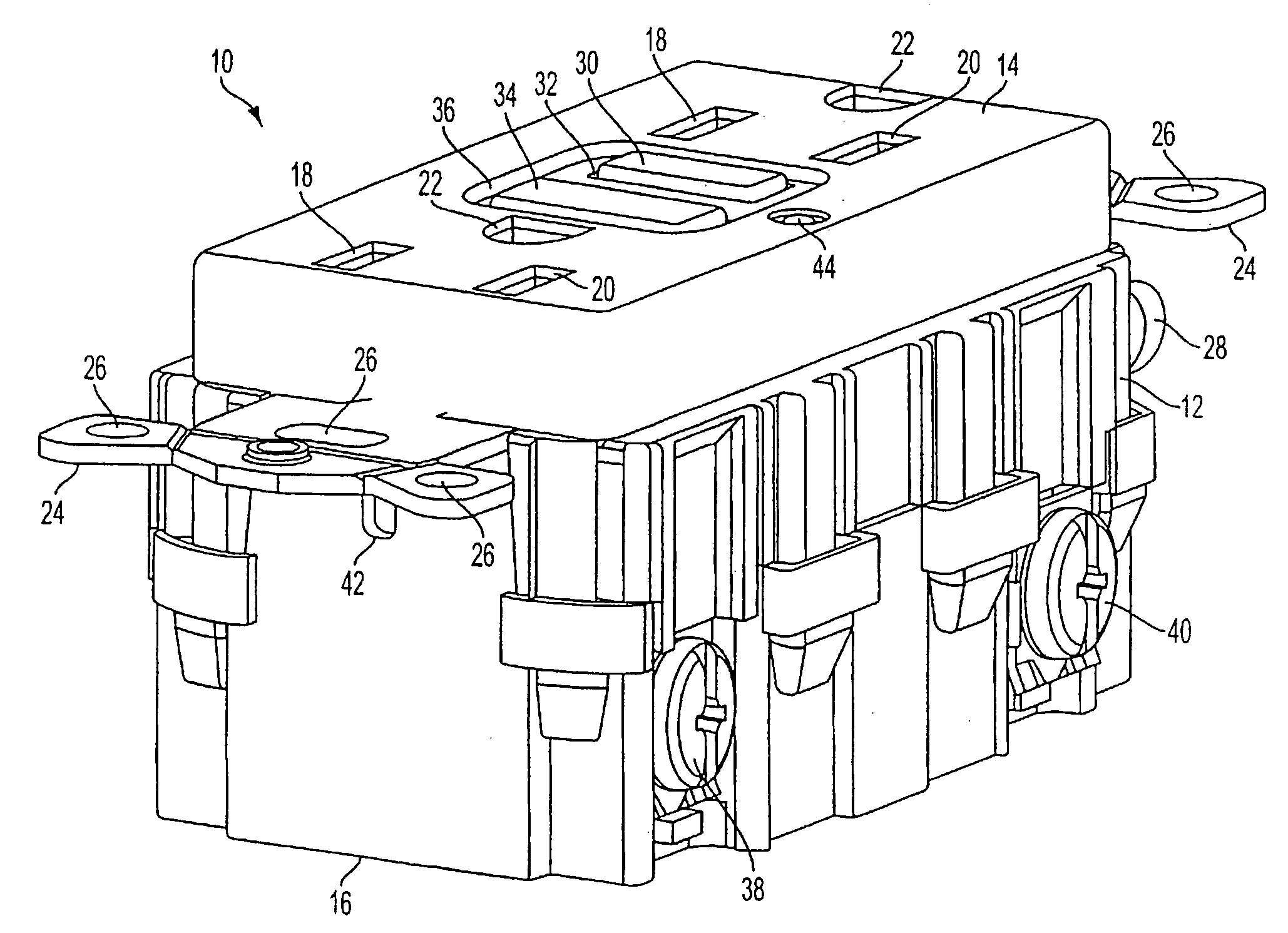
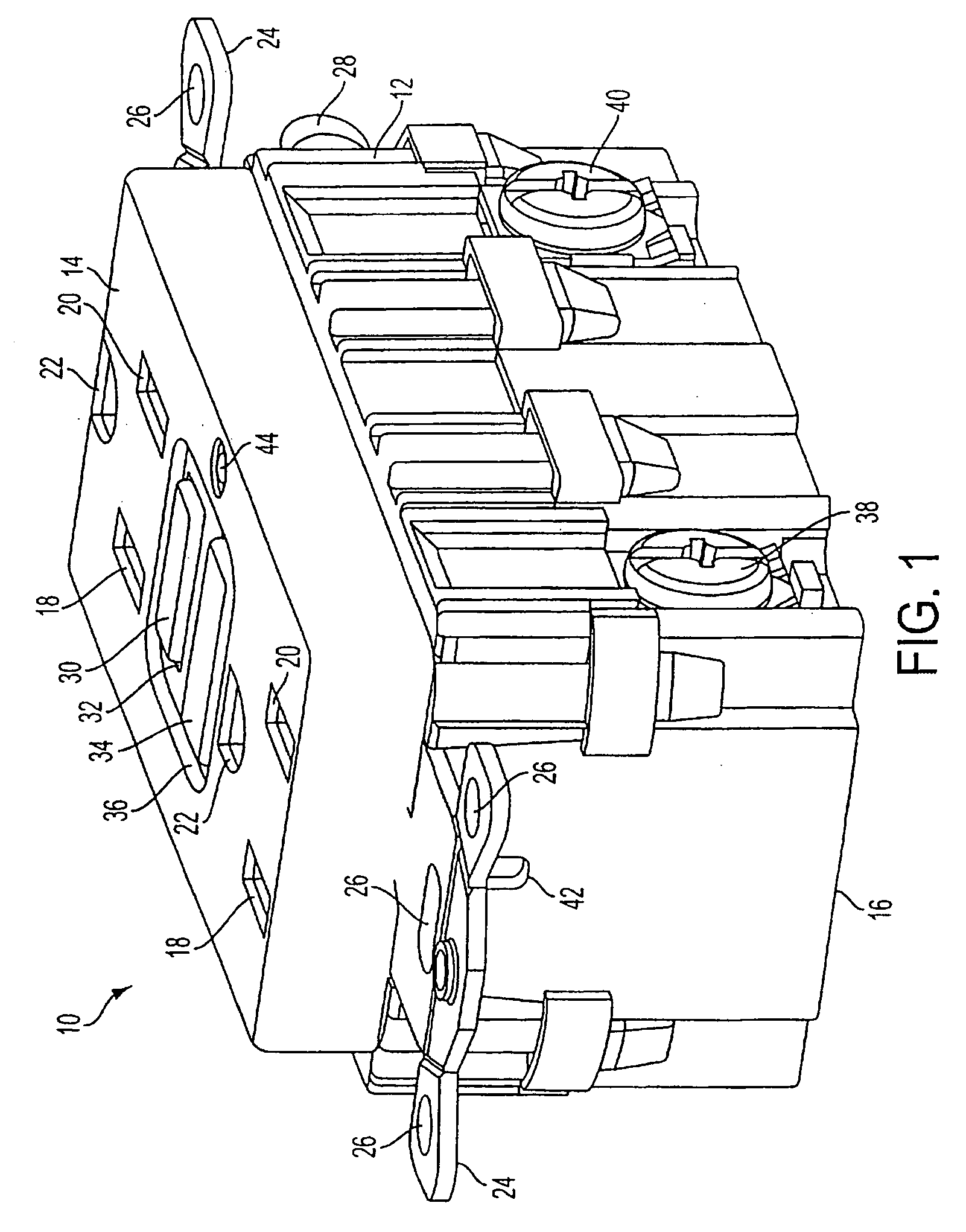
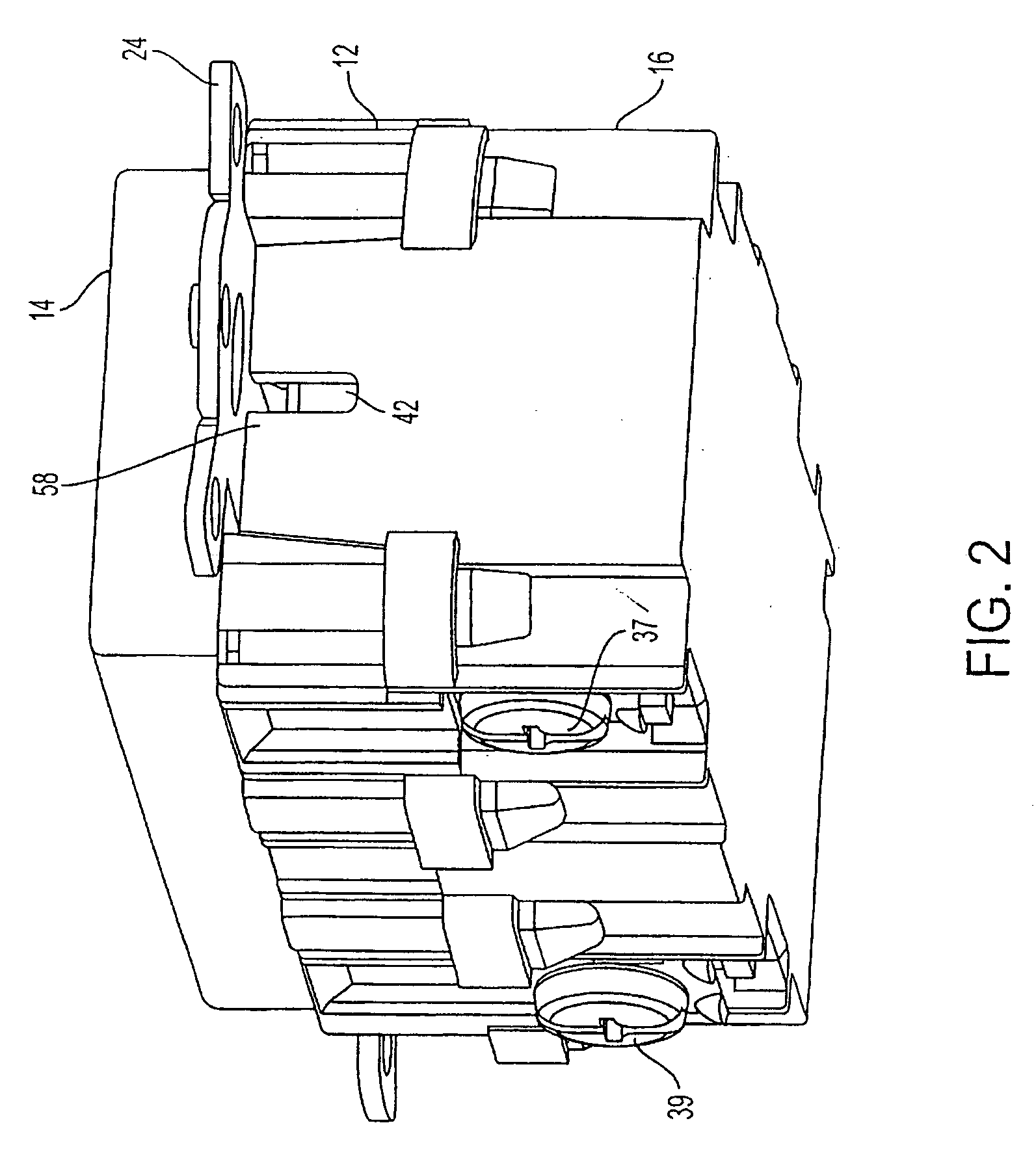
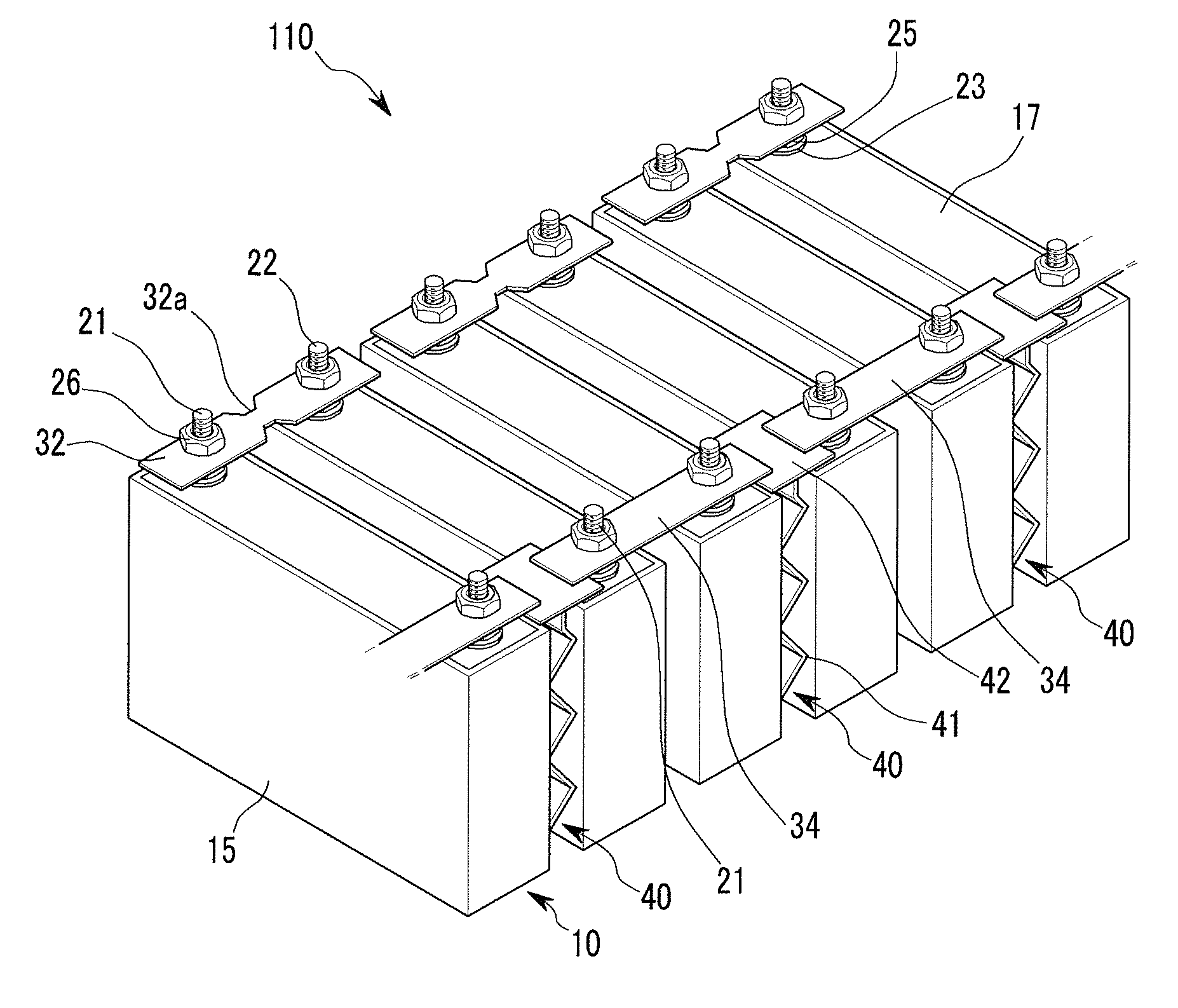
Battery module
ActiveUS20110039147A1Improve securityPrimary cell to battery groupingCurrent conducting connectionsOvercurrentRechargeable cell
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Multipolar circuit-protection assembly for a collector rail system
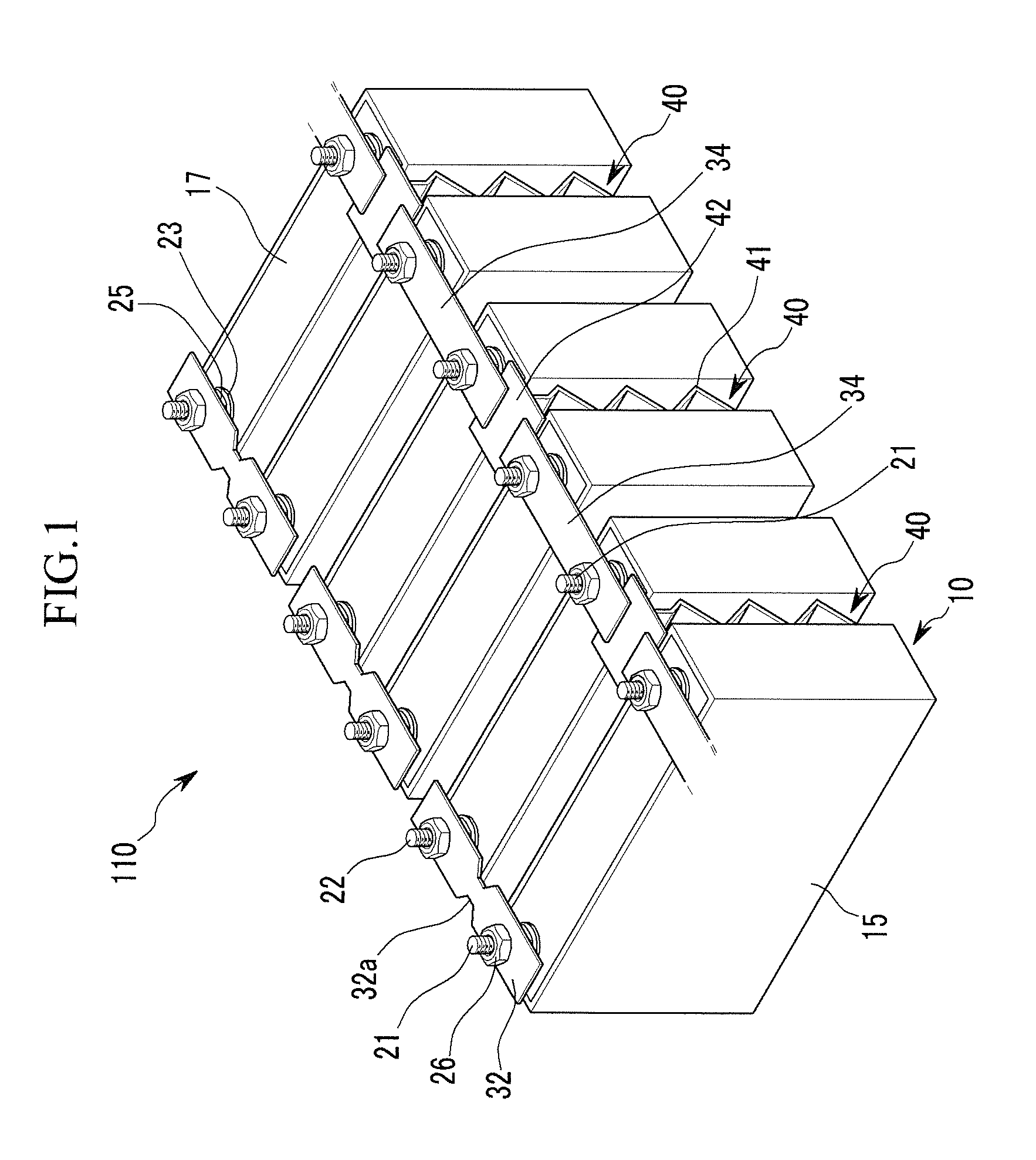
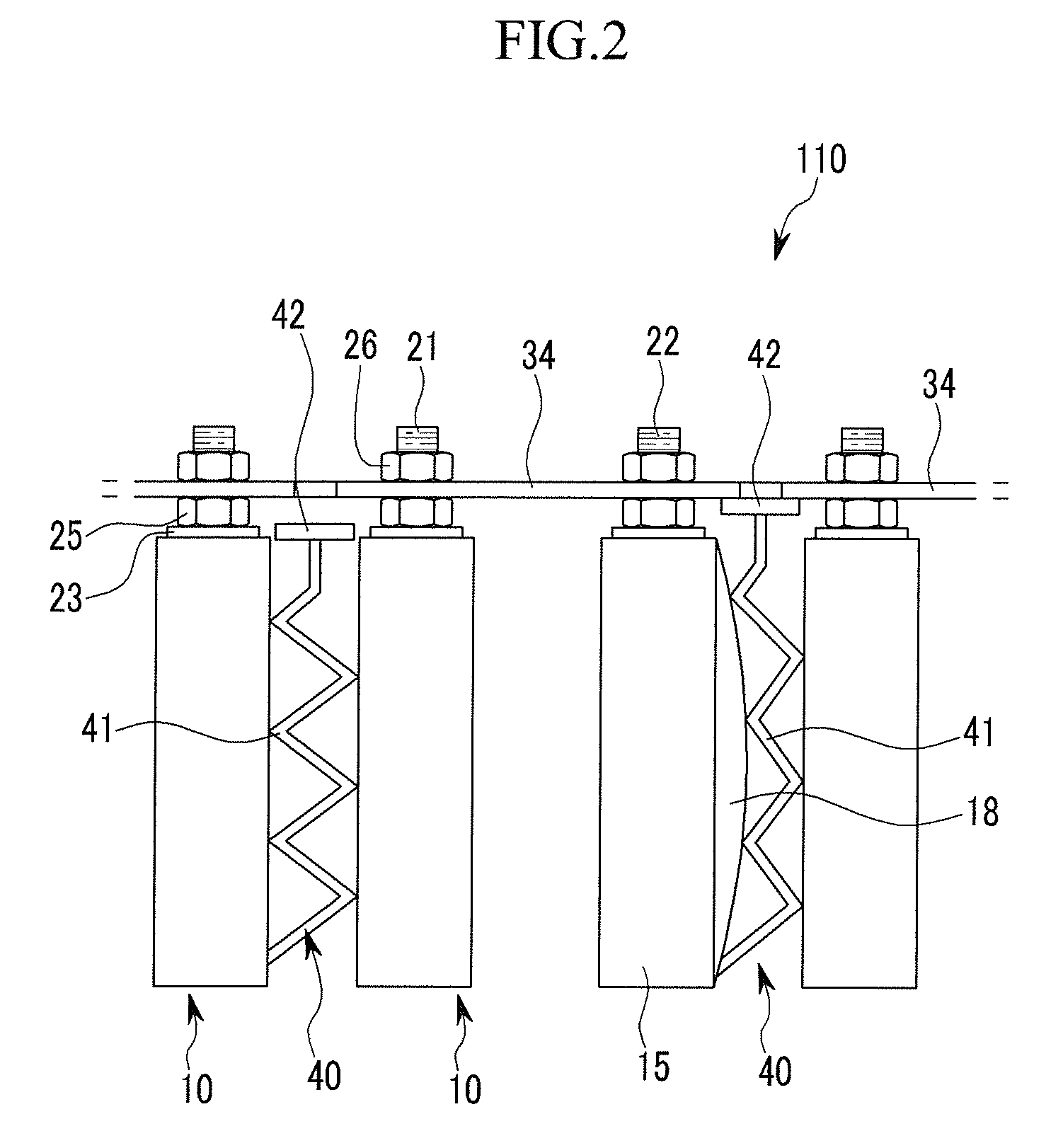
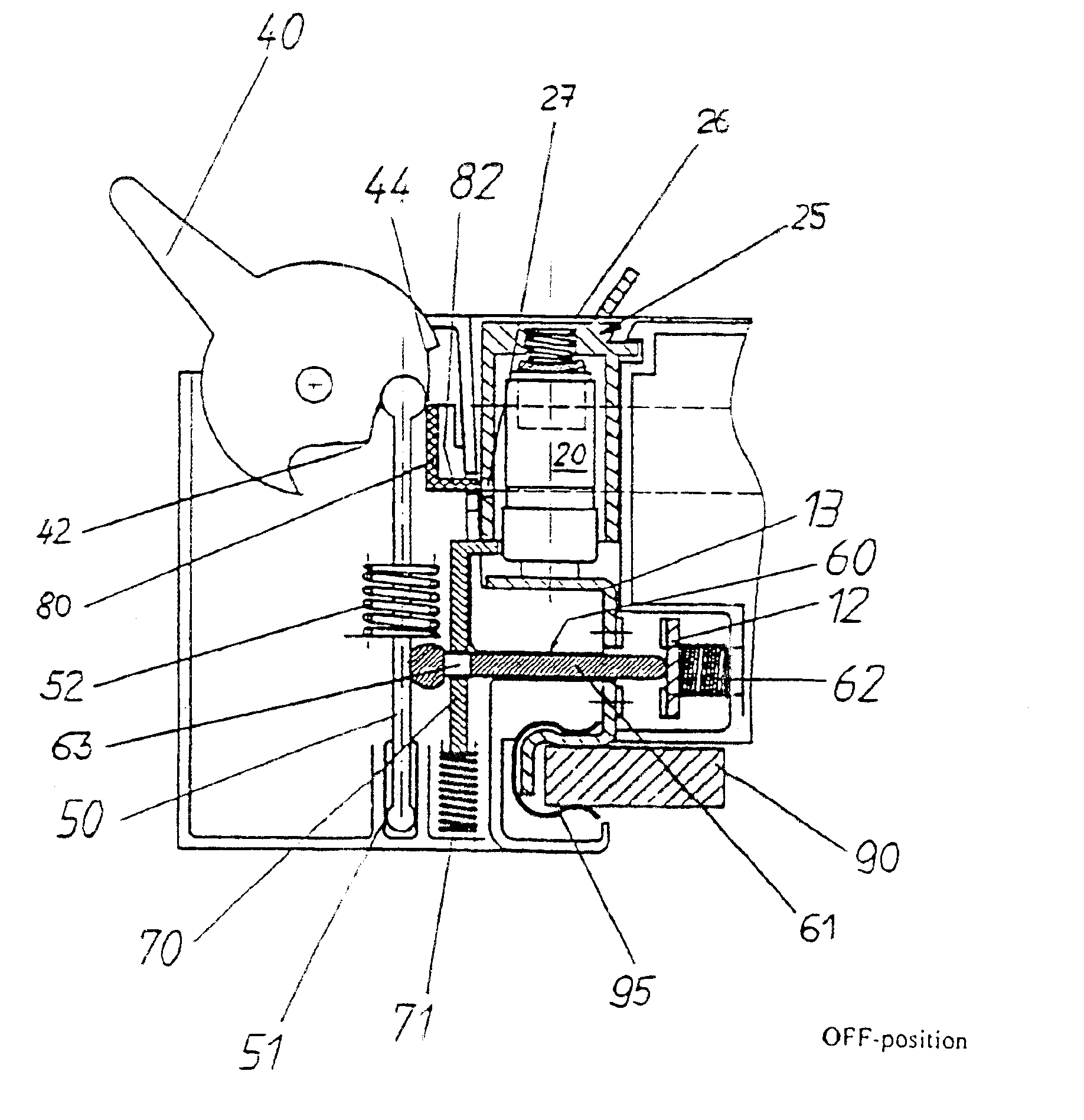
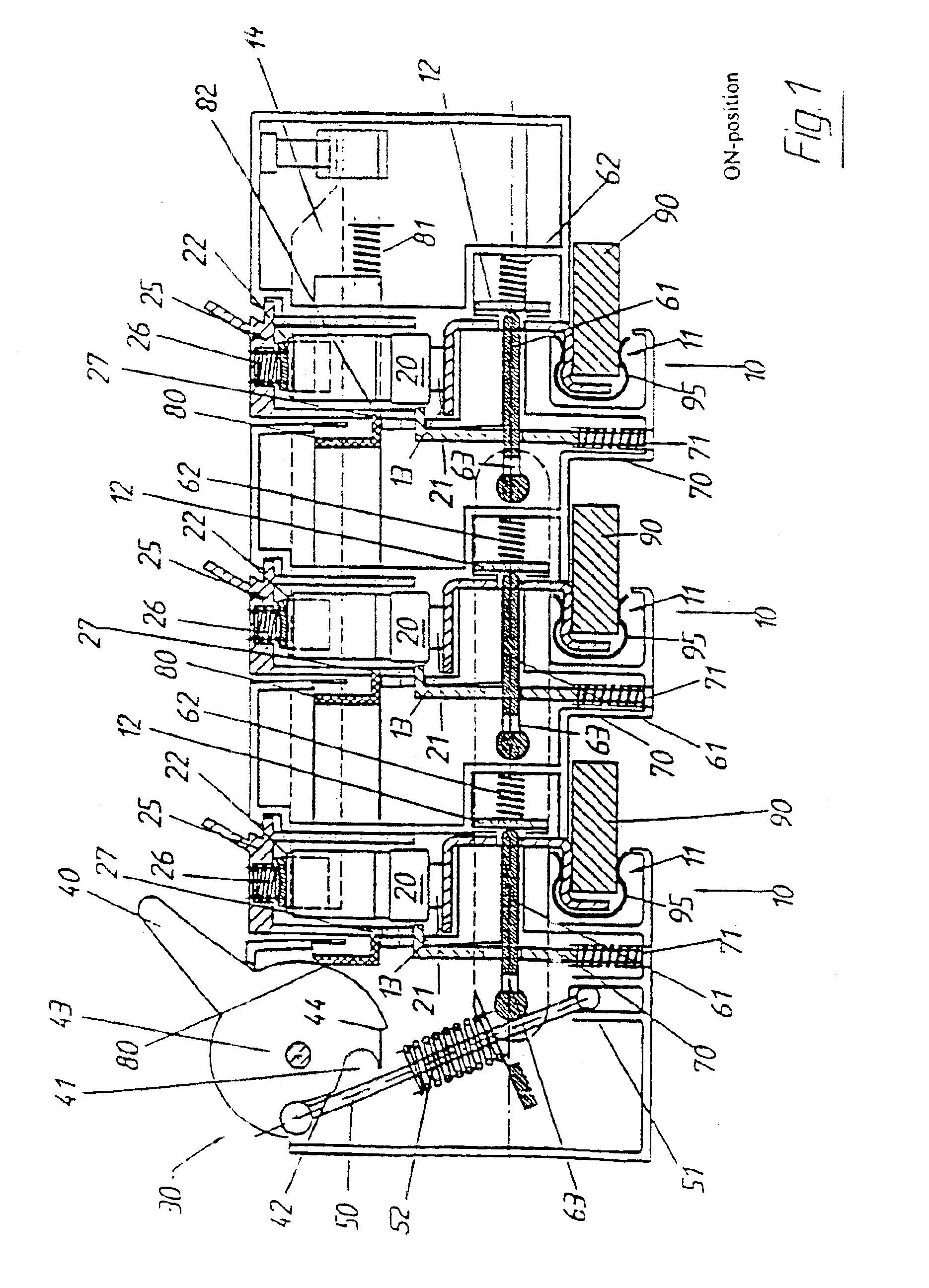
InactiveUS6864443B1Easy to operateRisk minimizationContact operating partsAir-break switchesBusbarEngineering
The invention relates to a multipole fused switch arrangement for busbar systems having at least two fused switch units (10) which each holds a fuse link (20), with the fused switch units (10) having a mounting and contact apparatus (11) for a busbar, and having a switching apparatus for closing and interrupting the circuit of all the switched fuse units, with the fused switch arrangement comprising a combined switching and blocking apparatus (30), having a switching lever (40), an operating arrangement (60), a blocking apparatus (70) for each fused switch unit (10), and a locking apparatus (80).
Owner:BRUCHMANN KLAUS
Multi-function power monitor and circuit protector
InactiveUS20050243491A1Lift restrictionsEliminate needEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionThree-phasePilot light
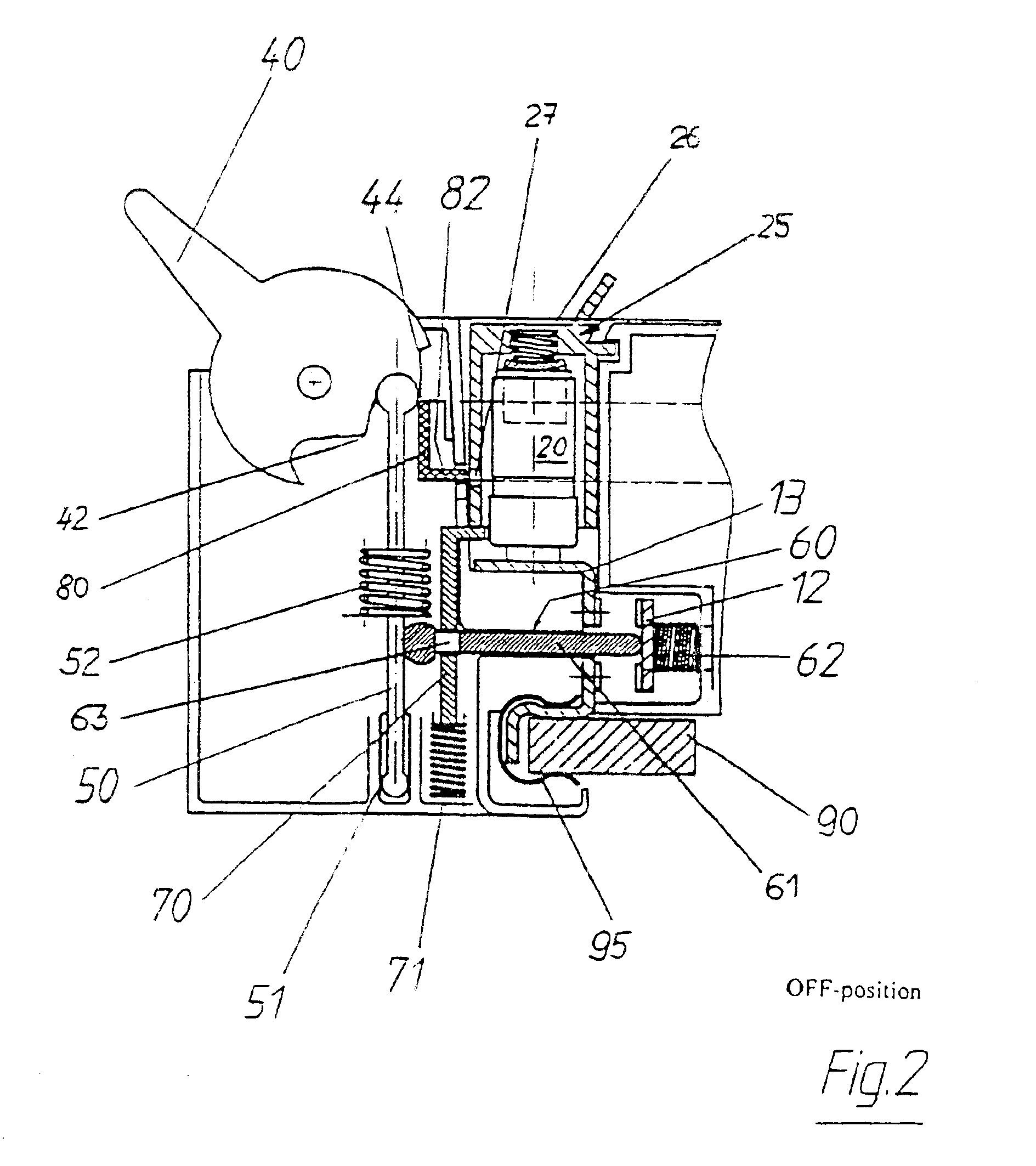
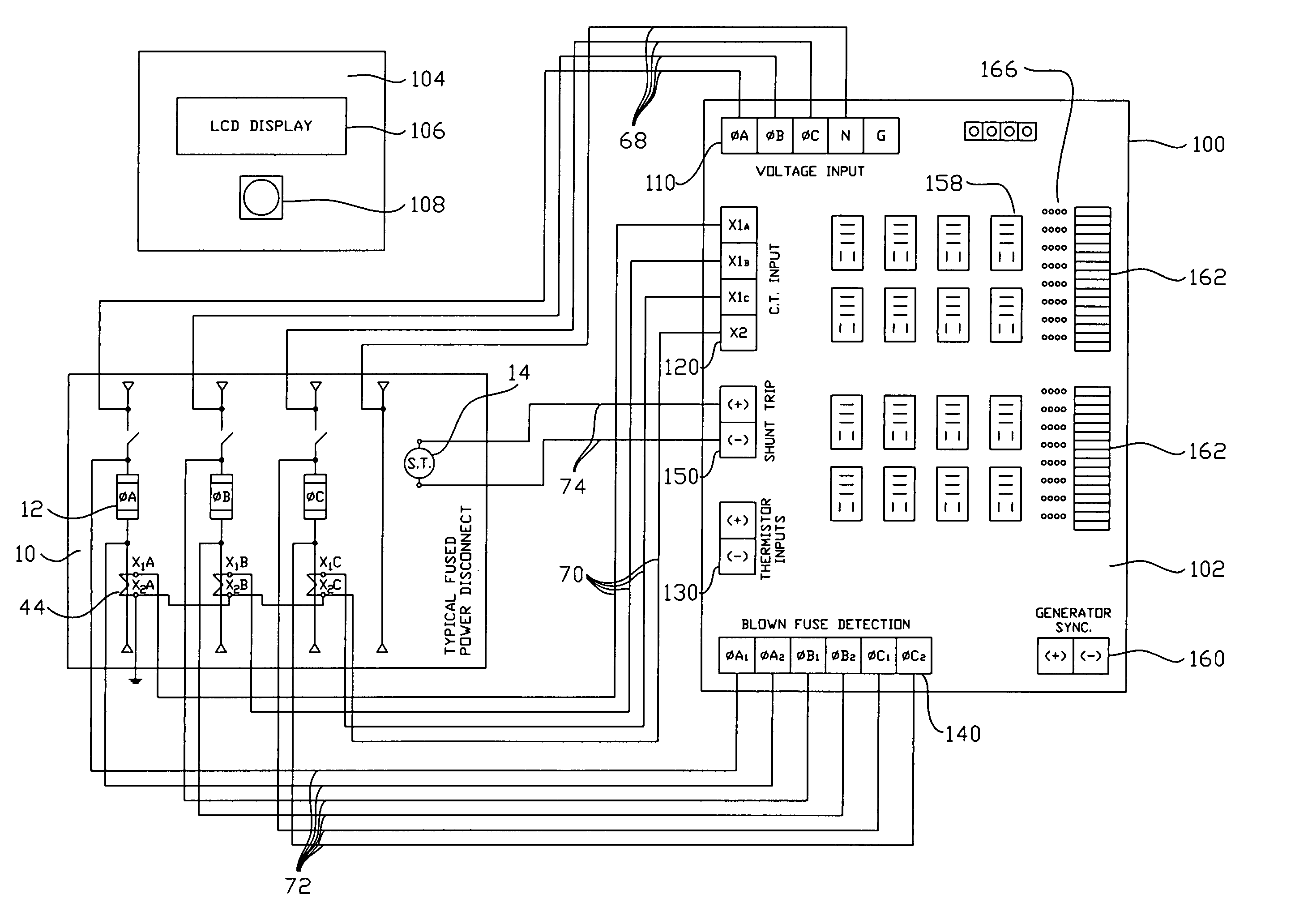
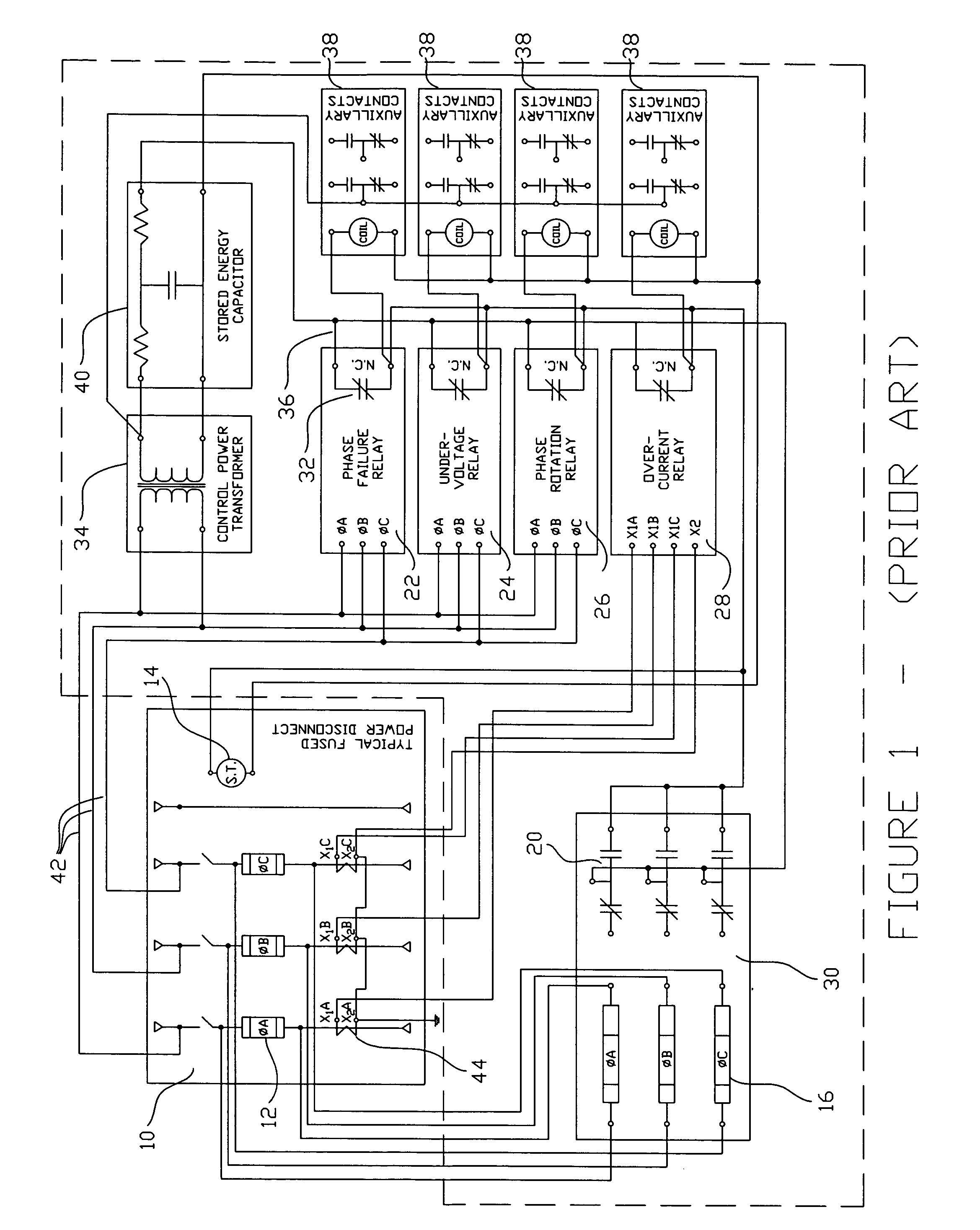
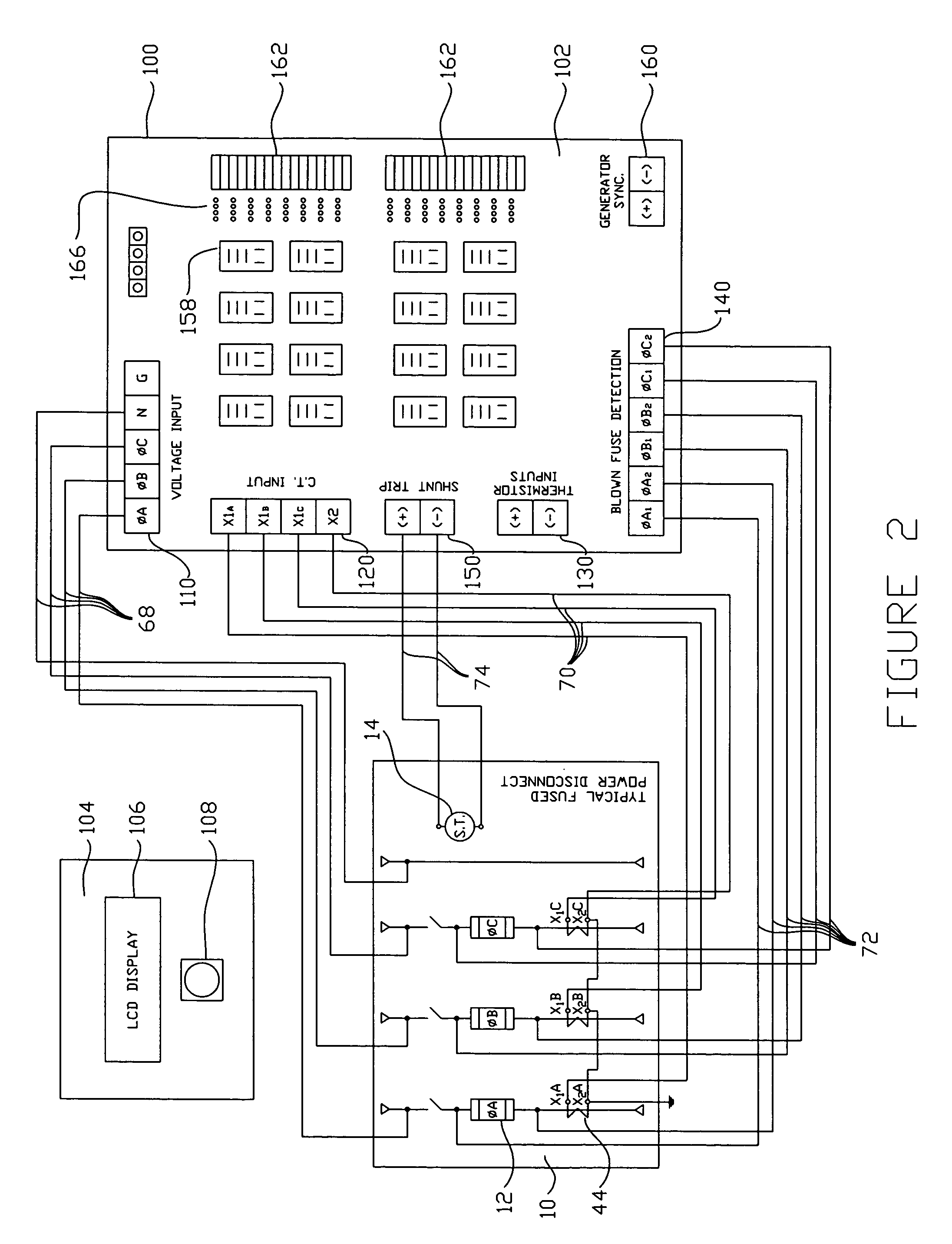
A compact and multi-functional power monitoring and circuit protection system is provided that is easily installed, used and modified, and internally derives all control and output power from the input voltages being monitored for abnormal power conditions. The functionality of all desired power monitoring and sensing devices is integrated into one unit controlled by a microprocessor. This substantially reduces the number of parts and control wiring required to achieve adequate power monitoring and circuit protection, and reduces the assembly and installation time. The integrated system uses only one set of voltage input wires, one set of current input wires, one set of blown fuse input wires and one output pair of wires to the power disconnect switch's shunt trip. Circuitry is provided to select one of the three power phases being monitored such that one of the three phases is always available to power the system. Control voltages for controlling the shunt trip and external circuits using output relays (to illuminate pilot lights, bell alarms, etc.) are also provided onboard the unit. A blown fuse detection circuit uses solid-state devices in lieu of replaceable trigger fuses. The unit can be instantly reset itself after a blown fuse condition in a power disconnect switch has been rectified.
Owner:TANIS JAMES
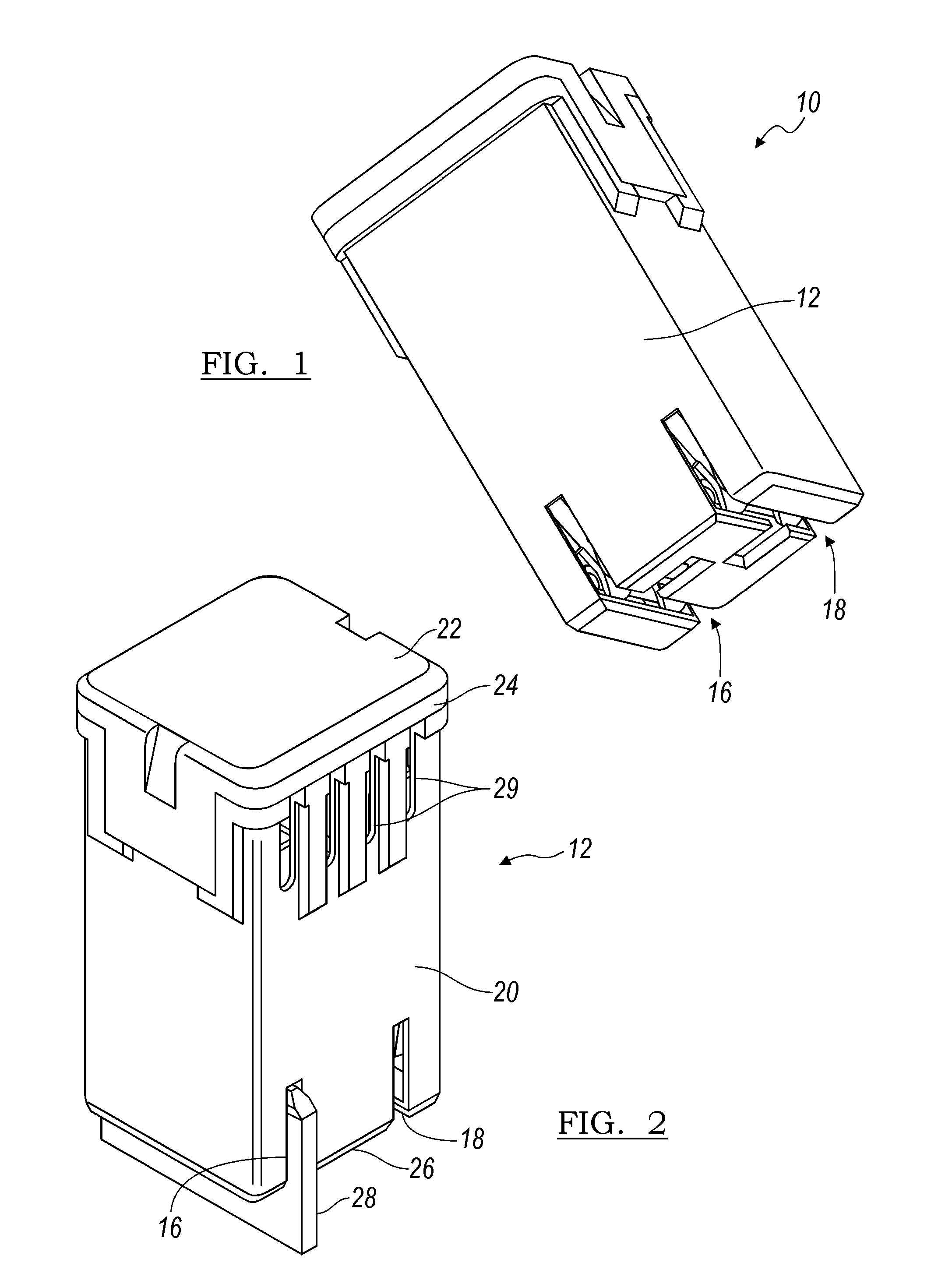
Electrical circuit apparatus with fuse access section
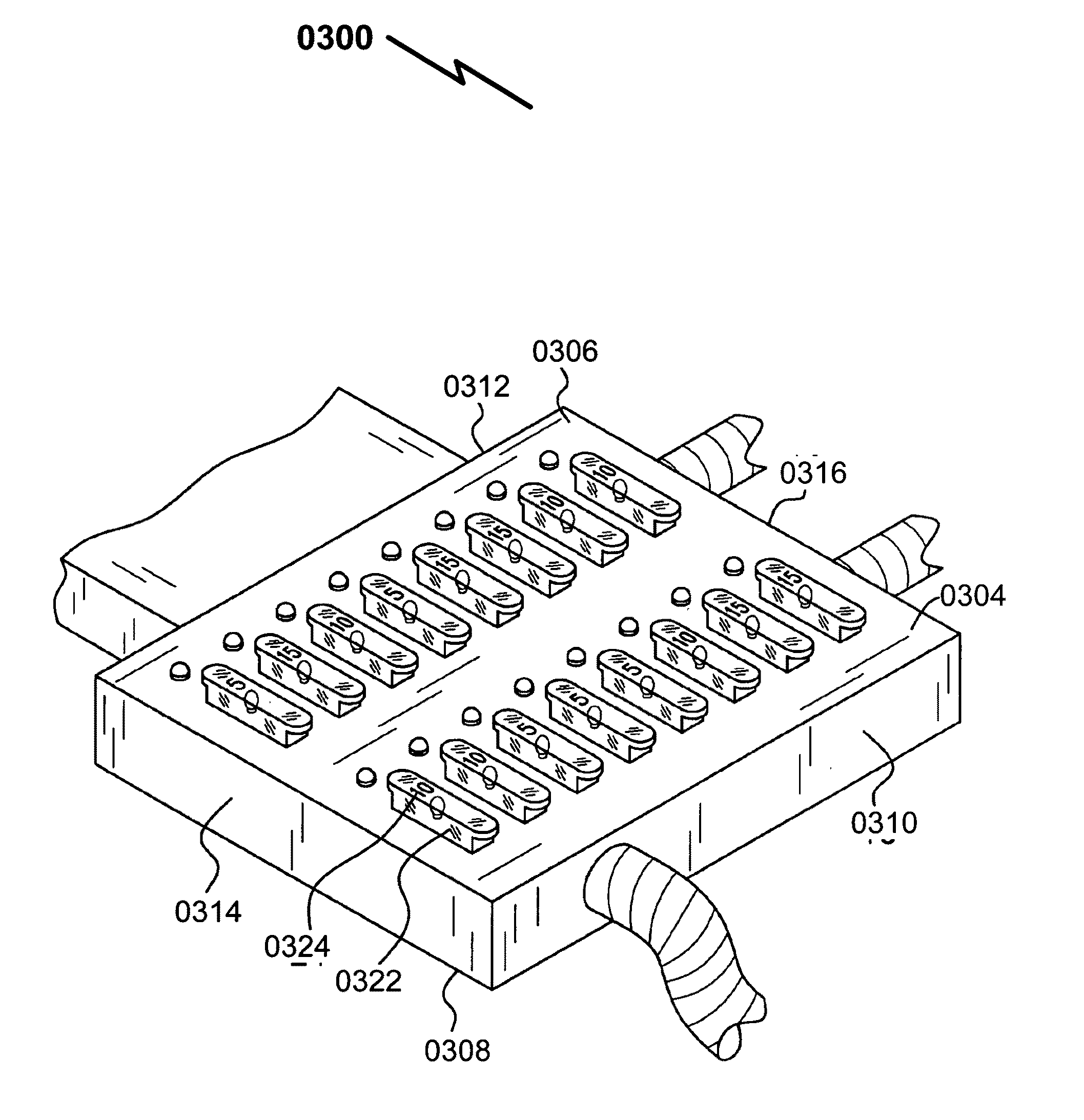
ActiveUS20050094357A1Easy accessFuse disposition/arrangementSubstation/switching arrangement casingsJunction boxFuse cutout
An electrical apparatus has an elongated housing with fuses located therein. Windows are provided in the housing to close apertures in registration with fuse locations to allow access to fuses by removing the window. Fuses may be carried on a circuit card removably engageable with a terminal block secured to a wall within the housing. A fuse compartment cover is removably secured to the housing. The window comprises a fuse condition indicator to allow determination of the condition of the fuse (i.e. blown or not blown) without having to open the window. Additionally, powered indicators such as LEDs visible through the windows may indicate the state of fuses. The housing may comprise a power distribution unit and may be rack mounted or mounted to a wall of a rack assembly. The windows are located on the housing to be removable free of engagement with the assembly. In various embodiments, the windows may be included in a different one of the walls so that the windows will be unobstructed when the housing is in one of a number of orientations. The fuse compartment may be opened without removing the unit from the rack.
Owner:SERVER TECHNOLOGY
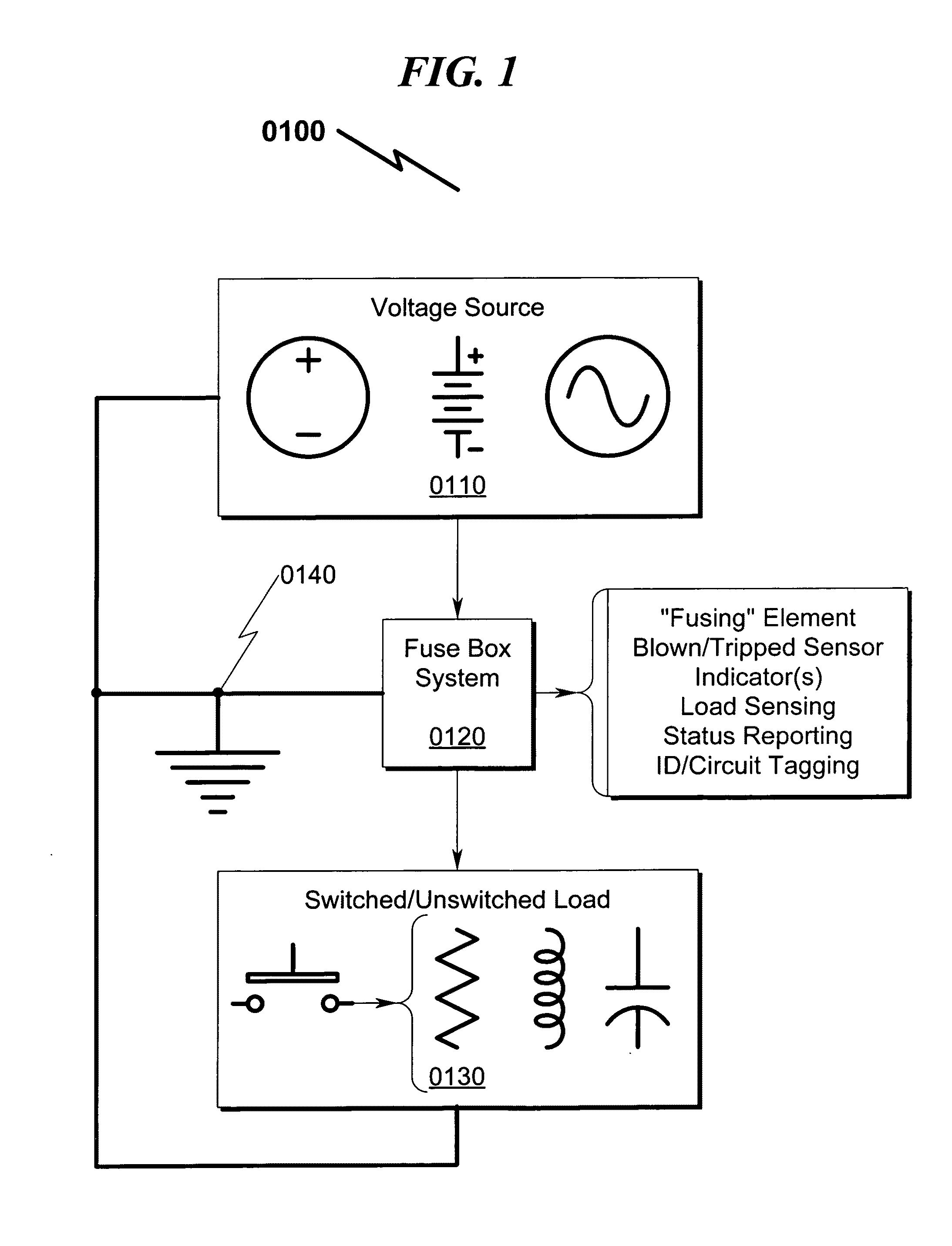
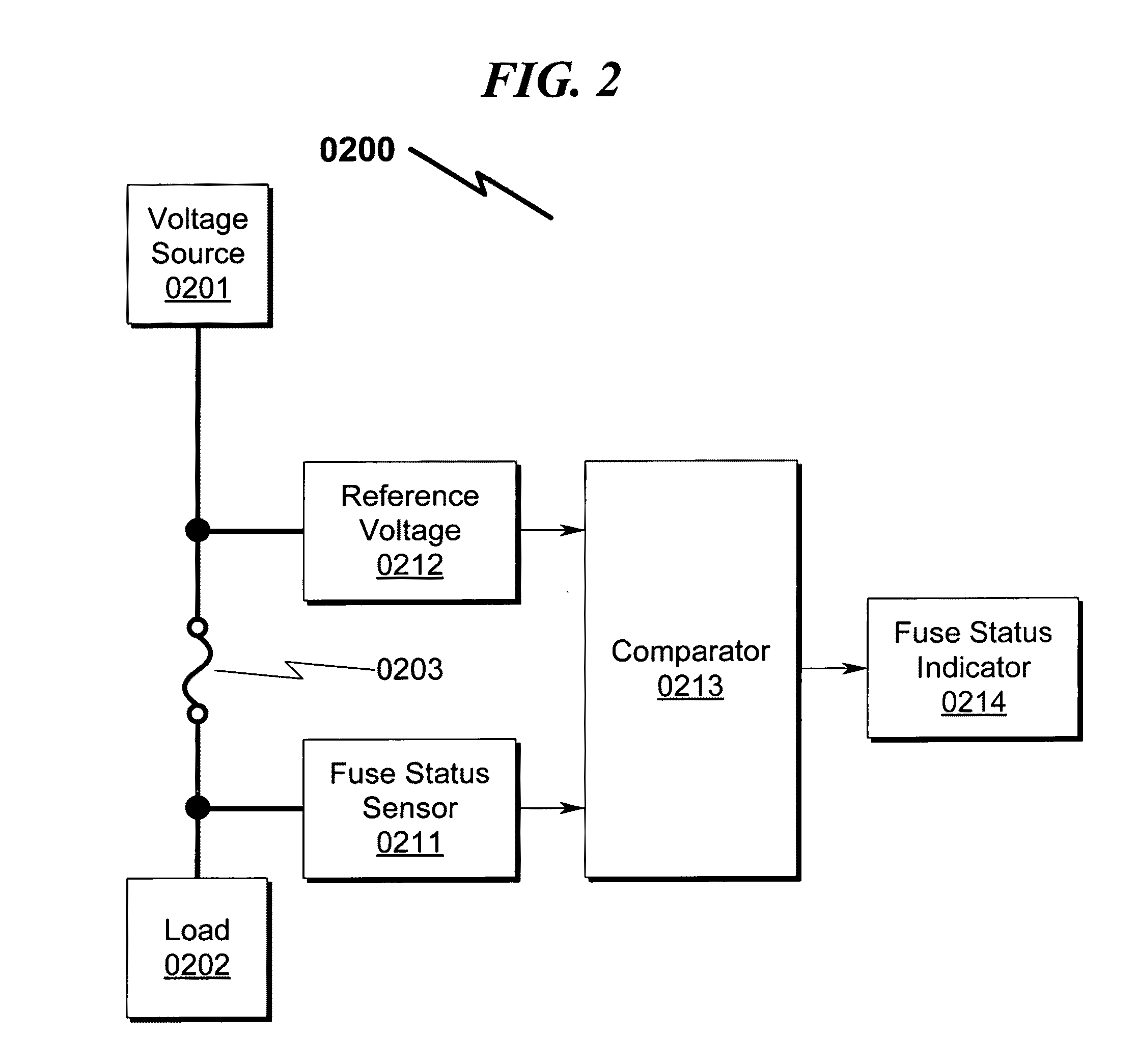
Fuse box system and method
InactiveUS20110175699A1Prohibitive to replaceEasy and efficient to manufactureSwitches with electrothermal releaseProtective switch operating/release mechanismsPower flowEngineering
A fuse box system and method providing for visual and / or remote sensing of interrupted fusing elements is disclosed. The system incorporates LEDs and / or remote sensing apparatus to permit indication of a “blown” fuse and / or circuit protection breaker. This system may be configured for both polarized and / or non-polarized applications and generally provides for indicator illumination when a fuse / breaker is blown. Some preferred embodiments may incorporate current sourcing technologies to permit operation of the system over wide range of system voltages, as well as provisions for wired and / or RF / wireless interrogation of the fuse / breaker status. Alternate embodiments including systems / methods to permit remote sensing of fuse status and / or circuit current monitoring, and may be retrofit within existing fuse / breaker panel systems in some configurations.
Owner:HUSS ROY ALLEN
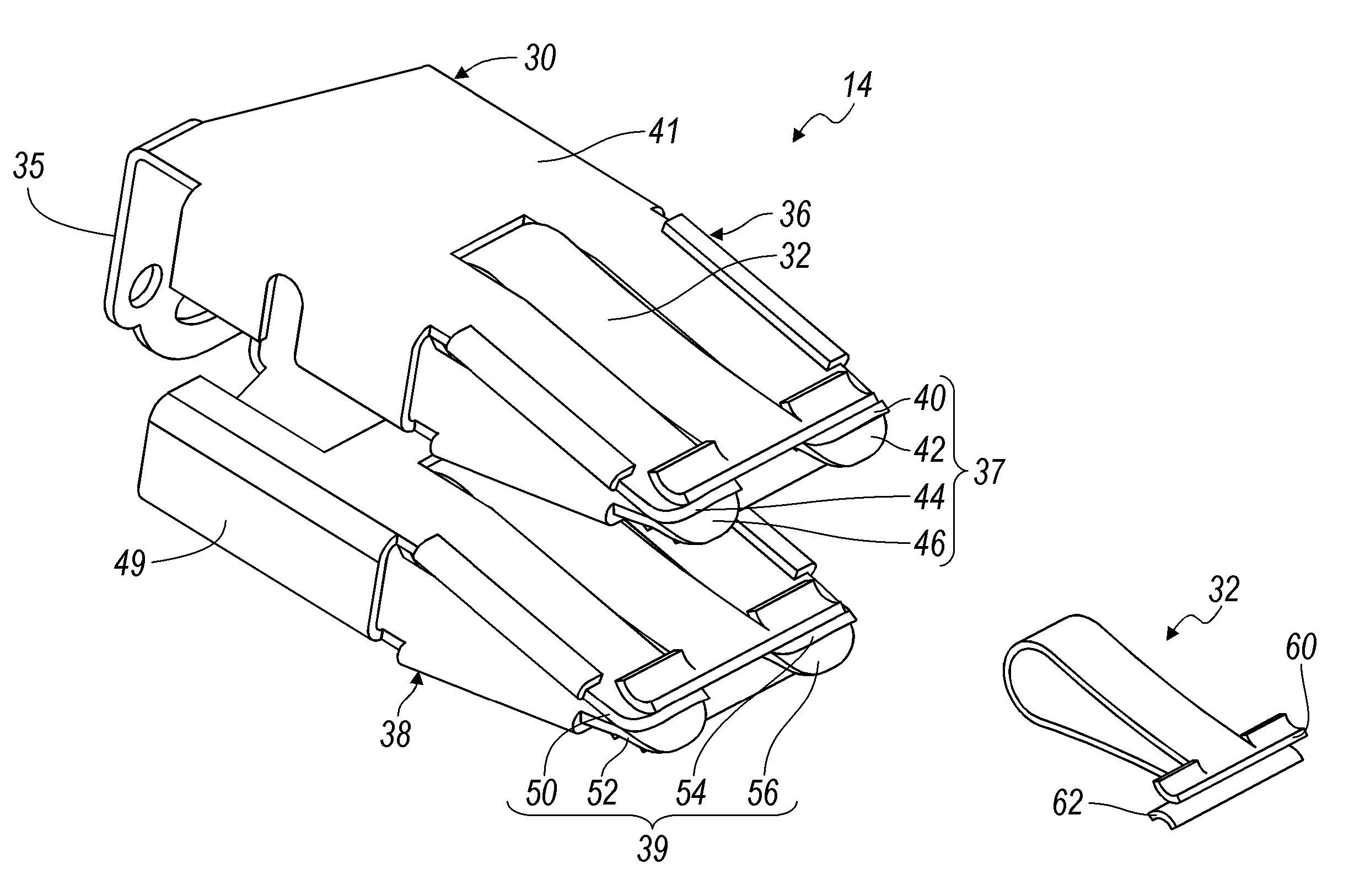
High power case fuse
InactiveUS7595715B2Increase powerGreat mechanical stress propertyIncorrect coupling preventionCoupling contact membersElectrical and Electronics engineeringFuse cutout
A high power fuse includes a fuse body having a first terminal receptor including a first set of terminal legs and a second terminal receptor in spaced relation to the first terminal receptor. The second terminal receptor includes a second set of terminal legs. A fuse element is disposed between the first terminal receptor and the second terminal receptor. A first clamp-like member is mounted to the fuse body for applying a predetermined compression force against the first set of terminal legs and is configured to secure a first male terminal between the first set of terminal legs. A second clamp-like member is mounted to the fuse body for applying a predetermined compression force against the second set of terminal legs and is configured to secure a second male terminal between the second set of terminal legs.
Owner:LEAR CORP
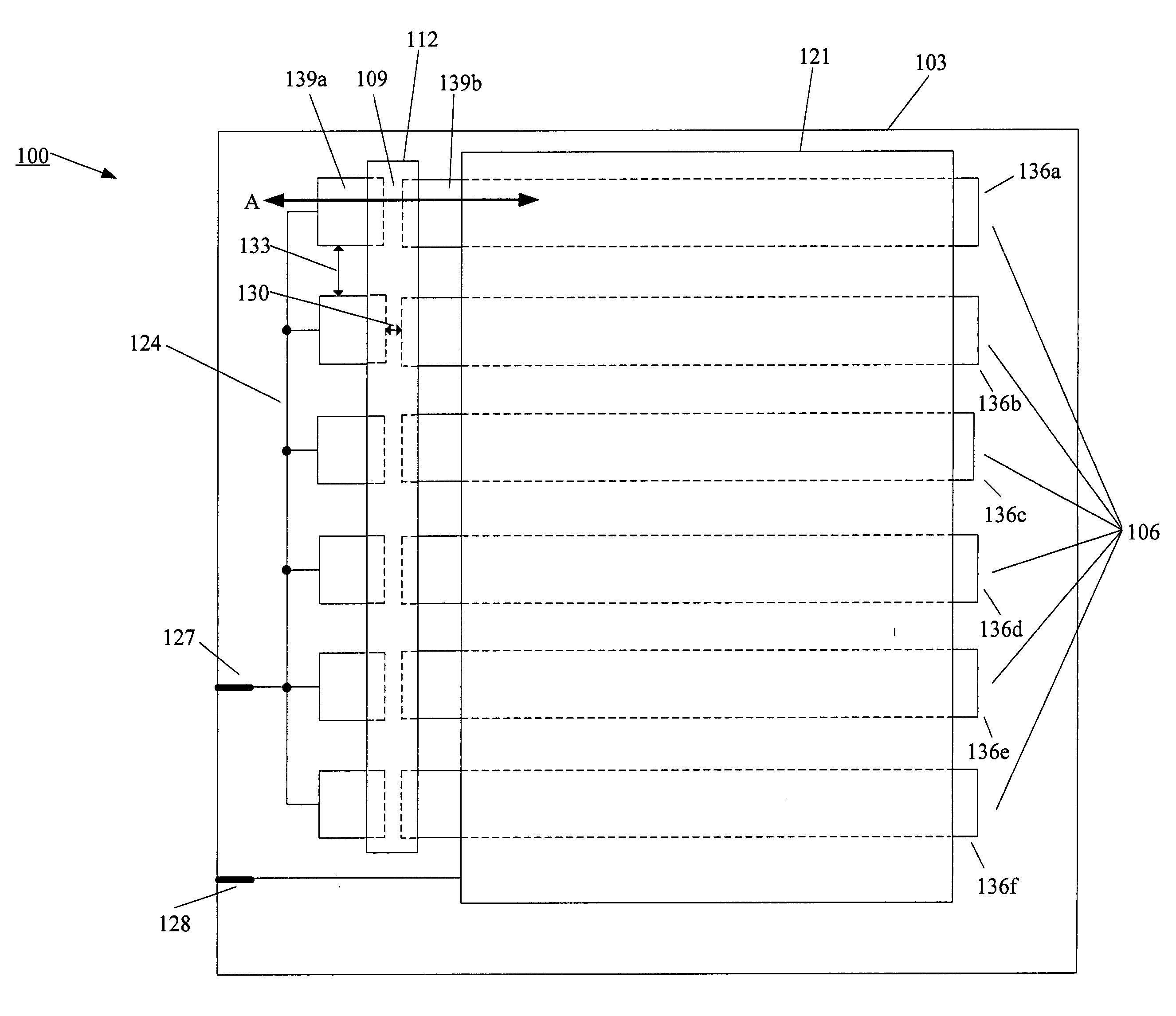
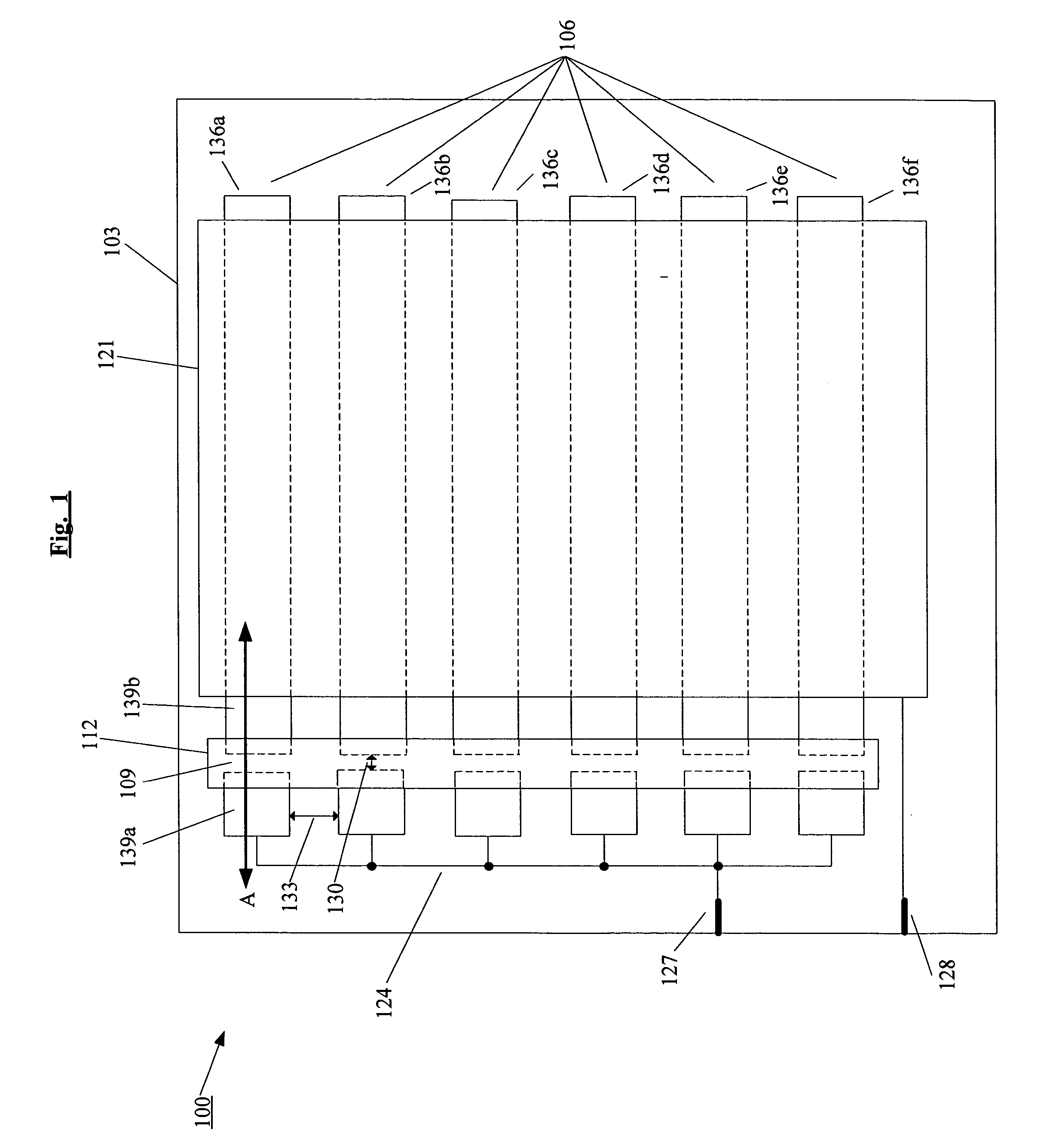
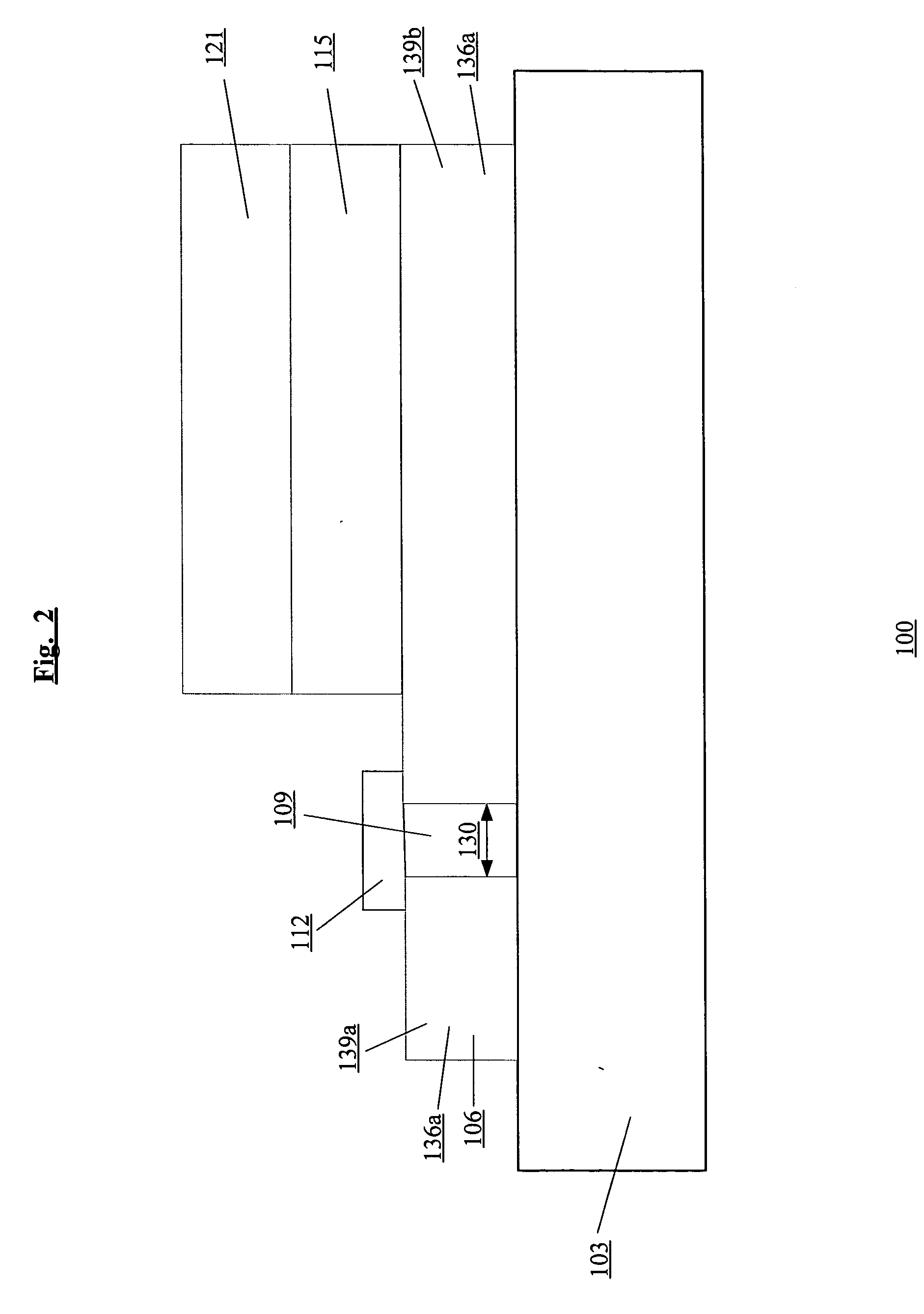
Integrated fuses for OLED lighting device
ActiveUS20060066223A1High resistivityReduce materialDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightThin layer
An embodiment of the present invention pertains to an electroluminescent lighting device for area illumination. The lighting device is fault tolerant due, in part, to the patterning of one or both of the electrodes into strips, and each of one or more of these strips has a fuse formed on it. The fuses are integrated on the substrate. By using the integrated fuses, the number of external contacts that are used is minimized. The fuse material is deposited using one of the deposition techniques that is used to deposit the thin layers of the electroluminescent lighting device.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Device for protecting against voltage surges
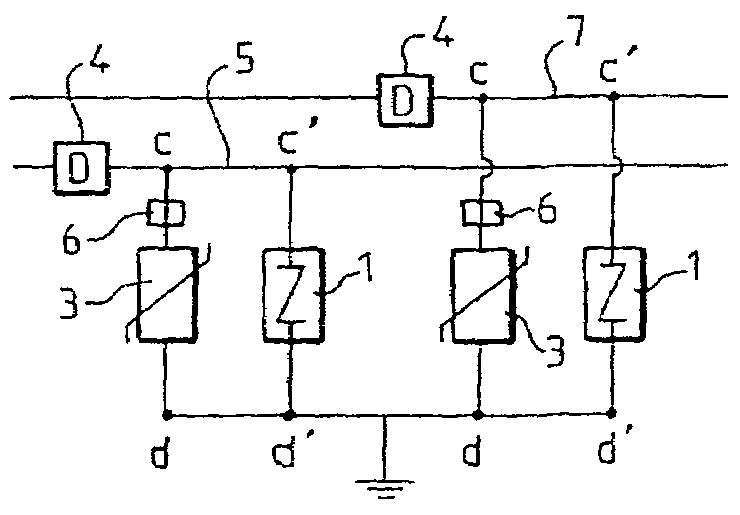
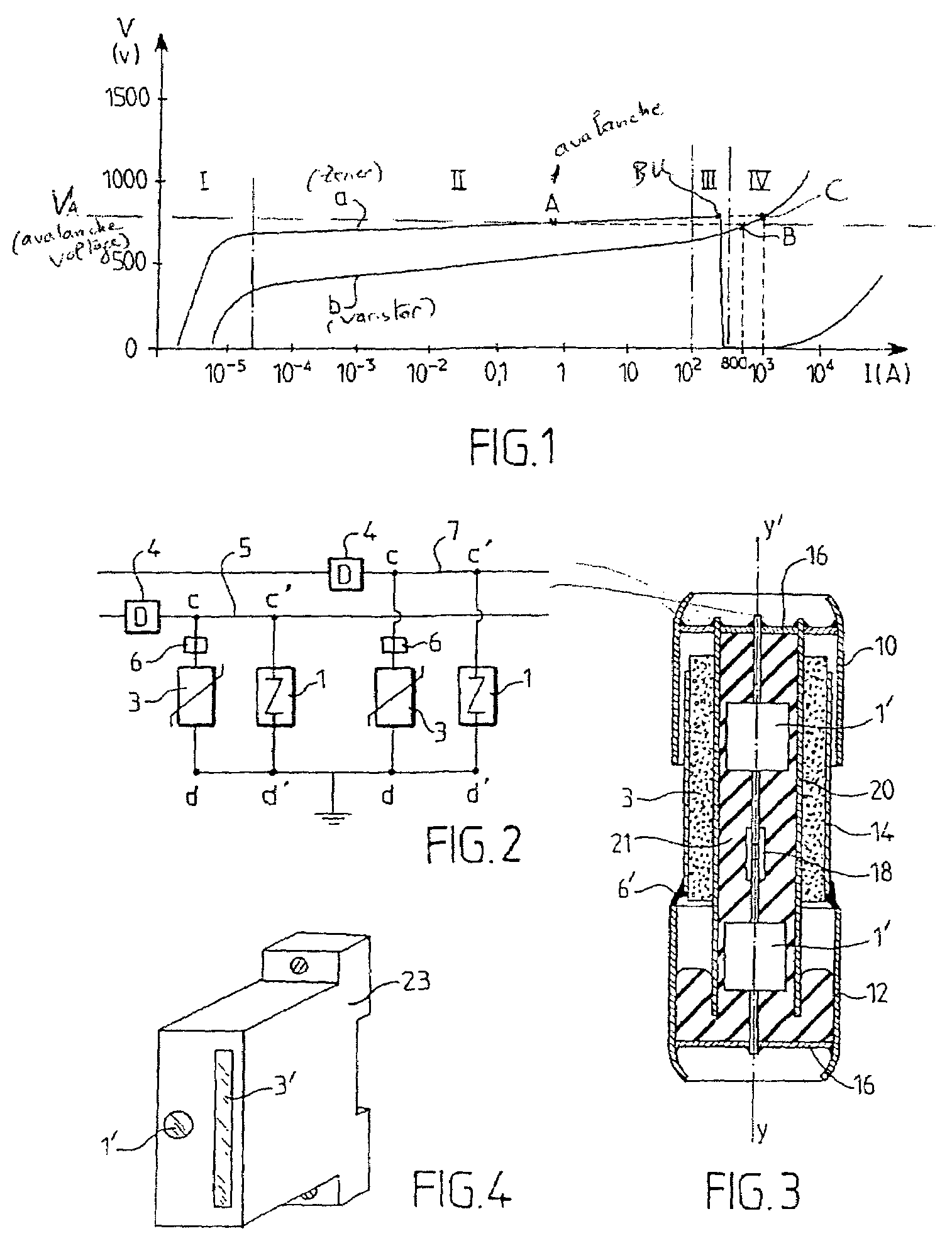
InactiveUS7106572B1Emergency protective arrangement detailsOvervoltage protection resistorsElectrical conductorZener diode
A device for protection against voltage surges in an electric power supply line includes at least two elements (1′, 3), namely a Zener diode lightning arrester (1′) fast-blow in short circuit, and a varistor (3), arranged in parallel. One of the terminals common to the two elements (1′, 3) is connected to the line to be protected, and the other common terminal is connected to earth or to a common conductor element.
Owner:ADEE ELECTRONICS
Stressed material and shape memory material MEMS devices and methods for manufacturing
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
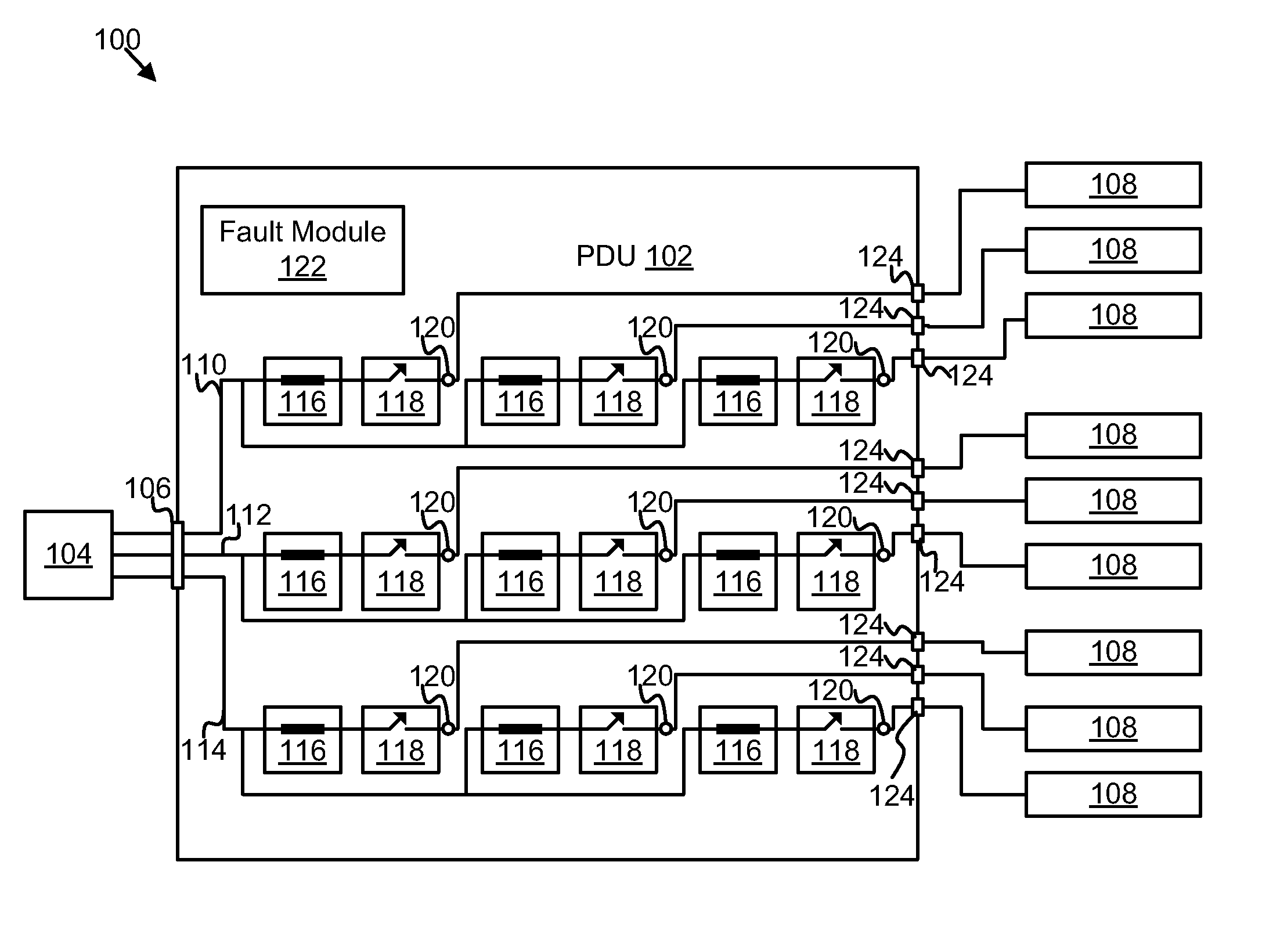
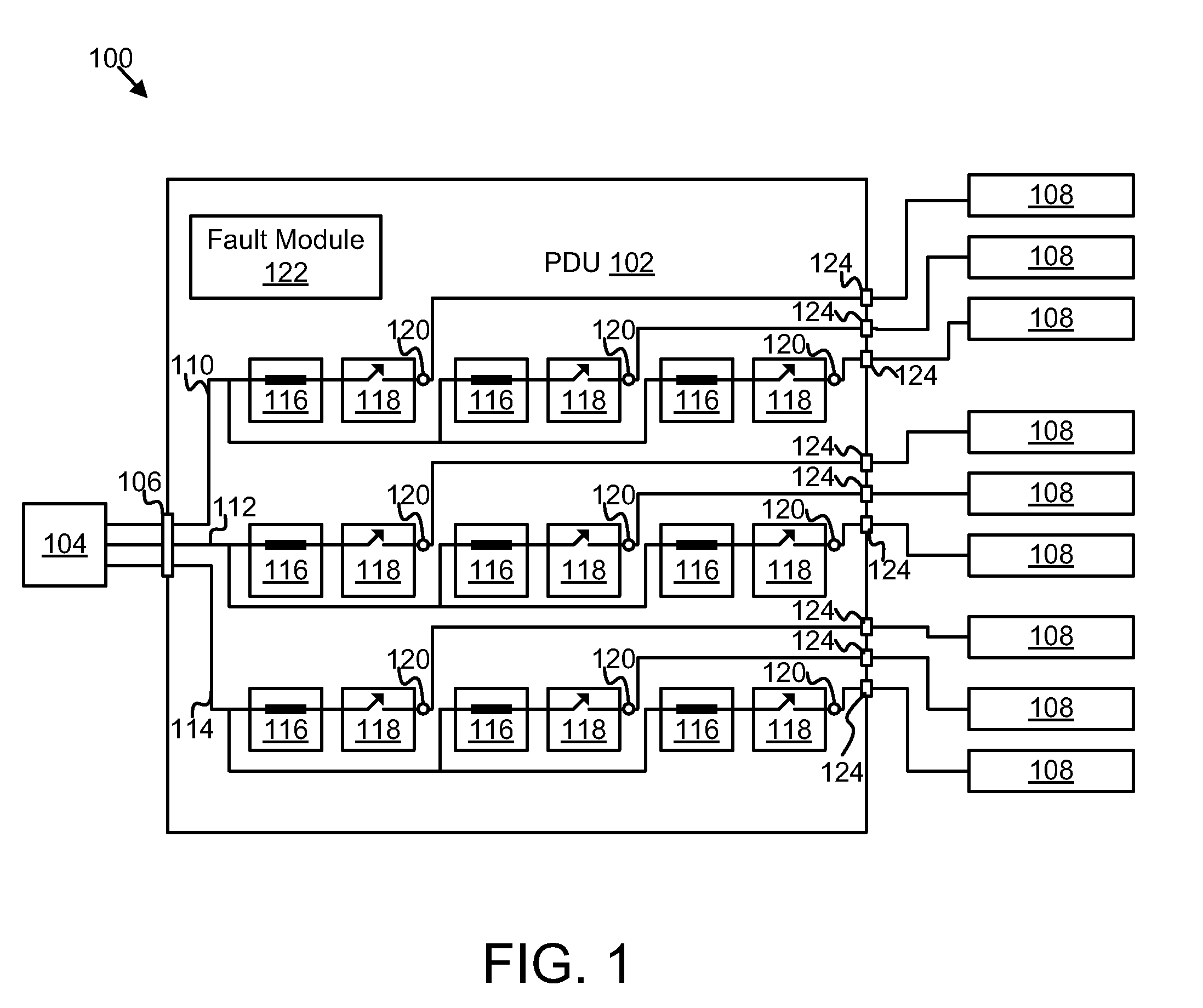
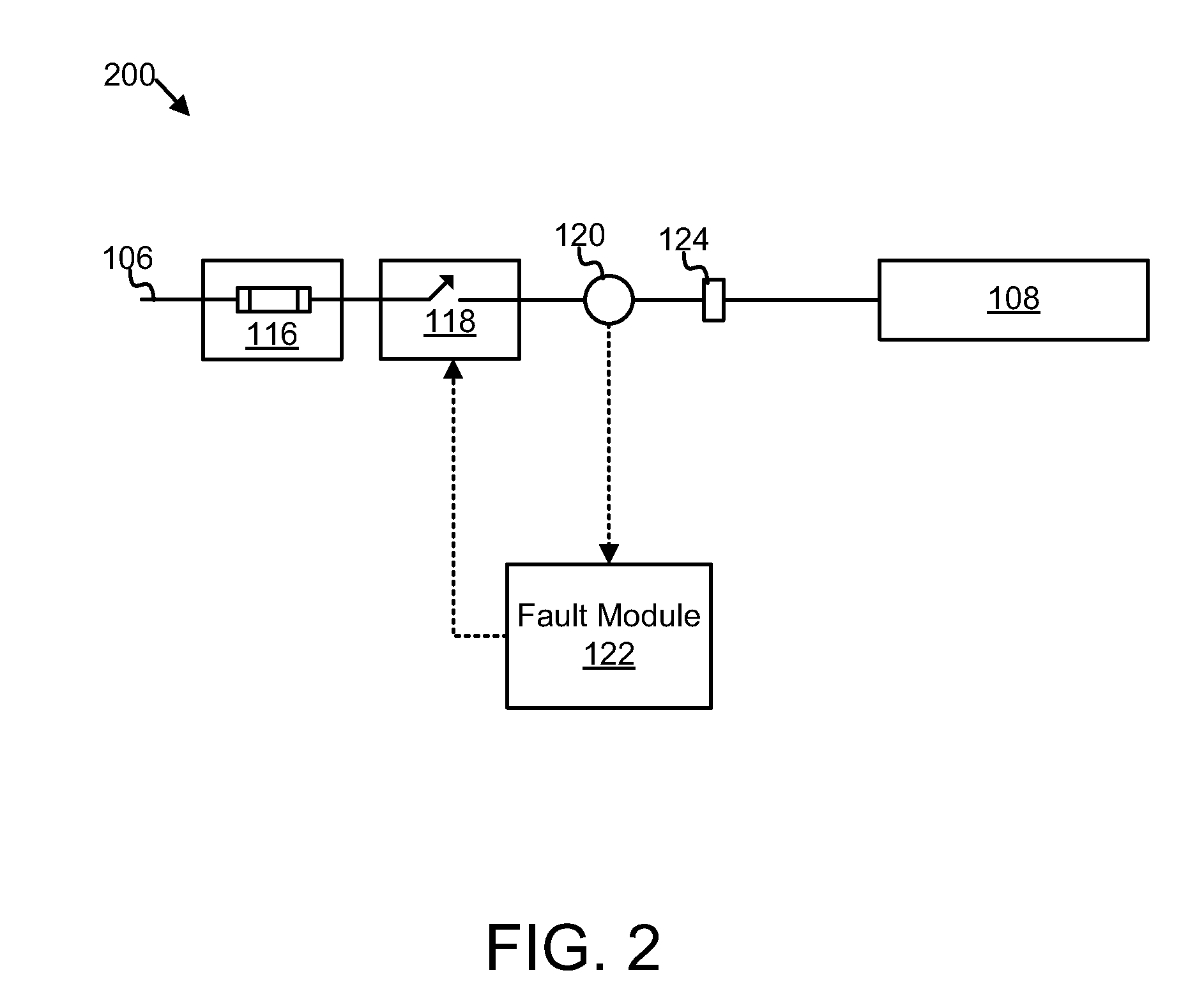
Power distribution unit branch protection
InactiveUS20110170223A1Low costSmall sizeElectric switchesArrangements responsive to excess currentElectrical FailureCurrent sensor
An apparatus and system are disclosed for protecting a power distribution unit from an electrical fault. A fuse interrupts a flow of electrical current in response to the electrical current rising above a current rating of the fuse. A current sensor measures the amplitude of the electrical current and outputs a current amplitude signal. A relay interrupts the flow of electrical current in response to an OFF signal. A fault module receives the current amplitude signal and sends the OFF signal to the relay in response to the amplitude of the electrical current exceeding a threshold value. The relay, the fuse, and the threshold value are selected so that a switching time of the relay is less than an opening time of the fuse for an amplitude of the electrical current between the threshold value and a maximum fault current value, so that the relay prevents the fuse from opening.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fuse relay junction block for use in automobiles
InactiveUS6437986B1Contact member assembly/disassemblySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNetwork structureJunction box
There is provided a fuse relay junction block for use in automobiles capable of not only considerably reducing the number of assembling process but also realizing small sized, lightweight compact block, thereby enhancing reliability and achieving a low cost material by aggregating the conventional plural pieces of boards to form a multilayered circuit structure. The fuse relay junction block comprises a box cover having a plurality of connection ports through which wirings of electronic wiring systems are connected to terminals of wiring members and a plurality of filling ports for fuses, a box body engaged in the box cover, a multilayered board housed between the box cover and the box body, wherein said wiring members being arranged on not less than two layers of board and integrated with primary molded portions by insert molding to form a network structure, said network structure is subjected to an insert to form a secondary molded portion.
Owner:KOHJIN CO LTD
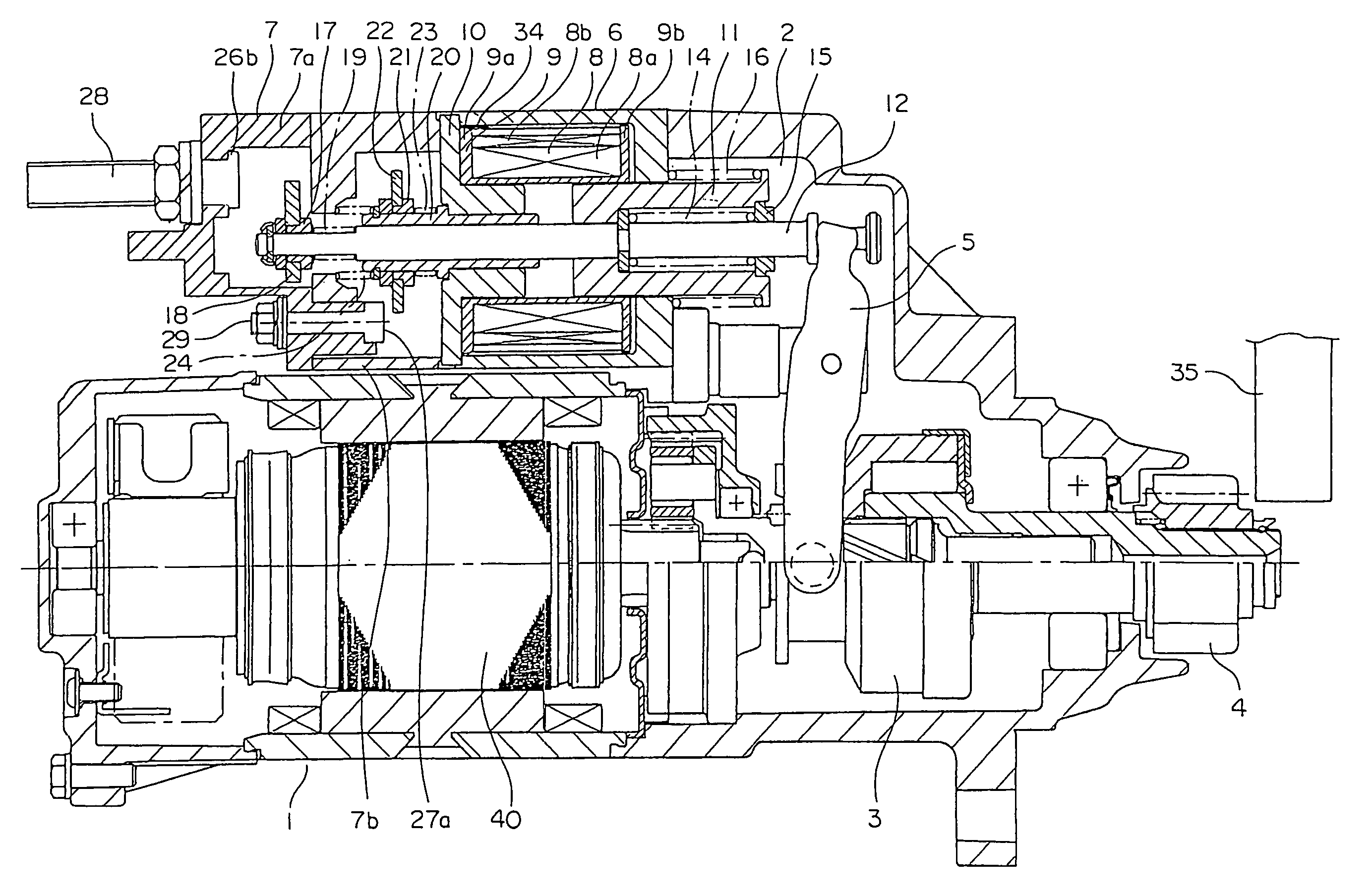
Electromagnetic starter switch
ActiveUS7034643B1Abnormal temperature increase can be preventedIncrease temperaturePower operated startersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringSecond ancillary
An electromagnetic starter switch in which a voltage from a power source is depressed by a resistor and applied to a motor by an auxiliary movable contact coming into contact with a first auxiliary fixed contact and a second auxiliary fixed contact before a pinion intermeshes with a ring gear, and the voltage from the power source is subsequently applied to the motor without modification by the main movable contact also coming into contact with a first main fixed contact and a second main fixed contact after the pinion intermeshes with the ring gear, wherein: a resistor is disposed between the first main fixed contact and the first auxiliary fixed contact or between the second main fixed contact and the second auxiliary fixed contact; and an electric current fuse is disposed between the second main fixed contact and the second auxiliary fixed contact or between the first main fixed contact and the first auxiliary fixed contact.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Diagnostic blown fuse indicator
InactiveUS6859131B2Technology moreElectrical testingEmergency protective devicesElectricityFuse cutout
The present invention provides a blown fuse indicator. More specifically, the present invention provides a blown fuse indicator adapted for use with multiple element fuses, which provides a perceivable distinction between a blown fuse due to a current overload and a blown fuse due to a short circuit. To this end, in one embodiment of the present invention, a diagnostic blown fuse indicator is provided for a fuse having both a short circuit element and a current overload element. The indicator includes a short circuit indicator in electrical communication with the short circuit element, wherein the short circuit indicator provides visual indication of a short circuit condition. The indicator also includes a current overload indicator in electrical communication with the current overload element, wherein the current overload indicator provides visual indication of an overload condition.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com