Heat exchange device
a heat exchange device and heat exchange technology, applied in the direction of heat exchange apparatus, thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effect, light and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of degrading the reliability of the thermoelectric module b>50/b>i, difficult to sufficiently release the thermal stress of the thermoelectric, and reducing the maximum heat absorption coefficient (qmax), so as to reduce the thermal resistance and improve the reliability against thermal stress. , the effect of increasing th
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
1. FIRST EMBODIMENT
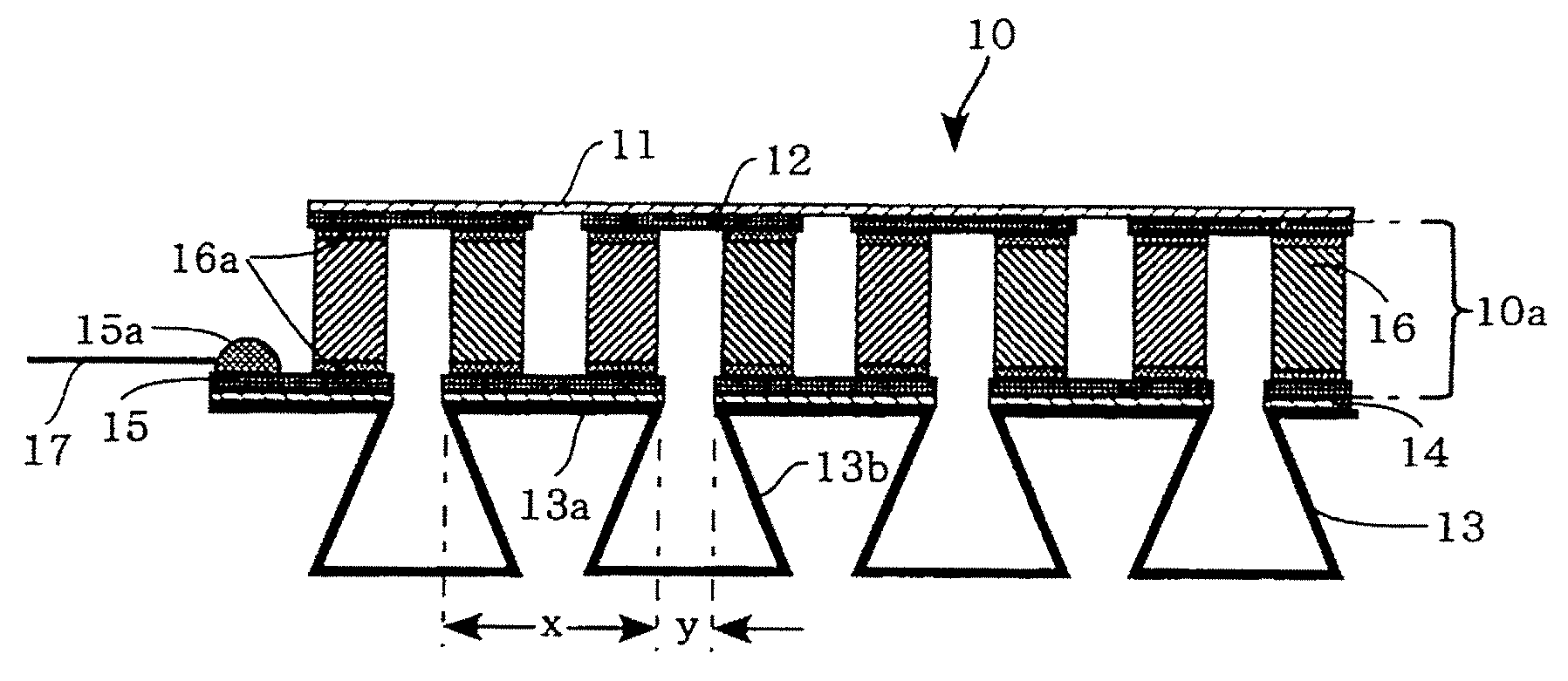
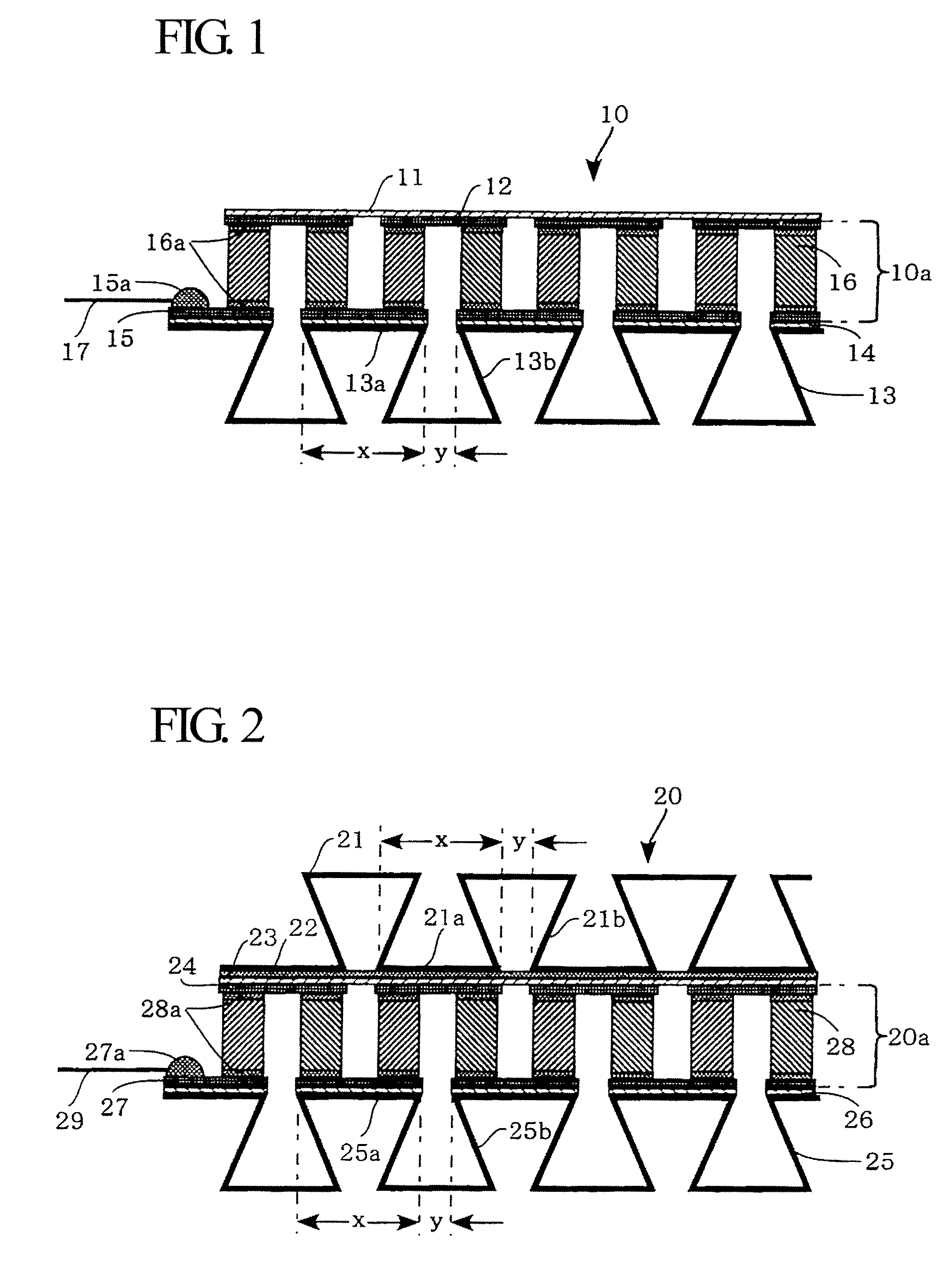
[0028]FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing the constitution of a heat exchange device 10 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The heat exchange device 10 is constituted of a substrate 11, a heat-dissipation electrode 12 which is formed below the substrate 11, a plurality of corrugated fins 13 (collectively serving as a heat exchanger on a heat-absorption side, a heat-absorption electrode 15 which is bonded onto the upper surfaces of the corrugated fins 13 via an insulating resin layer 14 having a high heat conductivity and an adhesive property, and a plurality of thermoelectric elements 16 which are electrically connected in series between the electrodes 12 and 15 via a soldering layer (or a metal) 16a.
[0029]A pair of terminals 15a is formed on one end of the heat-absorption electrode 15 in order to establish electric connections with leads 17. A thermoelectric module 10a is constituted of the heat-dissipation electrode 12, the heat-absor...
second embodiment
2. SECOND EMBODIMENT
[0041]FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing the constitution of a heat exchange device 20 according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0042]In contrast to the heat exchange device 10 where the corrugated fins 13 are arranged on the heat-absorption electrode 15 only, the heat exchange device 20 is designed such that corrugated fins are arranged on both of the heat-absorption and heat-dissipation sides. The heat exchange device 20 has a thermoelectric module 20a which is similar to the thermoelectric module 10a installed in the heat exchange device 10.
[0043]Specifically, the heat exchange device 20 includes first corrugated fins 21 (which collectively serve as a heat-dissipation side heat exchanger), a joint film 22 composed of a copper film or copper alloy film for entirely covering the lower surfaces of the first corrugated fins 21, and a heat-dissipation electrode 24 which is attached to the joint film 22 via an insulating resin layer 23 having ...
third embodiment
3. THIRD EMBODIMENT
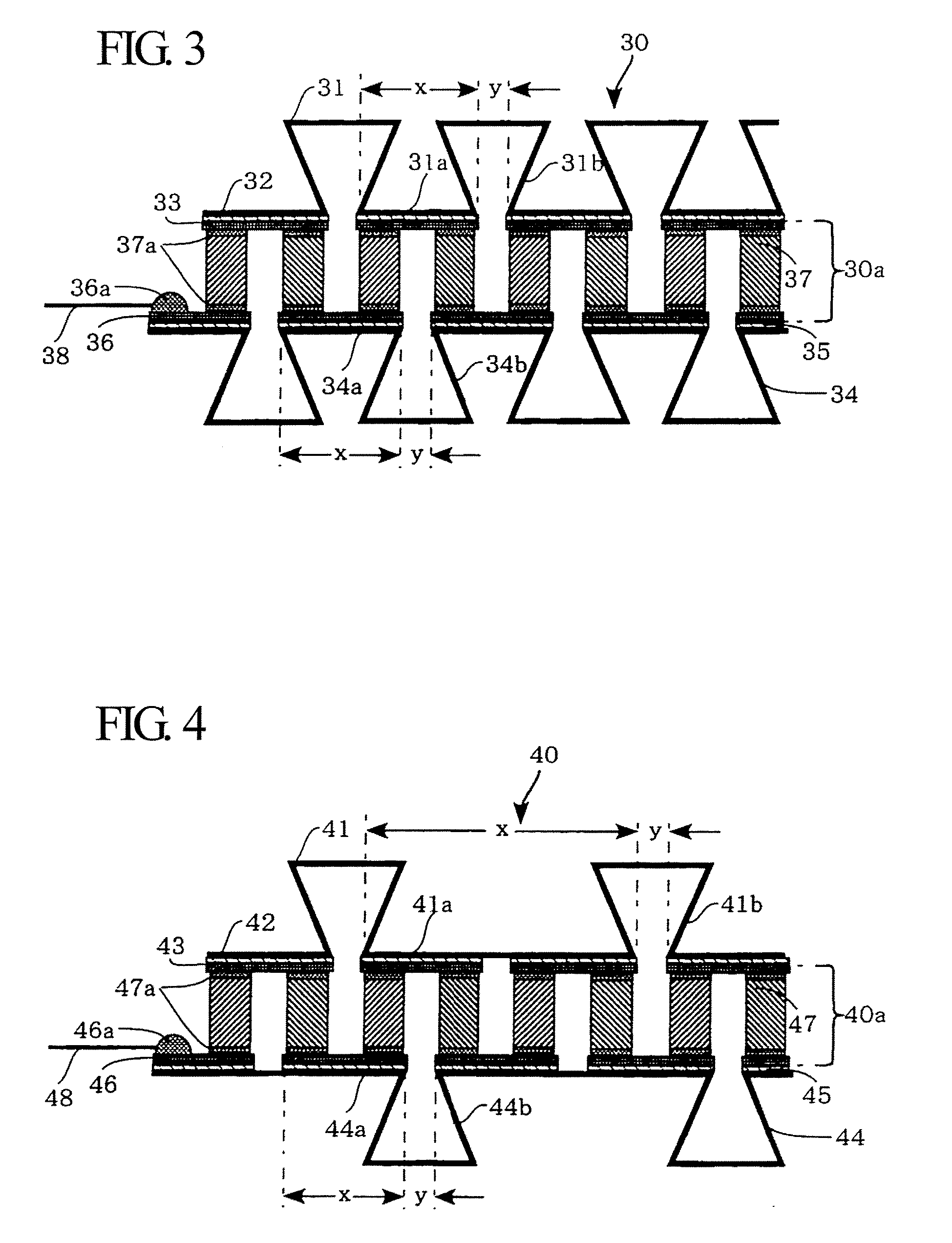
[0052]FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view showing the constitution of a heat exchange device 30 according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0053]In the heat exchange device 20, the lower surfaces of the corrugated fins 21 are entirely covered with the joint film 22, the lower surface of which is entirely covered with the insulating resin layer 23; but this is not a restriction. It is possible to dispose an insulating resin layer in connection with only the joint regions of corrugated fins without intervention of a joint film. The heat exchange device 30 is designed to dispose an insulating resin layer in connection with only the joint regions of corrugated fins without using a joint film. As shown in FIG. 3, the heat exchange device 30 has a thermoelectric module 30a similar to the thermoelectric module 10a installed in the heat exchange device 10.
[0054]Specifically, the heat exchange device 30 includes first corrugated fins 31 (which collectively serve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com