Predicting and Diagnosing Patients With Autoimmune Disease
a technology for predicting and diagnosing patients with autoimmune diseases, applied in the field of molecular biology, pathology and genetics, can solve the problems of complete debilitation and death, mild discomfort for patients, and continue to provide a considerable challenge to the healthcare industry, and achieve the effect of increasing risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methods
[0157]SLE patients and controls. Korean SLE patients and controls were recruited at the Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. All patients were of Korean descent and met the 1997 American College of Rheumatology SLE classification criteria. A total of 628 independent female SLE patients and 736 healthy unrelated female controls were studied. No two SLE patients or two controls are blood relatives to avoid intrafamilial correlation bias. Another independent cohort of SLE patients of European descent was studied. This cohort consisted of 1080 independent cases and 1080 healthy unrelated controls matched for race and sex and recruited in the SLE genetics studies at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation as well as from collaborators in the United States, United Kingdom, and Sweden. This cohort included 928 females and 152 males in each of the case and control groups. All SLE patients met the 1997 American College of Rheumatology SLE classification ...
example 2
Results
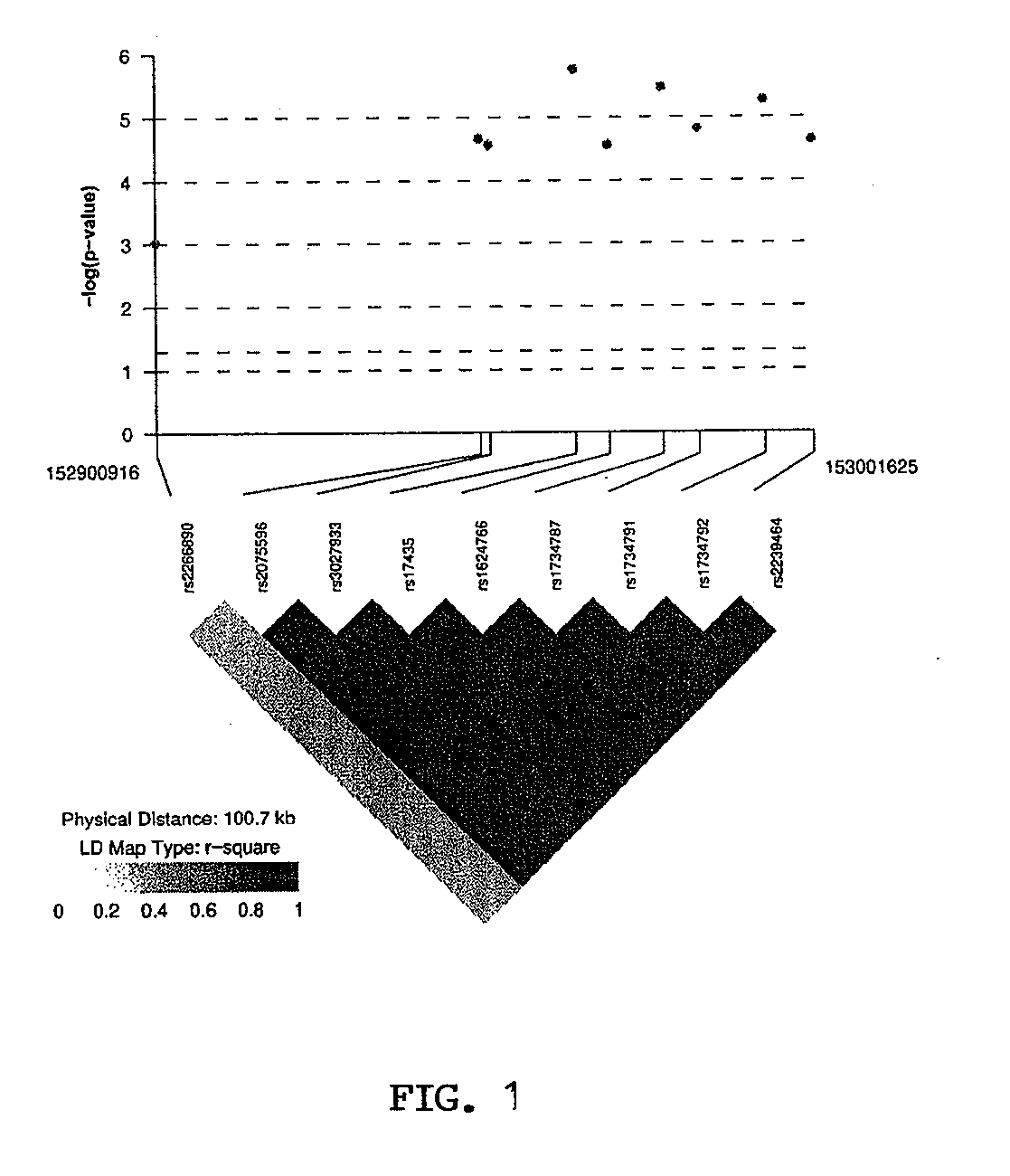
[0161]The inventors initially genotyped 628 Korean female SLE patients and 736 healthy female Korean controls across 21 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located within or around MECP2 (Table 1). Nine SNPs had a minor allele frequency of more than 5% in our Korean cohort and were used for further analysis. All 9 SNPs were within expected Hardy-Weinberg proportions in both cases and controls (Table 2). Eight out of the nine SNPs are within the MECP2 gene and showed significant association with SLE (Table 2 and FIG. 1). The SNP having the strongest association in the Korean SLE patients is rs17435 (Chi2=22.83, OR=1.58, p=0.0000018) followed by rs1734787 (Chi2=21.58, OR=1.55, p=0.0000034), rs1734792 (Chi2=20.68, OR=1.53, p=0.0000054) and rs1734791 (Chi2=18.70, OR=1.51, p=0.000015). The SNPs rs1734787, rs1734792, and rs1734791 are all in linkage disequilibrium with rs17435 (r2=0.88, 0.92, and 0.86, respectively).
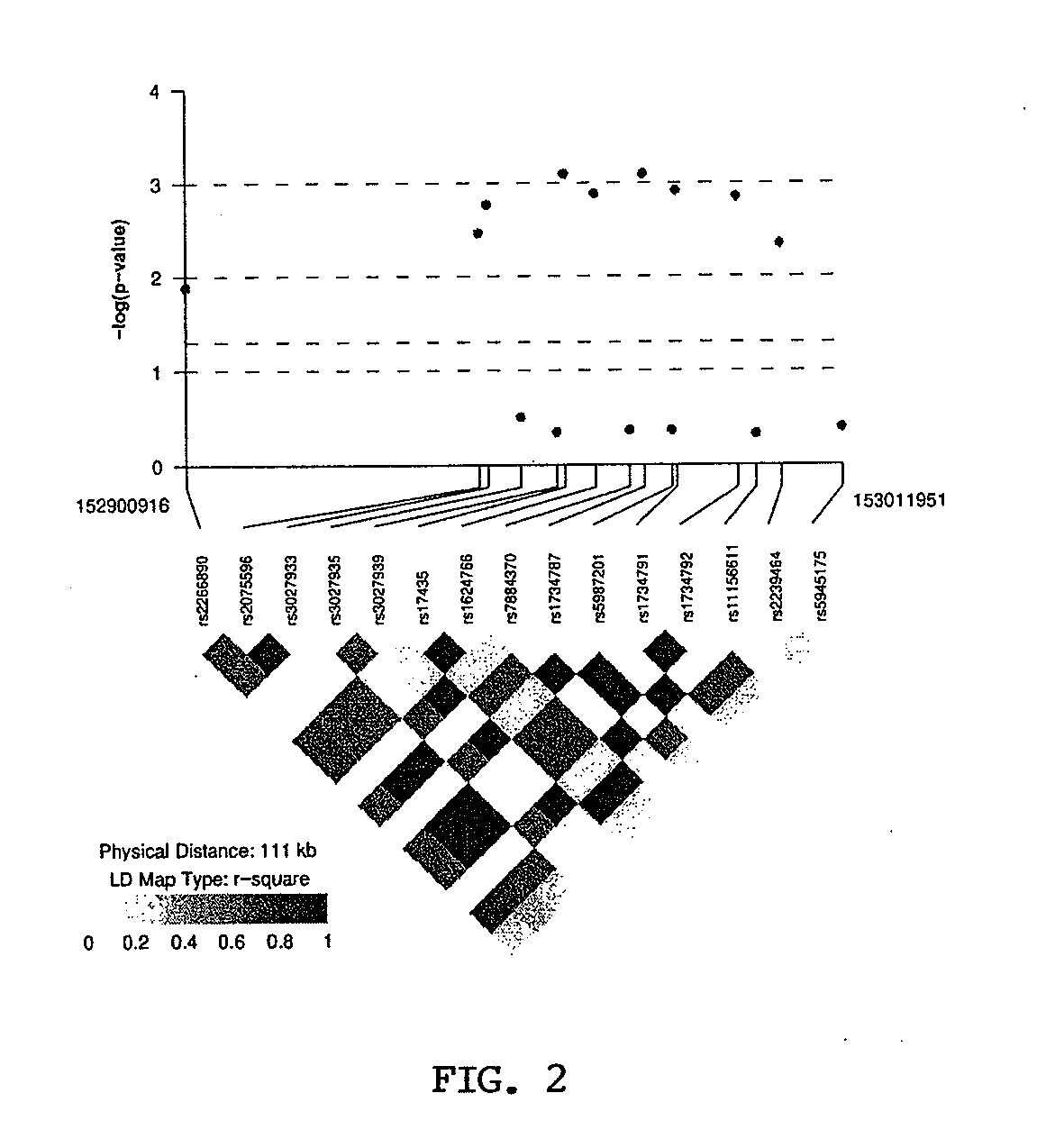
[0162]The inventors next performed haplotype-based association ...
example 3
Discussion
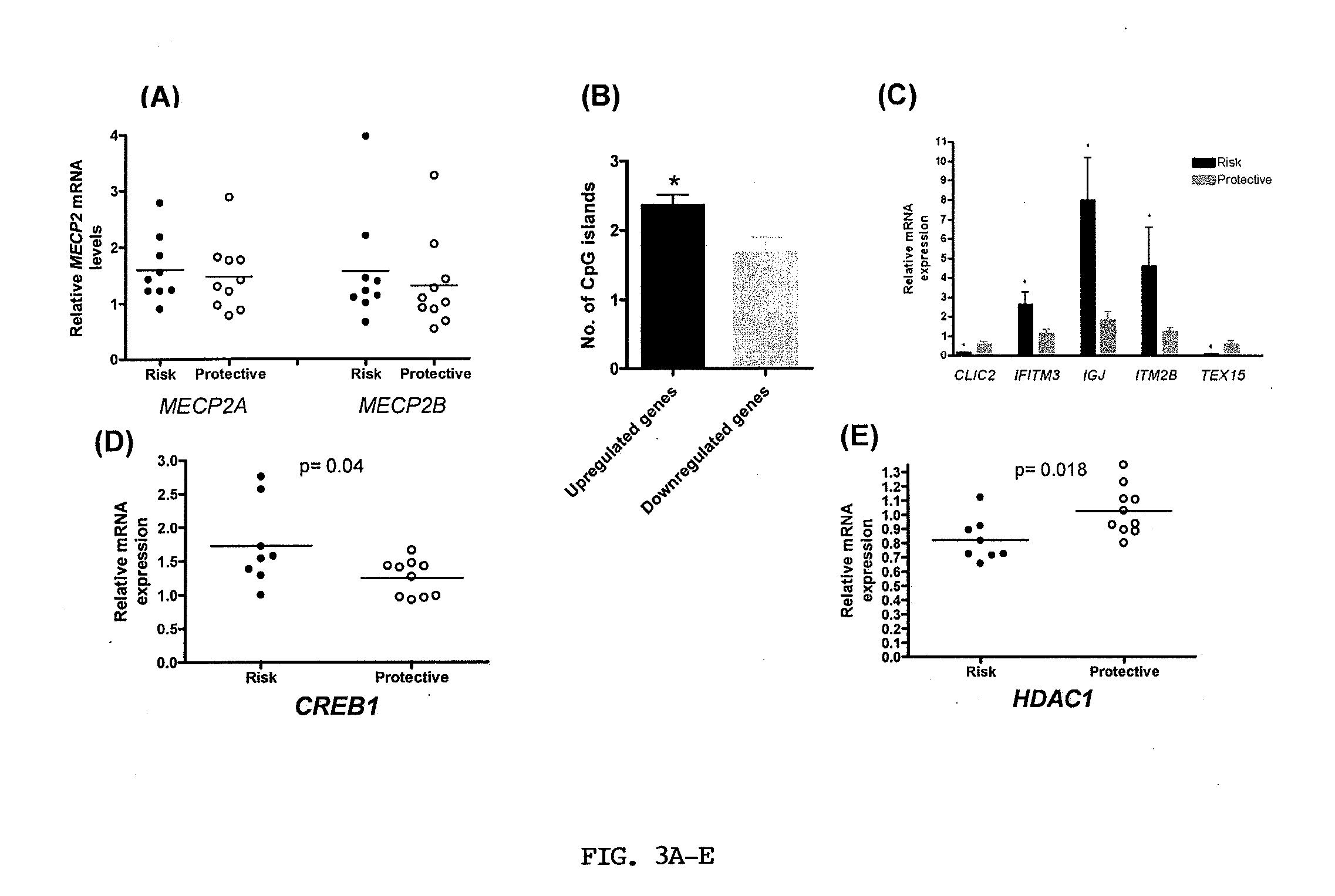
[0165]DNA methylation plays a critical role in tissue differentiation, imprinting, transcriptional suppression of parasitic DNA, silencing of transcriptional “noise,” and X-chromosome inactivation (Bird, 1993). Utilizing a candidate gene approach, the inventors first identified significant association with MECP2 SNPs and SLE in a cohort of Korean SLE patients and controls. Next, they replicated the association with MECP2 SNPs in an independent cohort of SLE patients and controls of European descent. Indeed, the disease-associated alleles in rs17435, rs1734787, rs1734792, and rs1734791 (T, C, A, and A respectively) have meta analysis p values of 1.2×10−8, 1.6×10−8, 3.3×10−8, and 7.2×10−8 respectively (Table 7). Interestingly, the disease associated alleles in these four MECP2 SNPs are 4 times more common in Korean as compared to European-derived controls. This might suggest a possible explanation for the higher frequency of SLE in people of Asian descent as compared to Euro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flow rates | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com