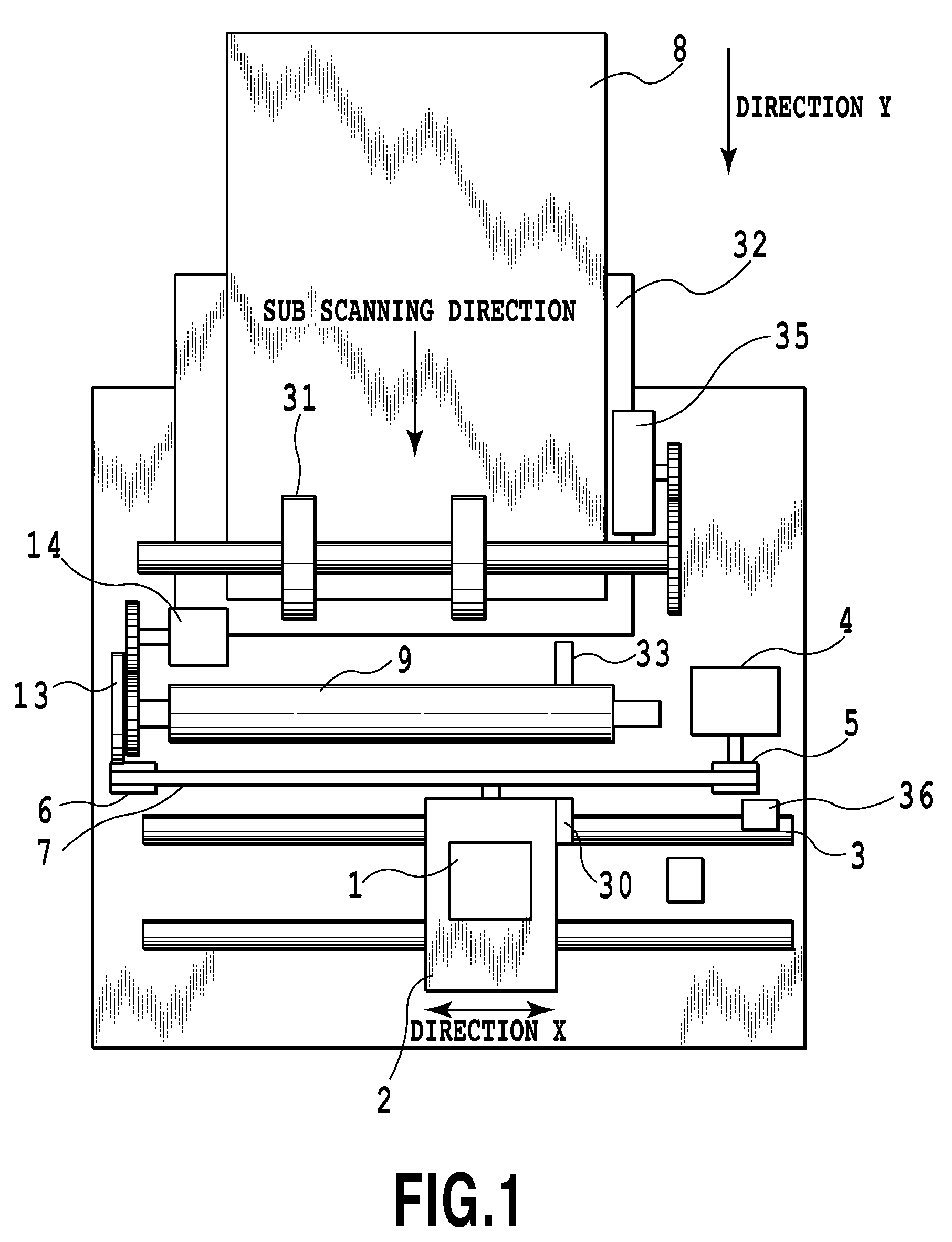
Conveying apparatus and printing apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
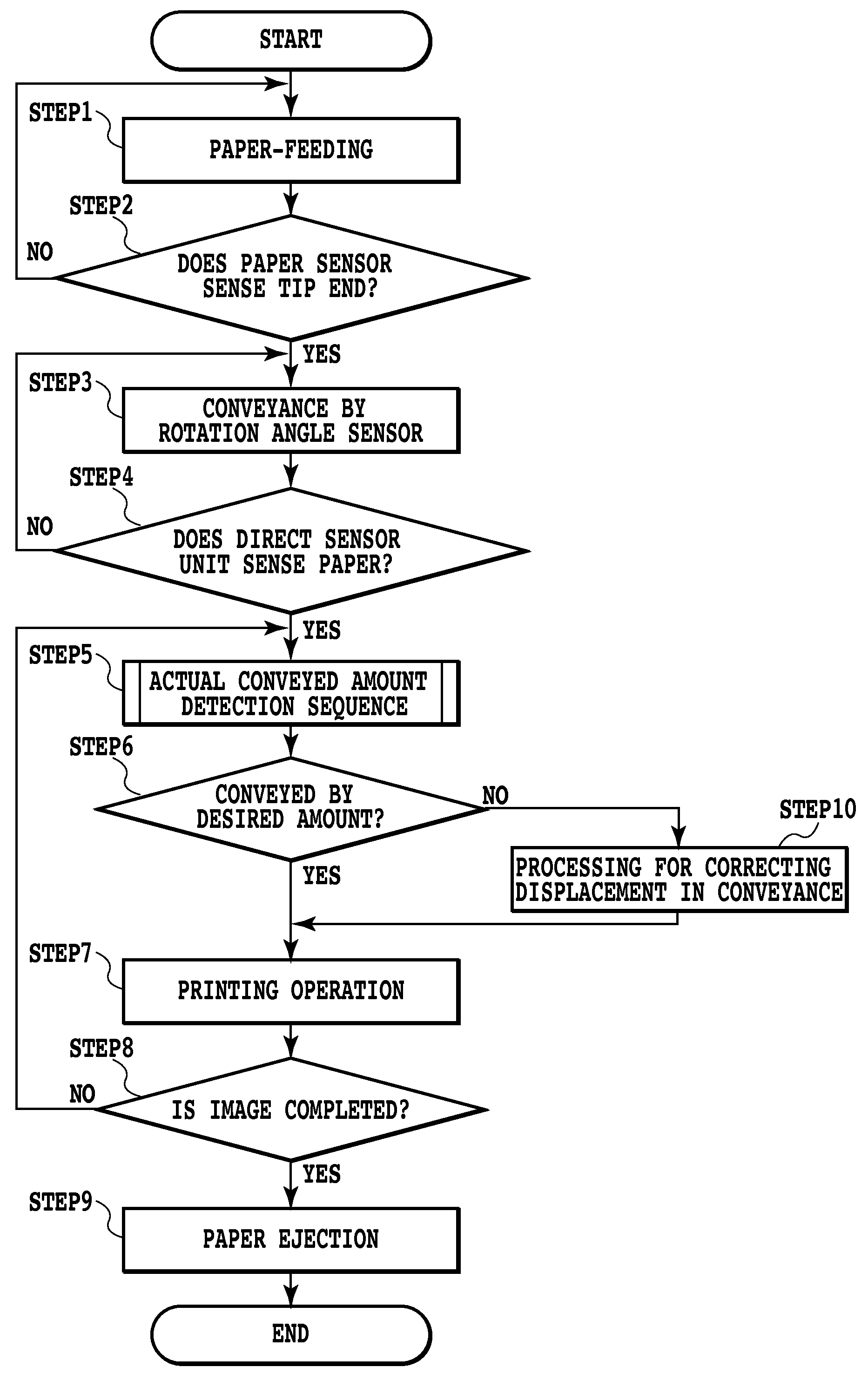
[0055]FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating the processing performed by a CPU 101 in the control of the conveyance of a print medium in this embodiment. FIG. 11 illustrates the conveyance status of a print medium in the respective steps shown in the flowchart.
[0056]When the printing operation is started based on a printing start command from the host apparatus 110, the CPU 101 drives the paper-feeding motor 35 to feed one print medium 8 from the auto sheet feeder 32 (STEP 1). Next, STEP 2 causes the CPU 101 to determine whether the paper sensor 33 senses the tip end of the print medium 8 or not. When determining that the tip end of the print medium 8 is detected, then the processing proceeds to STEP 3. When determining that the tip end of the print medium 8 is not yet detected in STEP 2 on the other hand, the processing returns to STEP 1 and continues the paper-feeding operation. Thereafter, until the tip end of the print medium is sensed, STEP 1 and STEP 2 are repeated. In FIG. 11, t...
example 2
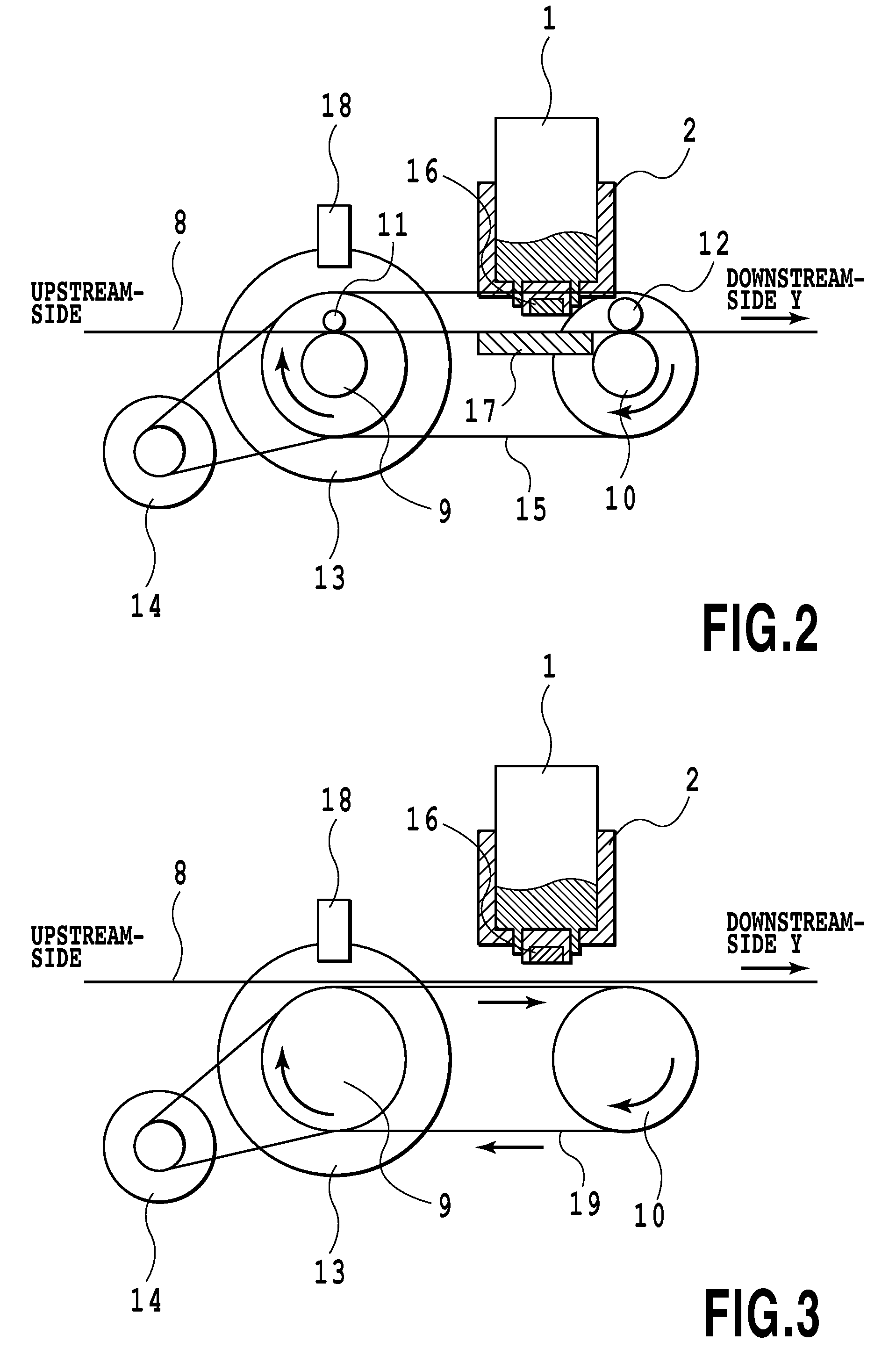
[0080]Example 1 assumes a case where one target conveyed amount (one stepwise conveyance operation) is smaller than the detection region of the capturing element of the direct sensor unit 16 and one characteristic pattern (cross-shape pattern) is included in both of two pieces of image data acquired at different timings. In contrast with this, Example 2 is a control method for a case where one stepwisely-conveyed amount is larger than the length of arranged pixels of the direct sensor unit 16. The basic concept of this method is that a plurality of pieces of the image data are acquired in one stepwise moving to thereby perform the conveyance control.
[0081]The construction of the apparatus in Example 2 is the same as that in Example 1. The entire sequence is the same as that described in the flowchart of FIG. 10 except for that the method for the actual conveyance amount detection sequence in STEP 5 is different from that in Example 1. FIG. 17 is a flowchart illustrating the actual c...
example 3
[0094]Example 1 and Example 2 assume a case where one target conveyed amount is smaller or larger than the detection region of the direct sensor unit 16. On the other hand, Example 3 is a control method for a case where, even in the middle of one printing job, a set search range is within the range of the second image data or not within this range.
[0095]The apparatus in this example has the same configuration as that of Example 1. The entire sequence is the same as that described in the flowchart in FIG. 10 except for that the method of actual conveyance amount detection sequence in STEP 5 is different from that of Example 1. FIG. 20 is a flowchart illustrating the actual conveyance amount detection sequence in this example.
[0096]When the actual conveyance amount detection sequence is started, the CPU 101 in Step D01 firstly uses the direct sensor unit 16 to acquire the image of the print medium 8 as the first image data. When the direct sensor unit 16 is used to capture the surface...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com