Element for emission of thermal radiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
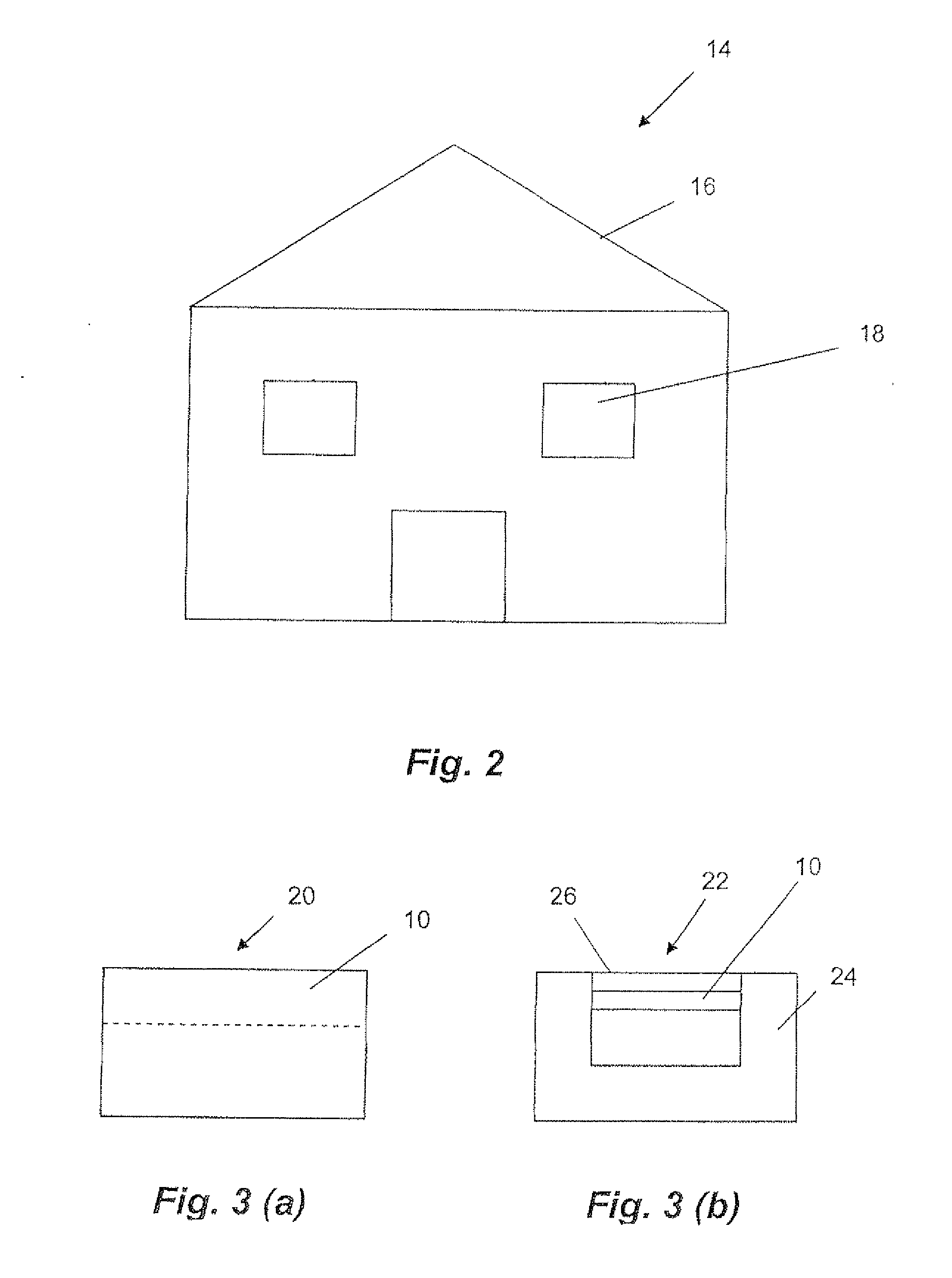
[0101]Generally, the element comprises particles that are arranged for emission of radiation having a wavelength within a range referred to as the “atmospheric window wavelength range”. The atmospheric window wavelength range is a wavelength range within which the absorption and emission of radiation by the atmosphere of the Earth is strongly reduced or zero. Radiation emitted from the element within that wavelength range is largely transmitted through the atmosphere to Space where the average temperature is 4 Kelvin. Further, as within that wavelength range typically very little or no radiation is received by the element, the element functions as a pump of thermal energy.
[0102]The element comprises a cooling material that is disclosed in Australian provisional patent application No 2007903673 and U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11 / 765,217. These patent applications are hereby incorporated by cross-reference. Further details of the function of the element will be discussed with ref...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com