Dry reagent particle assay and device having multiple test zones and method therefor
a technology of dry reagents and assays, which is applied in the direction of biological material analysis, measurement devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve quantitative results, methods generally undesirable for point-of-care testing, and color generation on these devices is not always uniform, so as to achieve accurate quantitative results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
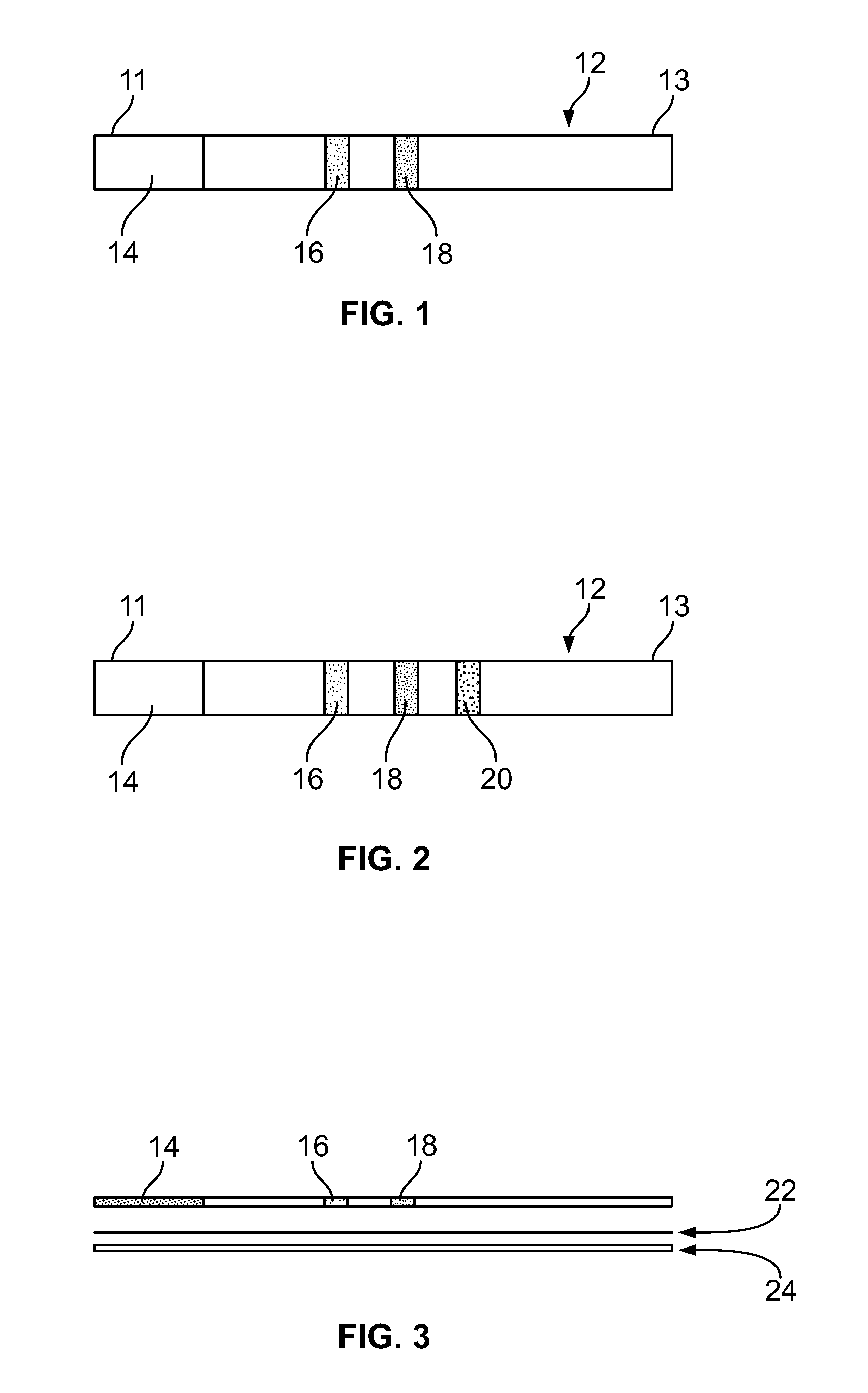
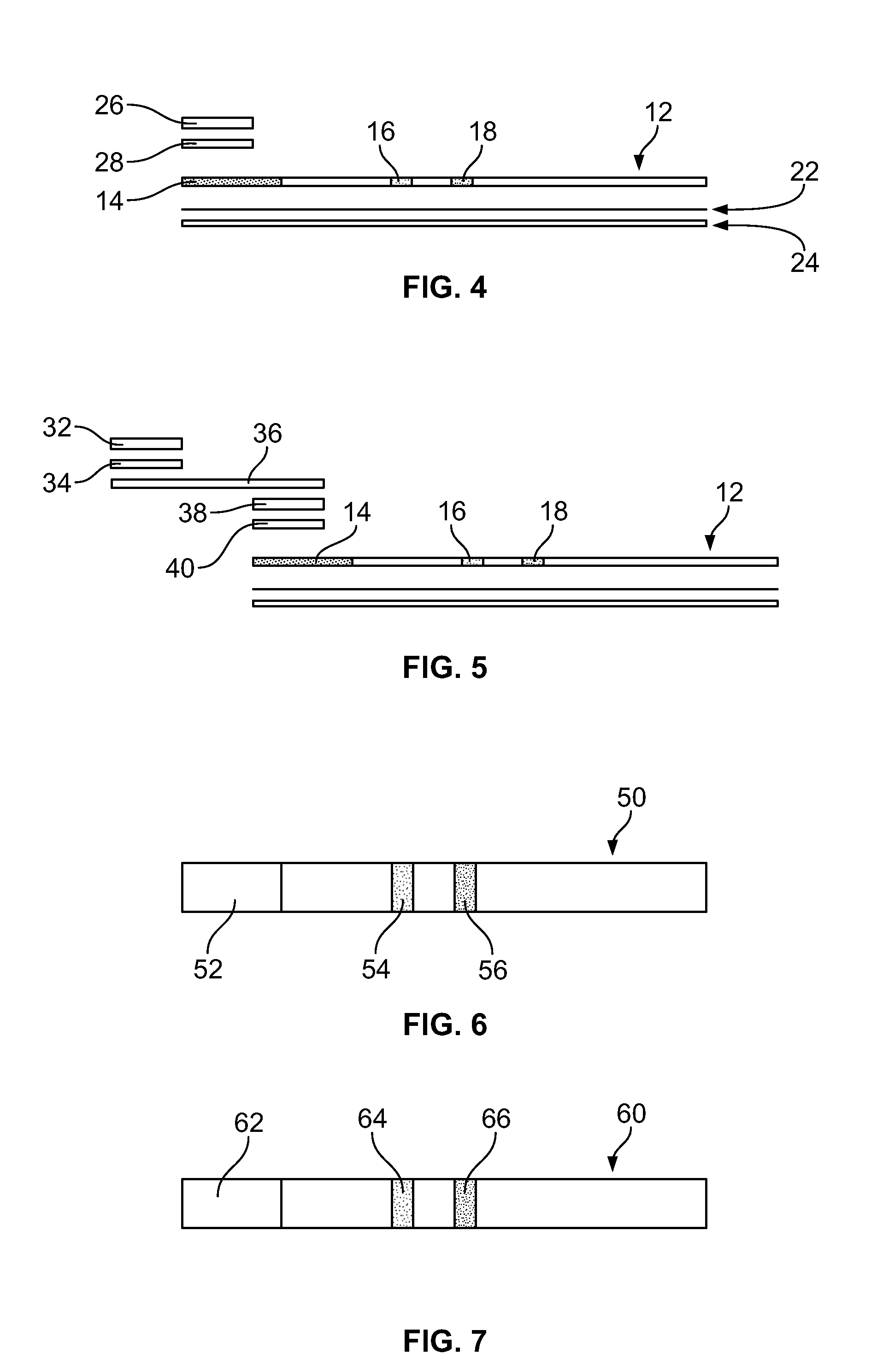
[0123]The devices of the embodiments shown in FIGS. 1-7 are quantitative or qualitative immunoassay strips. The assay strips shown in these embodiments can be configured by one of two assembly methods.
[0124]In a first strip assembly method, the strip is composed of several Separate bibulous membrane sections in fluid communication by lamination to a plastic strip. The reagents can be diffusively or non-diffusively immobilized to the membrane prior to lamination. Alternatively, the reagents can be immobilized after lamination.
[0125]For convenience, the assay strips are constructed in bulk in a card form with the discrete assay zones forming lines along the length of the card. Each card can be of any convenient size, depending only on the length of the assay strip and the number of assay strips desired. For example, if the assay strip (as shown in FIG. 1) is 6 cm long and 0.5 cm wide, then the card can be 6 cm by 10 cm (20×0.5 cm), thus providing 20 strips. Two sizes of strips were us...
example 2
[0141]This example demonstrates a single-step, quantitative, lateral flow, inhibition type immunoassay for a small molecule using colored particles as the detection method. The assay summarized below in Table 1 was conducted using reagents and methods as described in Example 1.
[0142]The assay strips of this example were 6 cm wide and 0.5 cm long and were similar to those shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 3, with the exception that the third zone 18 (second test zone) was not included. The immunoassay strip configuration was as follows:[0143](1) a lower 8 μm pore size nitrocellulose section containing a reagent zone 14 having diffusively applied MAb-1H11-colloidal gold, prepared as described above;[0144](2) a 0.5 cm test zone 16 containing non-diffusively immobilized NTx covalently linked via the native primary amine group to Pall IMMUNODYNE® ABC, prepared as described above; and[0145](3) an upper wick area of 8 μm pore size nitrocellulase that extended from the upper edge of zone 16 to the t...
example 3
[0148]This example demonstrates a quantitative, lateral flow, inhibition typo, immunoassay which shows excellent performance using colored particles at the indicator. The assay summarized below in Table 2 was conducted using strips, reagents and methods as described in Example 2.
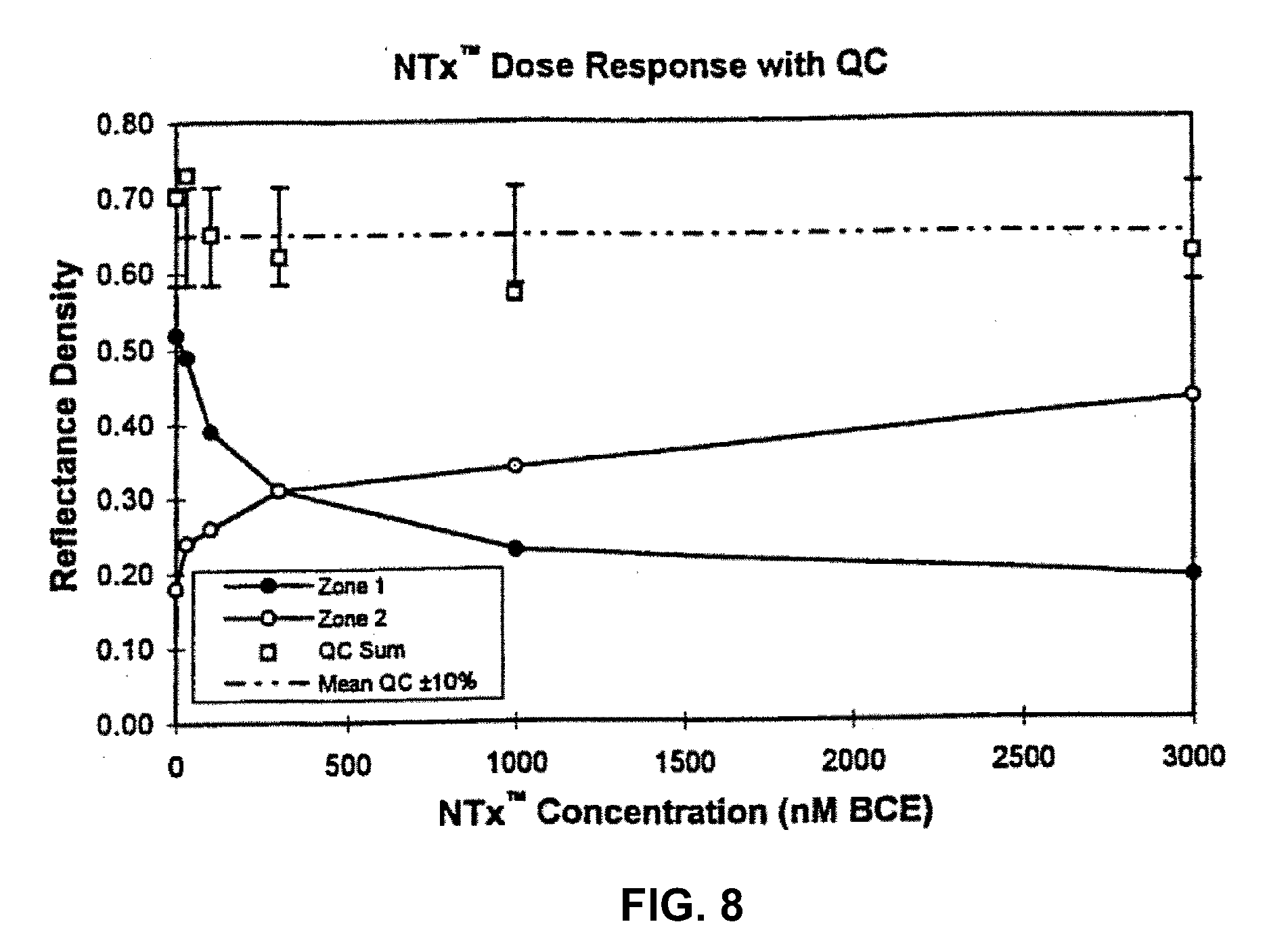
[0149]The assay protocol as indicated above in Example 1 was used to generate data in the non-amplified data. column of Table 2. For the silver amplified assays, the protocol was, followed as in Example 1, with the exception, that a silver enhancement reagent was added to the test zone after the colloidal gold binding. The results in Table 2 demonstrate a dose-response showing excellent. sensitivity and quantitative performance, for the present invention.
TABLE 2NTx Dose Response Silver AmplificationConjugate: Colloidal-Gold-1H11Reflectance DensityGretagNTxNon-Silver-(nM)AmplifiedAmplified10.301.07300.250.911000.190.843000.150.5910000.090.2330000.080.02
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com