Devices and methods for percutaneous access, hemostasis, and closure
a technology of percutaneous access and hemostasis, applied in the field of devices and methods for percutaneous access, hemostasis, and closure, can solve the problems of minimally invasive approaches, introduce new complexities of surgery, and minimally invasive approaches, and achieve the effect of high-profile configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Deployment of A Medical Closure Device of the Present Invention
[0046]The following example provides an exemplary deployment procedure for an exemplary medical closure device. This example should not be viewed as limiting, as deployment procedures, delivery components, and medical devices may differ from the example presented herein.
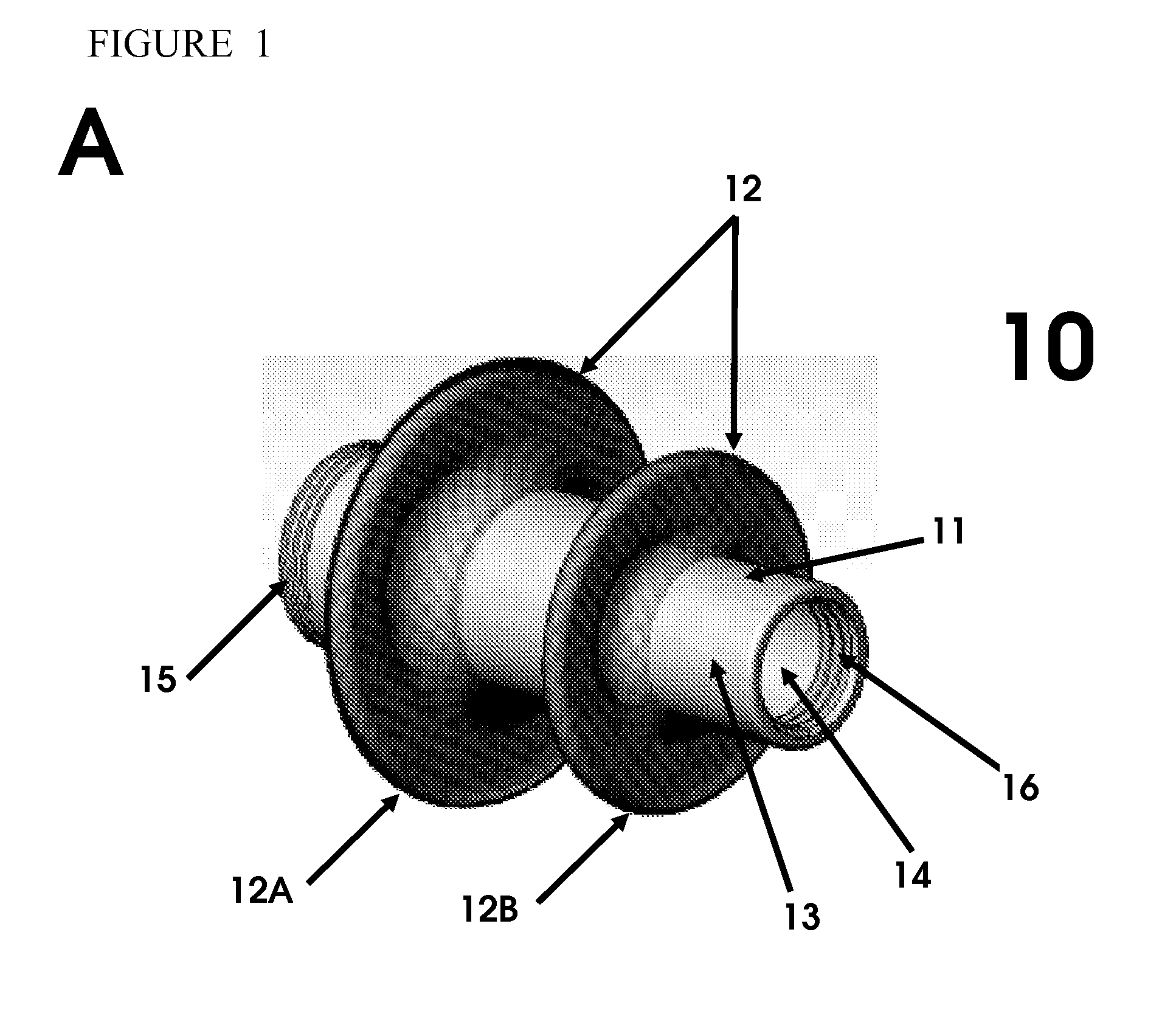
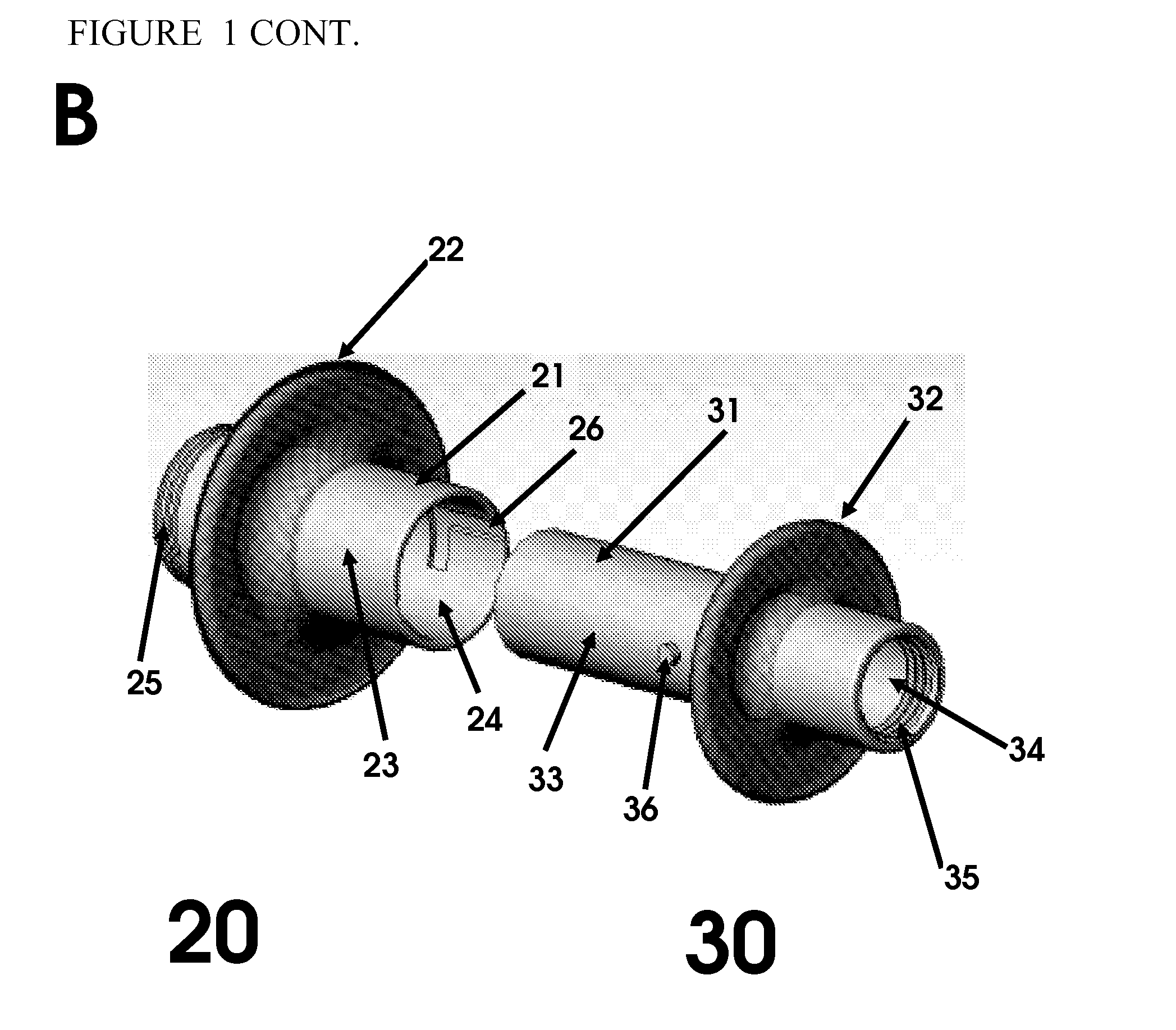
[0047]A medical closure device is placed into the lumen of a delivery catheter and positioned at the distal end of the catheter. The distal end of the medical closure device is positioned facing outward from the distal end of the delivery catheter. The confined space of the lumen of the delivery catheter compresses the distal and proximal expanded elements causing the expanded elements to adopt a reduced cross-sectional profile configuration.
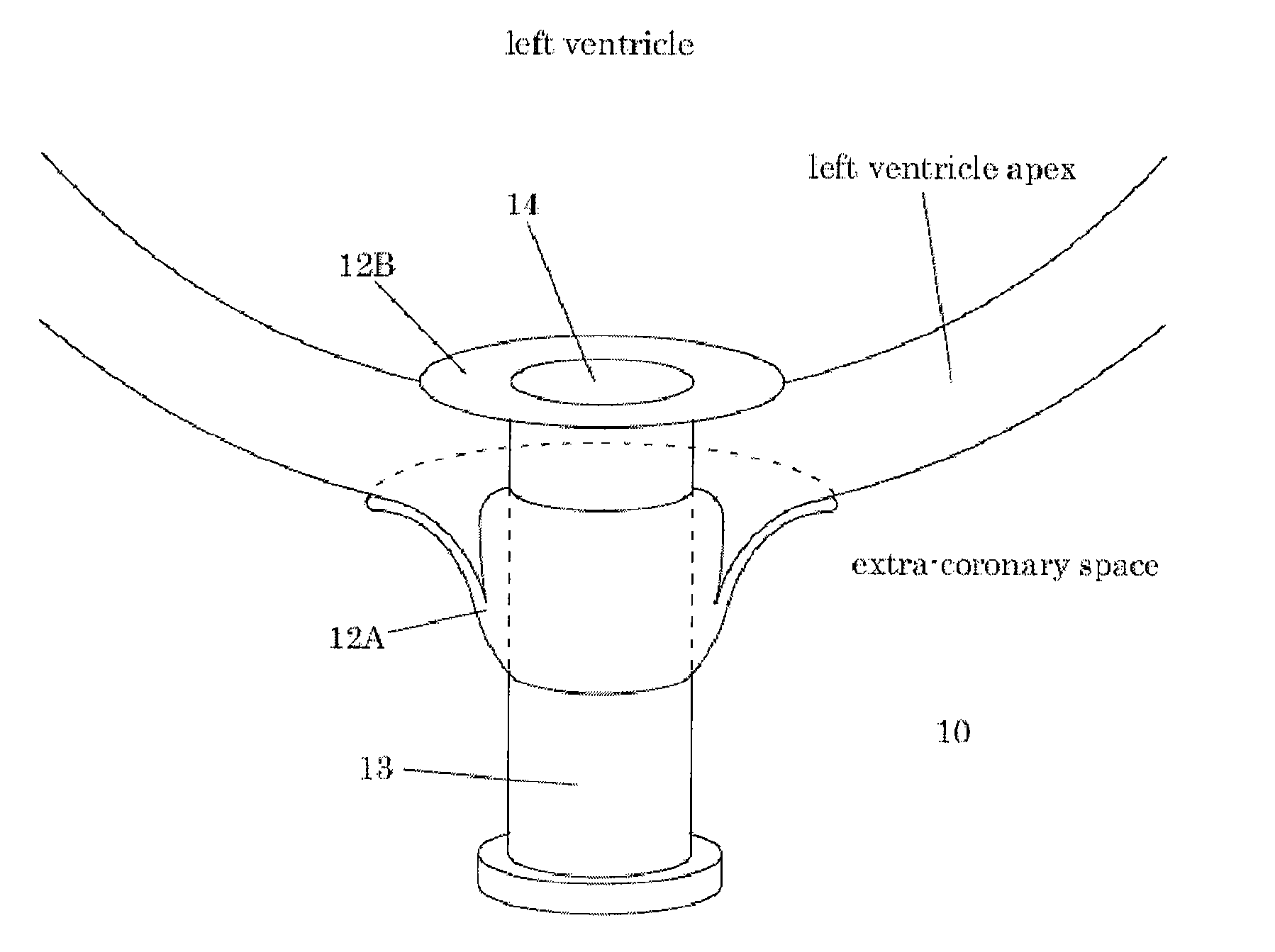
[0048]The delivery catheter is deployed via a minimally invasive pathway through a rib space directed toward the ventricular apex of the heart of a human patient (SEE FIG. 4A). The delivery catheter is positioned upon...
example 2
Access, Hemostasis, And Closure
[0050]The following example provides exemplary methods of use for an exemplary medical closure device. This example should not be viewed as limiting, as medical closure devices of the present invention find utility in a range of procedures and surgeries not detailed in the following example.
[0051]A medical closure device is deployed during a medical procedure to provide access to the procedure site. The device is deployed, as described in Example 1 for example, to the left ventricular apex of the heart of a patient. Upon insertion into the apical tissue, the device provides an access port for performing medical and surgical procedures within the left ventricular space. A one-way valve within the inner lumen of the medical closure device prevents the outflow of blood and fluid from the left ventricle or other heart chambers into the extra-cardiac space. The valve further provides access to the chambers of the heart for surgical and medical instruments. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com