Film of plastics material stretched to present a privileged shrinkage orientation, a heat-shrink sleeve made out of the film, and an article covered in such a sleeve
a technology of plastics material and shrinkage orientation, applied in the direction of shrinkage connection, flexible cover, container, etc., can solve the problems of random tears, method failure to give satisfactory results, and prone to cracks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
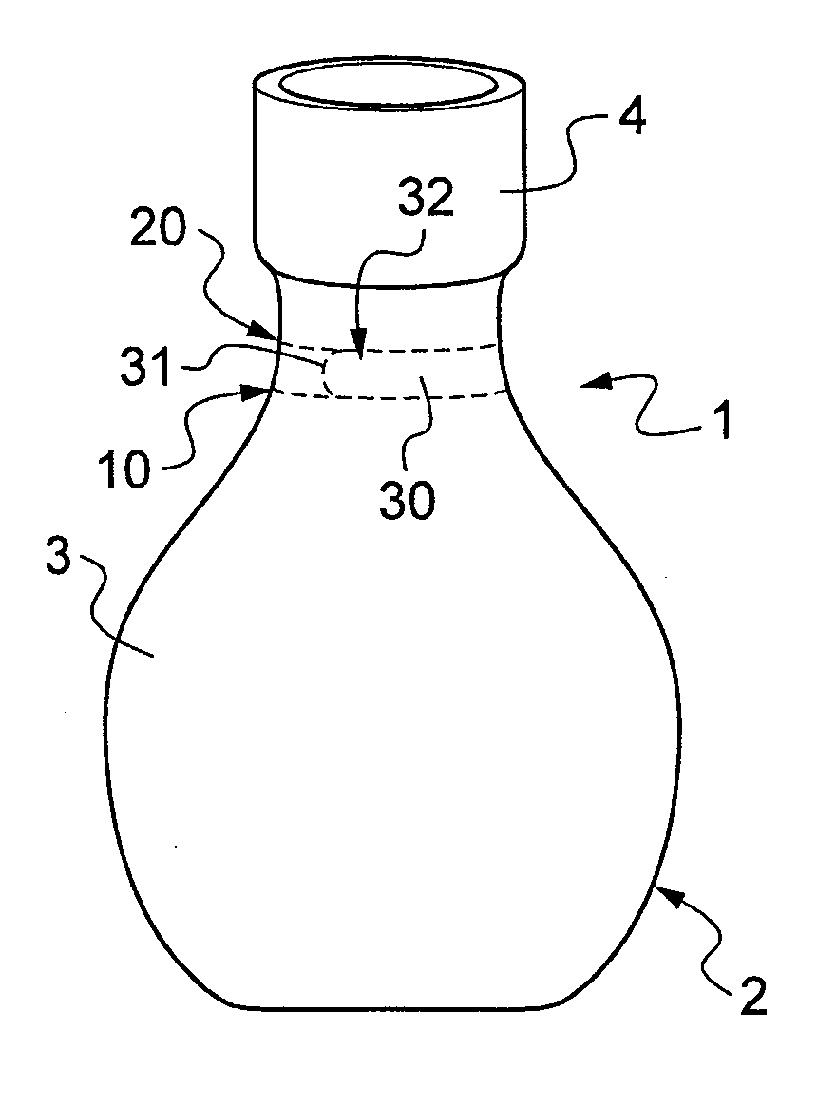
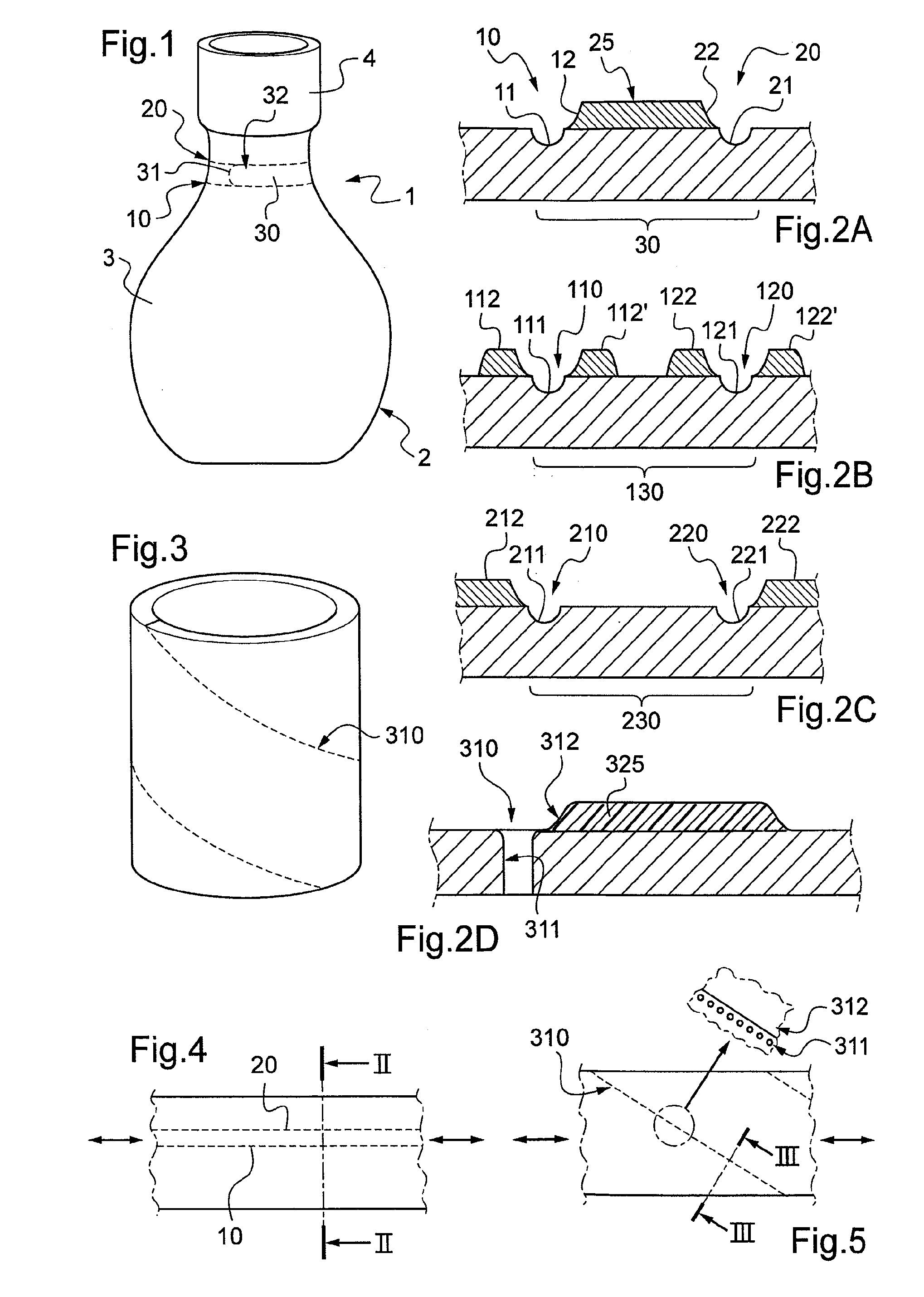
[0029]In a first embodiment shown in FIG. 2A, two lines of weakness 11, 21 are made in the film, in this example by laser cutting to half-depth in the thickness of the film (for reasons of simplification, the film is shown as comprising a single layer, but that is not limiting, and the film could comprise a plurality of layers). In the figure, there can be seen the furrows left by the cutting. Then, according to the invention, a layer of polymer varnish 25 is applied to the surface of the film so as to form a strip that extends between the lines of weakness 11, 21 up to the vicinity thereof so as to form local extra thicknesses 12, 22 bordering the lines of weakness 11, 21. Associating a line of weakness with an adjacent local region of extra thickness defines a tear line along which the sleeve can be torn. The two tear lines as defined in this way define between them the tear strip 30.
[0030]When making a sleeve, the film as prepared in this way is subjected to heat-shrinking, inclu...
second embodiment
[0034]In a second embodiment shown in FIG. 2B, tear lines 110, 120 are formed by making lines of weakness 111, 121 in the film that are bordered by local regions 112, 112′ of extra thickness that extend on either side of the line of weakness 111, and local regions 122, 122′ of extra thickness that extend on either side of the line of weakness 121. Between them, the two lines of weakness 110, 120 define a tear strip 130. In this embodiment, as in the above-described embodiment, the lines of weakness are made by laser cutting to half-depth, while the regions of local extra thickness are made by applying polymer varnish.
third embodiment
[0035]In a third embodiment shown in FIG. 2C, the tear lines 210, 220 comprise lines of weakness 211, 221 bordered on the outside of the tear strip 230 by local regions 212, 222 of extra thickness.
[0036]Although in these examples, the tear line extends parallel to the stretch direction of the film, this configuration is not essential. As shown in FIG. 5, it is possible to make a film with a tear line 310 that extends obliquely relative to the stretch direction of the film. As shown in FIG. 3, such a film enables sleeves to be made in which the tear line extends along a spiral, thus making it possible, on initiating tearing at the top of the sleeve, to separate the sleeve entirely from the container.
[0037]As shown in FIG. 2D, the tear line 310 includes both a weakness line 311, constituted by a sequence of microperforations in alignment, and also a local region 312 of extra thickness bordering the line of weakness 311.
[0038]Thus, making a local region of extra thickness on the stretc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mechanical weakness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com