Emulsions useful in beverages
a technology of emulsions and beverages, applied in the field of emulsions useful in beverages, can solve the problems of affecting the stability of adding to the complexity and length of processing the beverage, and difficult to stabilize emulsions and their resulted beverages, etc., and achieves excellent stability and high oil loading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of an Emulsion of 5-Fold Orange Oil with Resulting Mean Particle Size of 0.15 Microns
[0041]The volume fraction of the oil and the LMW surfactant, the total discrete phase's volume fraction, and the weight percentage are shown in the table 1.1.
TABLE 1.1IngredientsWeight Percent.Volume fraction.Orange Oil 5X48.9%56.9%Quillaja solid extract7.5% 7.5%Water phase43.6%43.6%Total volume fraction of 60%discrete phase
One kilogram of pre-emulsion was made as follows.
[0042]The water phase was prepared by adding Quillaja extract containing 7.5% of Quillaja solid extract to 43.6%. A pre-emulsion was made by slowly adding 48.9% of 5 fold Orange oil to the water phase using an LCI high shear mixer (Model HSM-100 LCI from Charles Ross & Son Company) at 7500 rpm for 3 minutes.
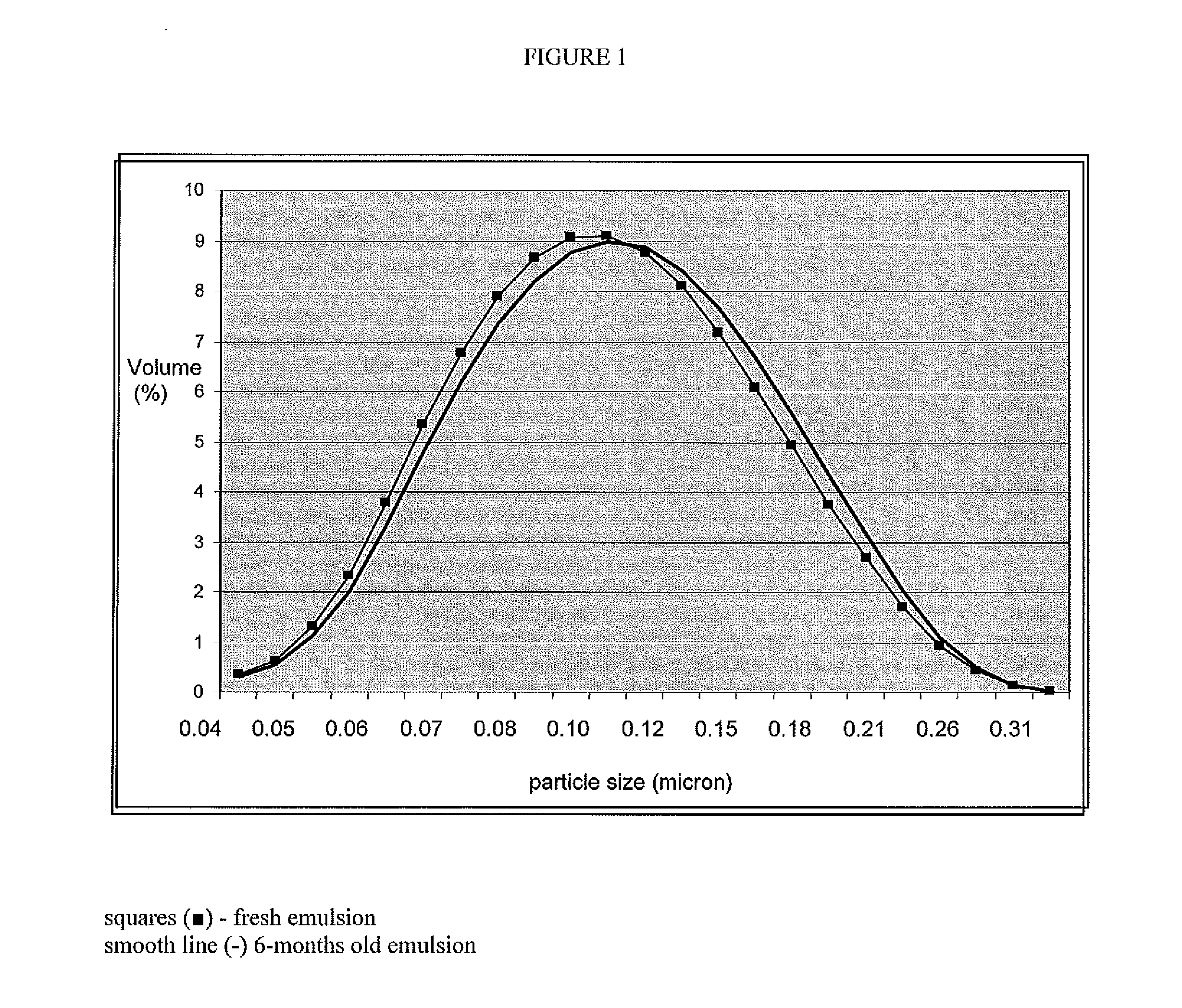
[0043]The above pre-emulsion was homogenized using an APV pressure homogenizer (Model 15 MR Laboratory Homogenizer from APV Gaulin) for 3 passes at 44.8 MPa. The particle size of the emulsion was then checked. The e...
example 2
Preparation of Emulsions of Vegetable Oil with Resulting Mean Particle Size of Less than 0.2 Microns
[0044]The volume fraction of each ingredient and the total volume fraction of the discrete phase of all three samples are shown in the table 2.1 and the weight percentages of all three samples are shown in table 2.2.
TABLE 2.1Volume fractionIngredientsSample 1Sample 2Sample 3Vegetable oil53%52%53%Tween 6012%10%11%Total discrete phase65%62%64%volume fraction
TABLE 2.2Weight percentageIngredientsSample 1Sample 2Sample 3Vegetable oil49%48%49%Tween 6012%10%11%Water39%42%40%
One kilogram of pre-emulsion was made as follows.
[0045]Tween 60 was heated to 65° C. to be fully liquefied. The water phase was prepared by adding 12%, 10%, or 11% of liquefied Tween 60 to 60° C. water at the amount of 39%, 42%, and 40% for sample 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The pre-emulsion were made by slowly adding the vegetable oil to the water phase using an LCI high shear mixer (Model HSM-100 LCI from Charles Ross & S...
example 3
Comparison of Emulsions of 5 Fold Oil with Discrete Phase Volume Fraction Outside the Claimed Range
[0046]Both volume fraction of the ingredients and total volume fraction of discrete phase of all 4 samples are shown in table 3.1. The weight percentages of all of the ingredients are shown in table 3.2
TABLE 3.1Volume fractionIngredientsSample 1Sample 2Sample 3Sample 45 fold Orange oil 33%38%43%51%Tween 60 4%12%15%17%Quillaja Solid extract 0.84%1.73% 0.84% 2%Total discrete phase37.84%51.73% 58.84% 70%volume fraction
TABLE 3.2Weight percentageIngredientsSample 1Sample 2Sample 3Sample 45 fold Orange oil28.38%32.98%36.98%43.86%Tween 60 4% 12% 15% 17%Quillaja Solid extract 0.84% 1.73% 0.84% 2%Water66.78%53.59%47.18%36.14%
One kilogram of pre-emulsion was made as follows.
[0047]Tween 60 was heated to 65° C. to be fully liquefied. The water phase was prepared by adding the liquefied Tween 60 (4%, 12%, 15%, or 17%) and Quillaja solid extract (0.84%, 1.73%, 0.84%, or 2%) to 60° C. w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com