Rotor of electric rotating machine
a rotating machine and electric technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/form/construction, windings, etc., can solve the problems of undetectable increase in the weight of the alternator, etc., to reduce the resistance or resistance of the magnetic force, reduce the total weight of the field coil, and shorten the length of the core layer unit in the axial direction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
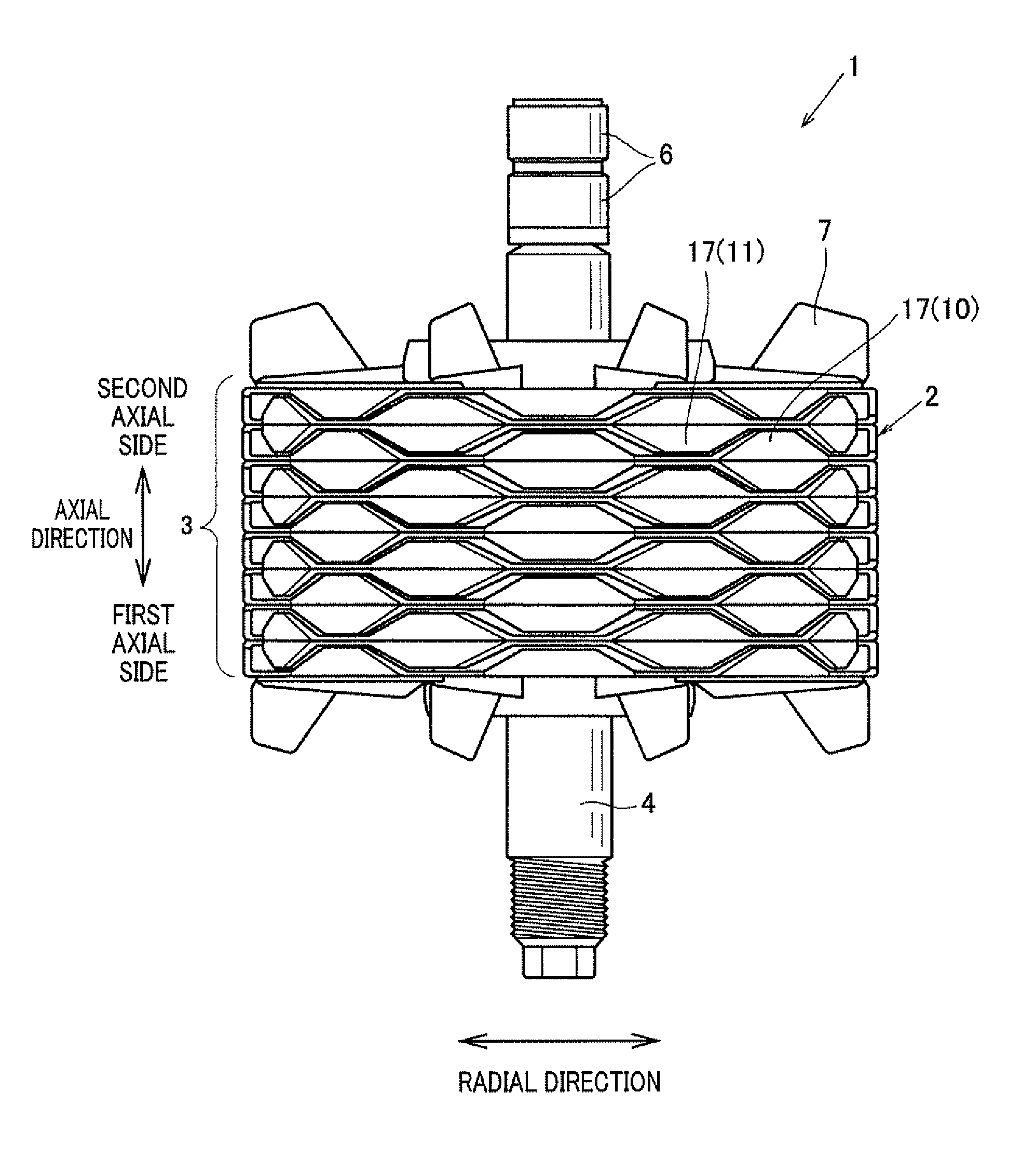
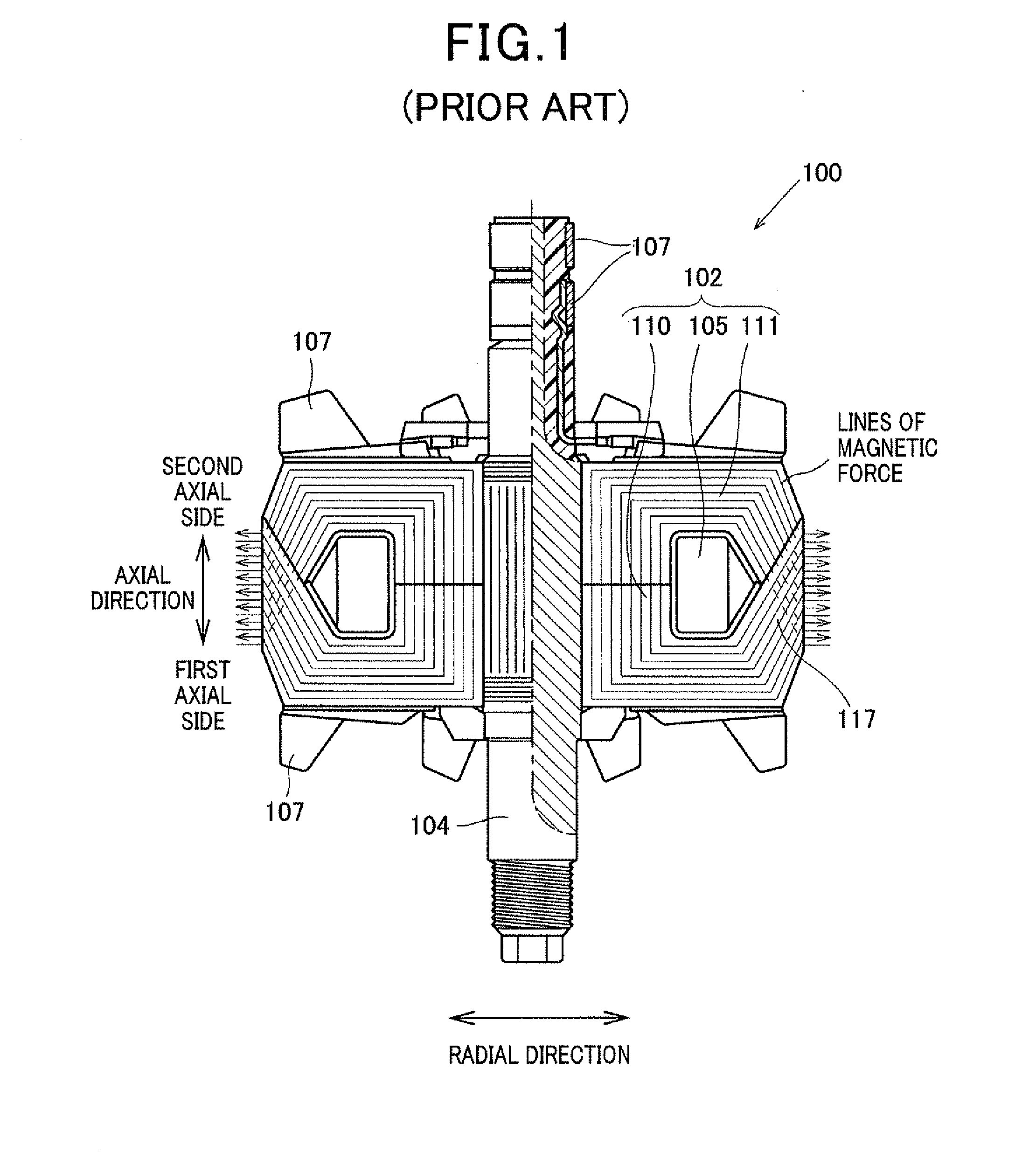
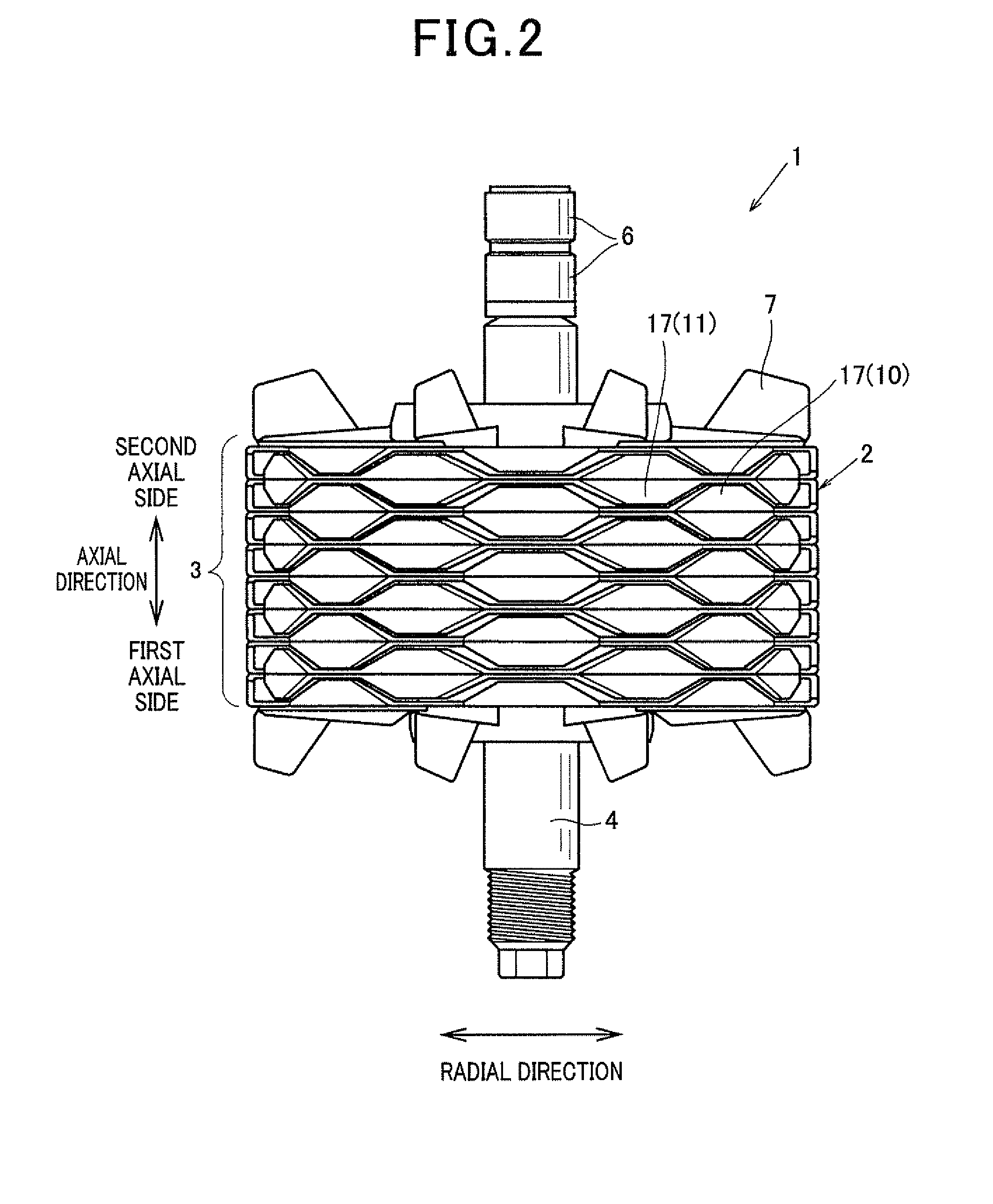
[0043]FIG. 2 is a side view of a rotor of an electric rotating machine according to the first embodiment, while FIG. 3 is a side view, partially in cross section, of the rotor. An electric rotating machine is, for example, used as an alternator mounted on a vehicle. As shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, this alternator representing the machine has a rotor 1 and a cylindrically-shaped stator (not shown) surrounding the rotor 1 on the outer side of the rotor 1 in the radial direction of the rotor 1. The rotor 1 has a laminated body 3 formed in a torus or cylindrical shape, a rotational shaft 4 located along the central axis of the body 3 so as to revolve on its shaft center, two slip rings 6 attached to the shaft 4 such that electric current flows to the body 3 through the rings 6, fans 7 fixedly located on respective axial side surfaces of the body 3, and a spacer 8 located between the body 3 and the shaft 4 and fixed to the body 3 and the shaft 4. The spacer 8 is made of non-magnetic metal...
second embodiment
[0081]FIG. 11 is a side view, partially in cross section, of a rotor of an electric rotating machine according to the second embodiment. As shown in FIG. 11, a rotor 1A differs from the rotor 1 shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 in that the rotor 1A has no spacer located between the laminated body 3 and the shaft 4. More specifically, each core layer unit 2 has a field coil 5A, a first rotor core 10A, a second rotor core 11A, a ring-shaped body 13A and a bobbin (not shown) assembled in the same manner as those in the unit 2 shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3. The coil 5A has an inner diameter and an outer diameter smaller than those in the coil 5 so as to approach the shaft 4. Each of the rotors 10A and 11A has a first yoke portion 15A having an outer diameter R2 smaller than that of the portion 15, a second yoke portion 16A extending from the portion 15A toward the outer side so as to substantially have the same outer diameter as that of the portion 16, and the magnetic poles 17 extending from the...
third embodiment
[0085]FIG. 12 is a side view of a rotor of an electric rotating machine according to the third embodiment, while FIG. 13 is an exploded view of rotor cores of one core layer unit of the rotor shown in FIG. 12. As shown in FIG. 12 and FIG. 13, a rotor 1B according to the third embodiment differs from the rotor 1 shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 in that the width of each magnetic pole in the circumferential direction is narrowed step by step toward the top end of the pole.
[0086]More specifically, a plurality of claw-shaped magnetic poles 17B in the cores 10 differ from the poles 17 of the cores 10 shown in FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 in that each magnetic pole 17B has stepped ends on both sides in the circumferential direction to narrow the width toward the second axial side and to have at least one tread surface 35B, facing toward the second axial side, at each stepped end. A plurality of claw-shaped magnetic poles 17C in the cores 11 differ from the poles 17 of the cores 11 shown in FIG. 4 and FIG....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com