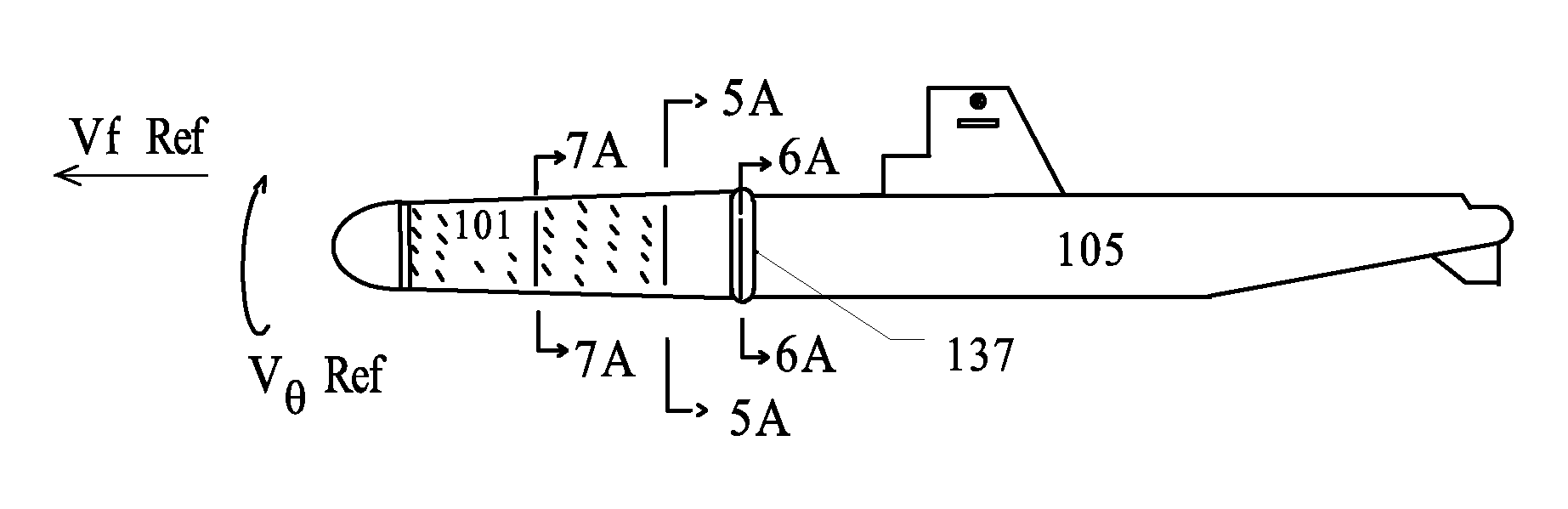
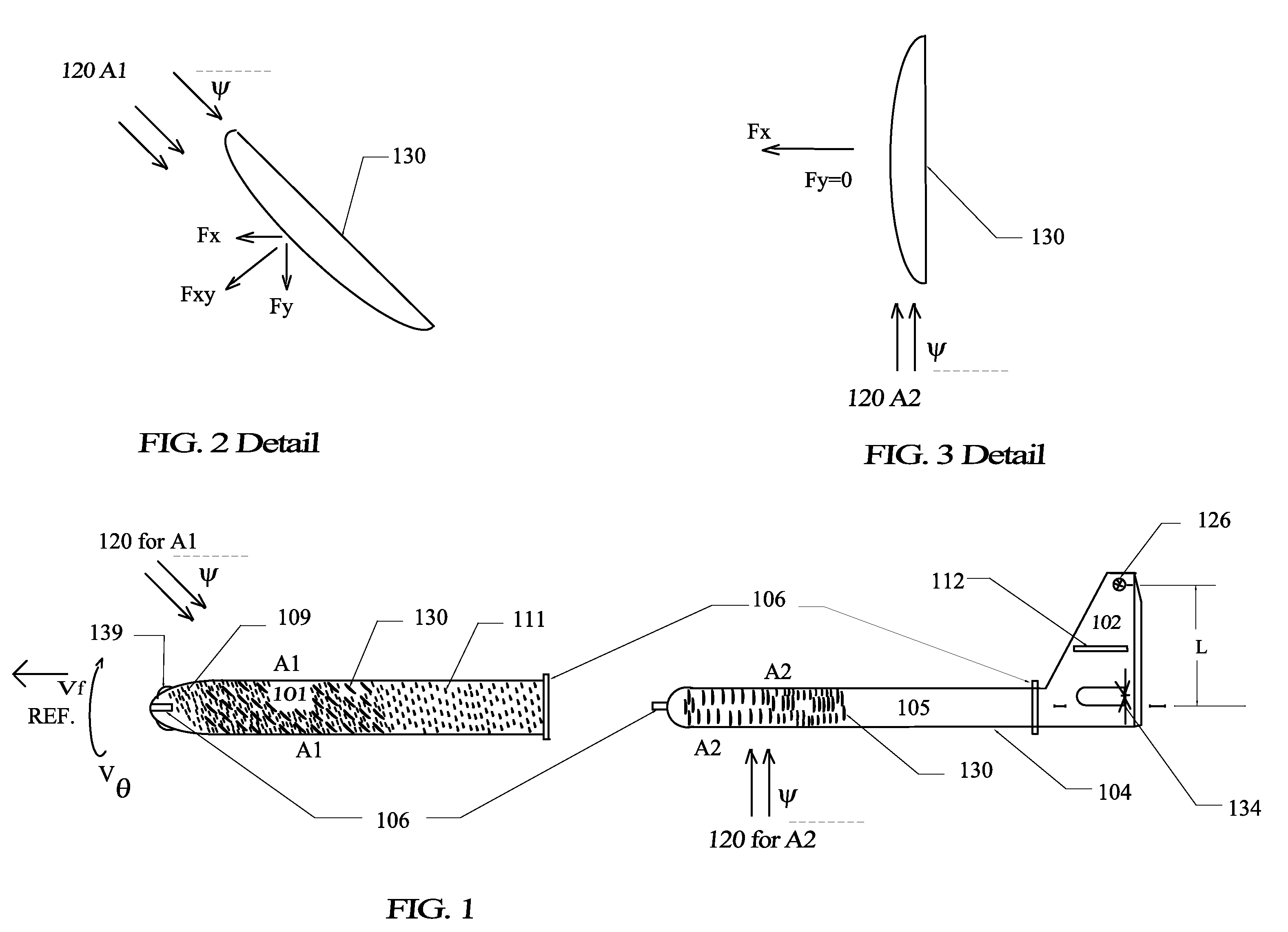
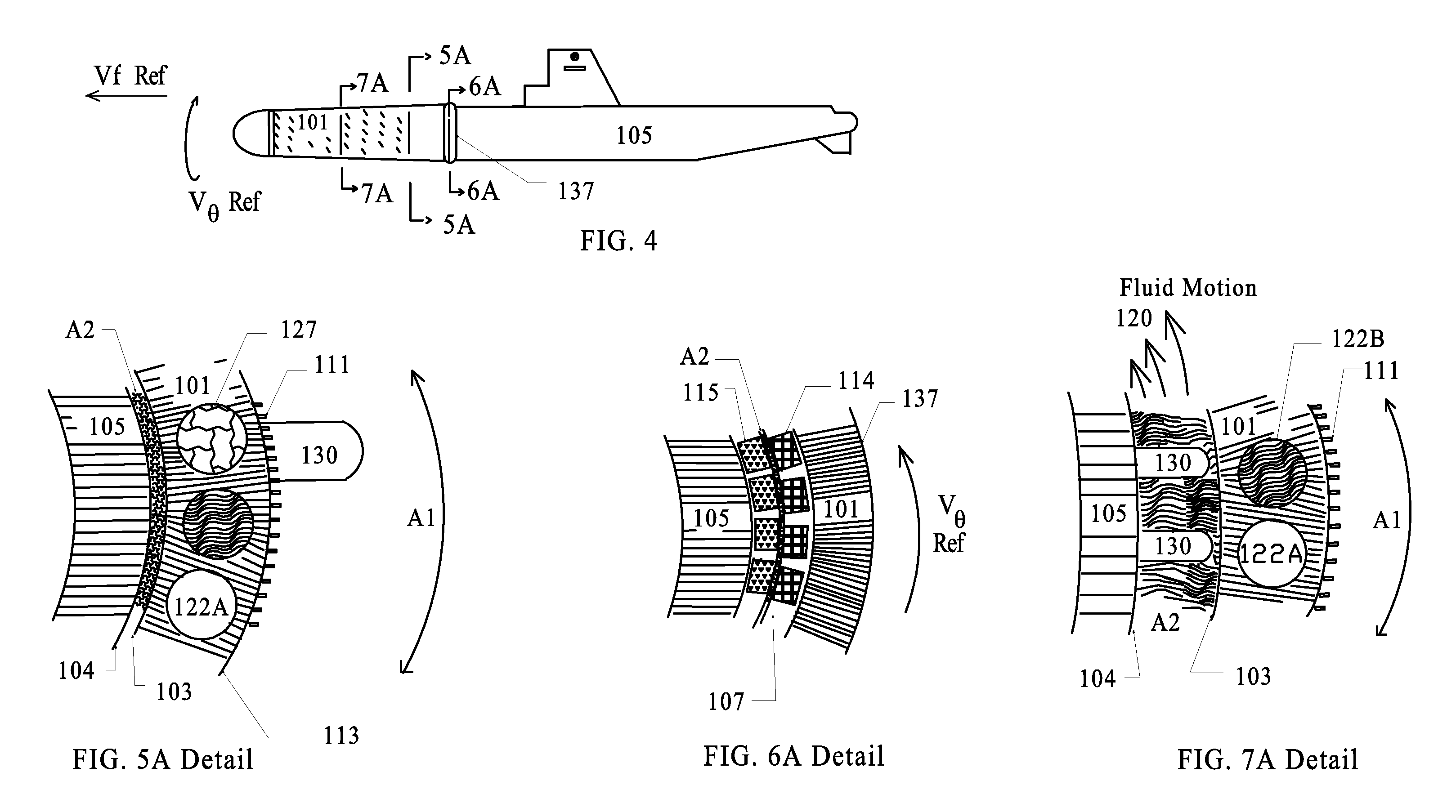
Subsurface Vortex Assisted Distributed Propulsion Active Hull
a distributed propulsion and active hull technology, applied in underwater equipment, special-purpose vessels, vessel construction, etc., can solve the problems of increasing drag and noise, and increasing hydrodynamic noise and cavitation around the propulsion system, so as to reduce drag and hydrodynamic noise and increase thrust
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0120]In the following detailed description of the invention, numerous specific details are provided for a thorough understanding of the invention. However, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the invention may be practiced without utilizing every one of these details in any one embodiment. In addition, well-known methods, procedures, materials, components and circuitry have not been described in elaborate detail to avoid an unnecessary obscuring of the invention. Many of these “means” are described by those in “related art” and as such are included as if written herein. However enough information is given so a Craft could be built and methods could be followed using the information contained herein along with state of the art methods and materials. The reference materials included herein and simplified drawings attached hereto and made a part hereof in absence of the ability to present a working model are deemed the best way to concisely convey the substance of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com