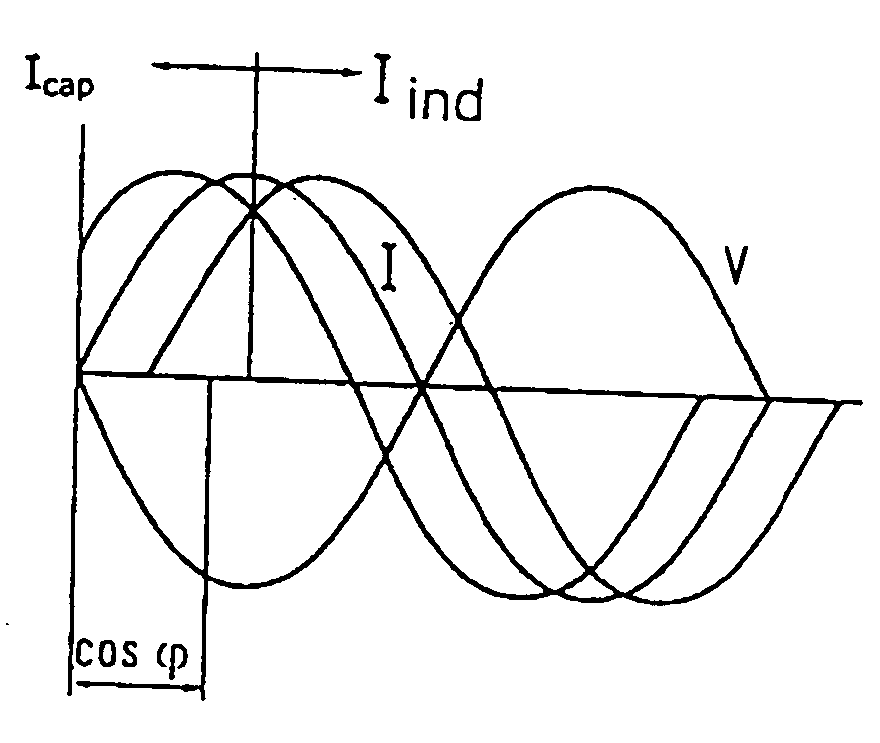Patents
Literature
1224results about "Propulsive elements of rotary type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
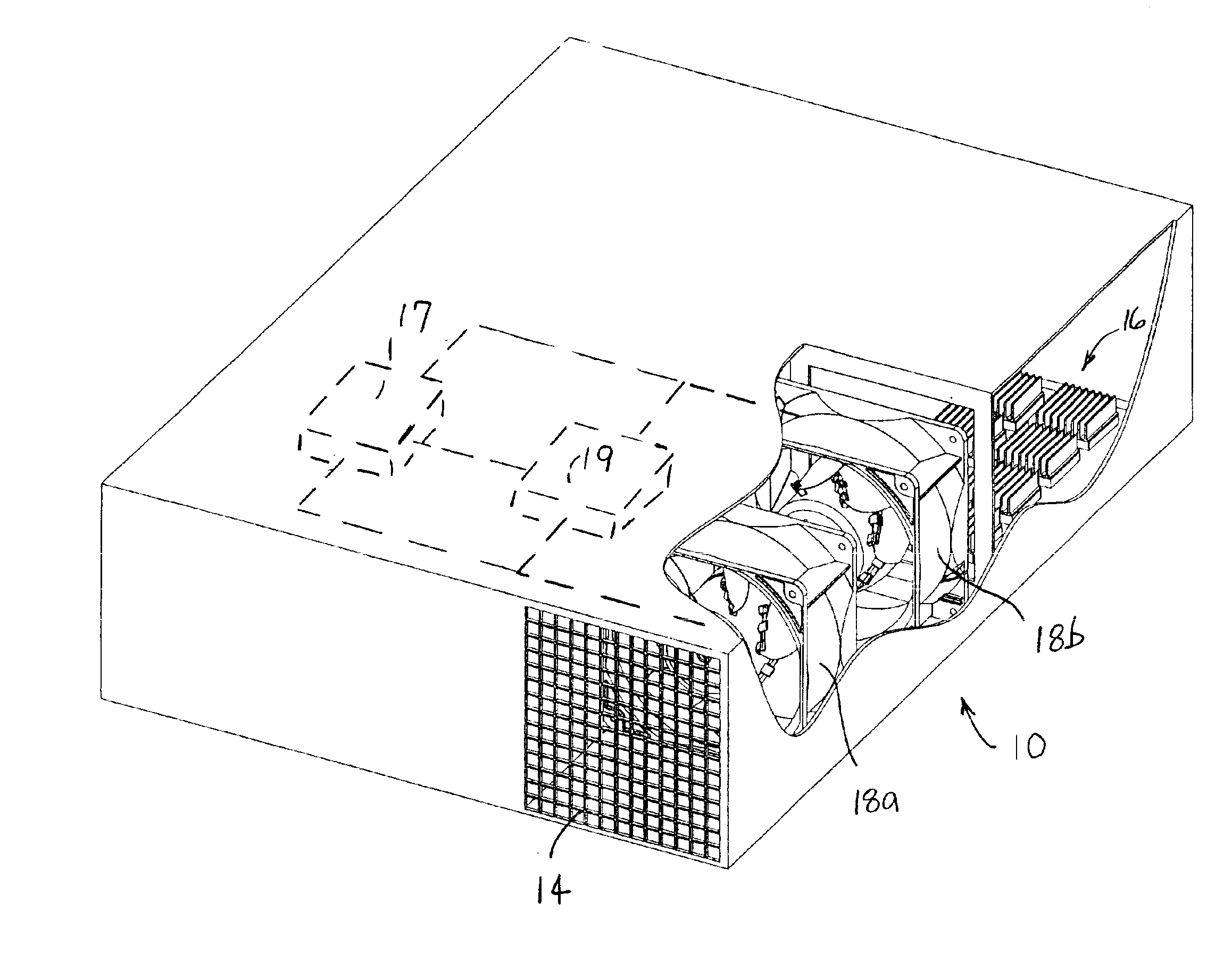
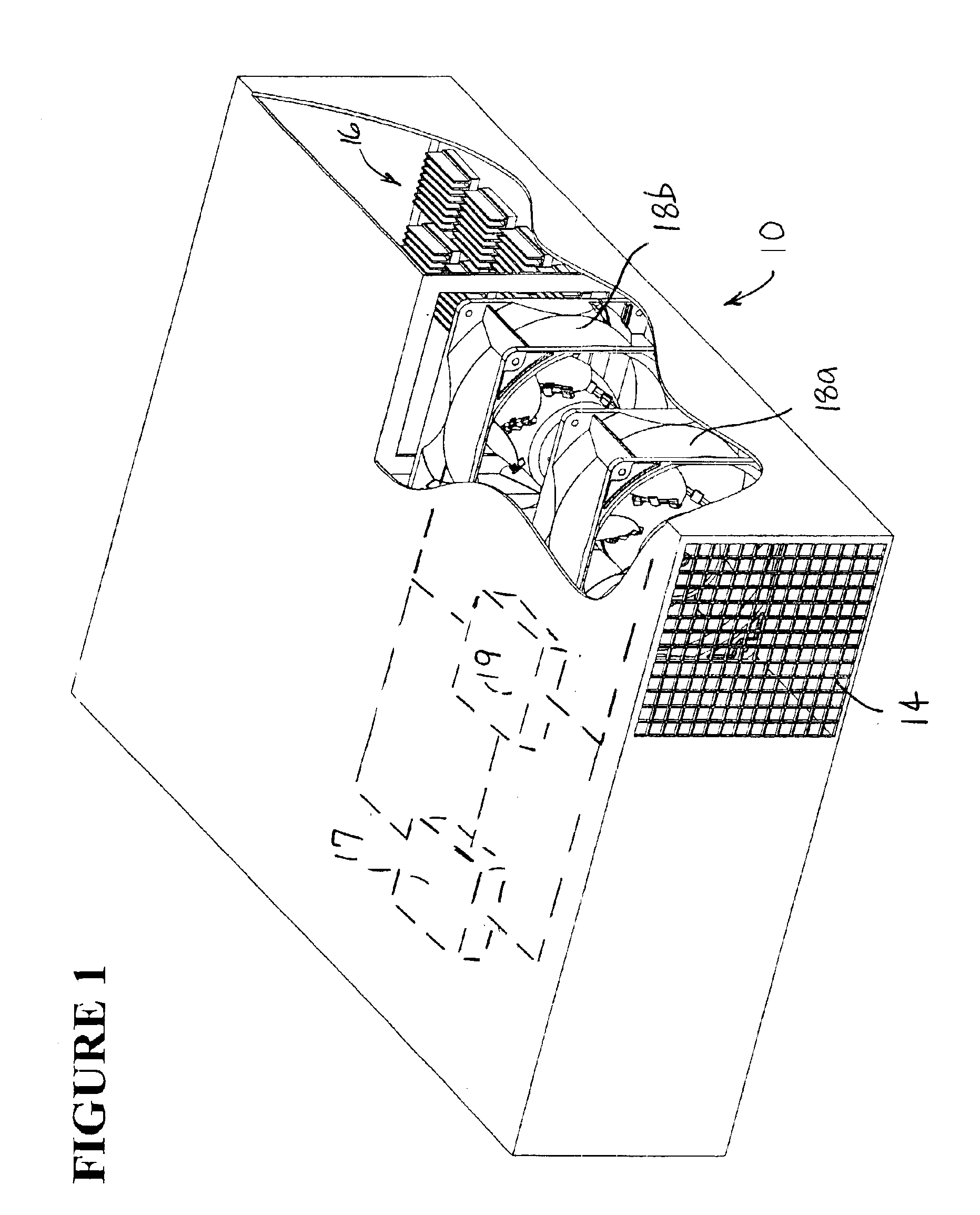
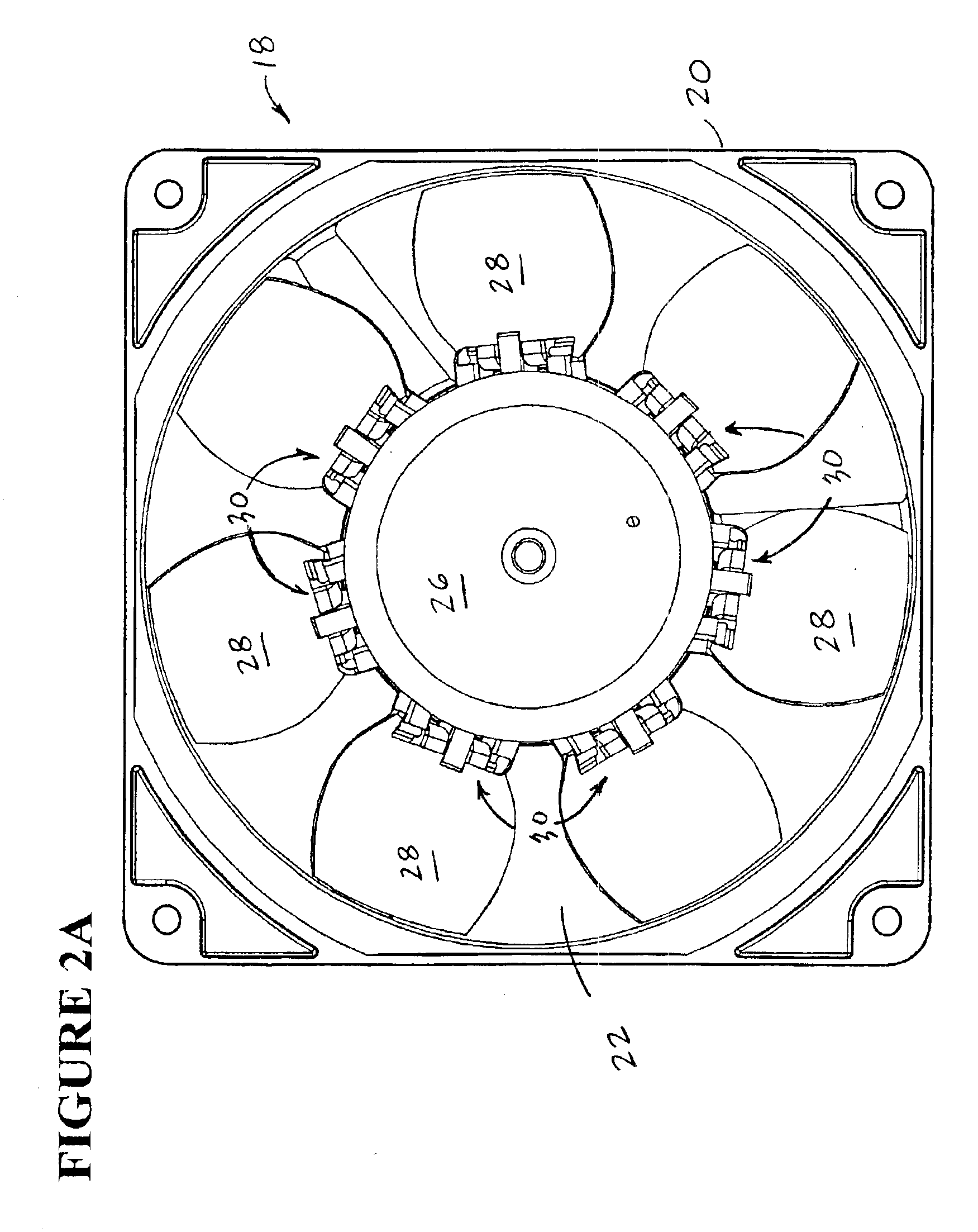
Fan with collapsible blades, redundant fan system, and related method
InactiveUS6860713B2Reduces fan inefficiencyPrevent undesirable blockagePropellersPump componentsFan bladeAirflow
A redundant fan system for a computer includes two fans installed in series with at least one of the fans having collapsible blades. A fan system of this type reduces the fan inefficiency caused when one fan in a series mounted pair is not operating, either because it is free-wheeling or in a locked rotor condition. When non-operational, the fan blades of the collapsible fan fold inward due to airflow generated by the operational fan over the collapsible blades. The ability of the blades to fold reduces the inefficiency of the operational fan, having less of an effect on fan life. Also, because the flow of air is less restricted, proper airflow can be maintained, thus preventing overheating of the computer.
Owner:NIDEC AMERICA CORP
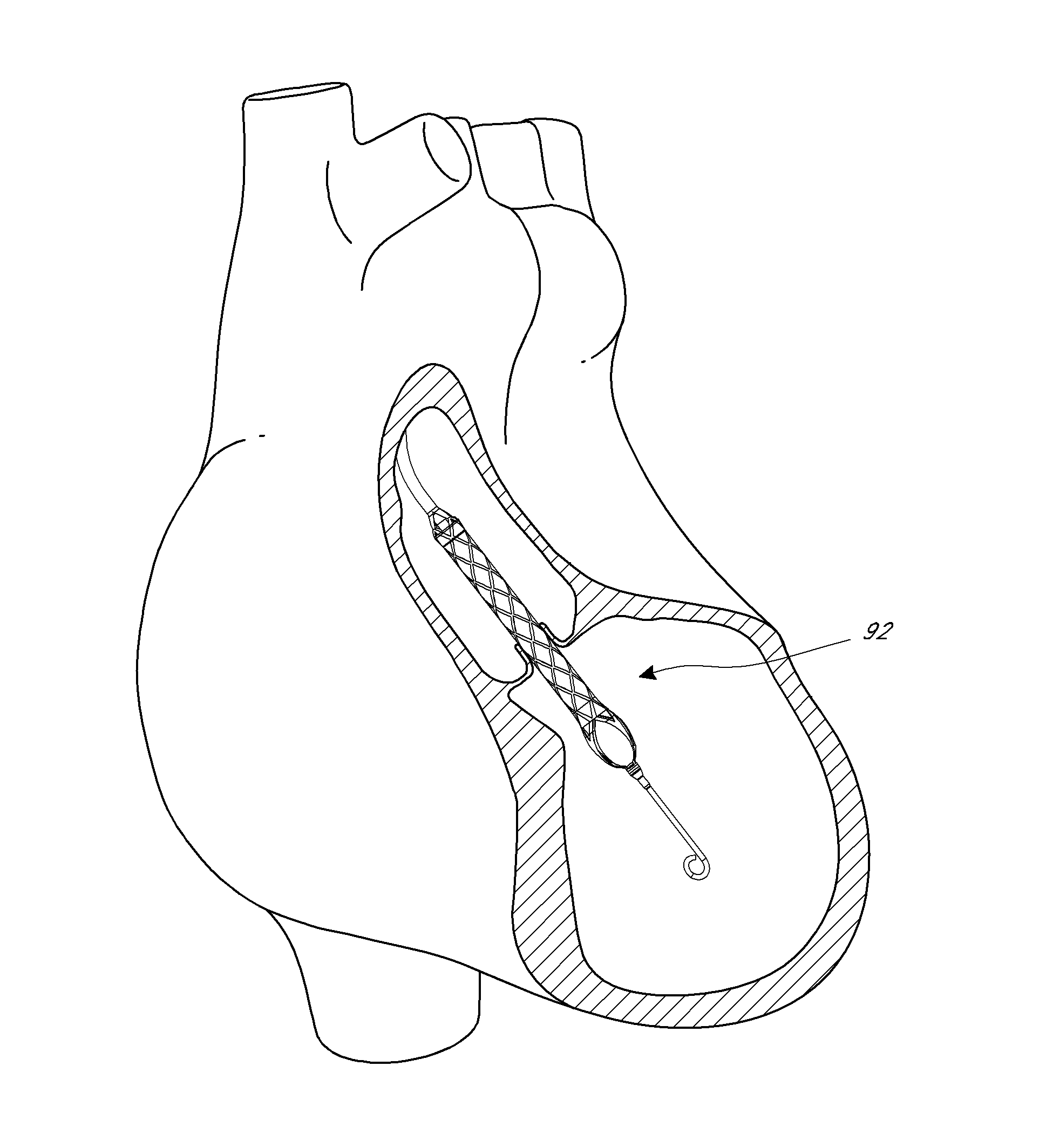
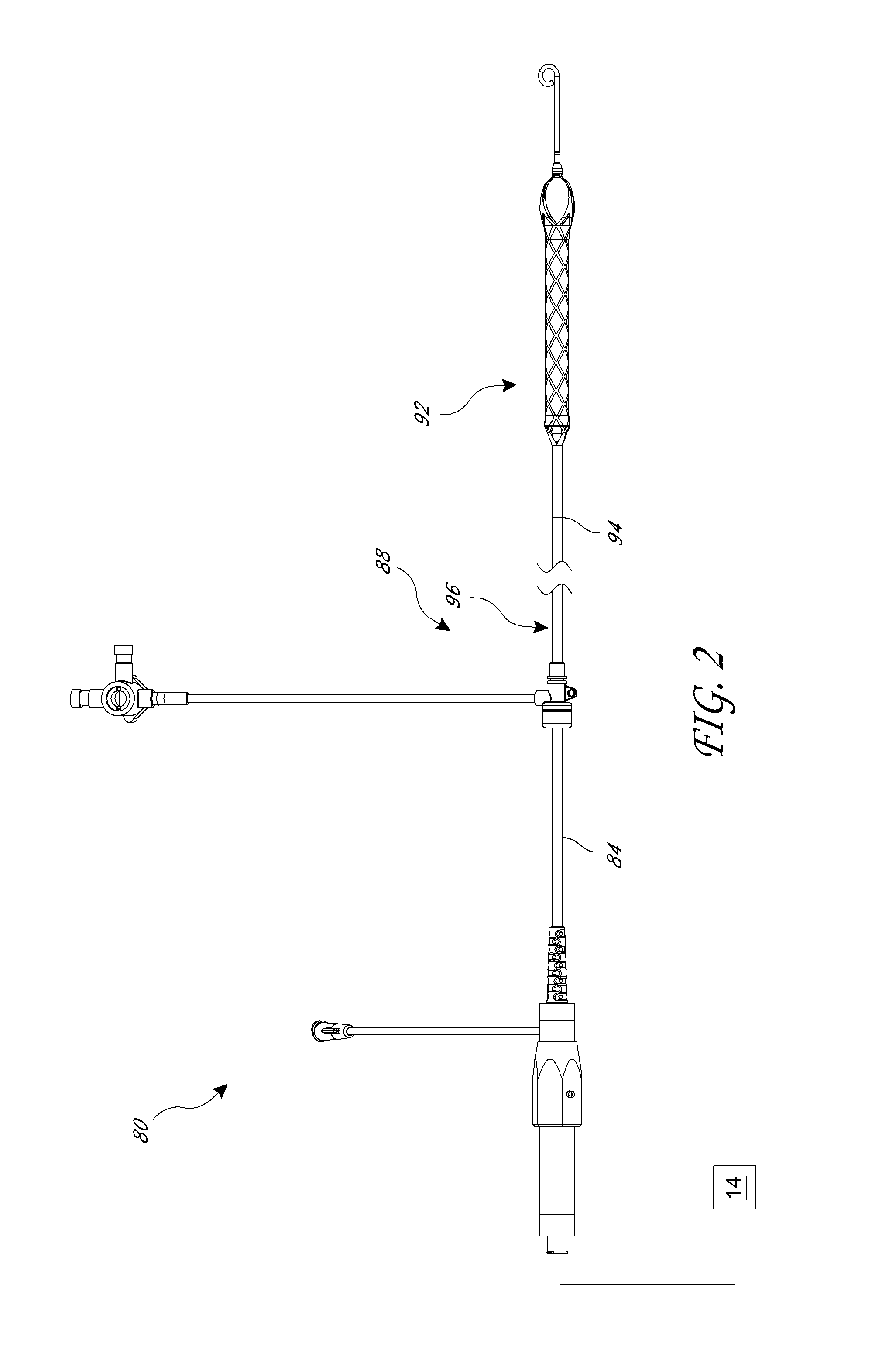
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
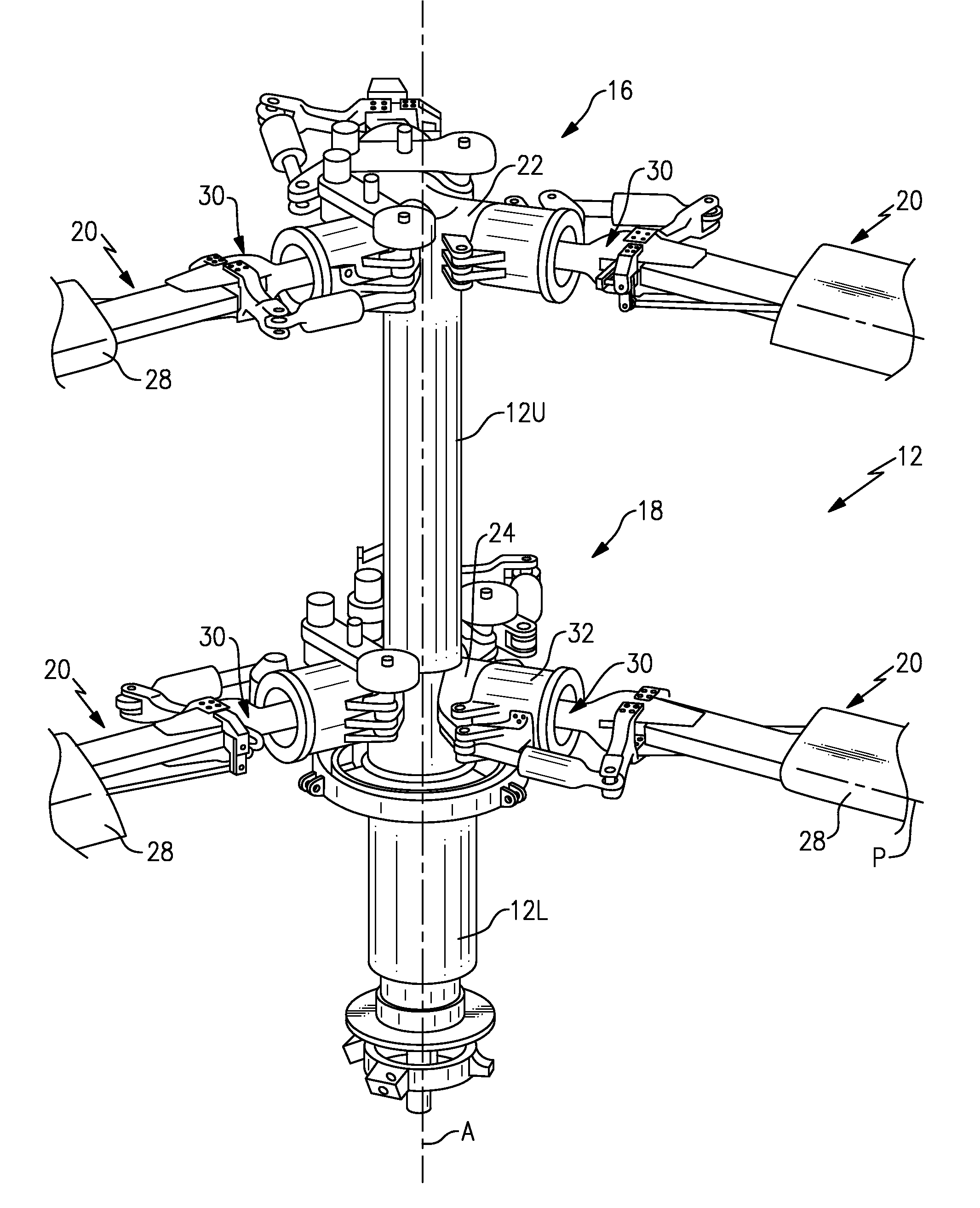
Windmill and windmill control method
A windmill includes a freely rotatable revolution shaft, a plurality of pairs of pivotal support rods provided at the revolution shaft, and wind receiving blades respectively and rotatably set between the pivotal support rods with wind receiving blade shafts. The windmill is applied to the driving of a lifting pump, a generator and the like by employing revolution driving force. An anemometer / anemoscope measures wind velocity and direction. A servo motor controls the direction of the wind receiving blades based on the detected velocity and direction. Various methods of control are also provided.
Owner:HIRAI TETSUO
Serpentine wind turbine
Multiple horizontal axis type rotors are coaxially attached along the upper section of an elongate torque transmitting tower / driveshaft, The tower / driveshaft projects upward from a cantilevered bearing means, and is bent downwind, until the rotors become sufficiently aligned with the wind to rotate the entire tower / driveshaft, Power is drawn from the shaft at the base. Surface mount, subsurface mount, and marine installations, including a sailboat, are disclosed. Blade-to-blade lashing, and vertical axis rotor blades may also be included. Vertical and horizontal axis type rotor blades may be interconnected along the length of the tower / driveshaft to form a structural lattice, and the central shaft may even be eliminated. Aerodynamic lifting bodies or tails, buoyant lifting bodies, buoyant rotor blades, and methods of influencing the tilt of the rotors, can help elevate the structure. This wind turbine can have as few as one single moving part.
Owner:SELSAM DOUGLAS SPRIGGS
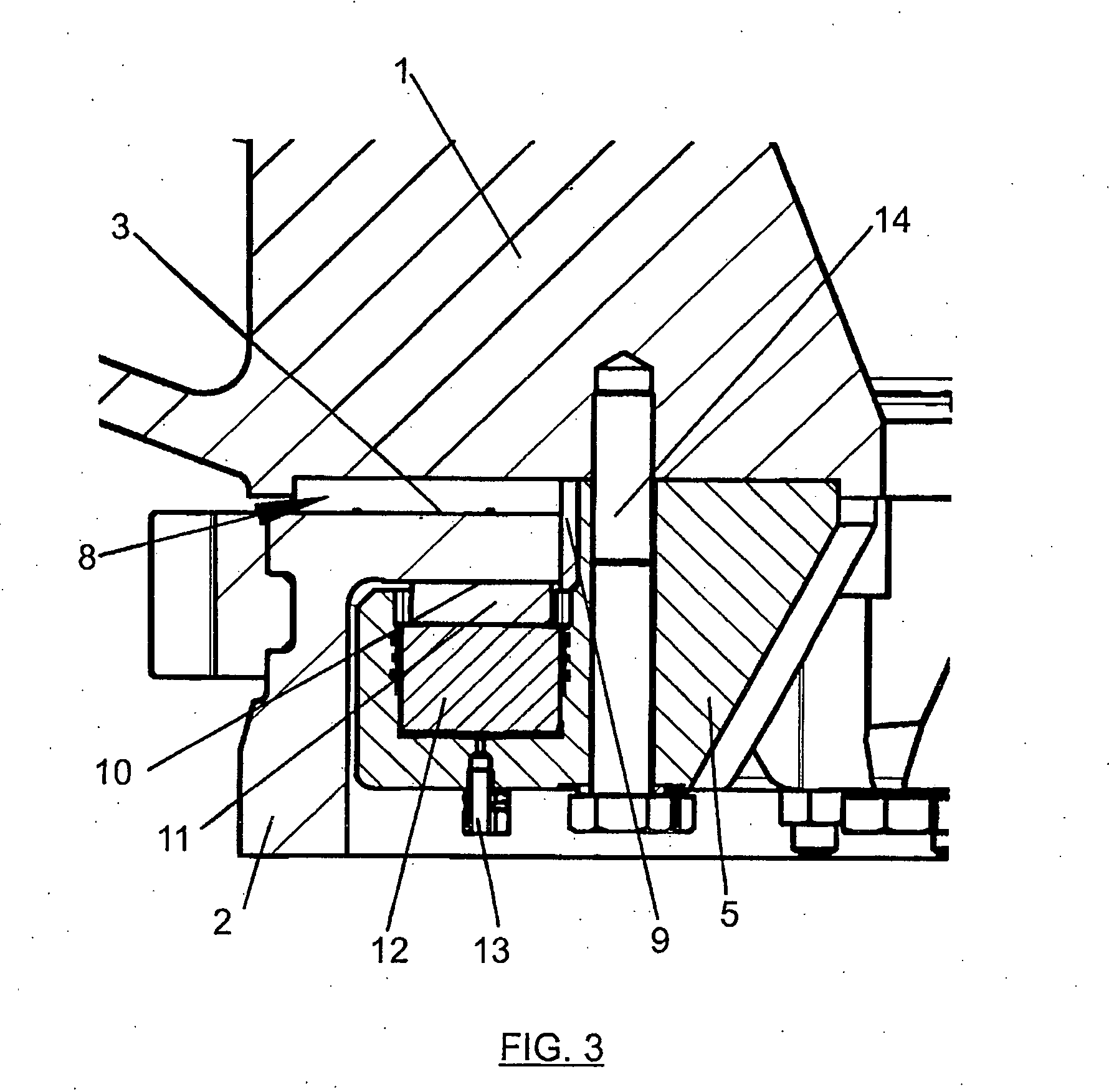
Ring segment of gas turbine
An object of the present invention is to provide a ring segment of a gas turbine in which the temperature is maintained low, damage due to high temperature oxidation is prevented, and high temperature deformation is prevented. In order to achieve the object, the present invention provides a ring segment of a gas turbine which comprises a blade ring, a main shaft and moving blades comprising a plurality of individual units which define an annular form by being arranged around the peripheral direction of the main shaft, and disposed so that its inner peripheral surface is maintained at a constant distance from the tips of the moving blades, wherein grooves which extend along the axial direction of the main shaft of the turbine are formed upon of the individual units so as mutually to confront one another; a seal plate which is inserted into each mutually confronting pair of the grooves so as to connect together the adjacent pair of individual units; and contact surfaces which are formed at positions more radially inward than the seal plates, which extend in the axial direction and the peripheral direction and which mutually contact one another.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wind turbine load control method
InactiveUS20070057517A1Sufficient capabilityOperation loadPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
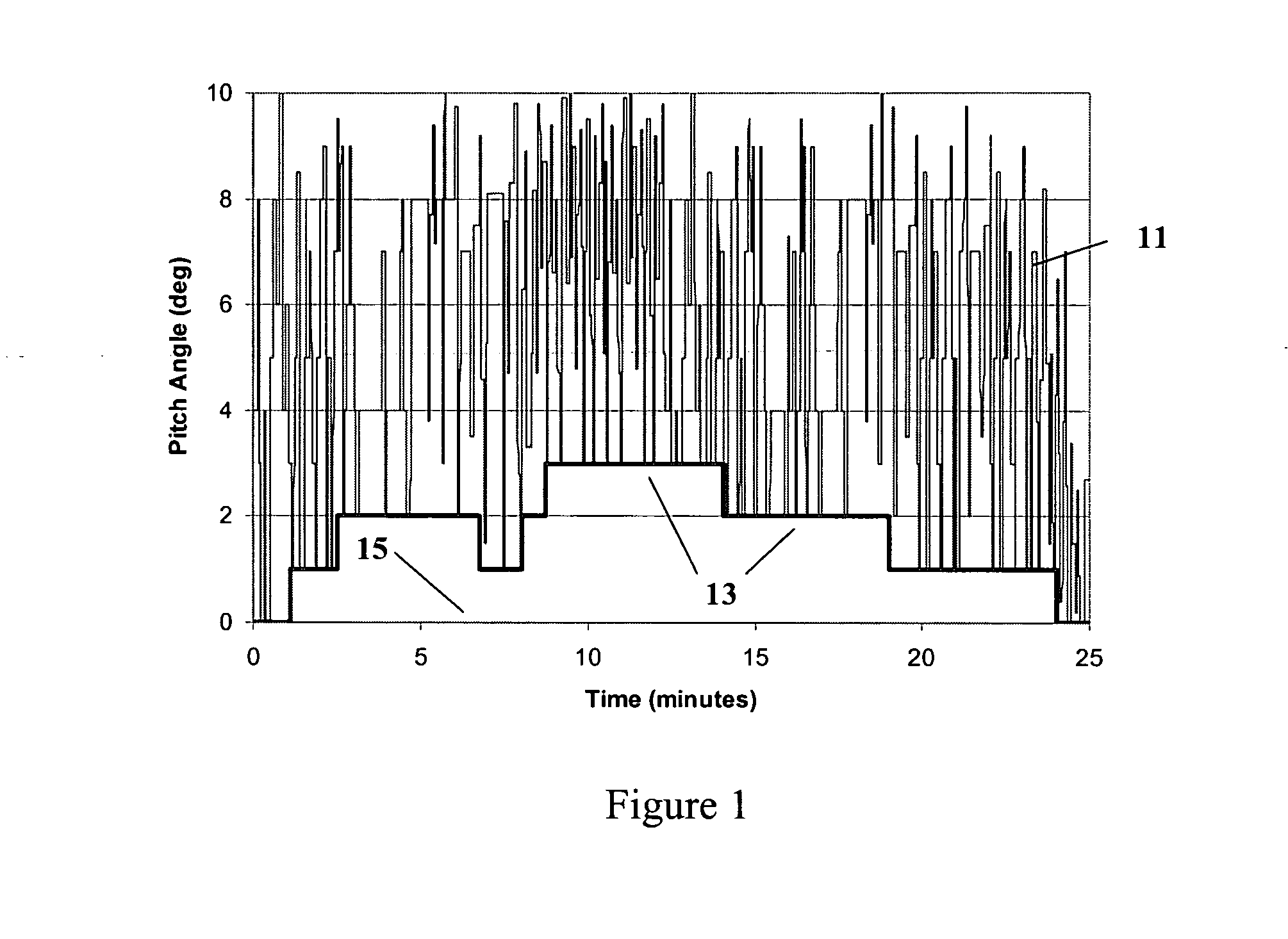
A method for limiting loads in a wind turbine by using measured loads or wind speed to increase the minimum pitch angle for extended periods. The minimum pitch angle will be allowed to relax down to the default when load excursions diminish. The method will allow turbines to capture more energy by operating in higher wind speeds and / or utilizing larger rotors without additional loss of fatigue life.
Owner:MCNERNEY GERALD
Methods and apparatus for operating a wind turbine
A method for operating a wind turbine having at least one blade includes determining an ambient air operating envelope and controlling a power output of the wind turbine at least partially based on the determined ambient air operating envelope. Determining an ambient air operating envelope includes measuring at least one of an ambient air temperature, an ambient air pressure, an ambient air humidity, and wind turbine power output. The method also includes comparing at least one of a measured ambient air temperature, a measured ambient air humidity and a measured ambient air pressure to predetermined ambient air temperature, pressure and humidity values. The method further includes referencing the predetermined ambient air temperature, pressure and humidity values to at least one operational parameter of the wind turbine. The method also includes determining if an existing wind turbine power output is within a range associated with the determined ambient air operating envelope.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Invertible aircraft
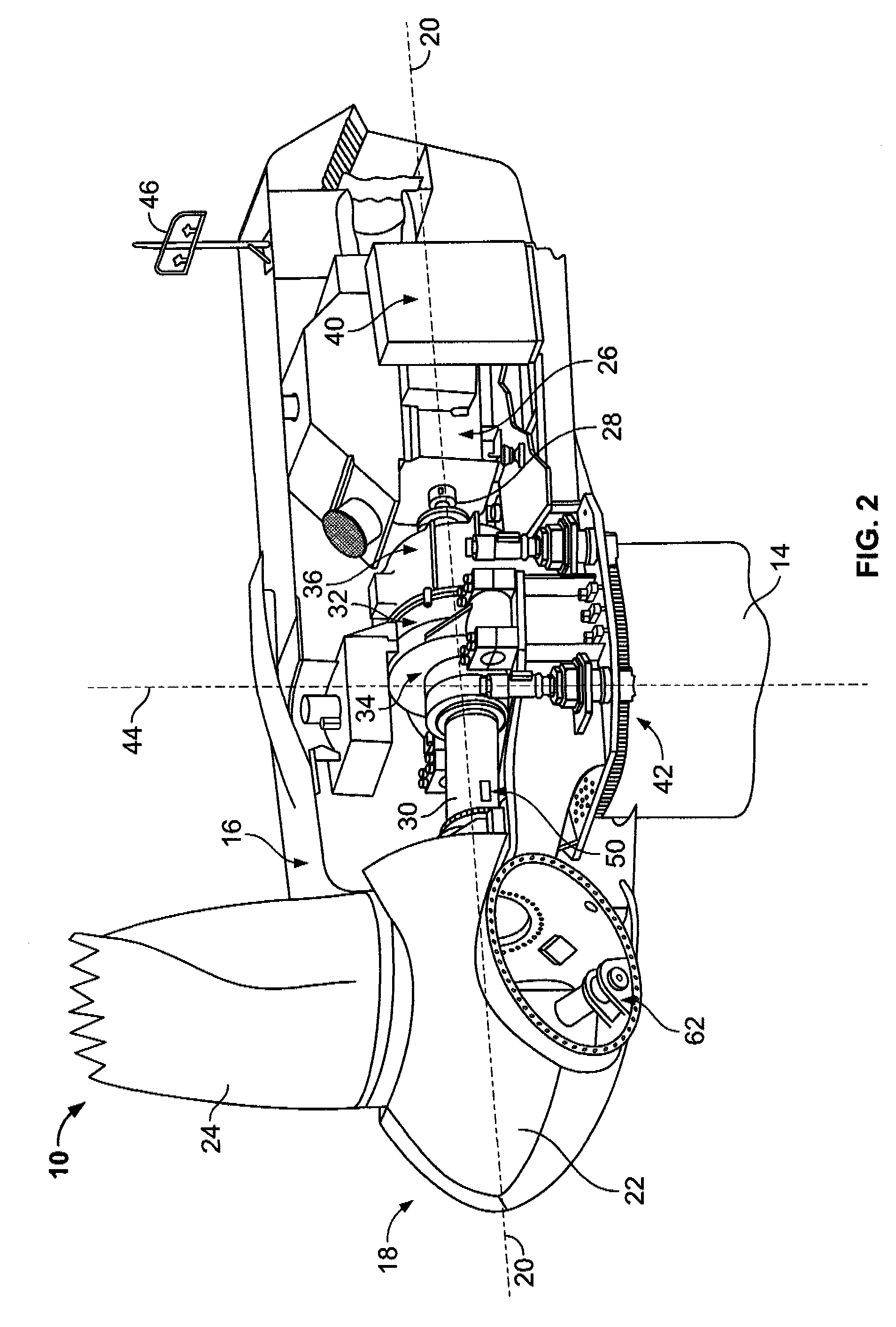
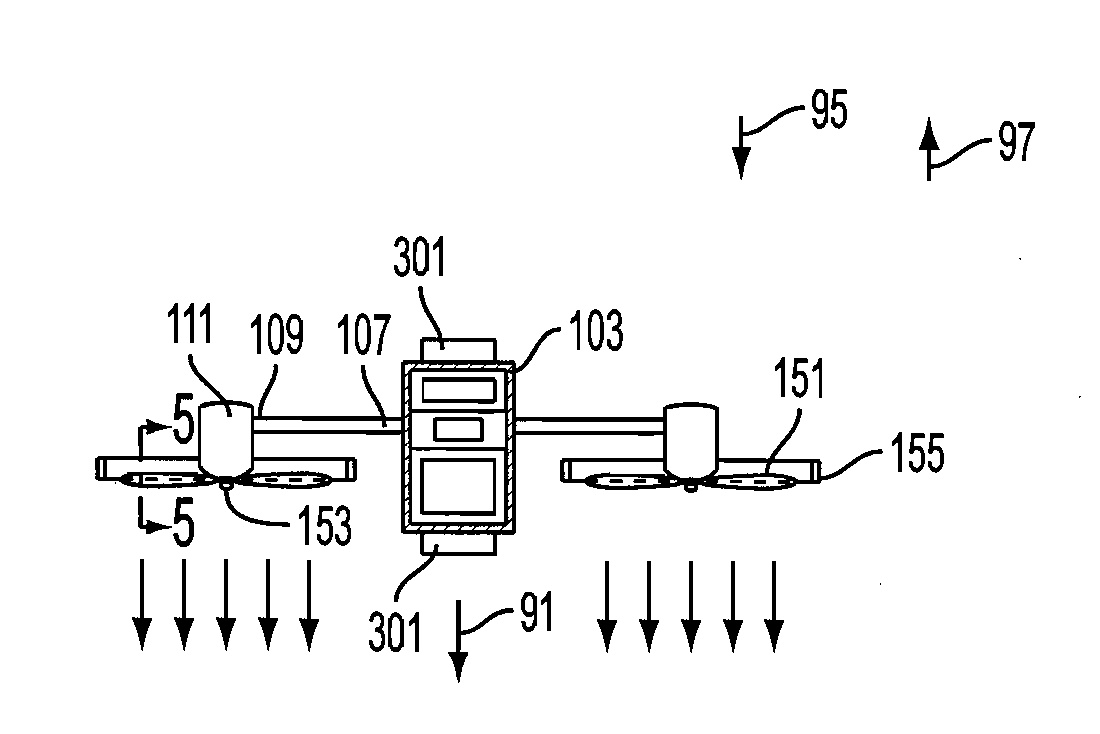
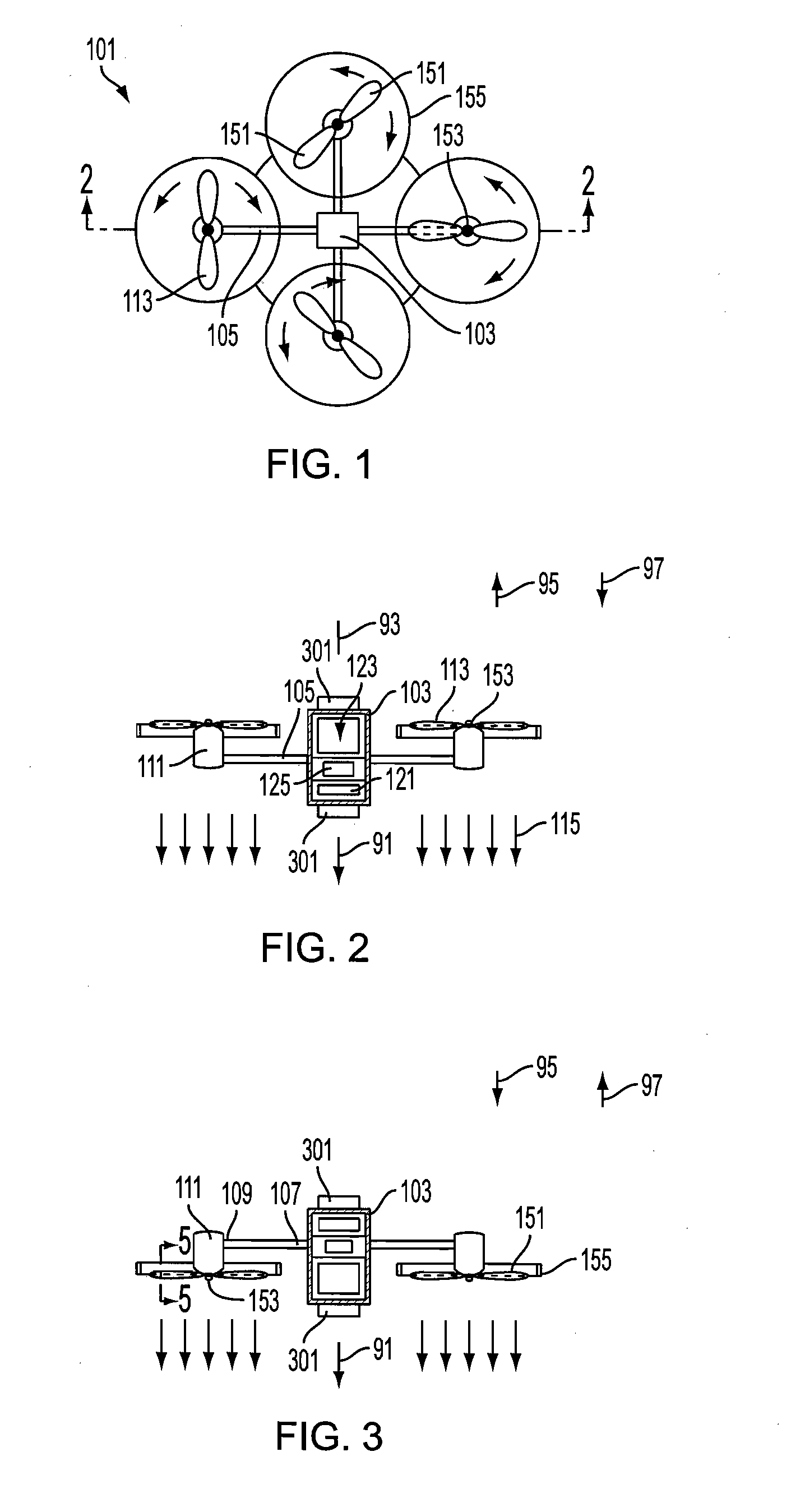
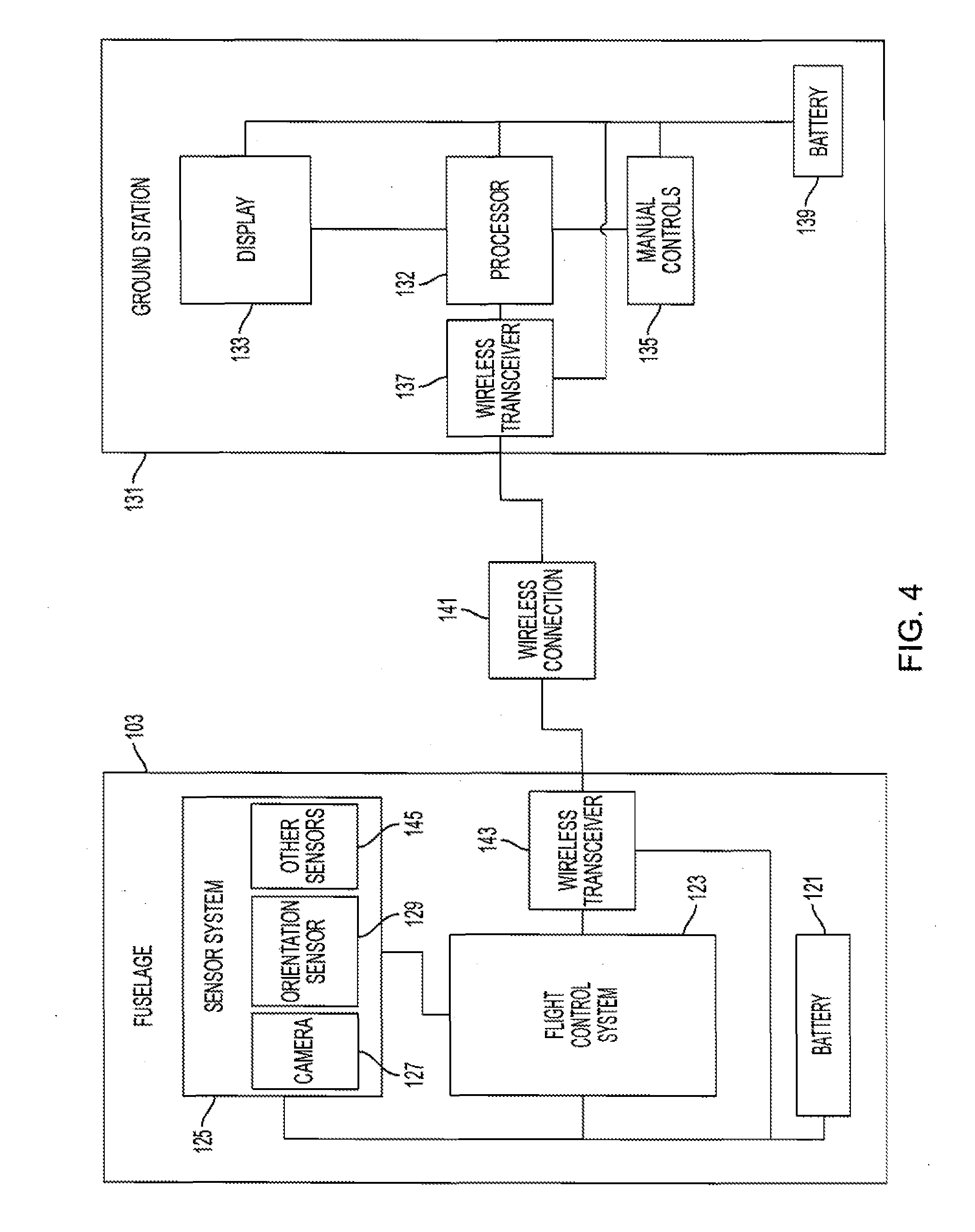
A rotorcraft including a fuselage, one or more motor-driven rotors for vertical flight, and a control system. The motors drive the one or more rotors in either of two directions of rotation to provide for flight in either an upright or an inverted orientation. An orientation sensor is used to control the primary direction of thrust, and operational instructions and gathered information are automatically adapted based on the orientation of the fuselage with respect to gravity. The rotors are configured with blades that invert to conform to the direction of rotation.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Propelling and driving system for boats
A propelling and driving system for boats having an outboard rudder propeller. The system provides the boat with reliable and comparatively good maneuverability. The system comprises at least two rudder propellers, each having driving motors configured in the form of a permanent magnet-excited synchronous machine. The stator winding of each synchronous machine has three winding phases connected to a three-phase alternating current, which are connected to the supply system of the boat. A modular controlling and regulating device comprising standardized modules is provided for each of the rudder propellers.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Load carrying structure having variable flexibility
InactiveUS6182929B1Simple wayReduce stiffnessPropellersPump componentsShape-memory alloyOperating temperature range
A load carrying structure having a selectively rigid or flexible characteristic includes a thermoplastic material (7) having a softening temperature above the operating temperature range of the load carrying structure, and a heating arrangement (8) provided to selectively heat the thermoplastic material to above its softening temperature. During normal operation, the thermoplastic material is in a rigid state and the overall load carrying structure is rigid to the prevailing loads. By activating the heating arrangement to heat the thermoplastic material to at least its softening temperature, the thermoplastic material and therewith the load carrying structure becomes flexible so that it may be deformed to a different configuration by applying a deforming load. Once the desired deformed configuration is achieved, the heating arrangement is deactivated, and the thermoplastic material is allowed to cool below its softening temperature so that it once again becomes rigid and rigidly fixes the new deformed configuration. The deforming force may be applied by any actuating mechanism, or for example by arranging shape memory alloys in connection with the thermoplastic material.
Owner:INST FUER VERBUNDWERKSTOFFE GMBH +1
Method and a device for adjusting the pitch and stopping the rotation of the blades of a wind turbine
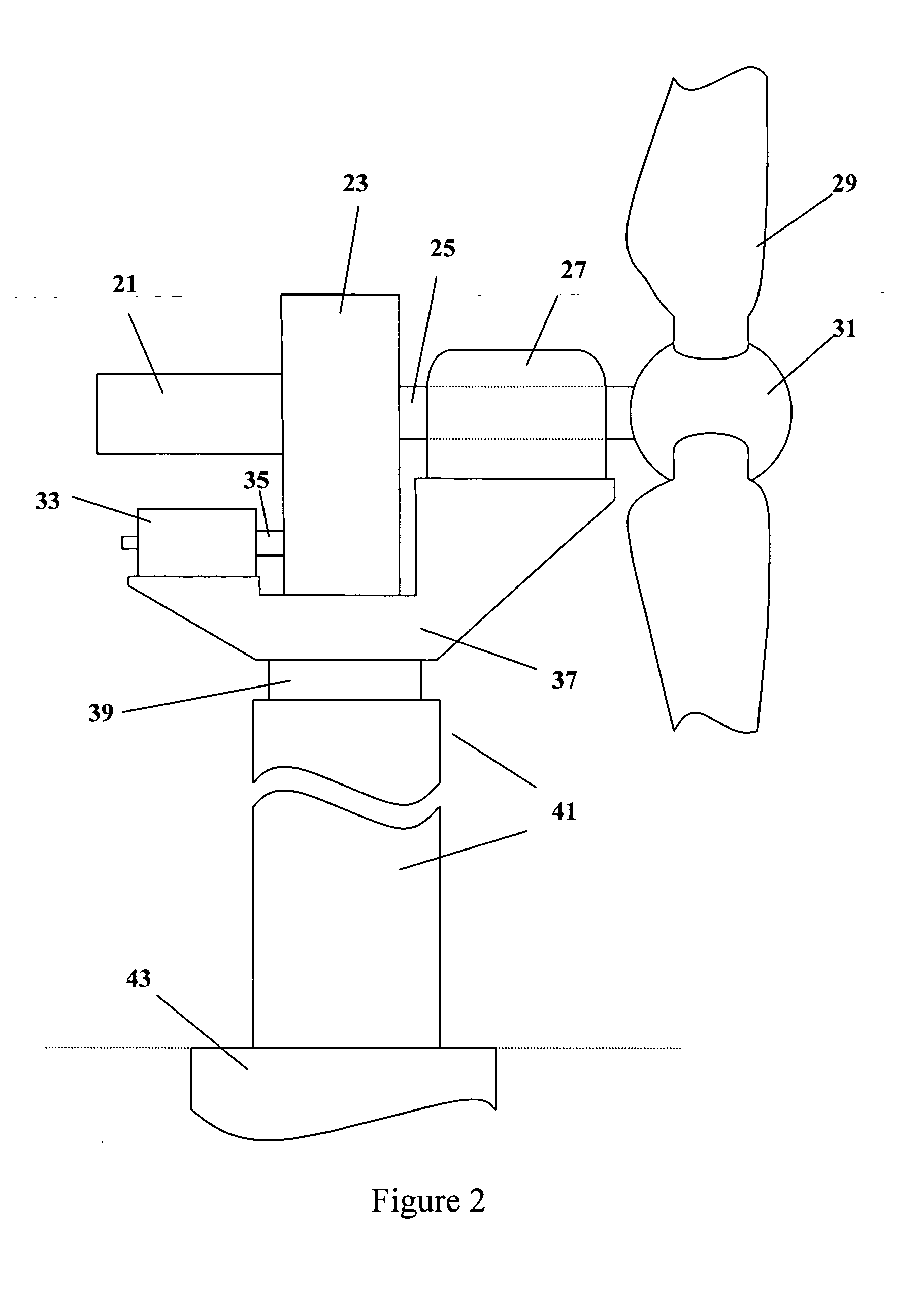
A method and mechanism for adjusting / controlling the pitch of at least one blade of a wind turbine relative to a wind direction parallel to a longitudinal main shaft of the wind turbine use a mechanism with a motor for rotating drive wheels in the angle gear around a longitudinal blade shaft via drive wheels of an angle gear. The method and mechanism can stop the complete turning of a main shaft of a wind turbine having a motor to rotate a drive pinion in an angle gear via a drive wheel, the angle gear being meant to pitch at least one blade around a longitudinal axis.
Owner:NEG MICON
Method for operating a wind park
InactiveUS20050042098A1Intuitive effectEasy to adaptPropellersPump componentsWind potentialElectric power
Wind power installations were initially always erected in the form of individual units and it is only in recent years that, caused also by administrative and building regulations, wind power installations are frequently installed in wind parks. In that respect a wind park in its smallest unit is an arrangement of at least two wind power installations, but frequently markedly more. By way of example mention may be made of the wind park at Holtriem (East Frisia) where more than 50 wind power installations are set up in an array. It is to be expected that the number of units and also the installed power of the wind power installations will also increase greatly in the forthcoming years. In most cases the wind potential is at its greatest in regions of the power supply networks with a low level of short-circuit power and low population density. It is precisely there that the technical connection limits are quickly reached by the wind power installations, with the result that it is then no longer possible for further wind power installations to be set up at such sites._A method of operating a wind park comprising a plurality of wind power installations, wherein the wind park is connected to an electrical power supply network into which the electrical power produced by the wind park is fed and the wind park and / or at least one of the wind power installations of the wind park has a control input, by means of which the electrical power of the wind park or one or more individual wind power installation or installations can be set in a range of between 0 and 100% of the respective power to be made available, in particular the nominal power, and that there is provided a data processing apparatus which is connected to the control input and by means of which the setting value is set in the range of between 0 and 100%, depending on how great is the power that the overall wind park provides at its output for feeding into the energy network and wherein the operator (PSU) of the electrical supply network to which the wind park is connected can adjust the power delivered by the wind park by way of the control input.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Helicopter vibration control system and rotary force generator for canceling vibrations
ActiveUS20060083617A1Reduce periodic vibrationInertia force compensationPropellersVibration controlControl system
A helicopter rotating hub mounted vibration control system for a helicopter rotary wing hub having a periodic vibration while rotating at a helicopter operational rotation frequency. The helicopter rotating hub mounted vibration control system includes an annular ring rotary housing attachable to the helicopter rotary wing hub and rotating with the helicopter rotary wing hub at the helicopter operational rotation frequency. The annular ring housing is centered about the rotary wing hub axis of rotation and has an electronics housing cavity subsystem and preferably an adjacent coaxial rotor housing cavity subsystem. The rotor housing cavity subsystem contains a first coaxial frameless AC ring motor having a first rotor with a first imbalance mass and a second coaxial frameless AC ring motor having a second rotor with a second imbalance mass. The electronics housing cavity subsystem contains an electronics control system which receives sensor outputs and electrically controls and drives the first coaxial frameless AC ring motor and the second coaxial frameless AC ring motor such that the first imbalance mass and the second imbalance mass are directly driven at a vibration canceling rotation frequency greater than the helicopter operational rotation frequency wherein the helicopter rotary wing hub periodic vibration is reduced.
Owner:LORD CORP
Modified Darrieus Vertical Axis Turbine
A lift-type turbine comprising at least three blades at circumferentially spaced positions is supported for rotation about a vertical axis. Each blade has an airfoil shape to generate a torque about the axis responsive to wind across the blades. A support comprising cables under tension is connected between adjacent ones of the blades to extend generally circumferentially about the turbine. Accordingly a minimum number of parts form the structure of the blades while minimizing the drag produced during rotation thereof due to the support members lying in a common circumferential path. The tension of the support members can support the blades in a pre-stressed condition to optimize the shape and performance thereof.
Owner:LUX
Blade pitch locking device for a main rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft
InactiveUS6032899AThe process is simple and effectiveLow costPropellersPump componentsTail rotorRotary wing
The present invention relates to a device for locking the pitch of the blades of a main rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft in which each blade is firstly rotated about an axis of rotation of the rotor by a rotor mast and is secondly constrained to pivot about a longitudinal pitch axis of the blade together with a pitch lever which is controlled by a pitch link connected to a rotary plate rotating with the rotor mast and belonging to a cyclic swash plate mechanism in which the rotary plate is rotatably mounted on a non-rotary plate capable of sliding axially along said rotor mast and of tilting in any direction relative to the rotor mast under the drive of at least three servo-controls each comprising a body fixed on a support secured to the aircraft and a rod having a free end secured to the non-rotary plate. The device includes immobilization means for holding the rod of each of the servo-controls relative to the corresponding body so as to lock the blades in a predetermined pitch position.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Impeller for catheter pump
An impeller for a pump is disclosed herein. The impeller can include a hub having a fixed end and a free end. The impeller can also have a plurality of blades supported by the hub. Each blade can have a fixed end coupled to the hub and a free end. The impeller can have a stored configuration and a deployed configuration, the blades in the deployed configuration extending away from the hub, and the blades in the stored configuration being compressed against the hub.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
System and method for automated real-time design checking
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
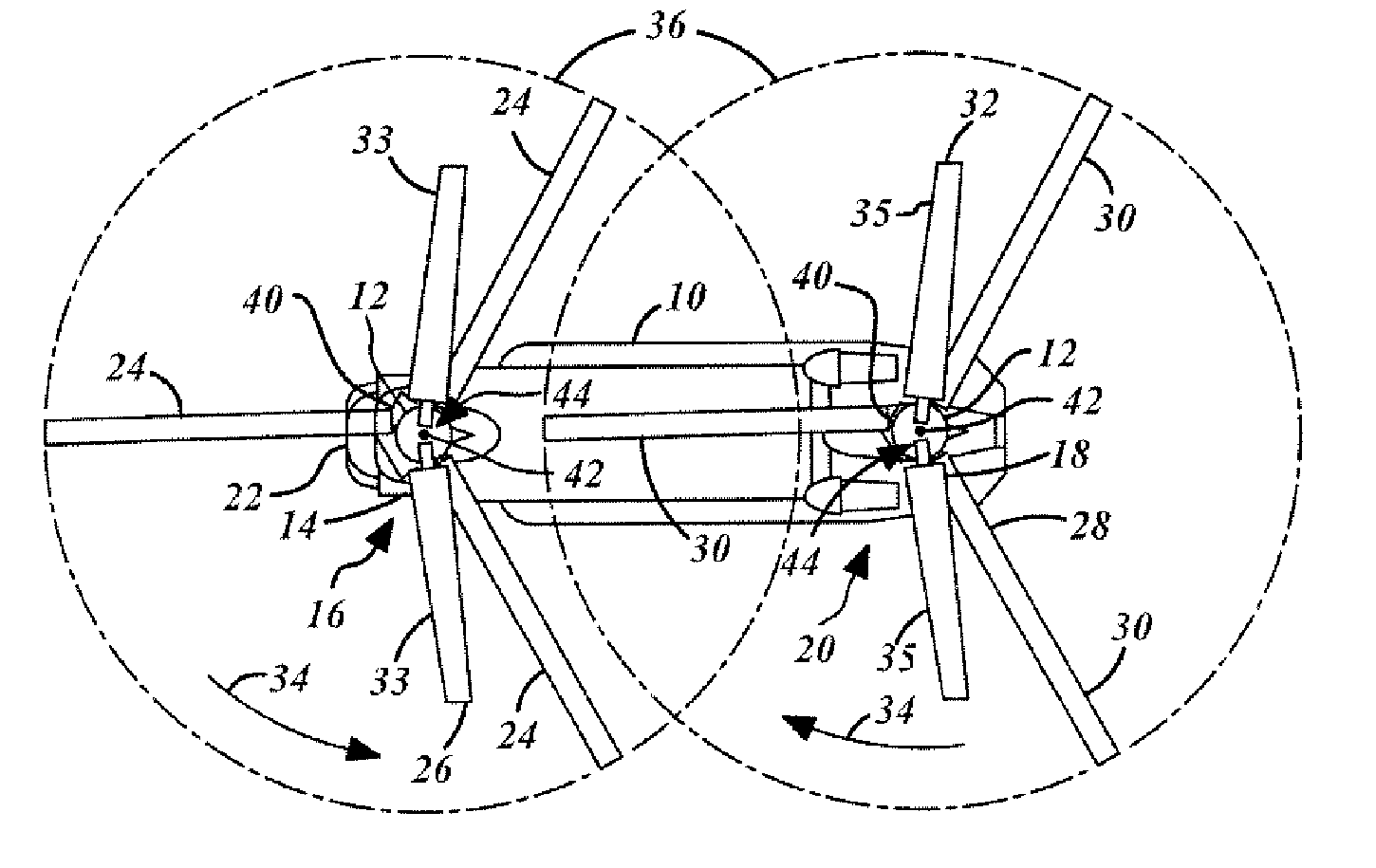
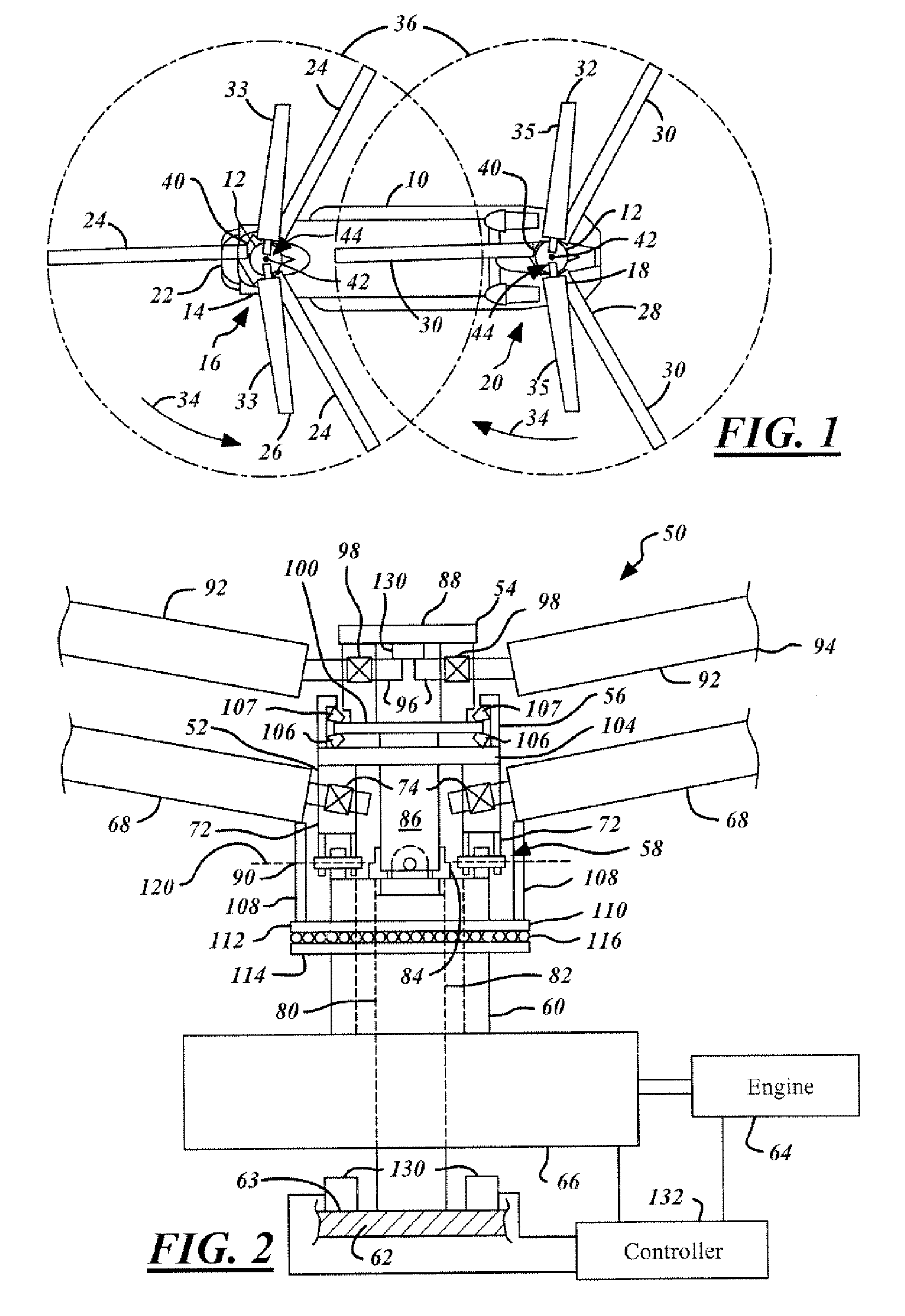
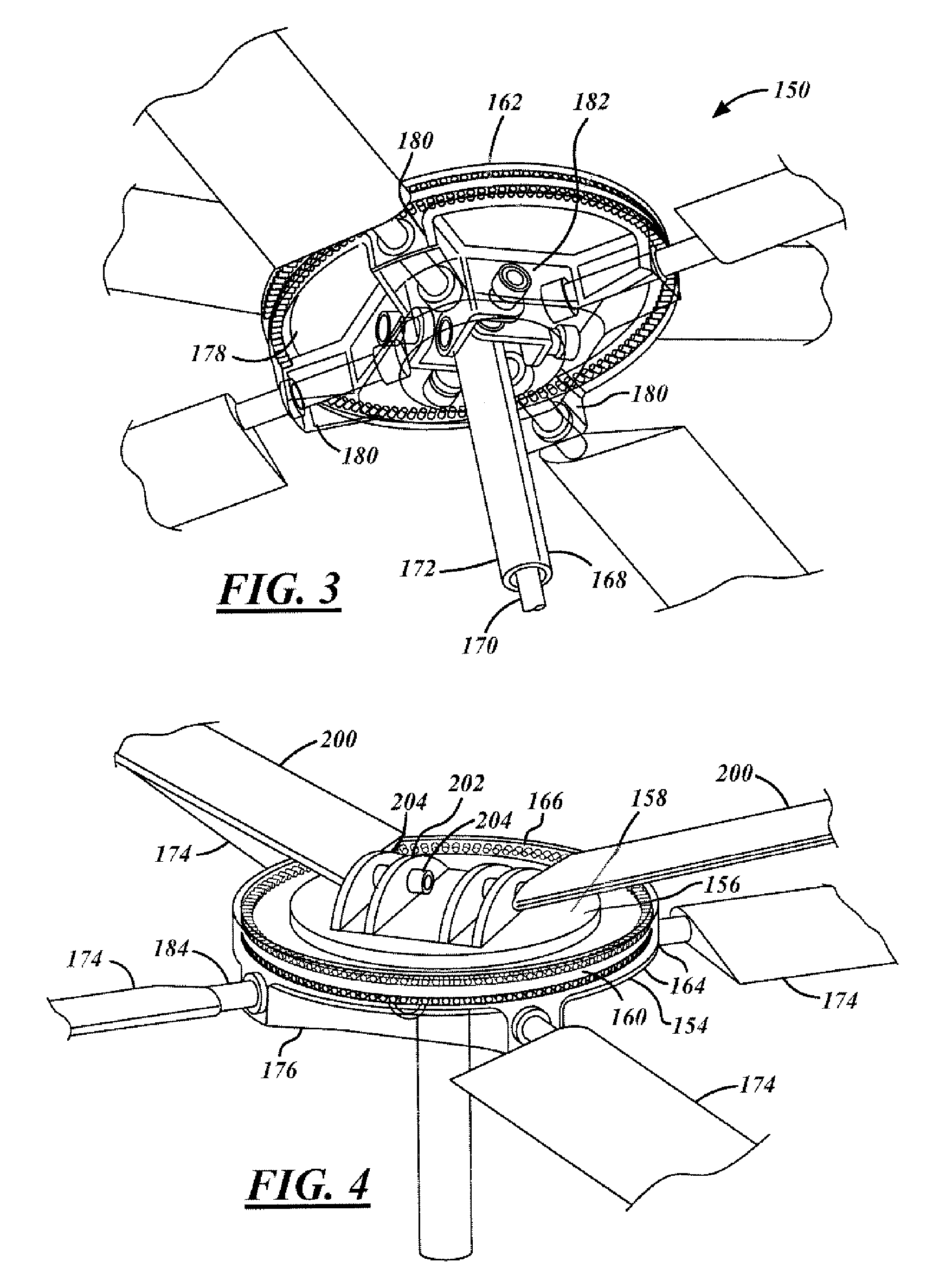
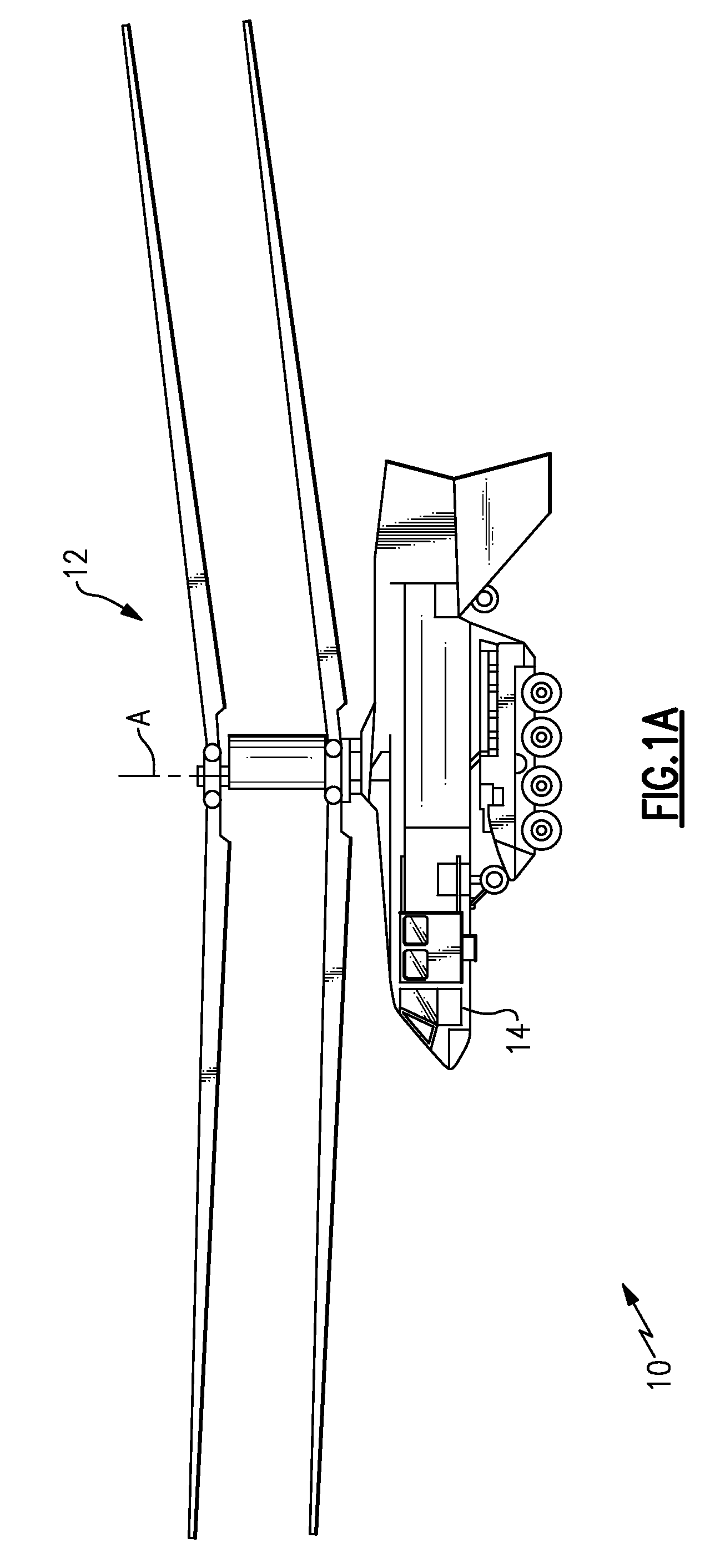
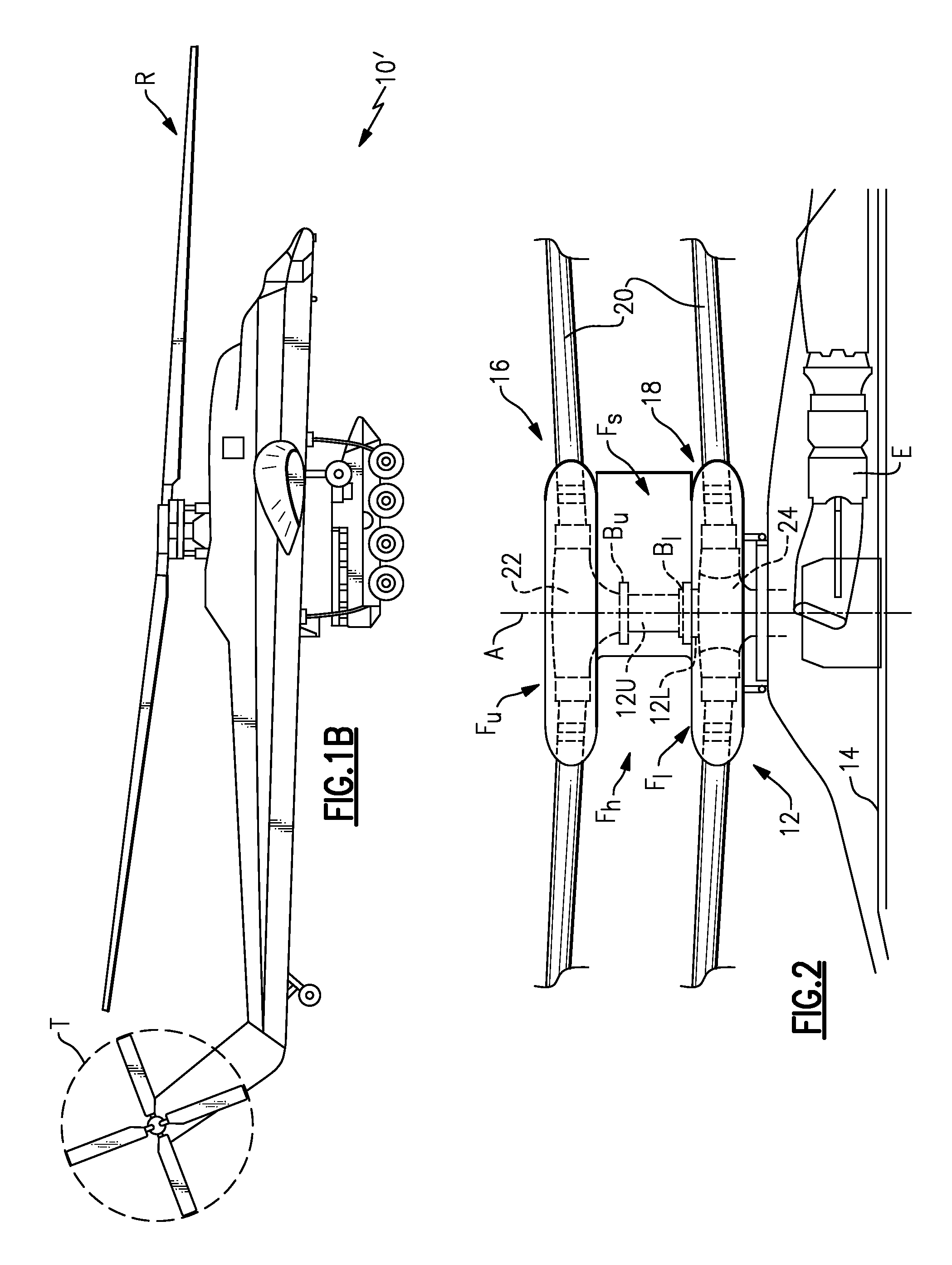
Unloaded lift offset rotor system for a helicopter
InactiveUS7264199B2Reduce resistanceFunctionality and performance improvementsPropellersPump componentsRolling momentEngineering
A rotor system (12) for a helicopter (10) includes a rotating shaft (82). A gimbaled hub assembly (56) is coupled to the rotating shaft (82). Rotating blades (24) and non-rotating blades (33) are coupled to the gimbaled hub assembly (56). The non-rotating blades (33) provide lift for the helicopter (10) in forward flight unloading the rotating blades. The rotating and non-rotating blades (24, 33) provide equal and opposite rolling moments for lift offset operation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Rotor system with pitch flap coupling
An articulated rotor system with a servo-flap rotor control system locates the focal point of a blade retention spherical elastomeric bearing inboard of a joint in the servo-flap pitch control tube which separates the flap hinge and supports the servo-flap pitch control tube on a single pivot bearing within a blade retention spindle. Rotor blade flapping produces relative movements between the servo-flap pitch control tube and the blade retention spindle which is converted through a servo-flap drive linkage into servo-flap pitch motions to provide flap / pitch coupling which reduces steady and transient blade flapping.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
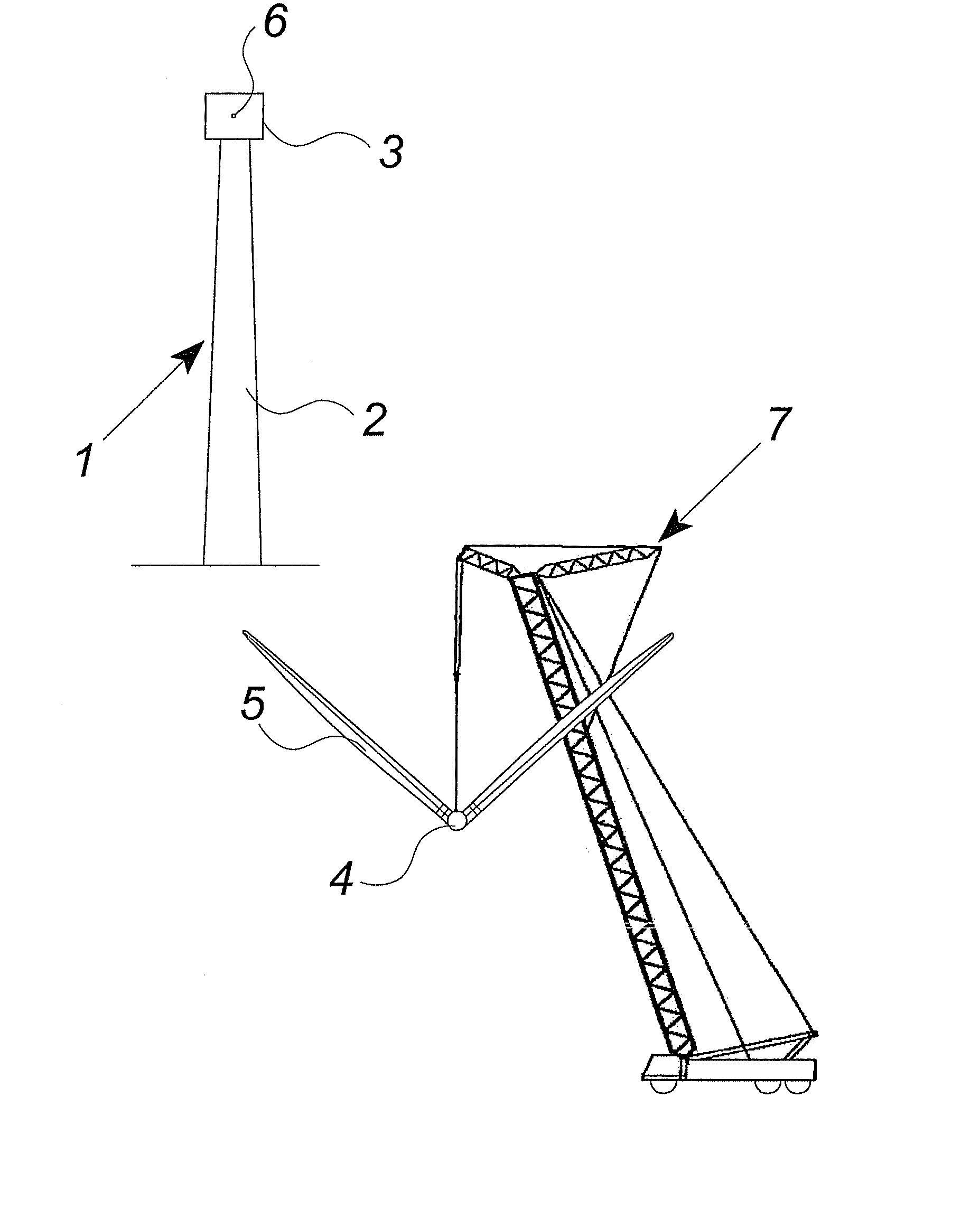
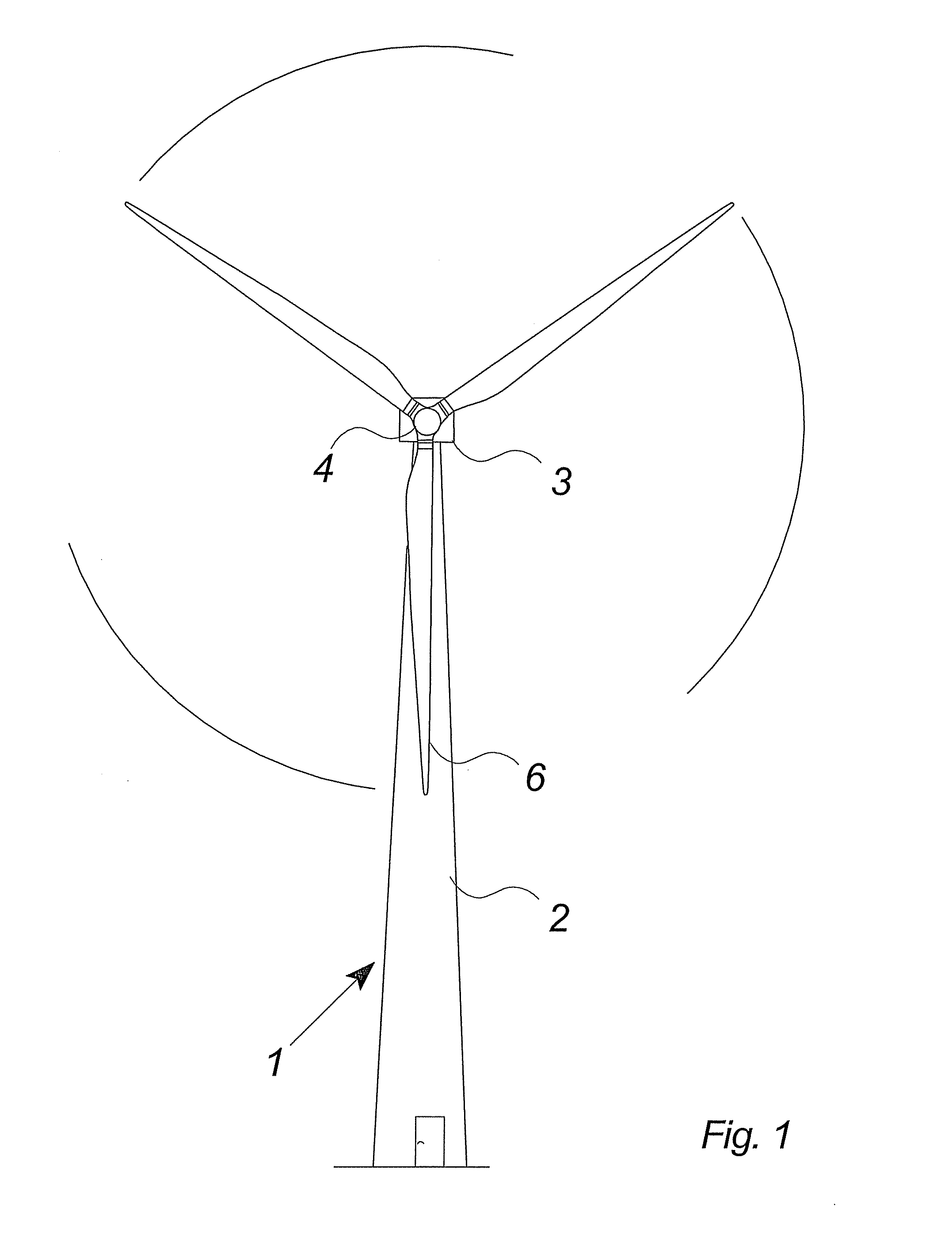
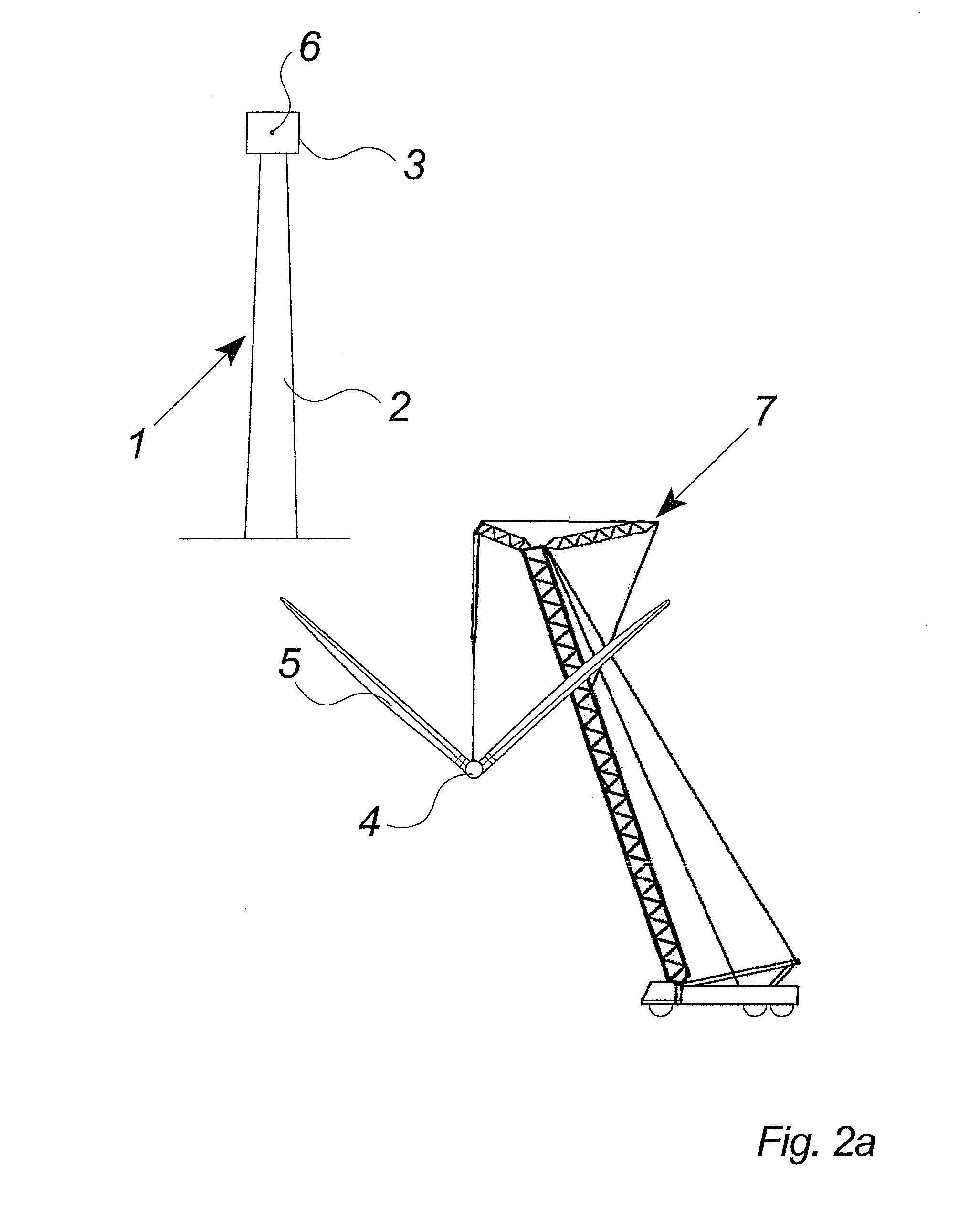
Methods of handling wind turbine blades and mounting said blades on a wind turbine, system and gripping unit for handling a wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20070266538A1Security costSafety functionalityPropellersPump componentsNacelleTurbine blade
The invention relates to methods of handling wind turbine blades and mounting said blades on a wind turbine, said method comprising the steps of lifting a wind turbine hub to the nacelle of wind turbine with a lifting system and mounting the hub on the nacelle. Further, the method comprises the steps of gripping at least one wind turbine blade with a lifting system including at least one gripping unit for handling wind turbine blades, lifting said at least one wind turbine blade into close proximity to said hub, and mounting said at least one wind turbine blade on said hub. The invention also relates to a gripping unit for handling a wind turbine blade during transport.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
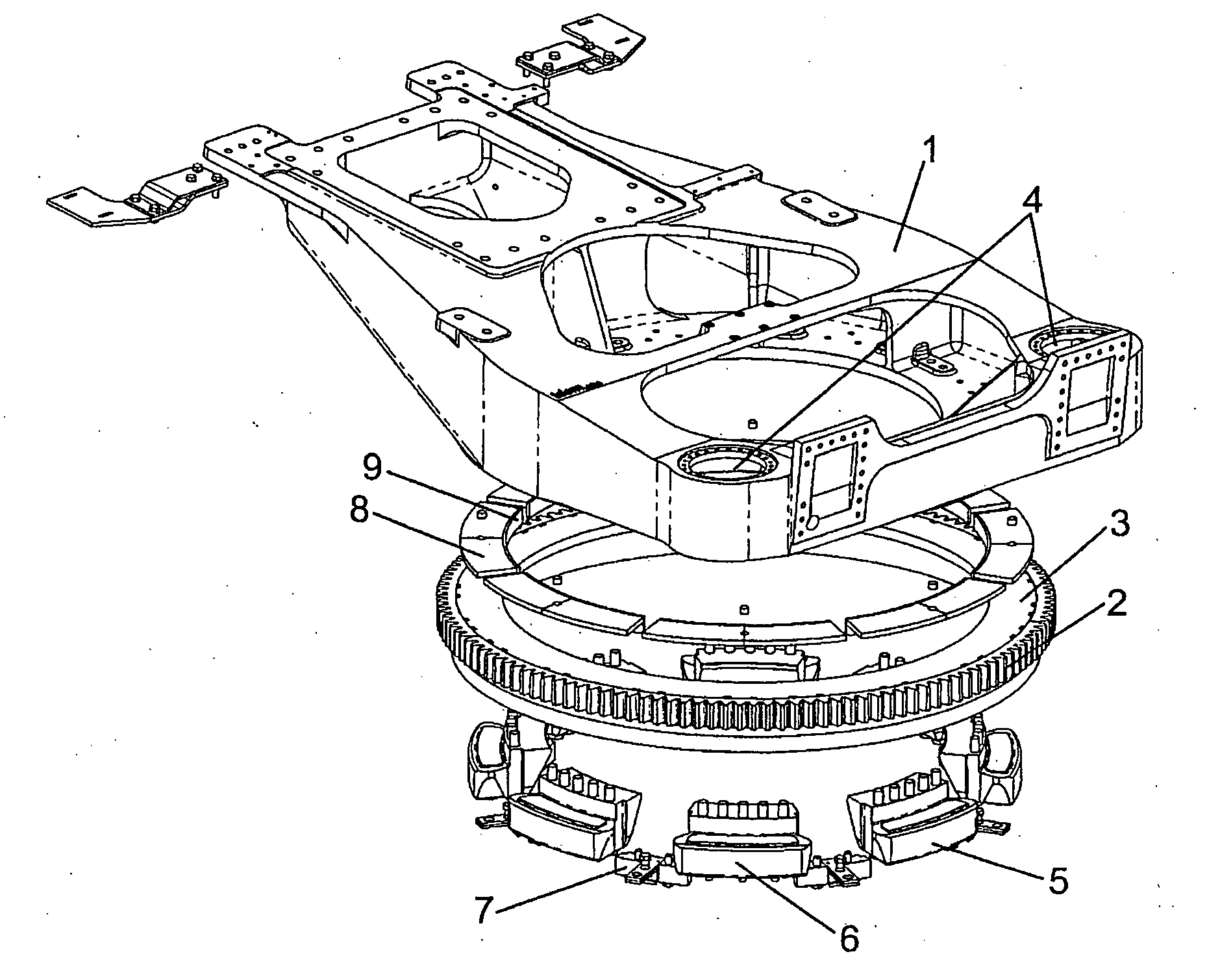
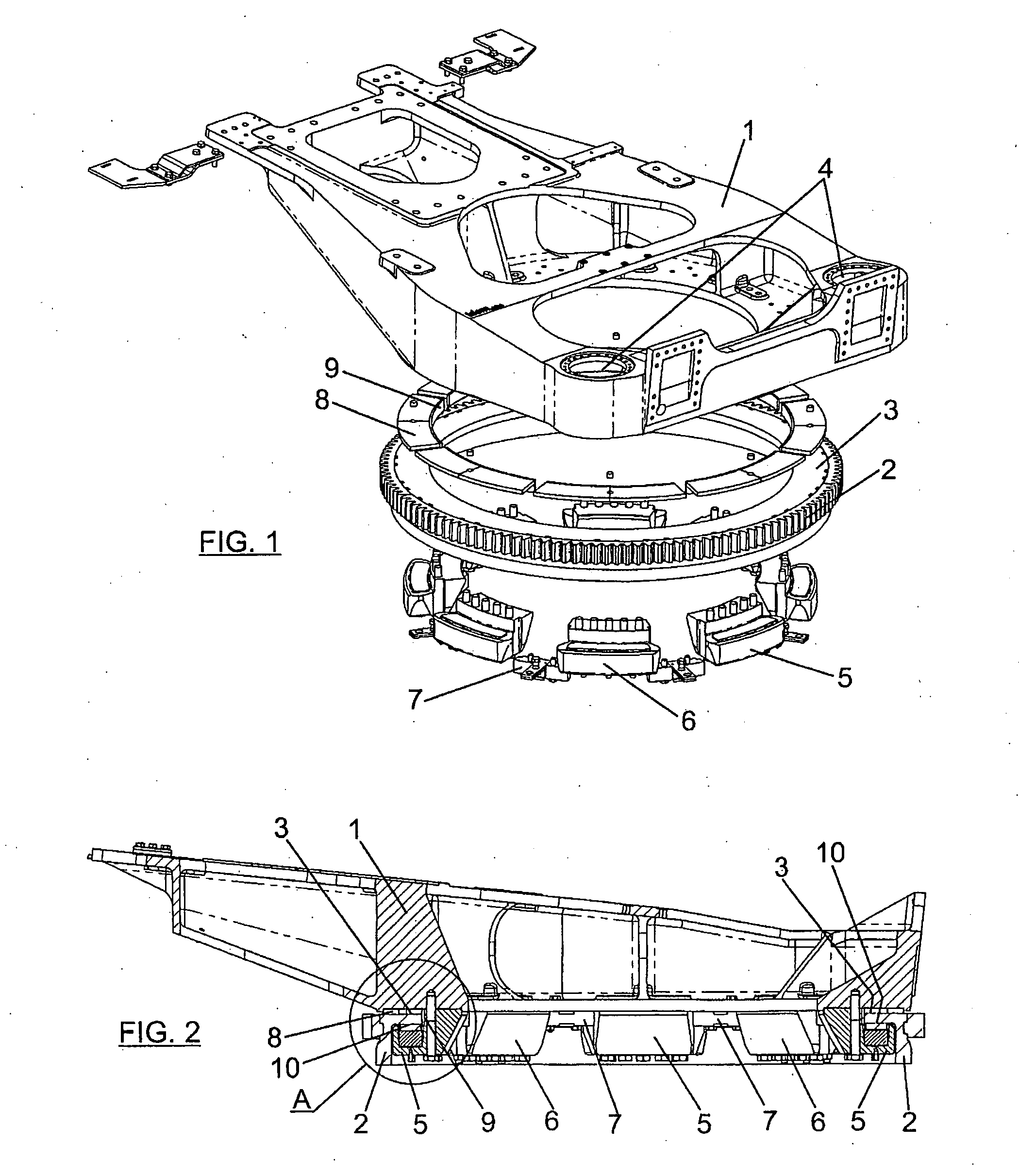
Wind turbine yawing system, wind turbine and yawing process
InactiveUS20050196280A1Improve braking effectEasily replaced in repairPropellersWind motor controlGear wheelTower
A yawing system for a wind turbine, the wind turbine comprising a tower fixed to the ground and a frame (1) housing an electric power generator, the tower and the frame (1) being joined by the yawing system which allows the orientation of the frame (1) with respect to the tower according to the direction of the wind. The yawing system comprises: a gear ring (2) fixed to the tower, the gear ring having a sliding track (3) on which the frame (1) rests and slides in its yawing movement, at least one geared motor fixed to the frame (1), meshed with the gear ring (2) through a gear wheel, at least one active braking module (5), and at least one passive braking module (6). The invention further comprises a sliding track (3) and a friction track on the gear ring, this friction track (10) being different from the sliding track (3), and the active braking modules (5) and passive braking modules (6) comprising a friction plate (11) acting on the friction track (10) of the ring. The frame (1) rests on the gear ring (2) by means of horizontal plates (8) and radial plates (9) made of a sliding material, and are kept in their position by separating parts (7). Furthermore, the gear ring (2) is divided into gear-toothed circular segments to favor its repair. Other aspects are a wind turbine with the previous yawing system and a yawing process of a turbine by means of the previous yawing system.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
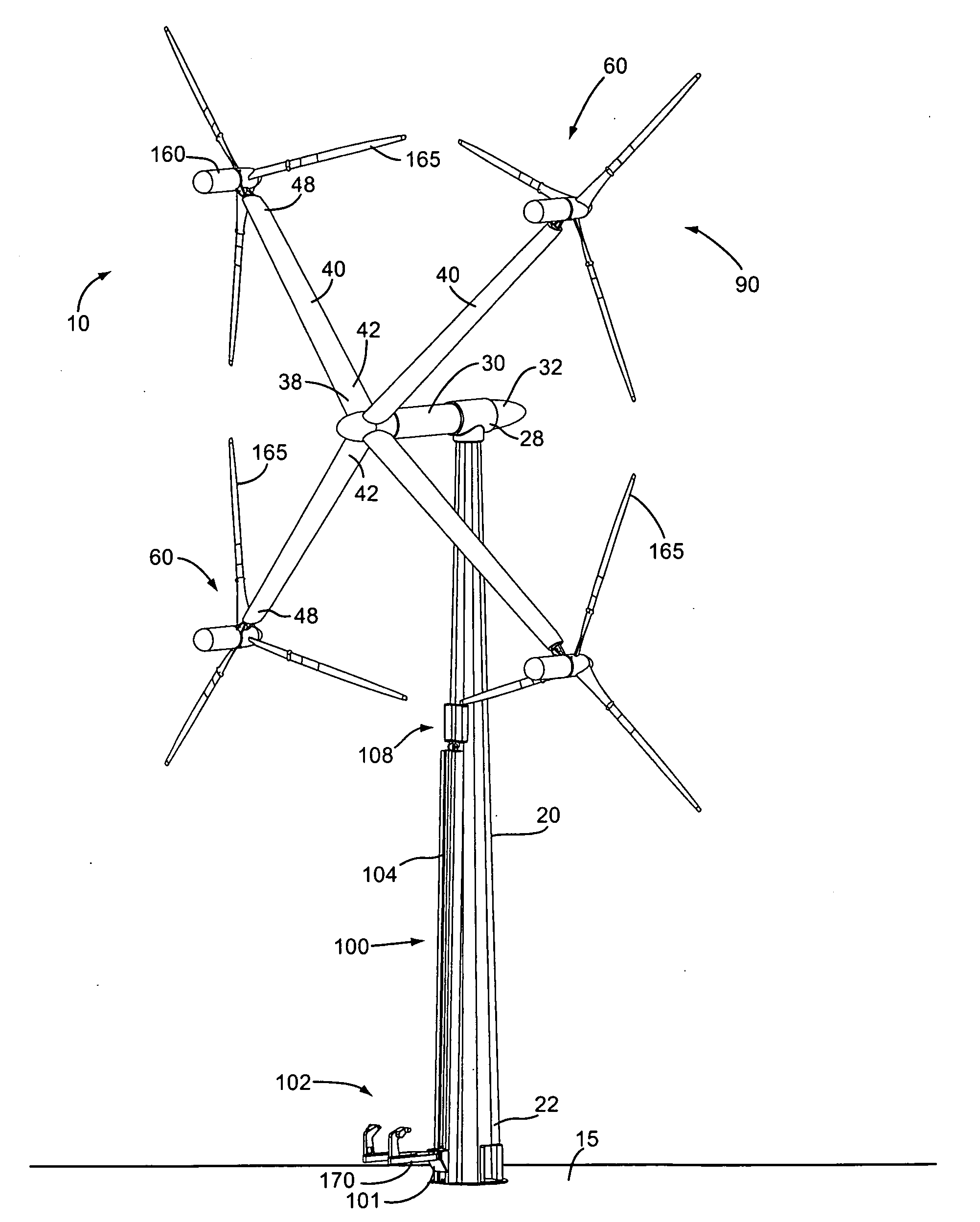
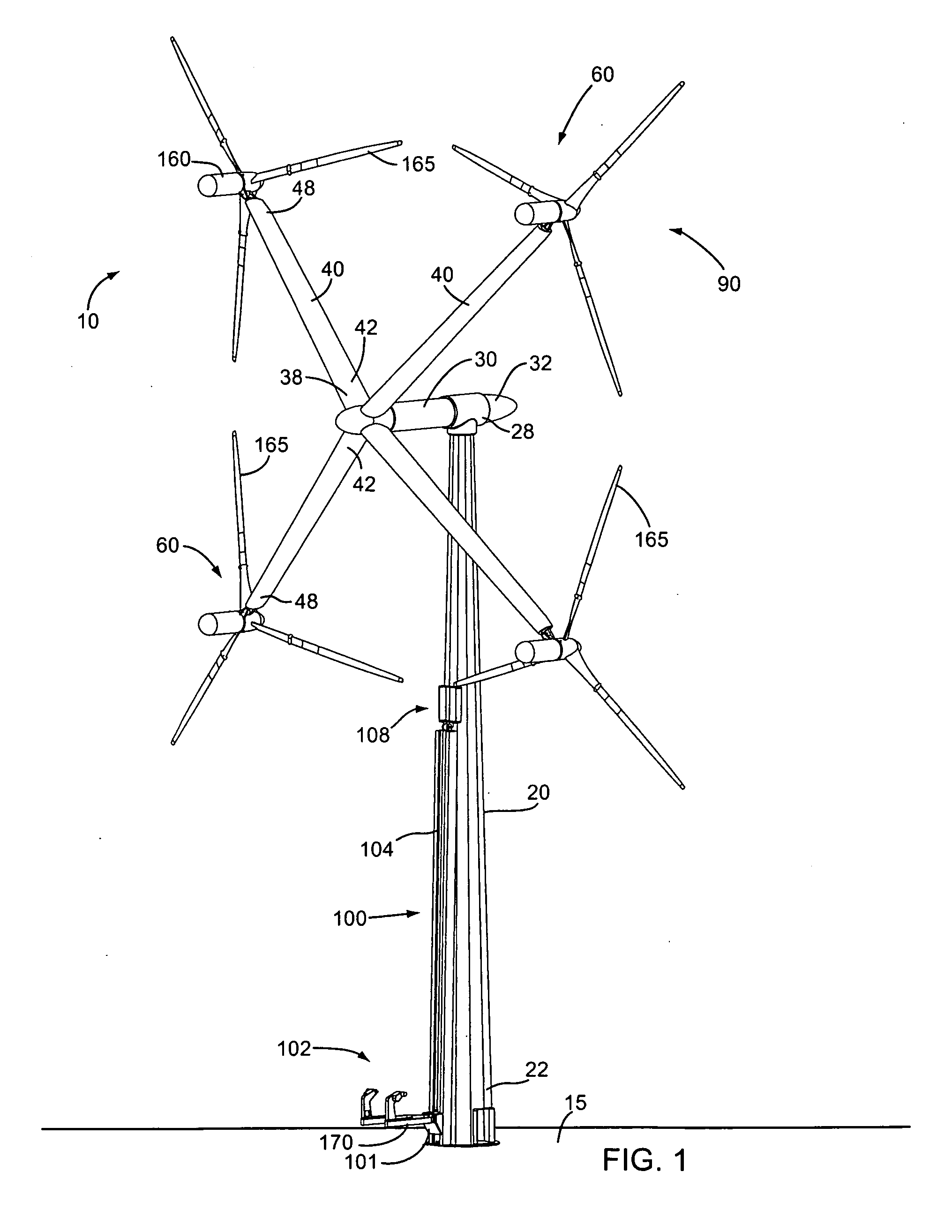
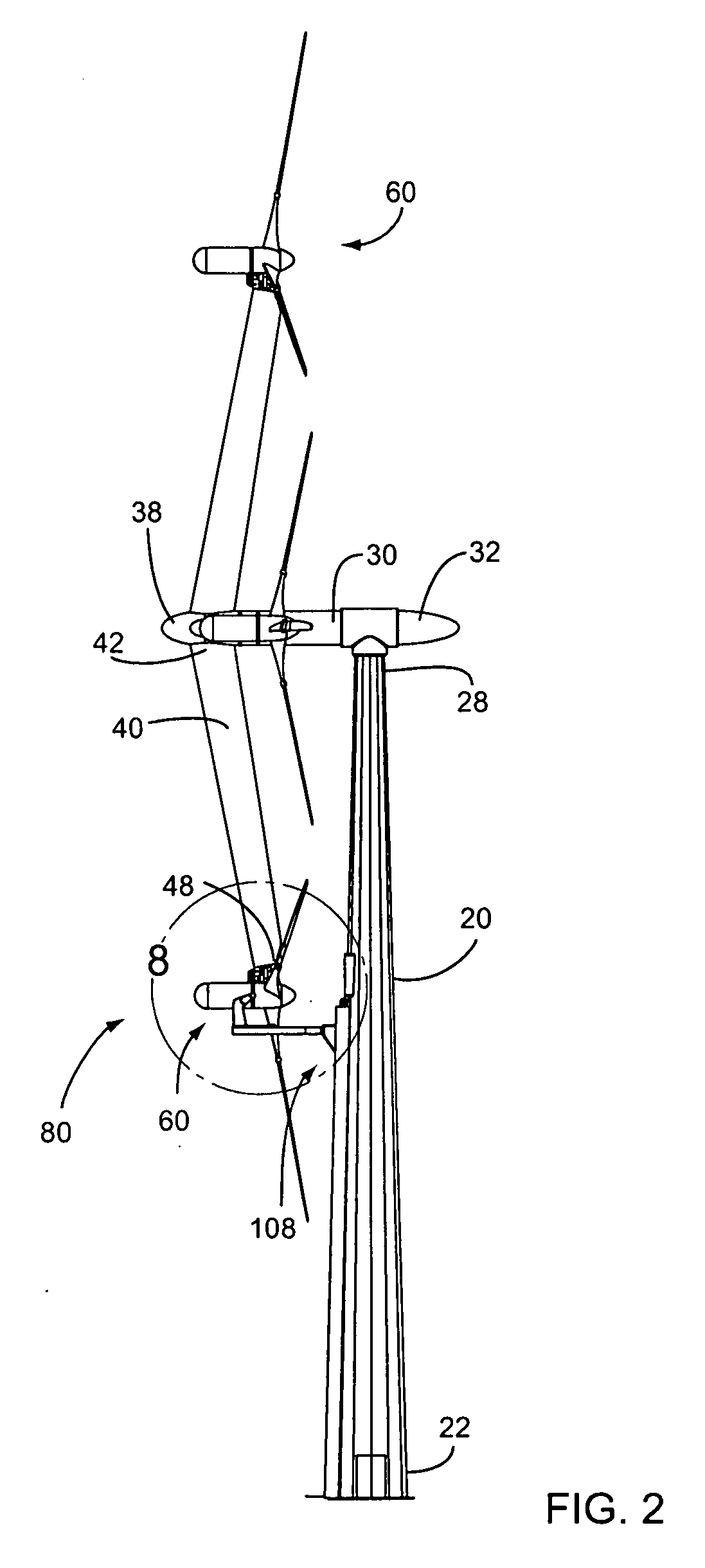
Wind turbine improvements
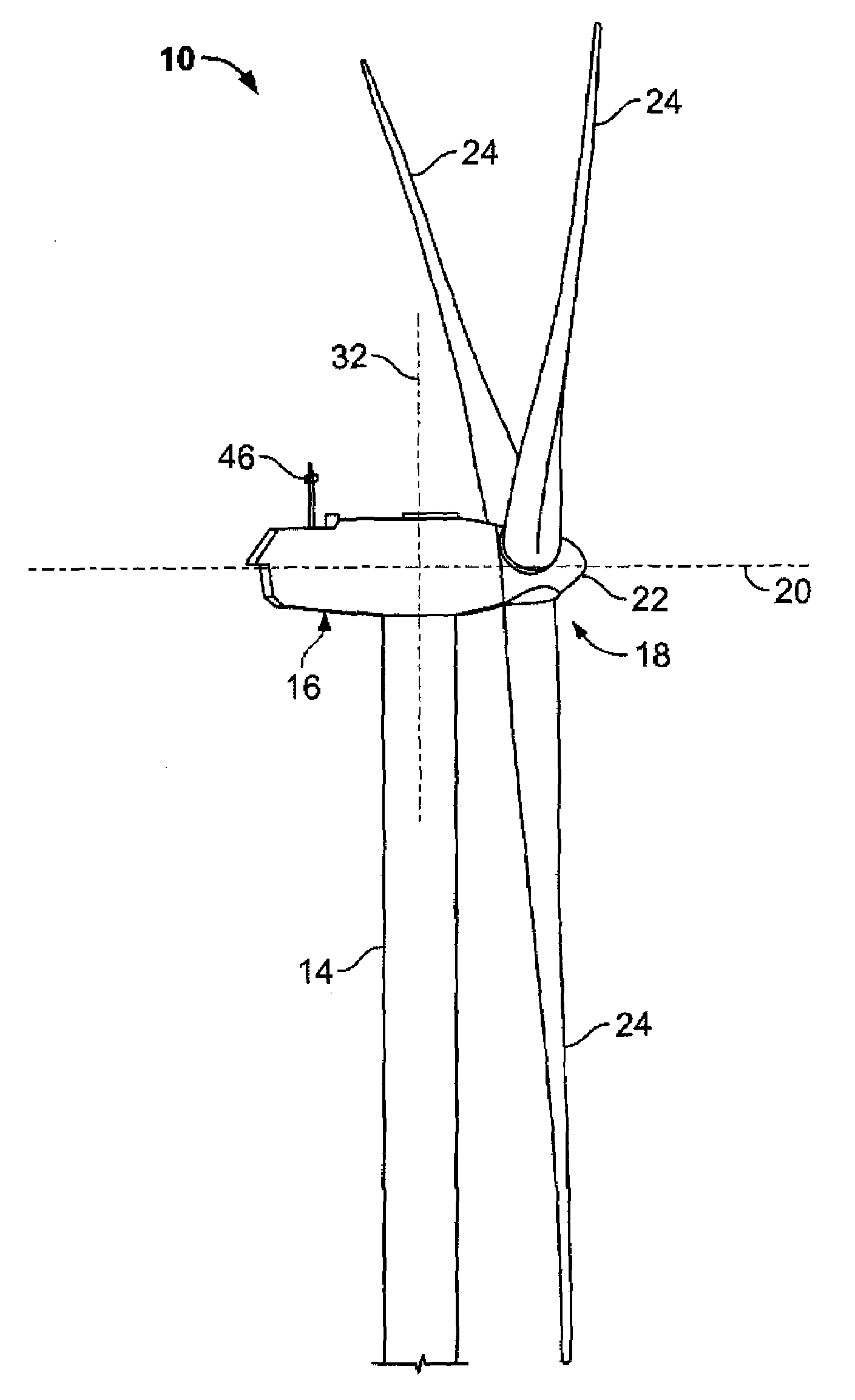
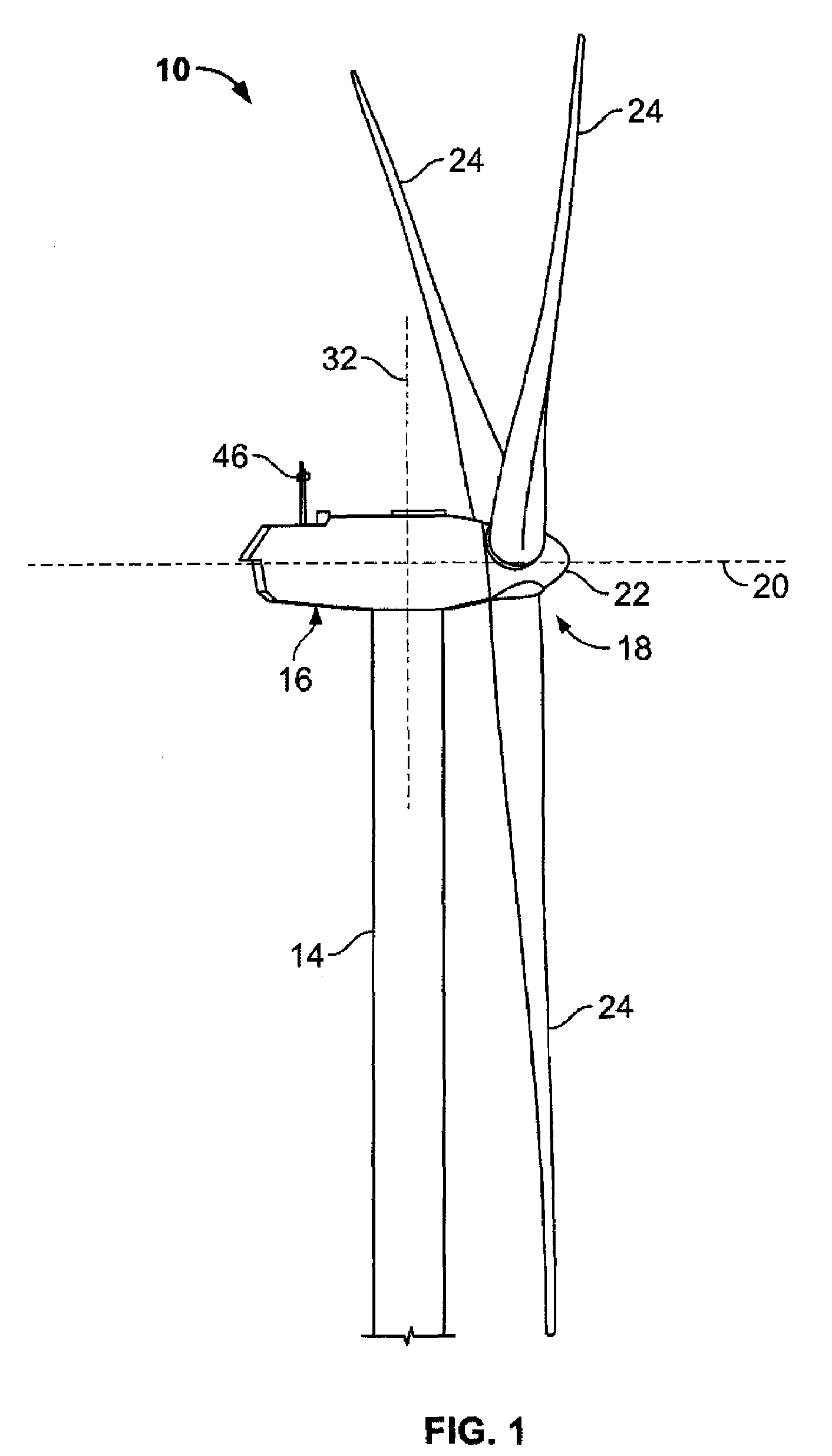
A wind turbine arrangement is disclosed that includes a substantially vertical tower mounted to a ground surface, a horizontally-extending hub rotatably fixed in a substantially horizontal plane to an upper end of the tower, at least one radial support arm rotatably fixed with a distal end of the hub, each support arm including a turbine mounting means at a distal end thereof, and at least one electricity-generating turbine selectively mountable with the turbine mounting means of the any of the support arms. An elevator means adapted to raise and lower each of the turbines between an upper loading position adjacent to a lower loading position of each support arm, and a lower loading position adjacent to the ground surface. In use, each support arm may be rotated to the loading position for receiving one of the turbines thereon. The support arm is then rotated about the hub into an operating position.
Owner:GREENWARD TECH
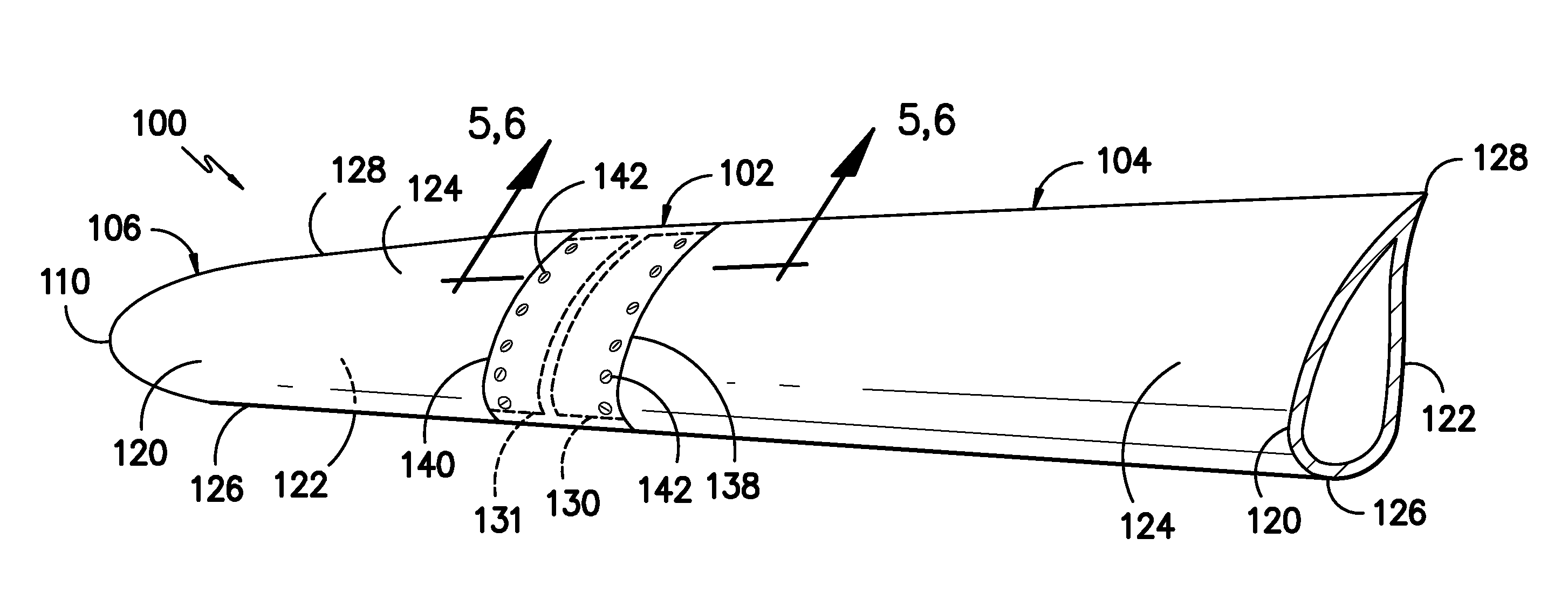
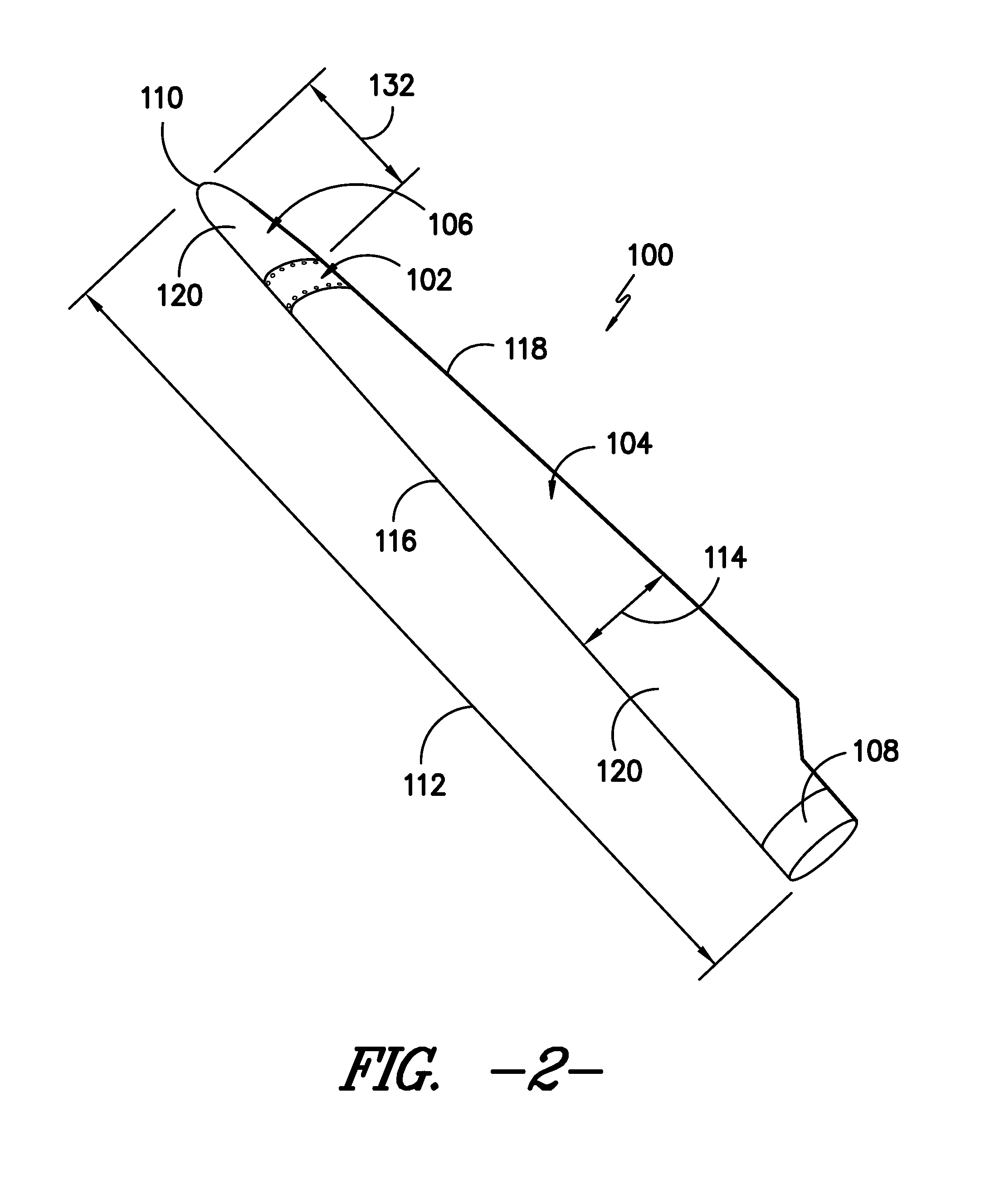
Joint sleeve for a rotor blade assembly of a wind turbine
A joint sleeve for assembling together a first blade section and a second blade section of a rotor blade assembly is disclosed. The joint sleeve may include an outer surface and an inner surface defining a cavity. The cavity may be configured to receive a joint end of the first blade section and a joint end of the second blade section. The joint sleeve may also include a plurality of openings defined between the outer and inner surfaces. The openings may be configured to receive fasteners for securing the joint ends of the first and second blade sections within the cavity. Additionally, a profile of the outer surface may be configured to generally correspond to an aerodynamic profile of the first and second blade sections such that a substantially continuous aerodynamic profile is defined between the first and second blade sections when the joint ends are inserted within the cavity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Annular flat plate paddle ship propulsion device
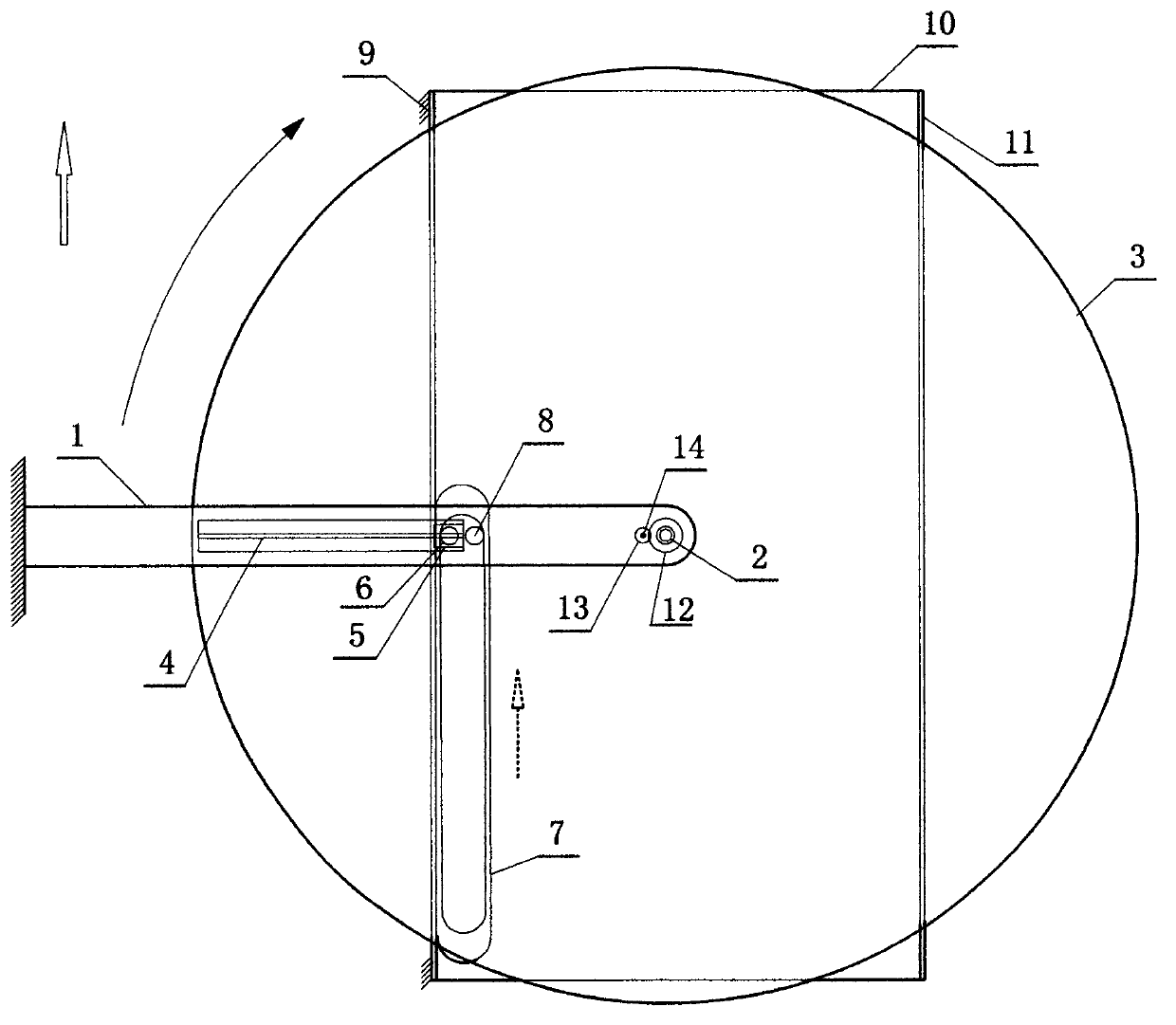
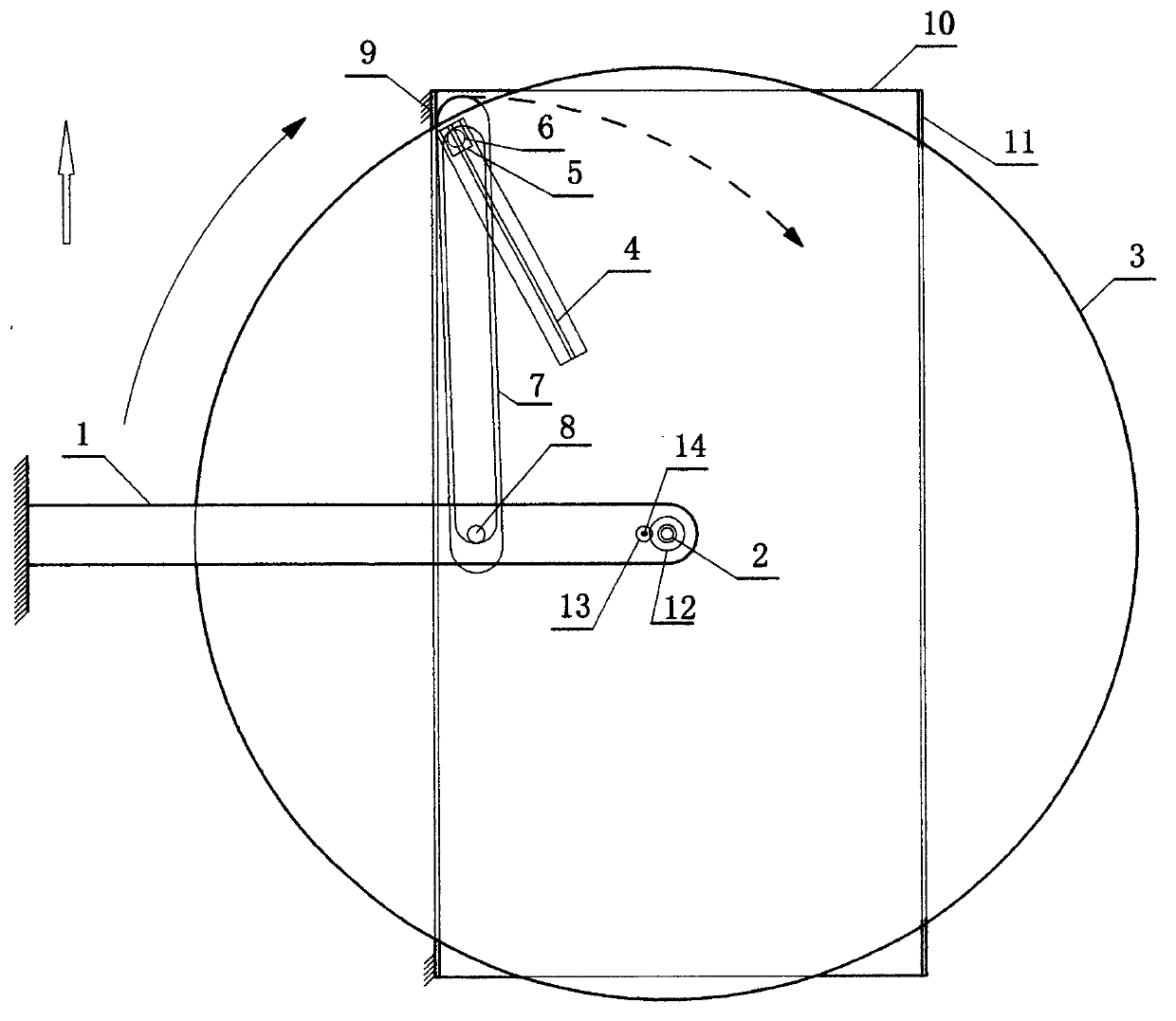
ActiveCN103121501AImprove mobilityThrust inefficiencyPropulsive elements of rotary typeRear quarterTrailing arm
The invention provides an annular flat plate paddle ship propulsion device and relates to the ship machinery technical field. The annular flat plate paddle ship propulsion device comprises a trailing arm, a rotary table shaft, a rotary table, a guide rail, a sliding block, a drag bar, a flat plate paddle, a paddle shaft, a guide plate, a base board, a side board, a driven gear, a driving gear and a power shaft, wherein the upper end and the lower end of the rotary table shaft are respectively connected with the right end of the trailing arm and the center of the rotary table; the guide plate, the base board and the side board surround to form a U-shaped groove which is placed below the rotary table; the flat plate paddle, the paddle shaft and the drag bar are vertically arranged in the U-shaped groove; power is transmitted to the rotary table through gears and then transmitted to the drag bar through the guide rail and the sliding block, and the drag bar drives the annular flat plate paddle to paddle and generate thrust. Due to limiting of the guide plate, the annular flat plate paddle moves ahead in a similar to a straight line mode after turning half circle. The annular flat plate paddle ship propulsion device is simple in structure, high in efficiency, and can be used as a thrust device for a ship and a ship model.
Owner:珠海杰腾造船有限公司
Magnetic vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7303369B2Reduce frictionMaximize operation of systemPropellersWind motor controlElectricityAlternator
A lift and drag-based vertical axis wind turbine in which the vertical axis and foils mounted thereon are magnetically levitated above the turbine's base, thereby reducing friction within the system. The foils or vanes are three-dimensionally shaped about the vertical axis so as to resemble the billowed sail of a sailing ship and capture wind through 360 degrees of rotation under any wind condition. The system has an axial flux alternator using variable resistance coils which can be individually and selectively turned on or off depending on wind conditions and electrical draw requirements. The coils can also be used to produce mechanical drag on the system as desired to brake the turbine in high wind conditions or for maintenance. The system may be programmed to assess whether electricity generated by the system can be or should be transmitted to a public grid or stored locally on a chargeable battery system.
Owner:NIAGARA CENT RES
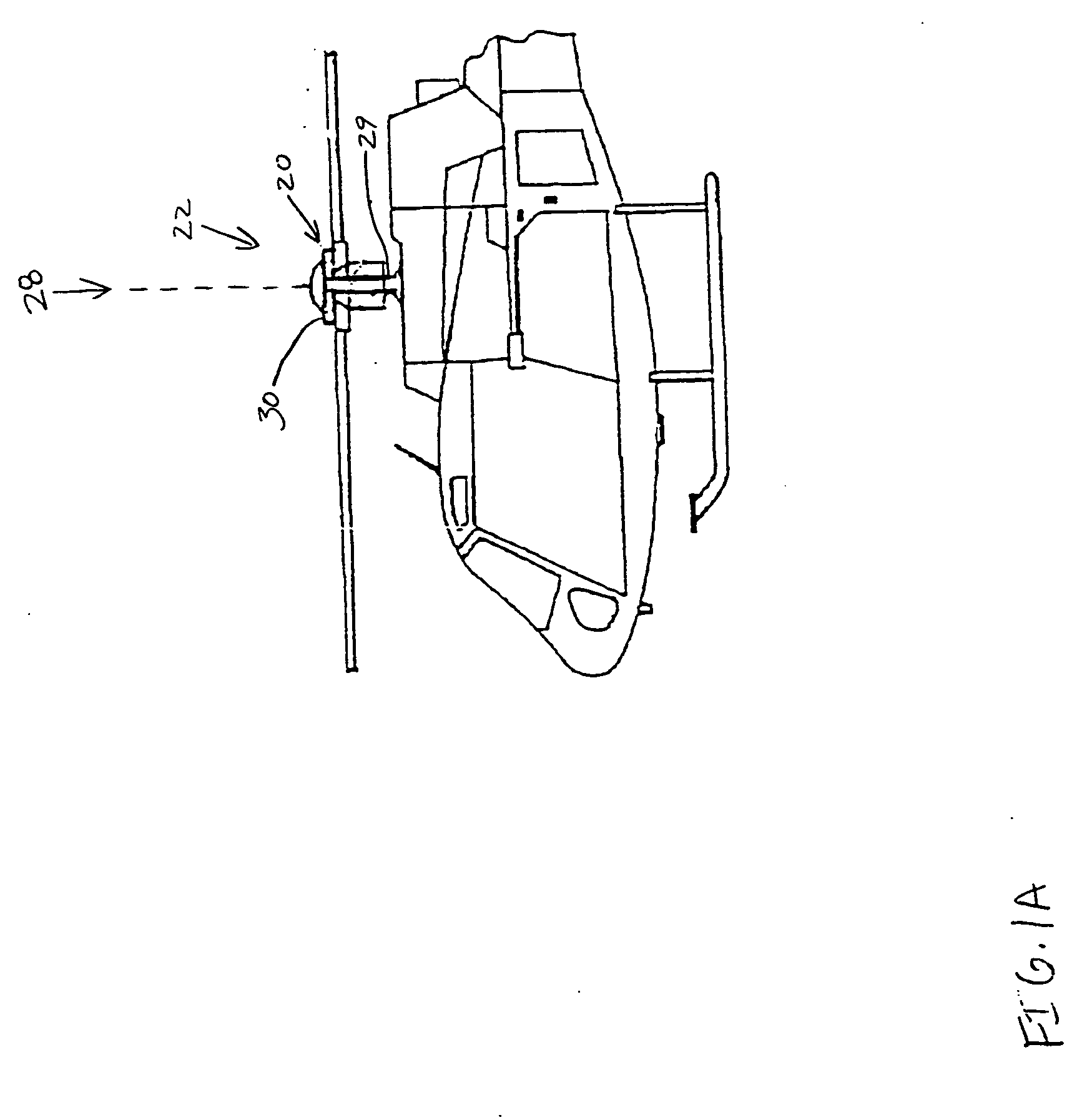
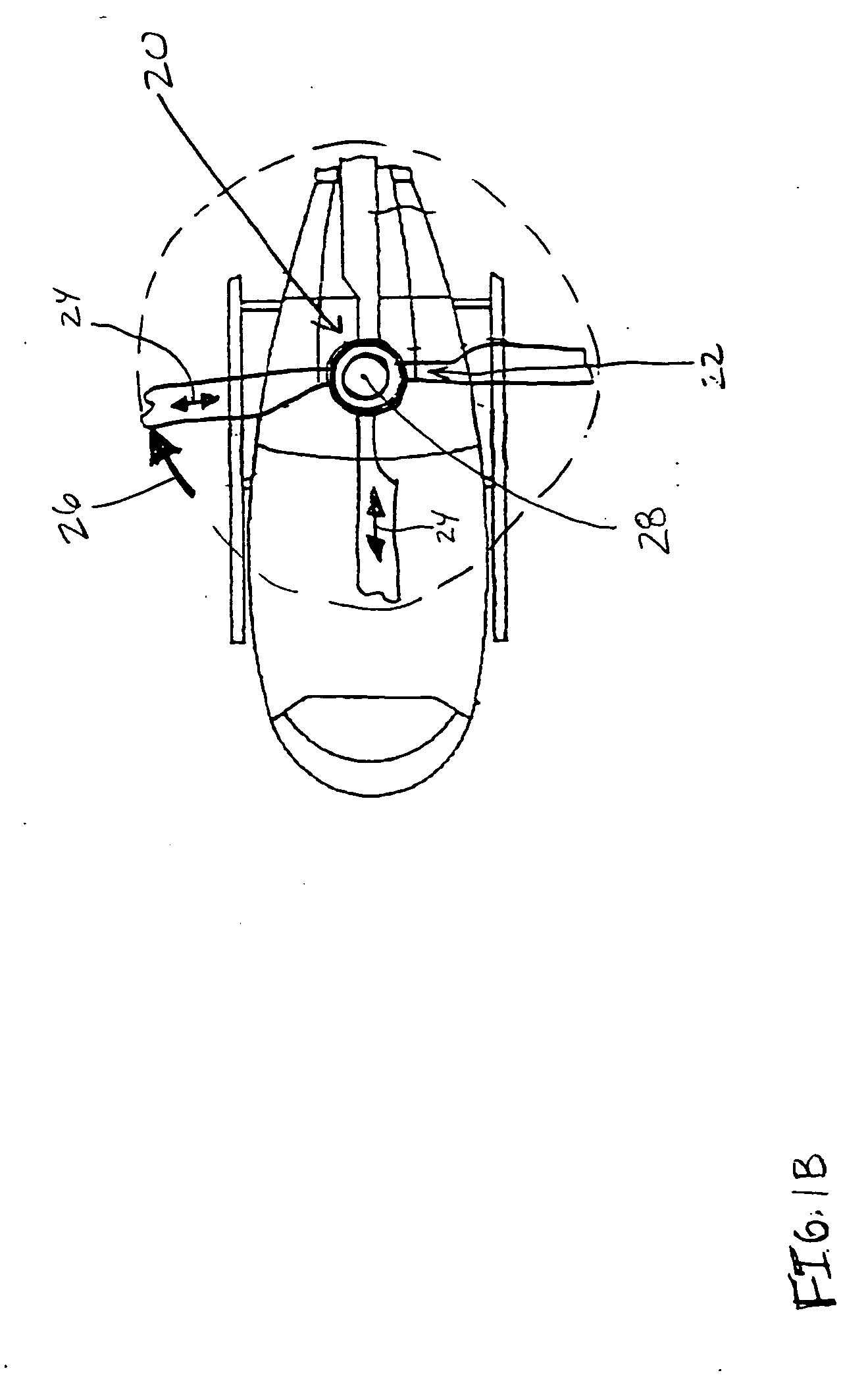
Self-guiding wind turbine
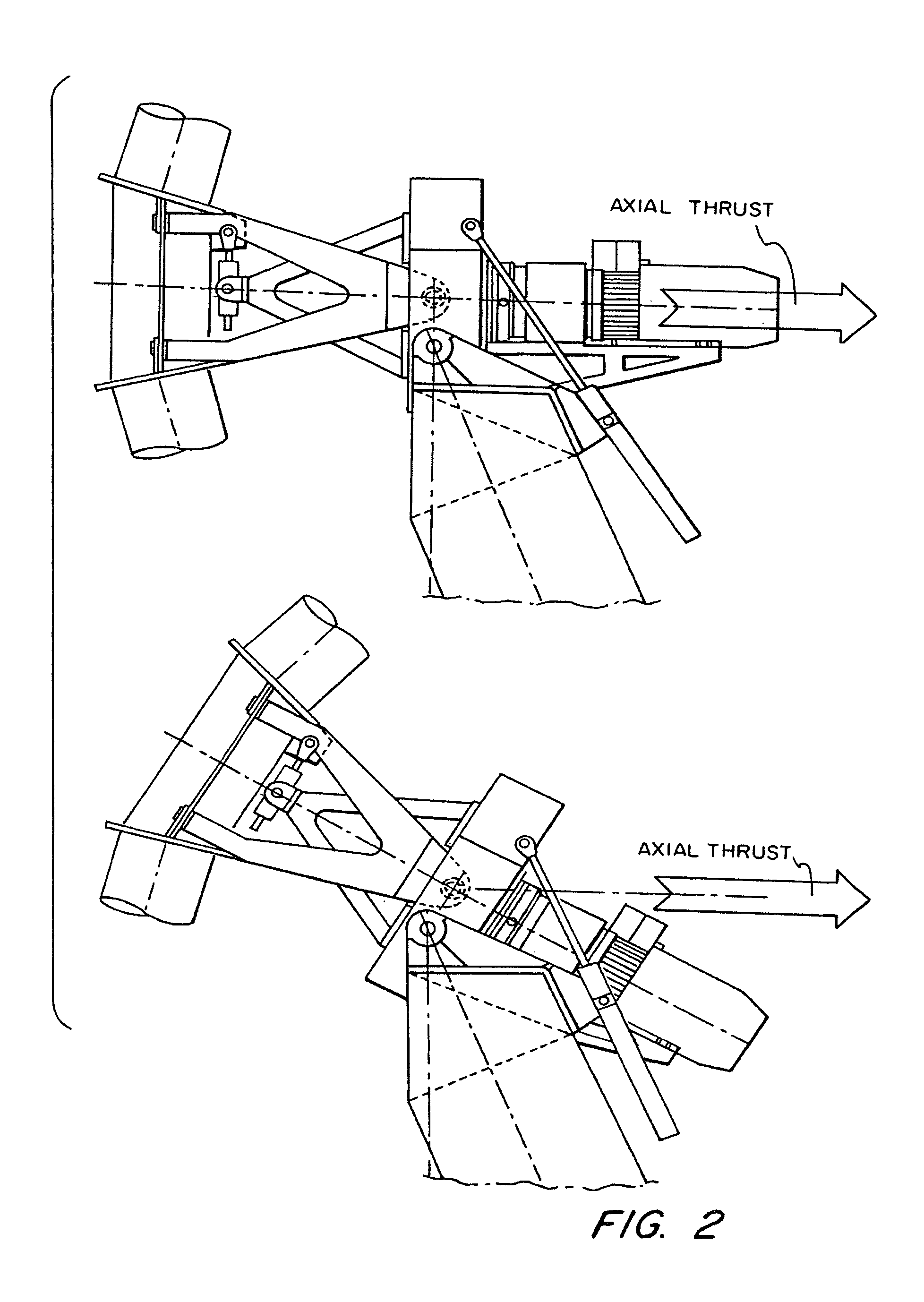
A self-guiding wind turbine made of two reinforced parallel girders whose side center of thrust is displaced from the column axis where it is supported and turns. Its dihedral-shaped two-bladed rotor is self-stabilizing since its center of thrust is behind its center of gravity and the guiding axis of the turbine, thus improving self-guiding whilst in motion. The axial thrust is controlled, whilst the head and rotor are tilting, hydraulically by counter-pressure, ensuring they do not surpass the power collected and the moments on the structure, shoe and ground. The self-guiding structure can tilt hydraulically lowering its head and rotor and facilitating its assembly and maintenance, and can remain “asleep” when not in use, thus reducing the visual impact on the environment. This turbine makes use of the force of the wind to control itself, simplifying the manufacture of large turbines connected to the network or in isolated applications.
Owner:ANTOUNE IVAN LAHUERTA
Blade-pitch-angle control device and wind power generator
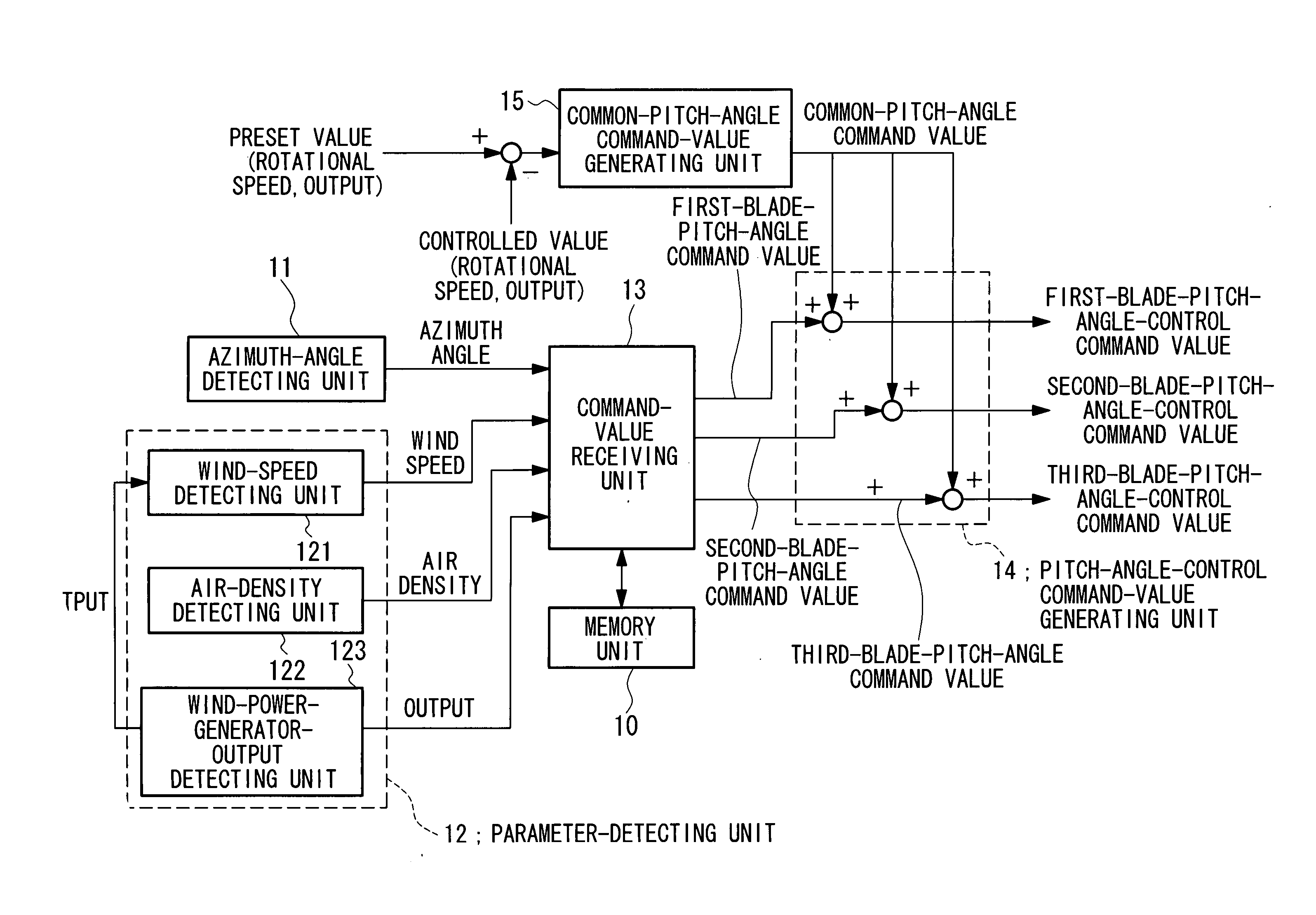
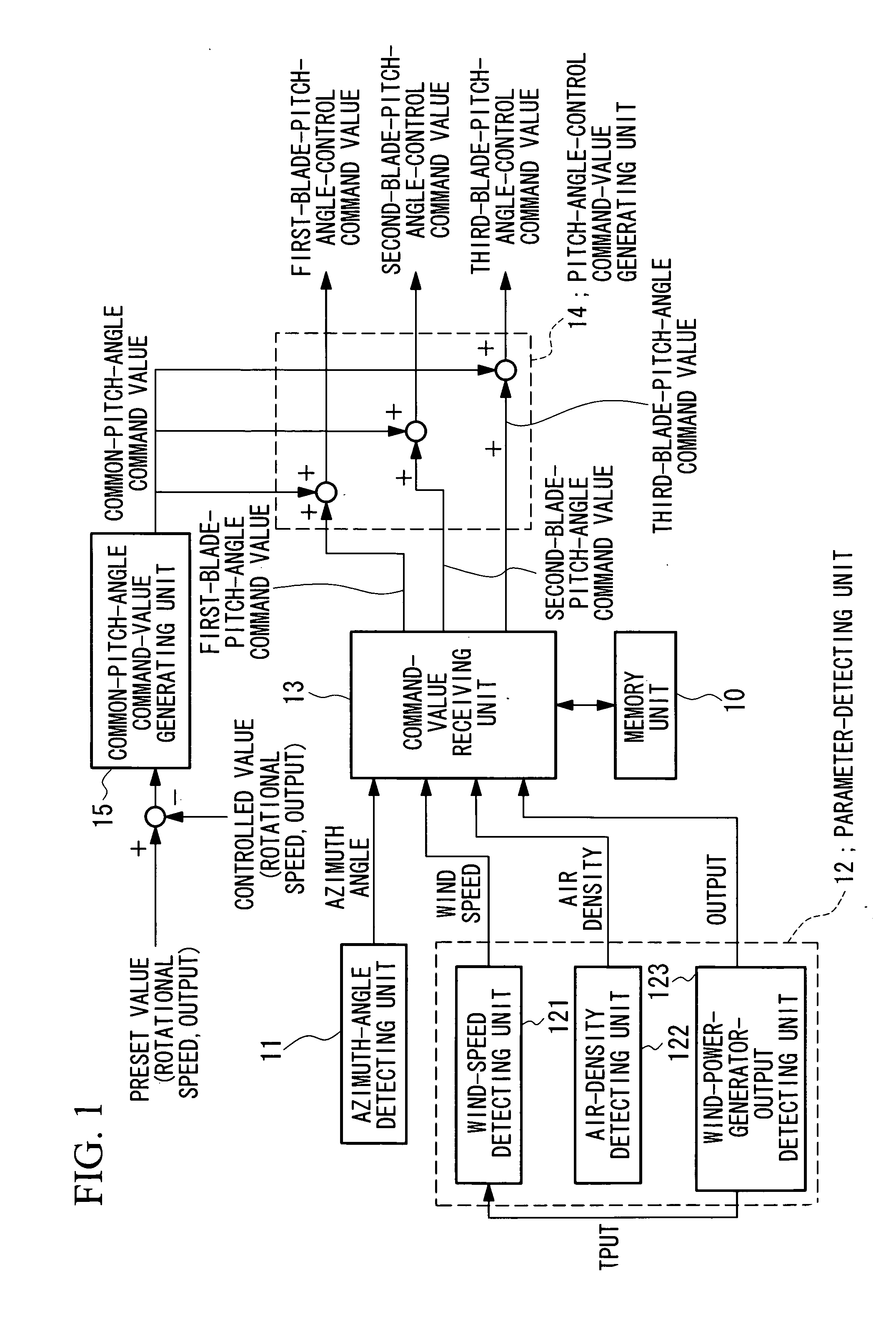
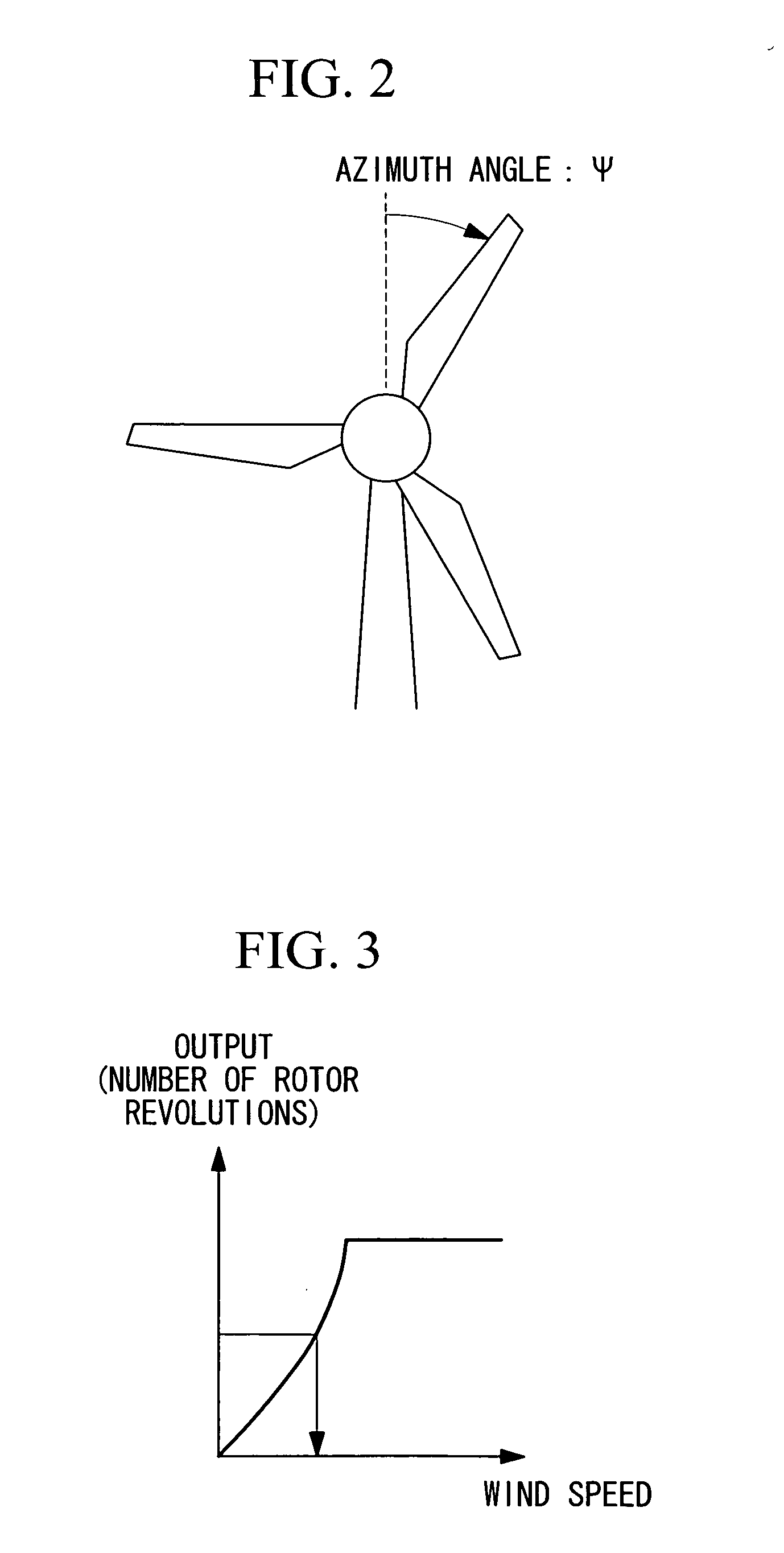
ActiveUS20070041837A1Improve accuracyReduce load fluctuationPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringBlade pitch
A blade-pitch-angle control device includes a memory unit in which predetermined parameters that affect the load fluctuation of blades, azimuth angles, and pitch-angle command values are stored in association with each other; an azimuth-angle detecting unit that detects the azimuth angle of each of the blades; a parameter-detecting unit that detects the predetermined parameters; a command-value receiving unit that receives pitch-angle command values for each of the blades from the memory unit, the pitch-angle command values being selected on the basis of the azimuth angle of each blade detected by the azimuth-angle detecting unit and the predetermined parameters detected by the parameter-detecting unit; and a pitch-angle-control command-value generating unit that generates pitch-angle-control command values for individually controlling the pitch-angle of each blade on the basis of the pitch-angle command values and a common-pitch-angle command value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method and system for performing operations on a wind turbine
A wind turbine has a nacelle frame and a first hoist substantially permanently mounted on the frame. The method comprises the processes of hoisting a second, more powerful hoist and crane on the frame with the first hoist; removably mounting the second hoist and the crane on the nacelle frame; hoisting a winch using the second hoist and the crane on the frame, and removably mounting the winch on said frame; performing operations involving handling heavy parts employing said winch; and removing and lowering said winch, crane, and second hoist from the frame.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV +1
Vertical axis wind turbine
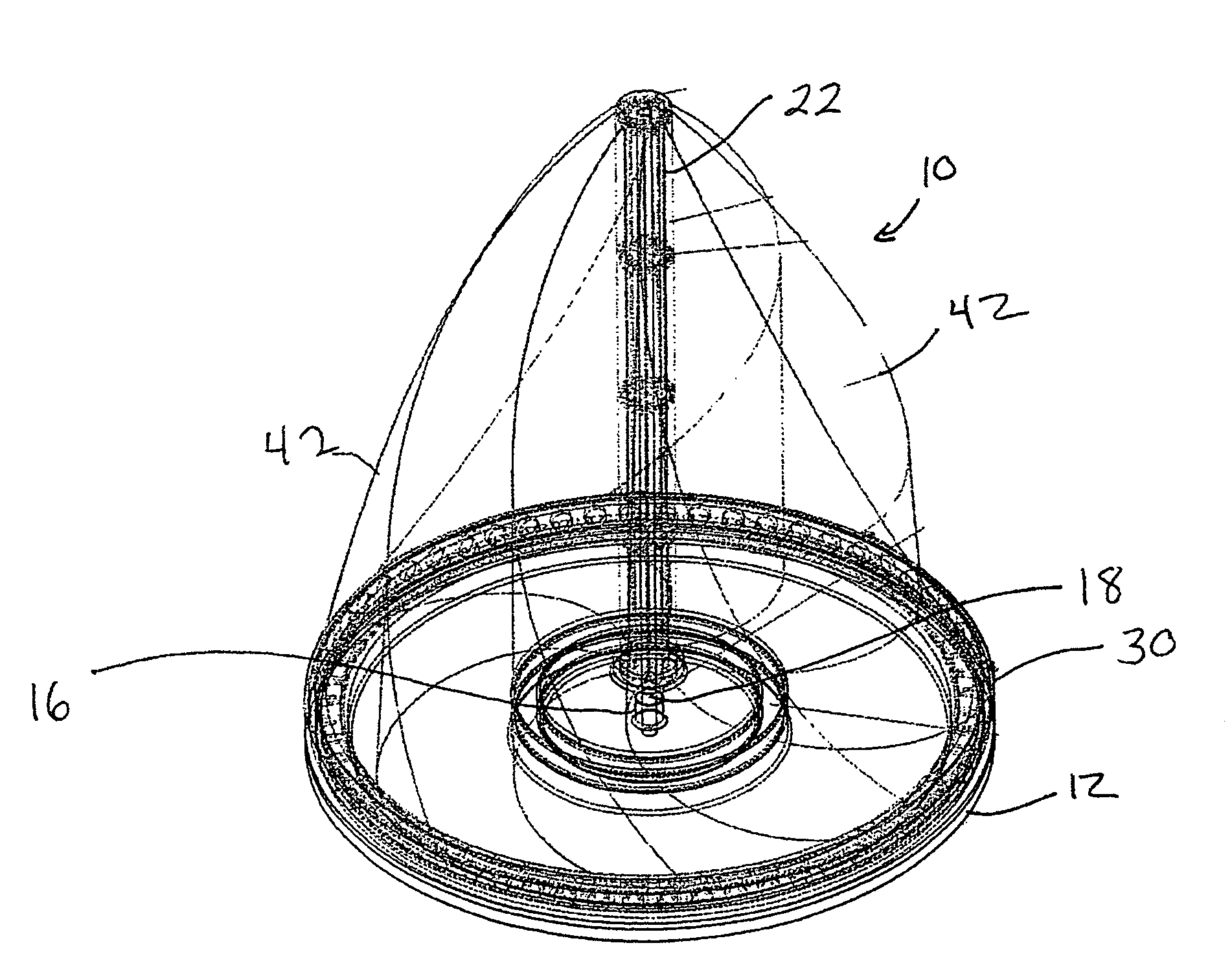
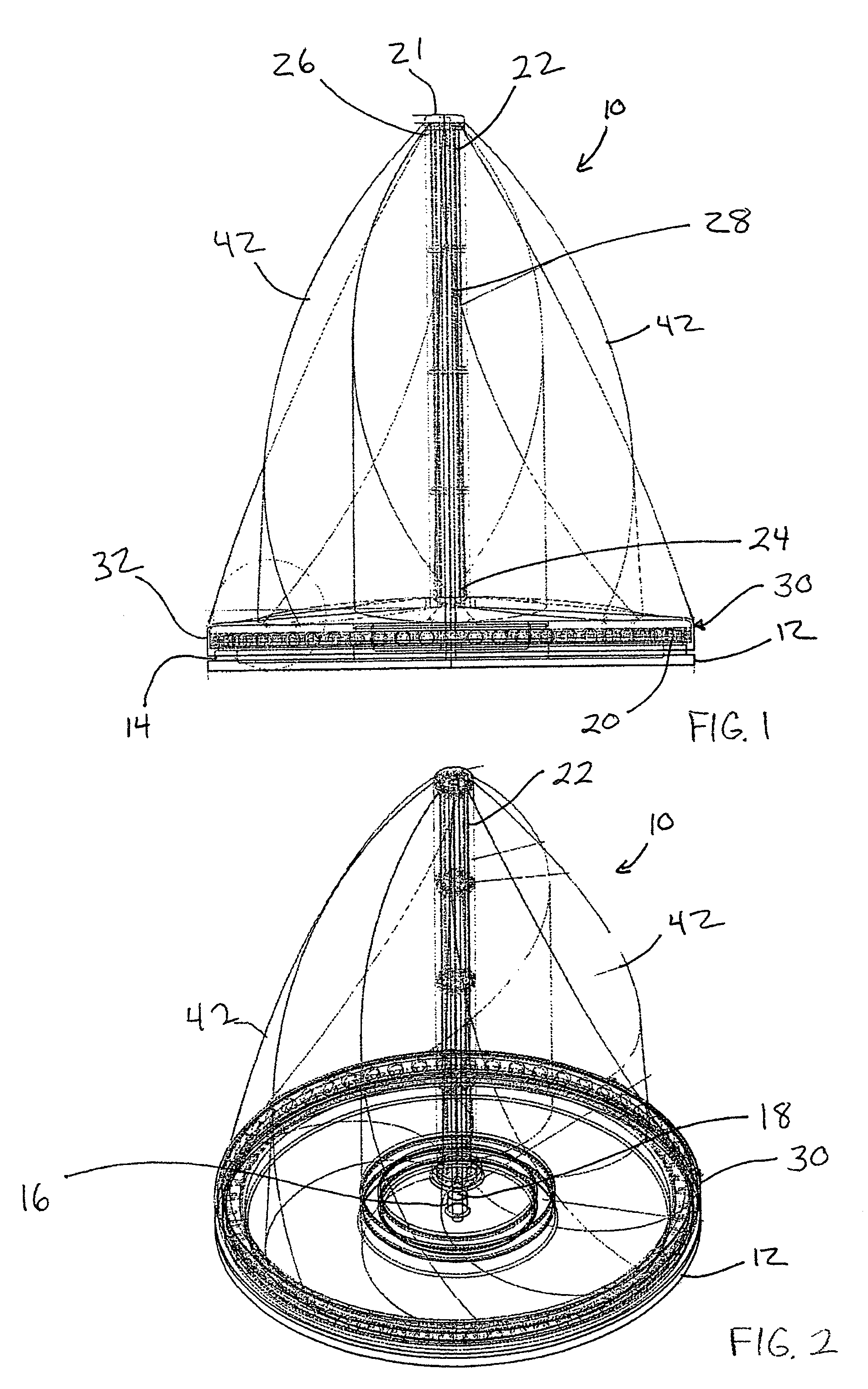
InactiveUS20070243066A1Less susceptible to flexion and extensionReduce maintenancePropellersPump componentsHydraulic pumpVertical axis wind turbine
A vertical axis sail-type wind turbine includes an array of sail-like structures that are mounted on rotating main masts. The sail-like structures can be oriented to interact with the wind. For example, when the sail-like structures are moving in a downwind direction, they are oriented to present a flat surface that is perpendicular to the wind direction. On the other hand, when the sail-like structures are moving in an upwind direction, they are oriented to present a surface that is at an angle that creates an upwind vector. The sail-like structures rotate about the sail masts, which are mounted to transverse mounting arms that are firmly mounted to a main mast. The main mast rotates, transferring power through a gear and shaft drive to hydraulic pumps in the tower. This hydraulic fluid pressure is then used to drive an electrical generator.
Owner:BARON RICHARD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com