Methods and apparatus for operating a wind turbine
a technology of wind turbines and control apparatuses, which is applied in the direction of liquid fuel engines, vessel construction, marine propulsion, etc., can solve the problems of short-term increase in generator speed and/or electric power output that may be difficult for a controller of the wind turbine to process, and the need of new, reinforced components, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the load acting on components and reducing the power outpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
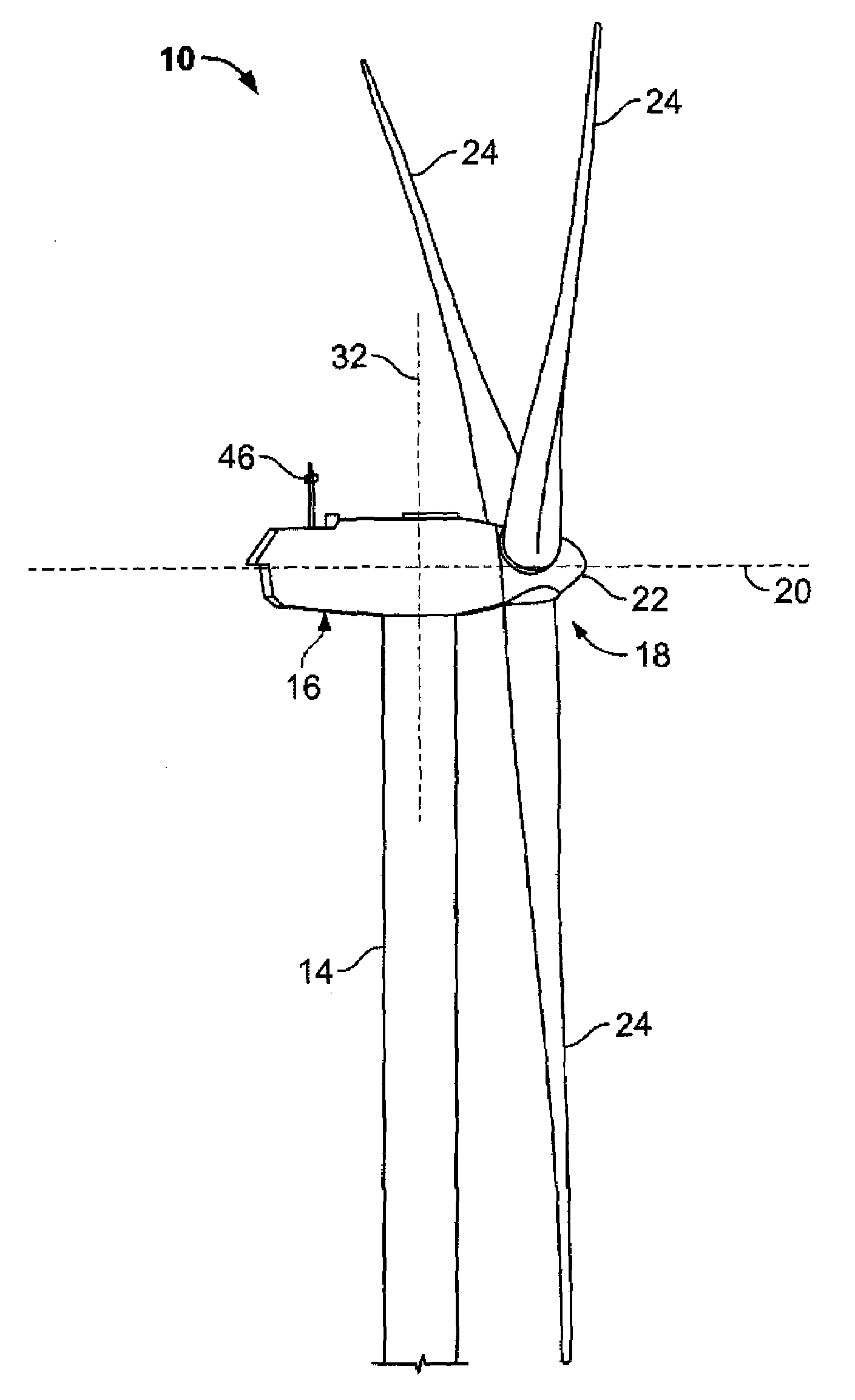
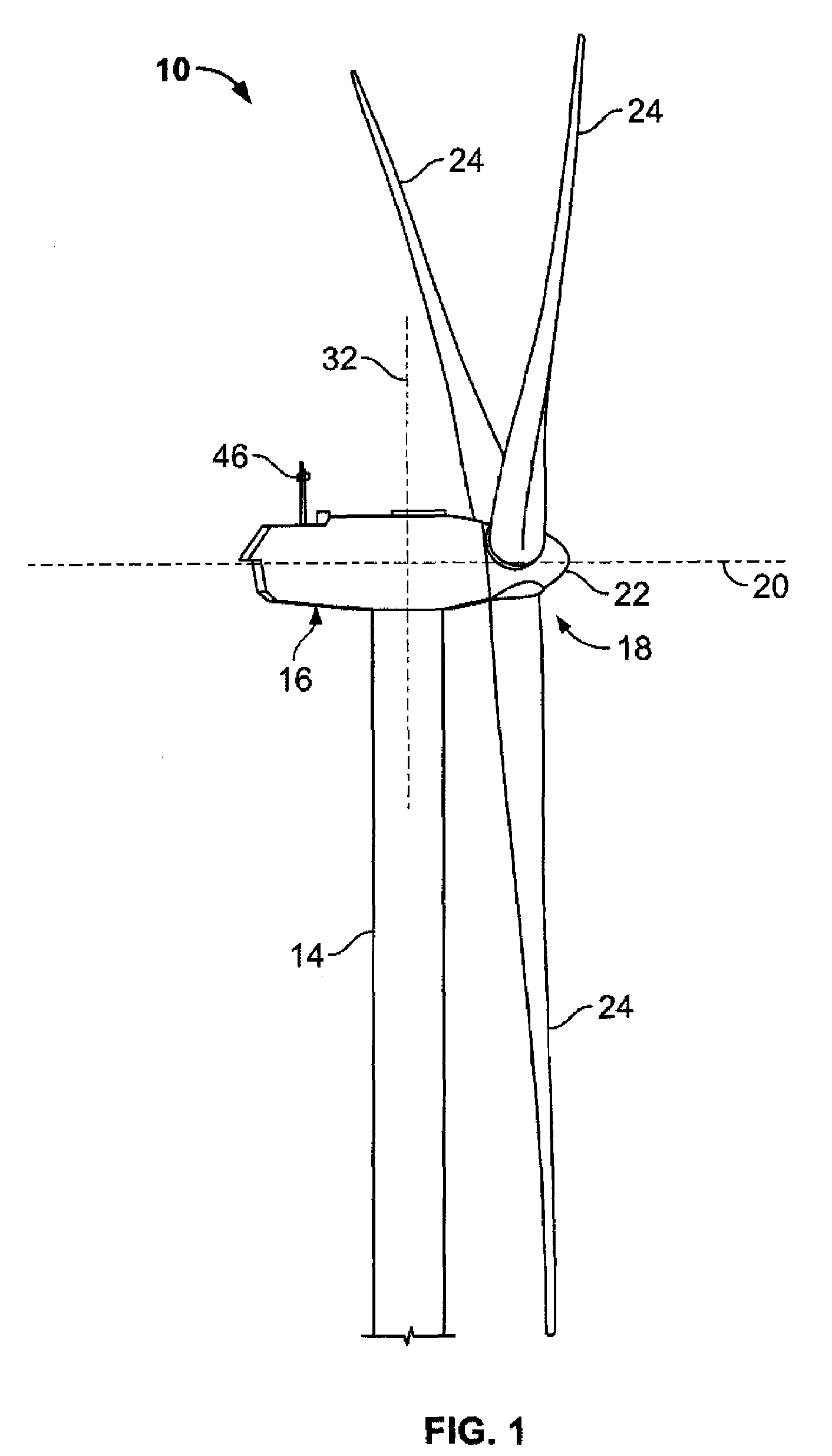
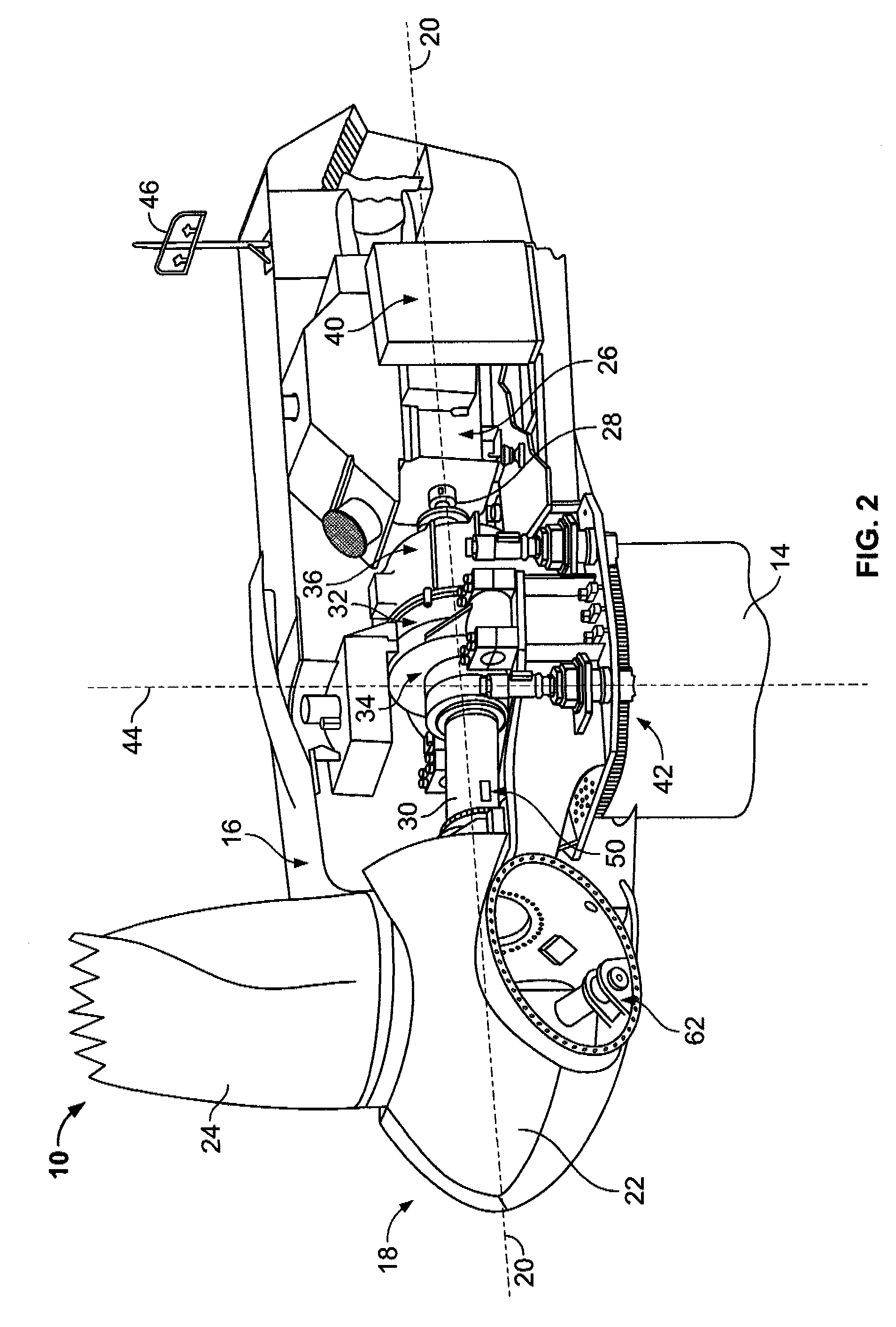
[0013]As used herein, the term “blade” is intended to be representative of any device that provides reactive force when in motion relative to a surrounding fluid. As used herein, the term “wind turbine” is intended to be representative of any device that generates rotational energy from wind energy, and more specifically, converts kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy. As used herein, the term “wind turbine generator” is intended to be representative of any wind turbine that generates electrical power from rotational energy generated from wind energy, and more specifically, converts mechanical energy converted from kinetic energy of wind to electrical power. As used herein, the term “windmill” is intended to be representative of any wind turbine that uses rotational energy generated from wind energy, and more specifically mechanical energy converted from kinetic energy of wind, for a predetermined purpose other than generating electrical power, such as, but not limited to, p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com