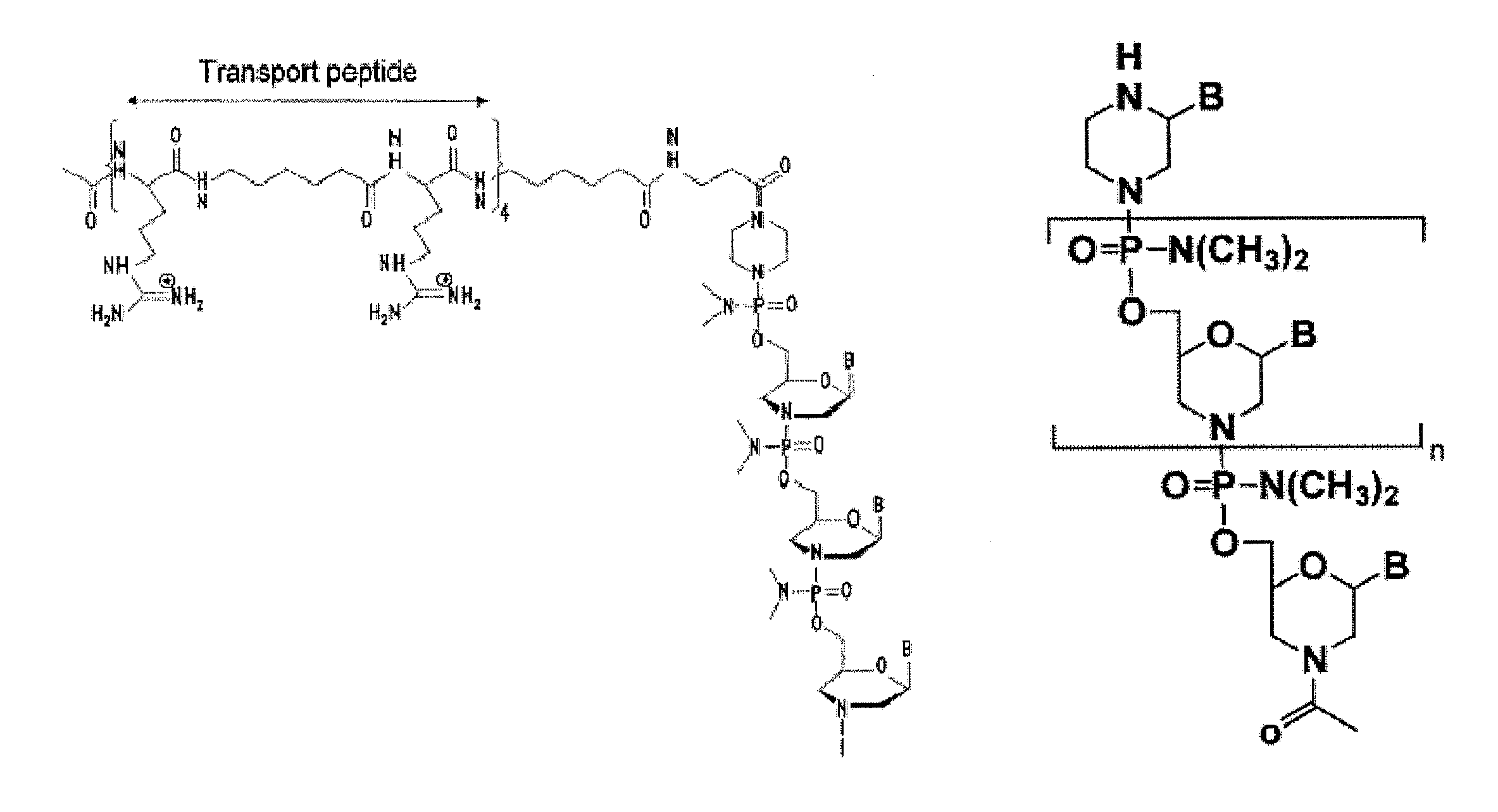
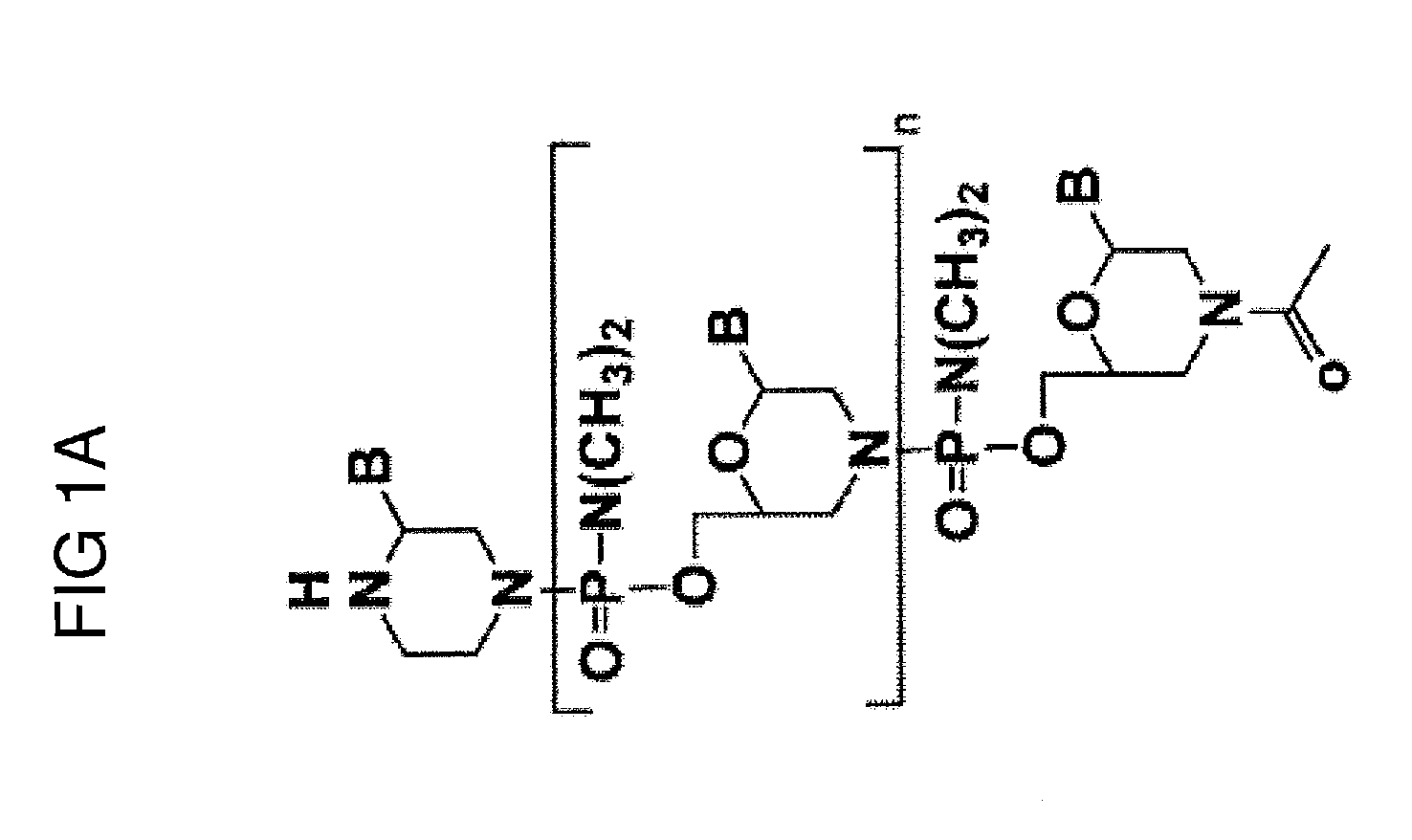
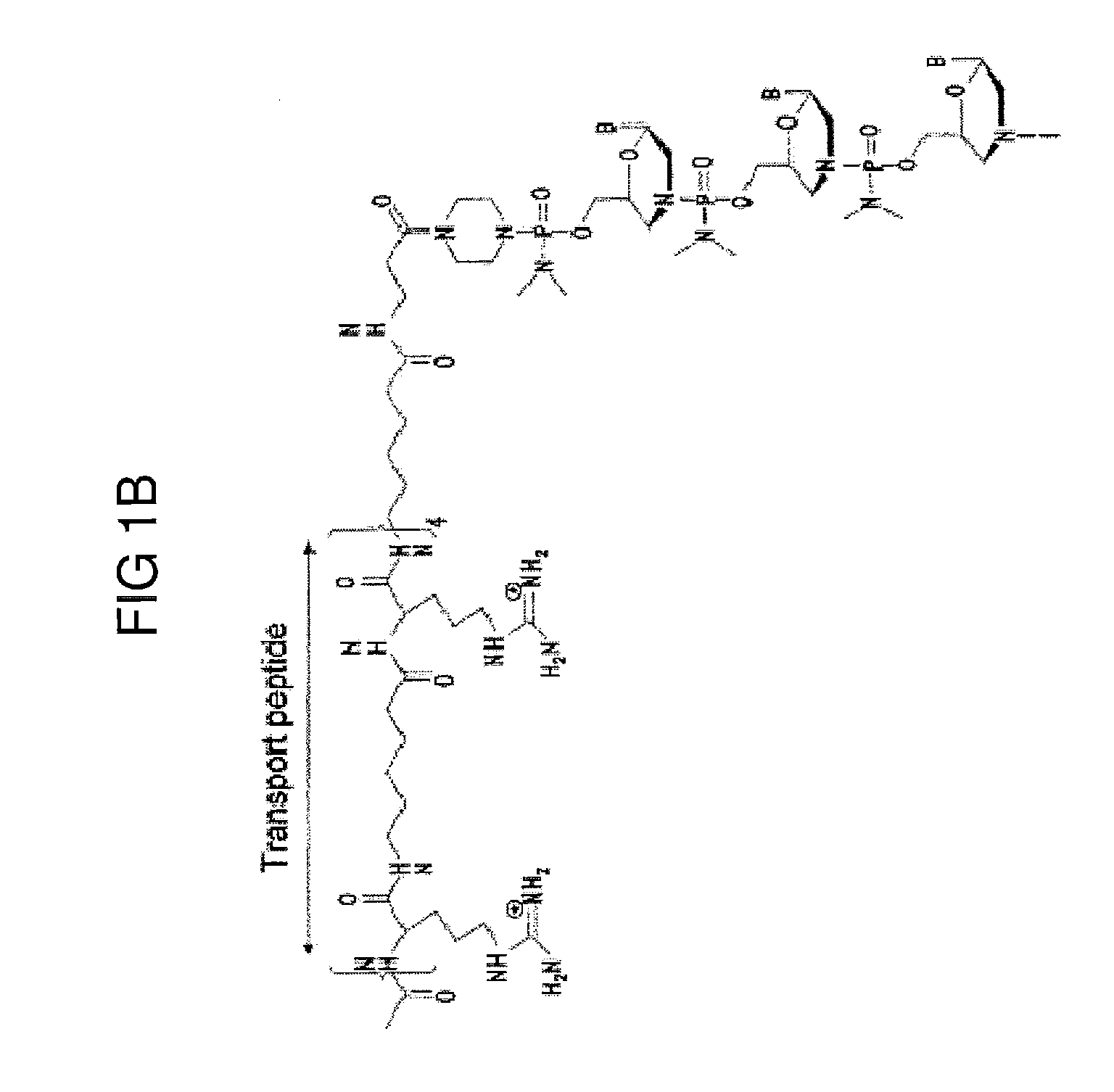
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
a composition and muscular dystrophy technology, applied in the field of new anti-sense compounds, can solve the problems of affecting the effect of cellular uptake, disrupting the production of functional dystrophin, and compound being much less efficient in immortalized cell cultures expressing higher levels of dystrophin, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptak
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Morpholino Oligomers
[0252]The preparation of the compounds of the invention are performed using the following protocol:
[0253]Preparation of trityl piperazine phenyl carbamate 35 (FIGS. 2A and 2B): To a cooled suspension of compound 11 in dichloromethane (6 mL / g 11) was added a solution of potassium carbonate (3.2 eq) in water (4 mL / g potassium carbonate). To this two-phase mixture was slowly added a solution of phenyl chloroformate (1.03 eq) in dichloromethane (2 g / g phenyl chloroformate). The reaction mixture was warmed to 20° C. Upon reaction completion (1-2 hr), the layers were separated. The organic layer was washed with water, and dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate. The product 35 was isolated by crystallization from acetonitrile.
[0254]Preparation of carbamate alcohol 36: Sodium hydride (1.2 eq) was suspended in 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (32 mL / g sodium hydride). To this suspension were added triethylene glycol (10.0 eq) and compound 35 (1.0 eq). The resulti...
example 2
[0279]Using the protocol described in Example 1, the following PMO was synthesized, NG-13-0391 H44A(−8+15), SEQ ID NO: 4 (5′-GAT CTG TCA AAT CGC CTG CAG GT-3′) and used in Examples 8 and 9.
example 3
[0280]Using the protocol described in Example 1, the following PMO was synthesized, NG-13-0392 H44A(−7+15), SEQ ID NO: 5 (5′-GAT CTG TCA AAT CGC CTG CAG G-3′) and used as described in Examples 8 and 9.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ring structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com