Antimicrobial compounds and methods of use
a technology which is applied in the field of antibacterial compounds and antifungal compounds, can solve the problems that many previously useful antibiotics are no longer effective against infectious organisms isolated from human and animal subjects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working examples
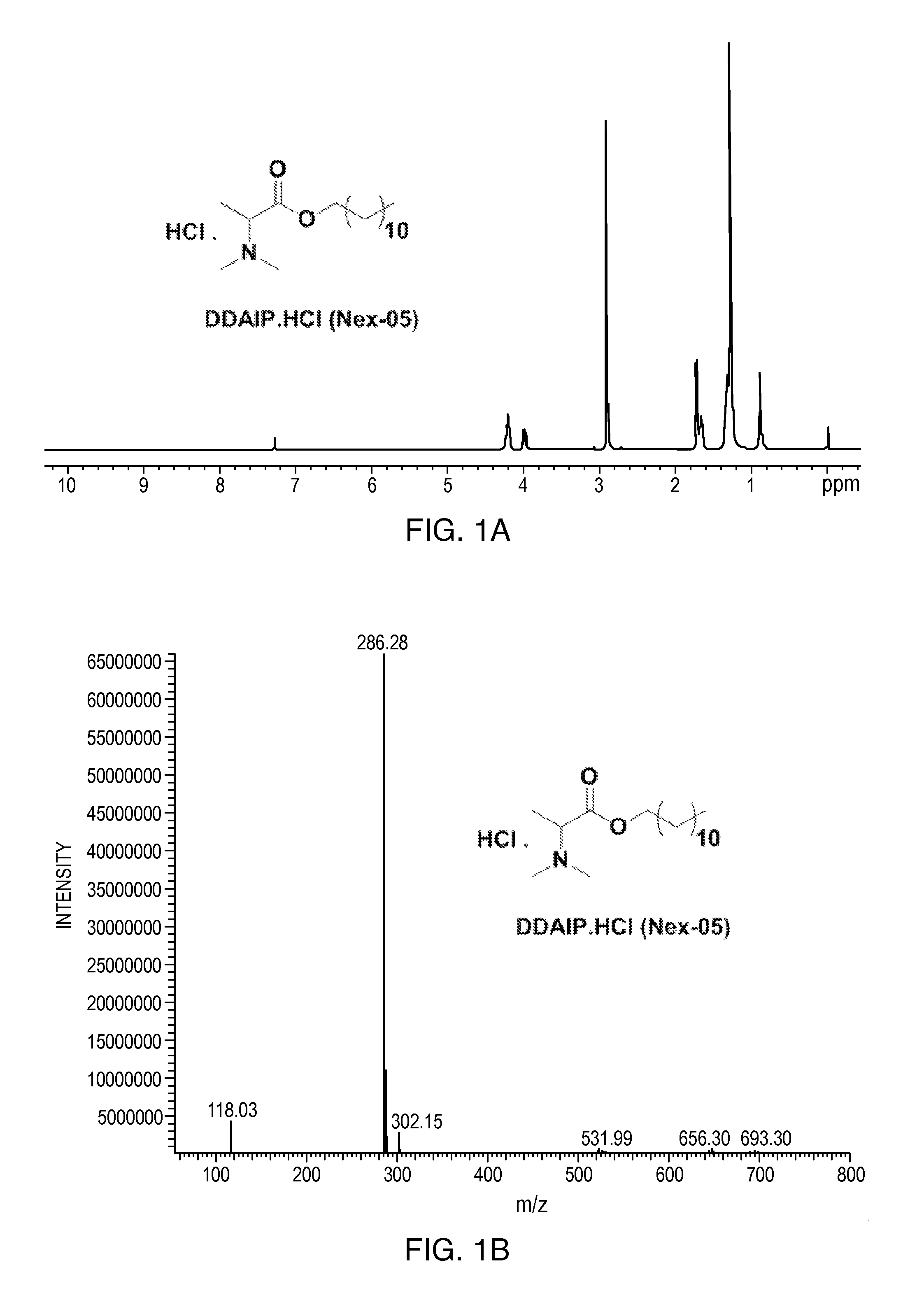
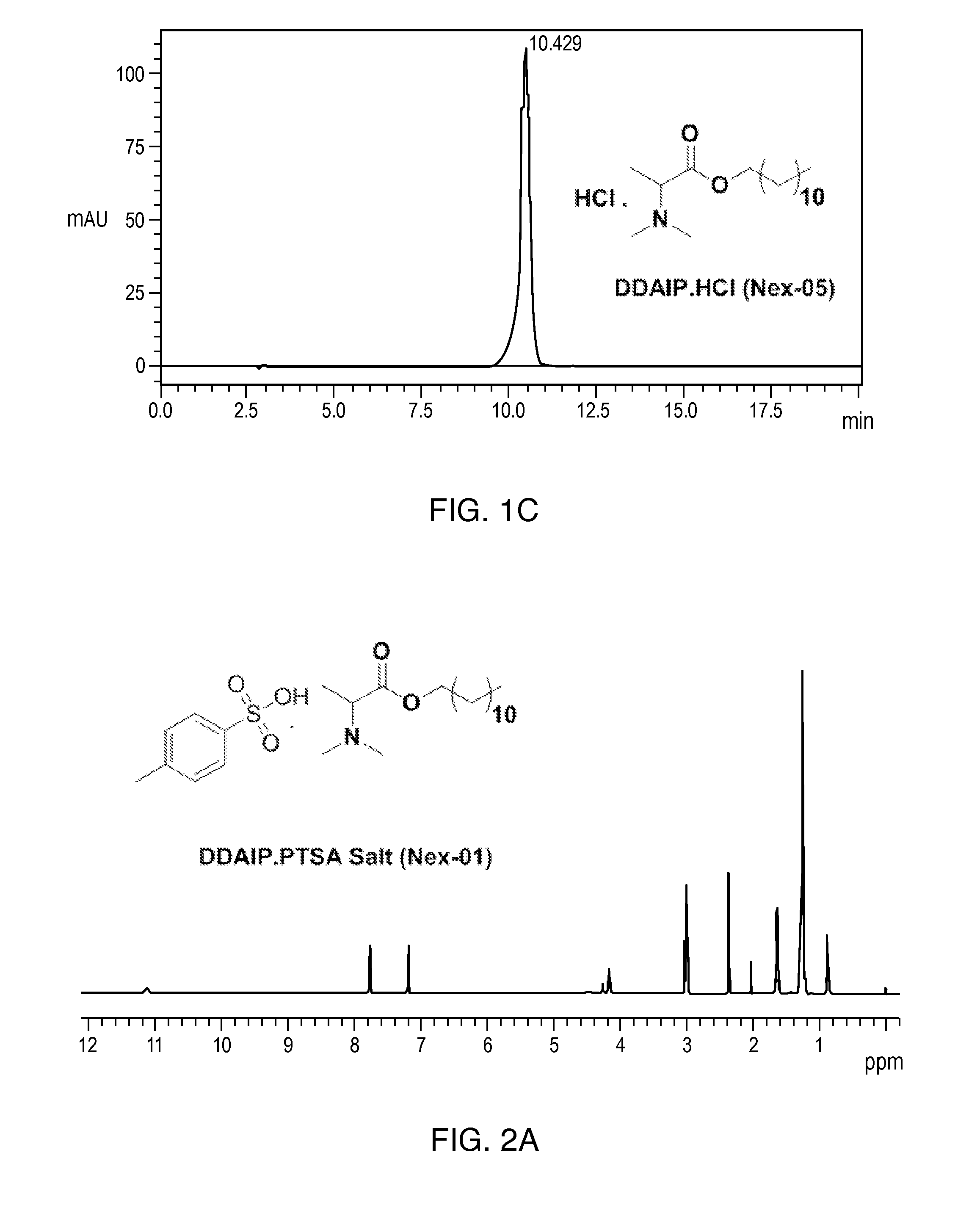
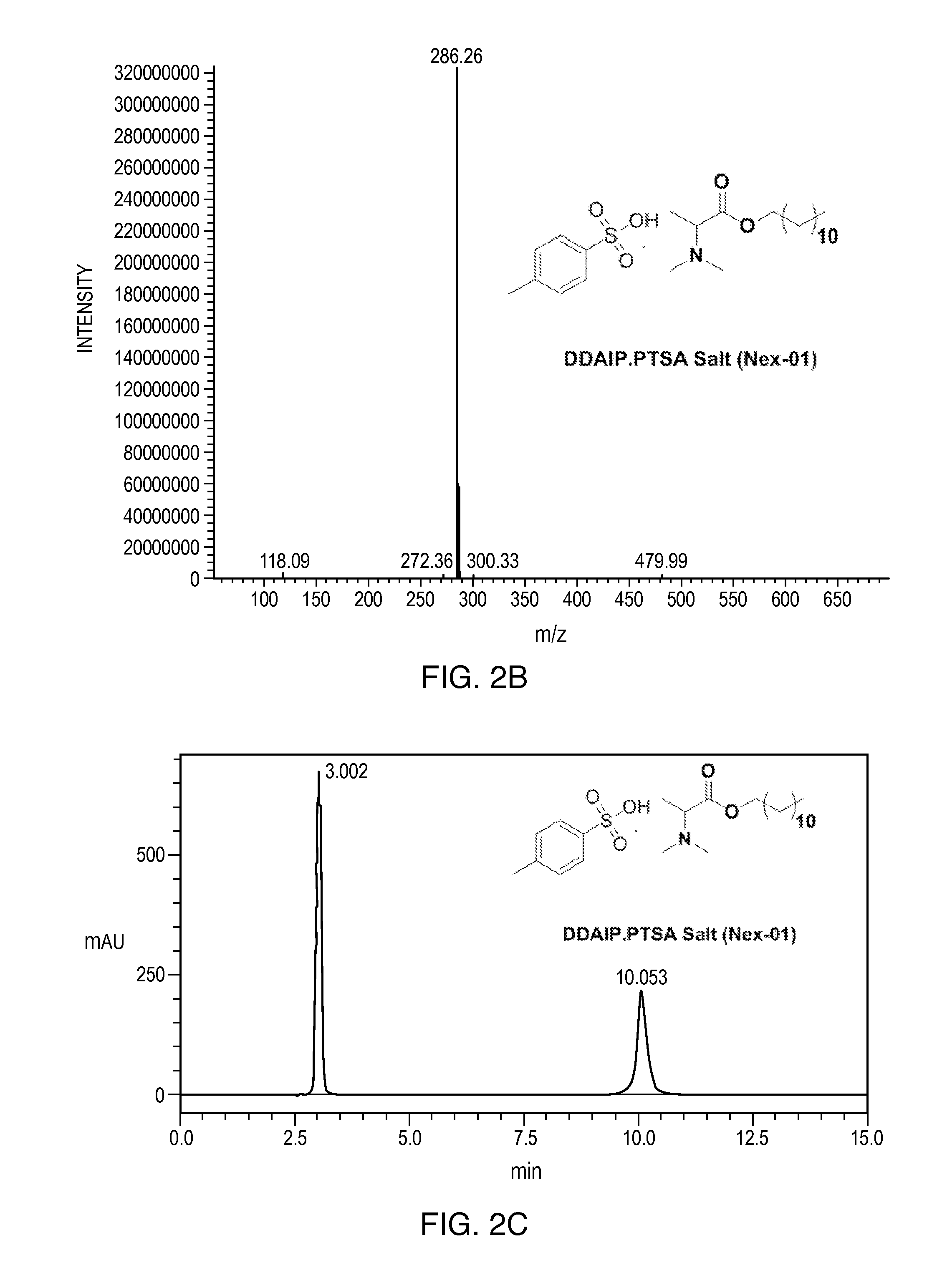
[0166]The following non-limiting examples further illustrate the various embodiments described herein. Example 1 provides a method of synthesizing dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate (DDAIP) and dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate hydrochloride salt. Examples 2-12 disclose methods of synthesizing other salts of DDAIP. The salts of DDAIP that were prepared include the sulfate, the phosphate, and organic salts including the 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, the 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate, benzenesulfonate, the maleate, the methanesulfonate, the ethanesulfonate, the heminaphthalene-1,5-disulfonate, and the 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate. Examples 13-32 describe the methods of making and the characterization of related compounds and their hydrochloride salts. In view of the teachings of Examples 2-12 and the knowledge of the skilled artisan, the production of salts disclosed herein, as well as other salts, of the antimicrobial compounds is routine.
example 1
Synthesis of Dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate and Dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate Hydrochloride salt
[0167]
Synthesis of Dodecyl 2-aminopropanoate (3)
[0168]To a stirred solution of DL-alanine 1 (5 g, 56.1 mmol) in toluene (100 mL) was added dodecanol 2 (9.42 g, 50.5 mmol) in one lot, followed by pTSA (11.75 g, 61.7 mmol). After addition, the temperature of the reaction mixture was slowly raised to reflux temperature, the water was separated azeotropically, and the reaction mixture was monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum, the obtained residue was taken in ethyl acetate (200 mL) and washed with aqueous 5% Na2CO3 (3×50 mL) followed by brine solution. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under vacuum to afford crude dodecyl 2-aminopropanoate 3 (14.4 g, yield: 100%) as a liquid.
Synthesis of Dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)Propanoate (DDAIP) (4)
[0169]To a stirred solution of dodecyl 2-aminopropanoate 3 (5 g, 19.4 mmol) in DCM (100 mL) was...
example 2
Synthesis of Dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate p-toluene sulfonate salt (Nex-01)
[0174]
Synthesis of Dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoatep-toluene sulfonate salt
[0175](7, Nex-01): A stirred solution of DDAIP base 4 (80 g, 280 mmol) in ethyl acetate (500 mL) was cooled to 0° C. then p-toluene sulfonic acid H2O 6 (53.4 g, 280 mmol) was added in one lot. After addition, the temperature of the reaction mixture was slowly raised to RT and stirred at RT for 12 h; the reaction mixture was monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum and flushed with hexane. The obtained residue was taken in n-hexane (20 mL) and stirred at RT for 2 h (No solid). The obtained sticky solid kept in a deep freezer for 12 h to afford dodecyl 2-(dimethylamino)propanoate PTSA salt (7, Nex-01) (130 g, yield: 97.4%) as a hygroscopic solid, Mp: 60-65° C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.9 (t, 3H), 1.3 (m, 18H), 1.6 (d, 3H), 1.6 (q, 2H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 3 (m, 6H), 4.1 (t, 2H), 4.25 (q, 1H), 7.18 (d, 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com