Antiparkinsonian Action of Phenylisopropylamines
a technology of phenylisopropylamine and antiparkinsonian effect, which is applied in the field of treatment of parkinson's disease with phenylisopropylamine, can solve the problems of affecting the effect of parkinson's treatment, so as to reduce the dosage of said antiparkinson's agent, reduce the undesired side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
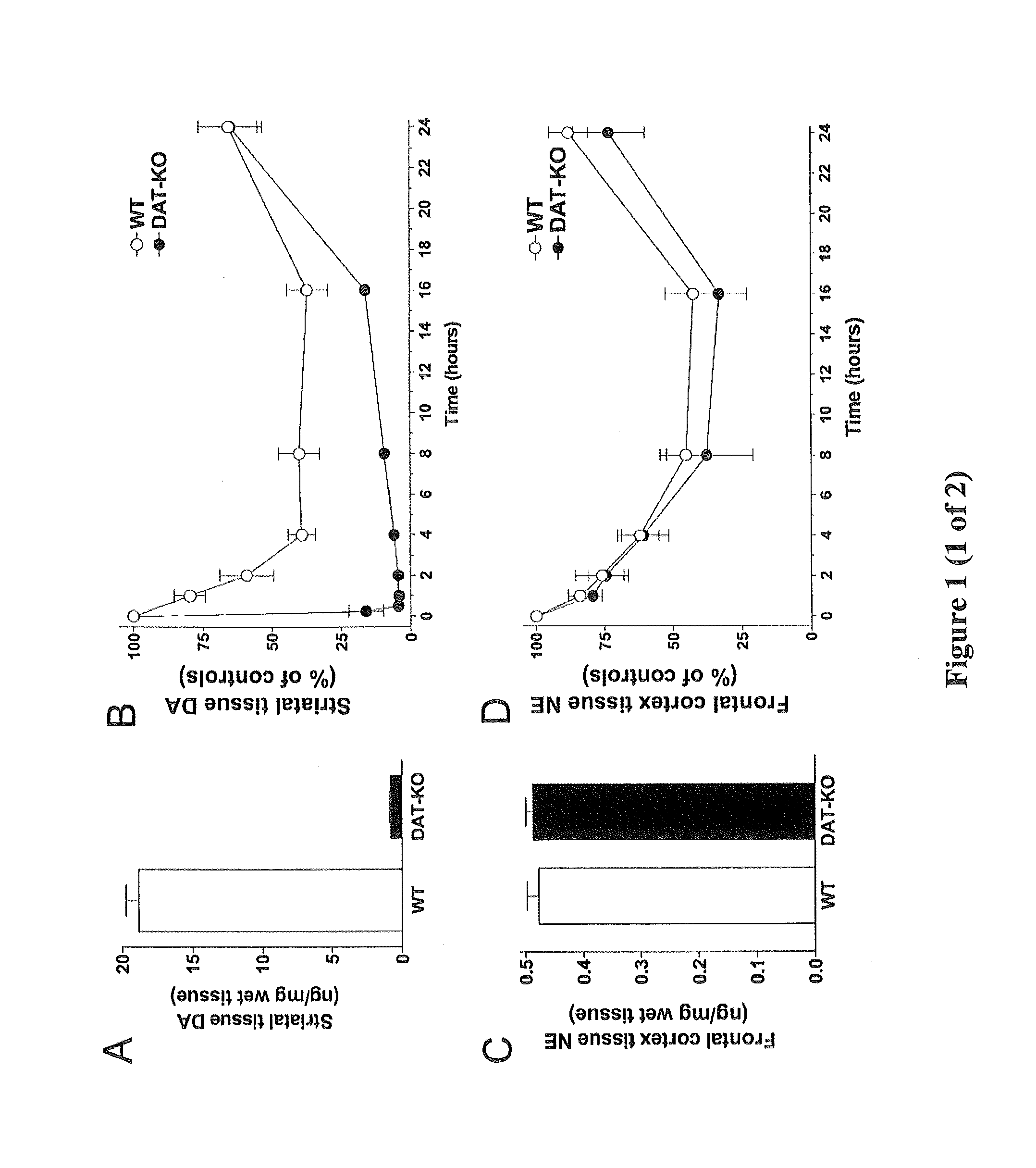
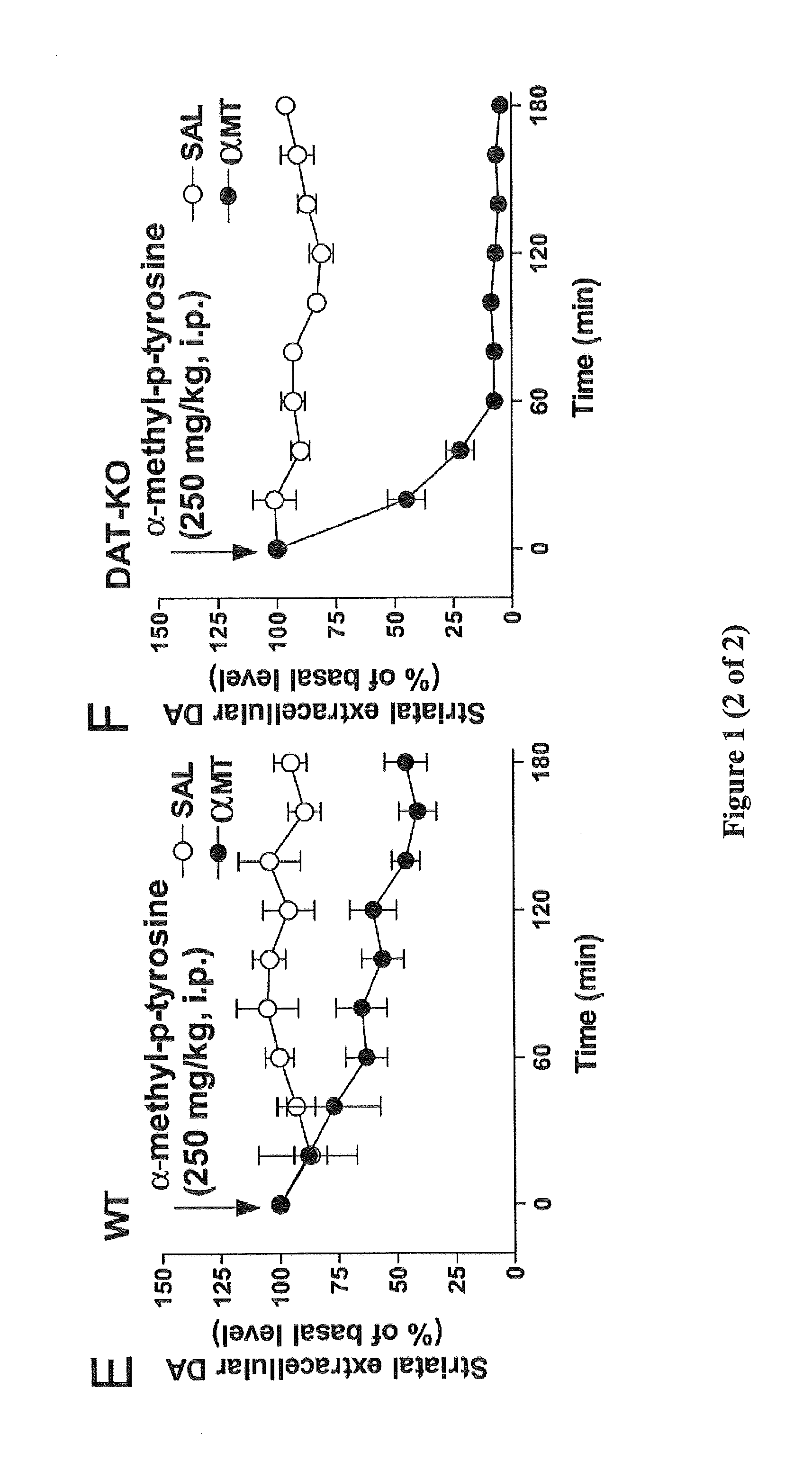
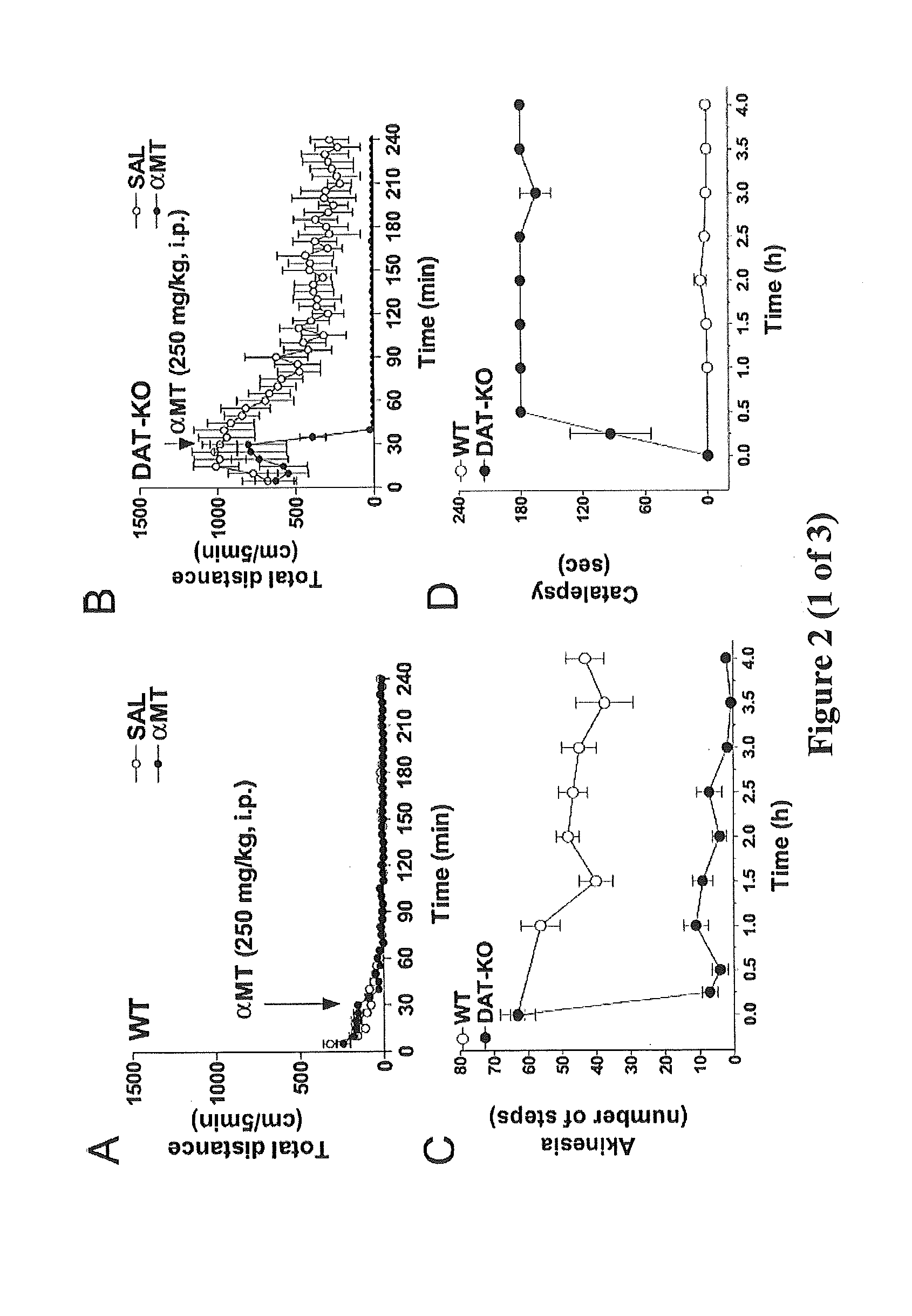
[0043]“Antiparkinson's agent” as used herein includes, but is not limited to: levodopa (L-DOPA; with or without carbidopa), dopamine agonists (such as apomorphine, bromocriptine, pergolide, pramipexole, ropinirole, etc.) anticholinergics such as atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate, trihexyphenidyl, benztropine mesylate, procyclidine, etc.), monoamine oxidase (MAO-B) inhibitors such as selegiline, COMT inhibitors (preferably taken with levodopa) such as entacapone and tolcapone and other medications such as amantadine, etc., and including pharmaceutically acceptable salts and prodrugs thereof, and combinations of any of the foregoing. See, e.g., U.S. Pat. No. 6,833,478.
[0044]“Parkinson disease” or “Parkinson's disease” as used has its conventional meaning and generally refers to a disease characterized by the chronic, progressive loss of neurons in the region of the brain known as the substantia nigra, at any point. Parkinson's disease (including early onset and late onset Parkinso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com