Preventing programming errors from occurring when programming flash memory cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
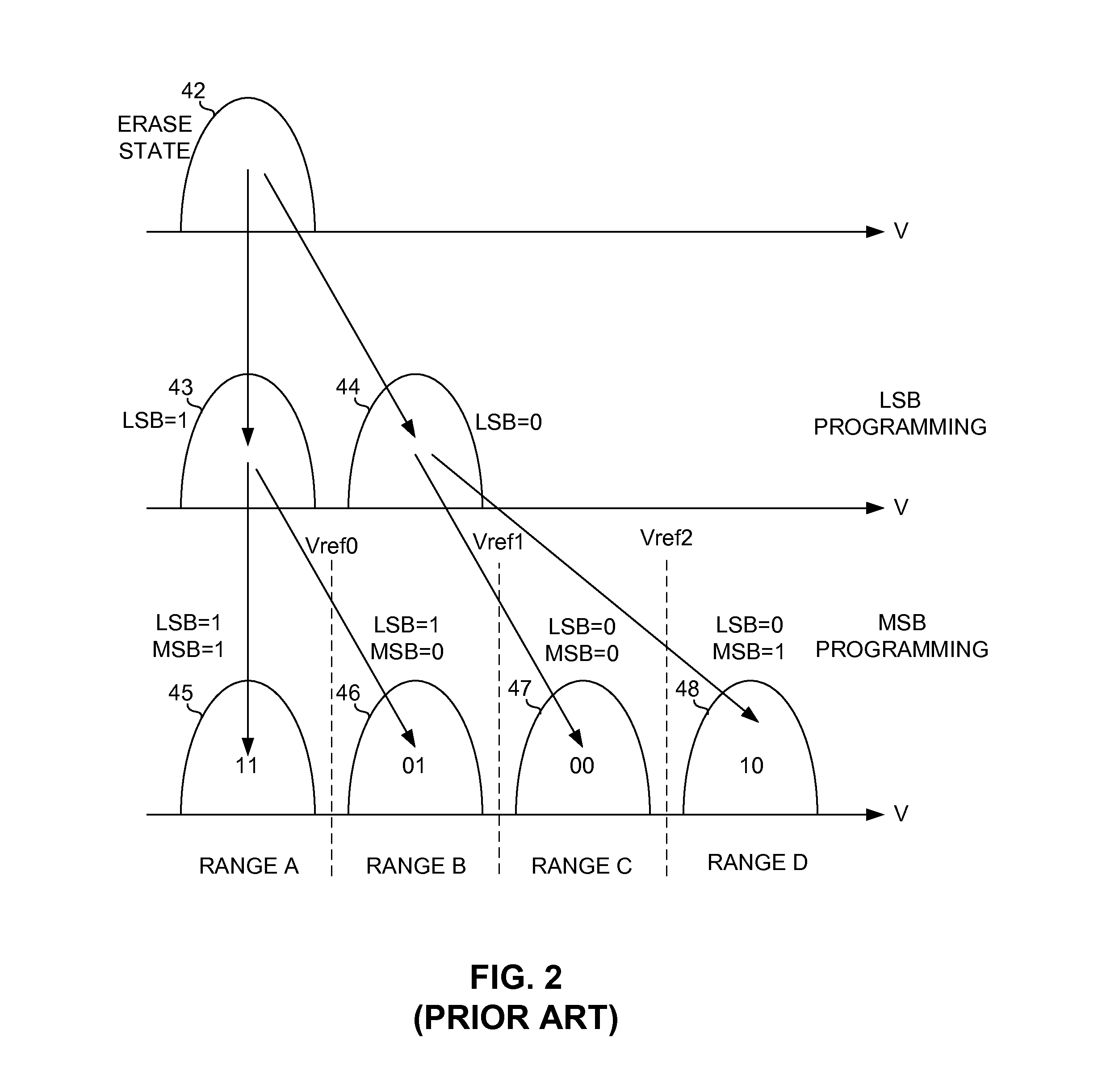
[0026]In accordance with exemplary, or illustrative, embodiments, the LSB values that are used in conjunction with the MSB values to determine the proper reference voltage ranges are error corrected by ECC decoding logic inside of the flash memory before being used in conjunction with the MSB values to determine the proper reference voltage ranges. Error correcting the LSB page data prior to using it in combination with the MSB page data to determine the reference voltage ranges ensures that the reference voltage ranges will be properly determined and programmed into the flash cells.
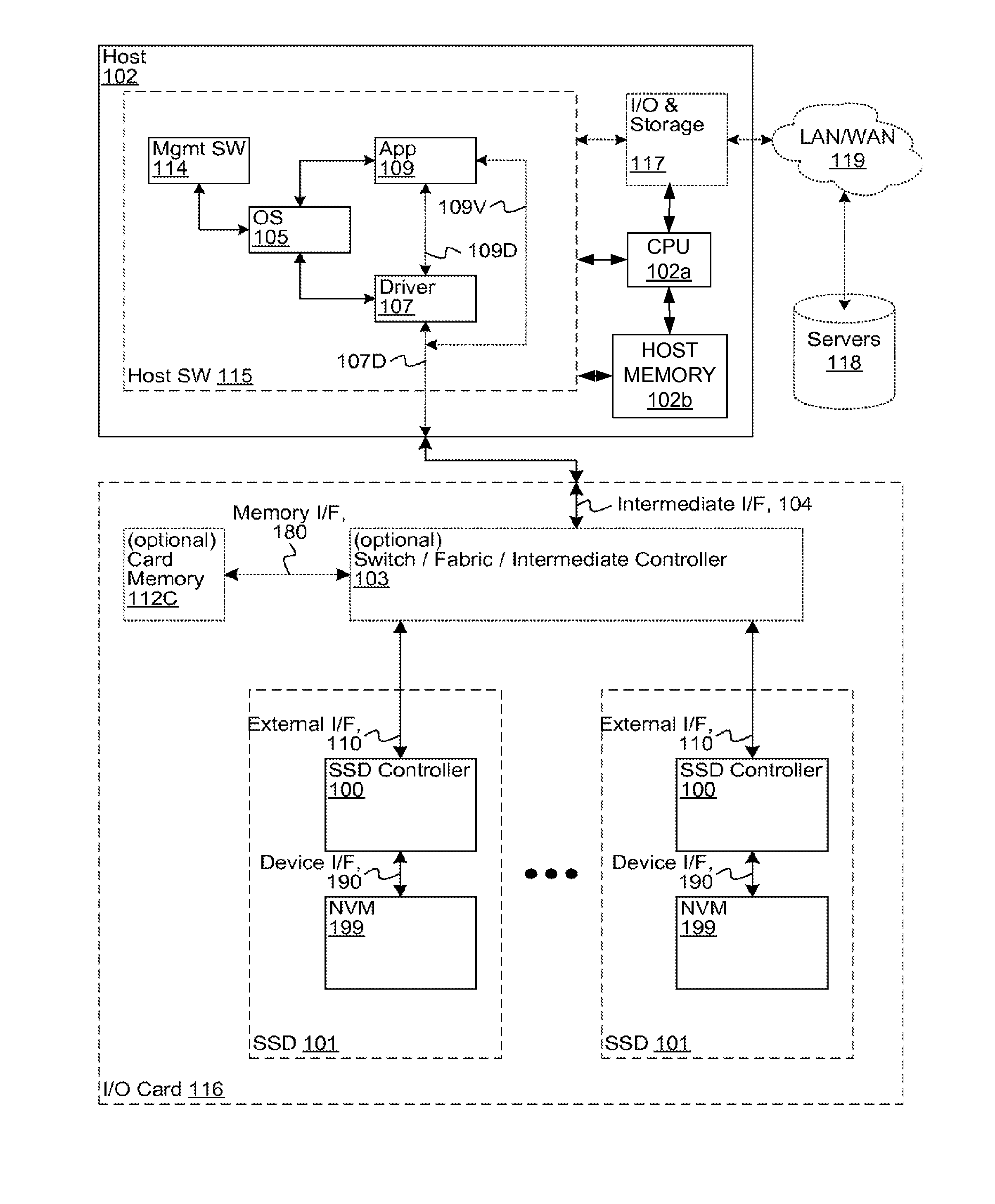
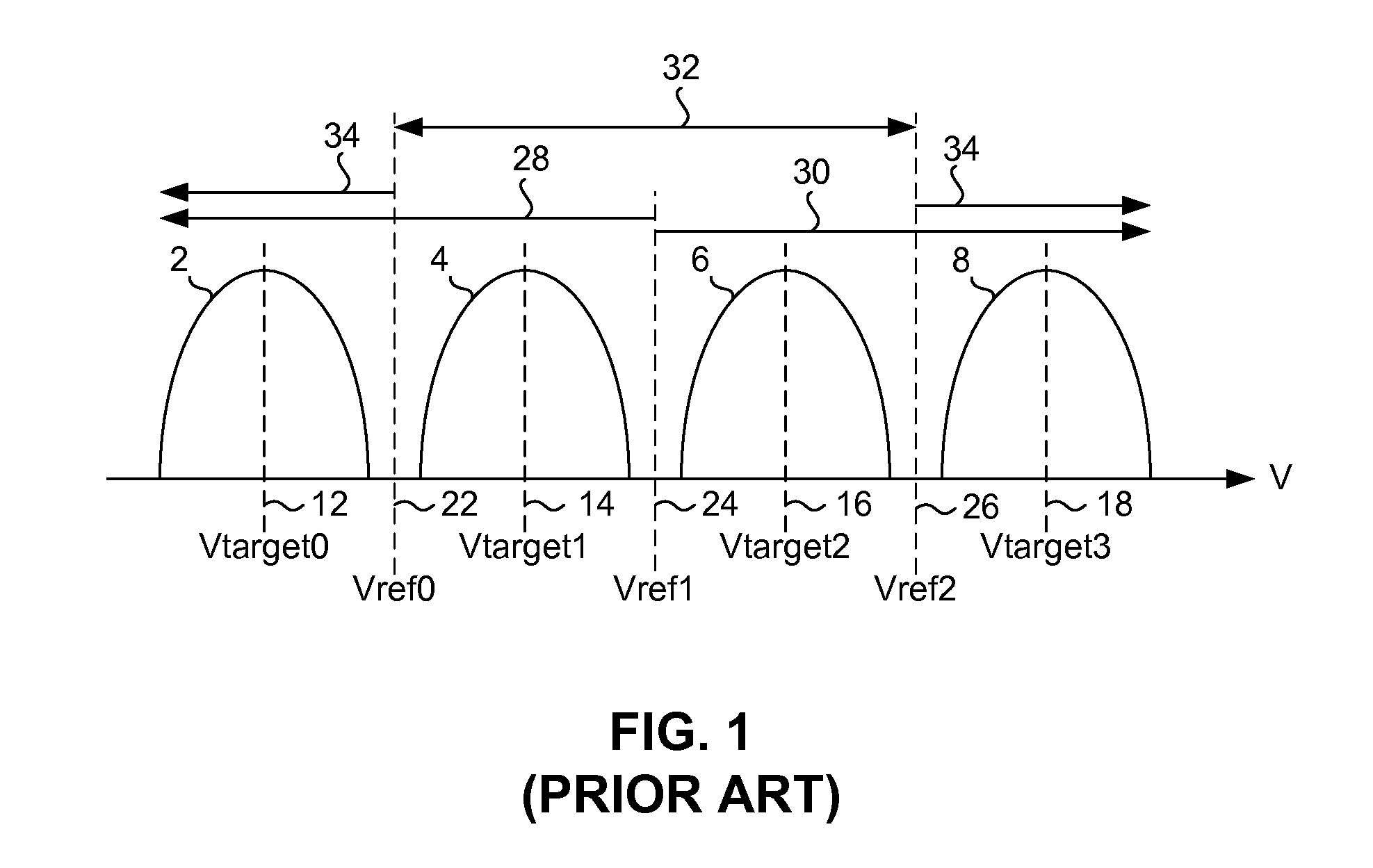
[0027]Embodiments of the invention can be implemented in a number of ways, and therefore a few illustrative embodiments are described below with reference to FIGS. 3-9, in which like reference numerals in the figures identify like features, components or elements. Before describing specific embodiments for ensuring that programming errors do not occur when programming the reference voltage ranges of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com