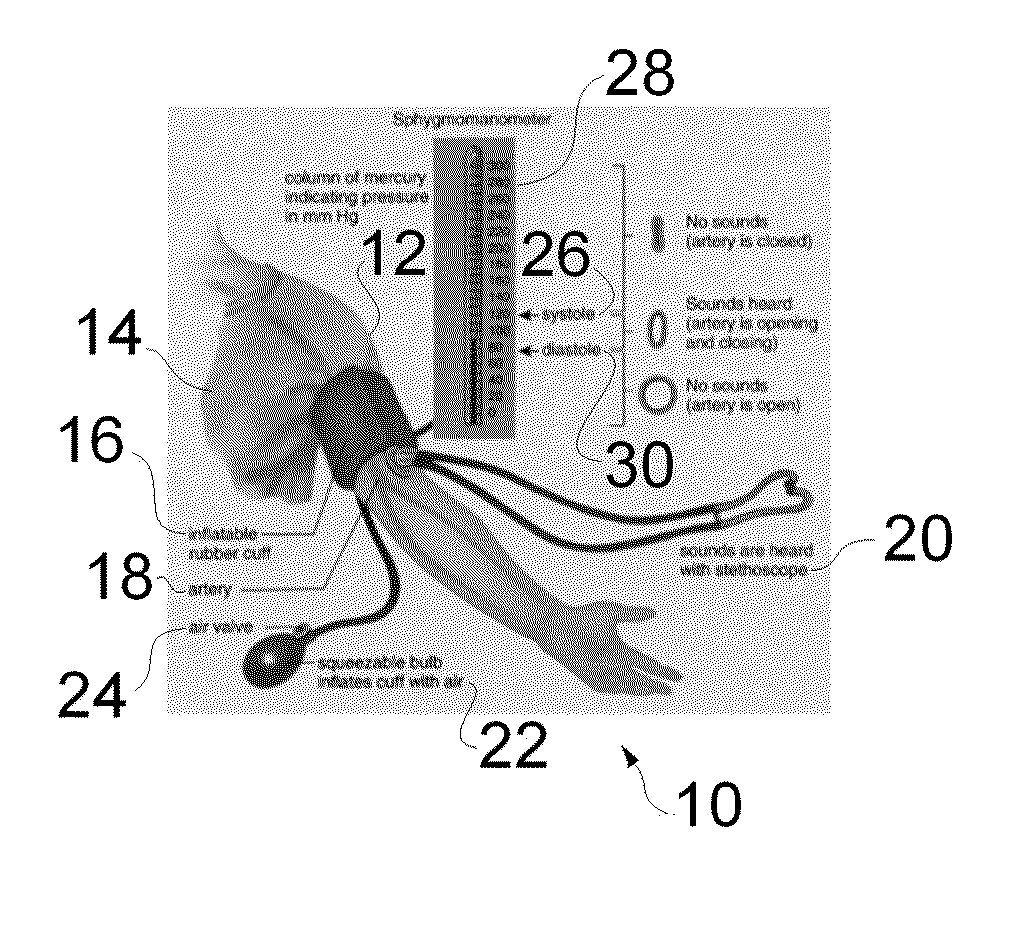
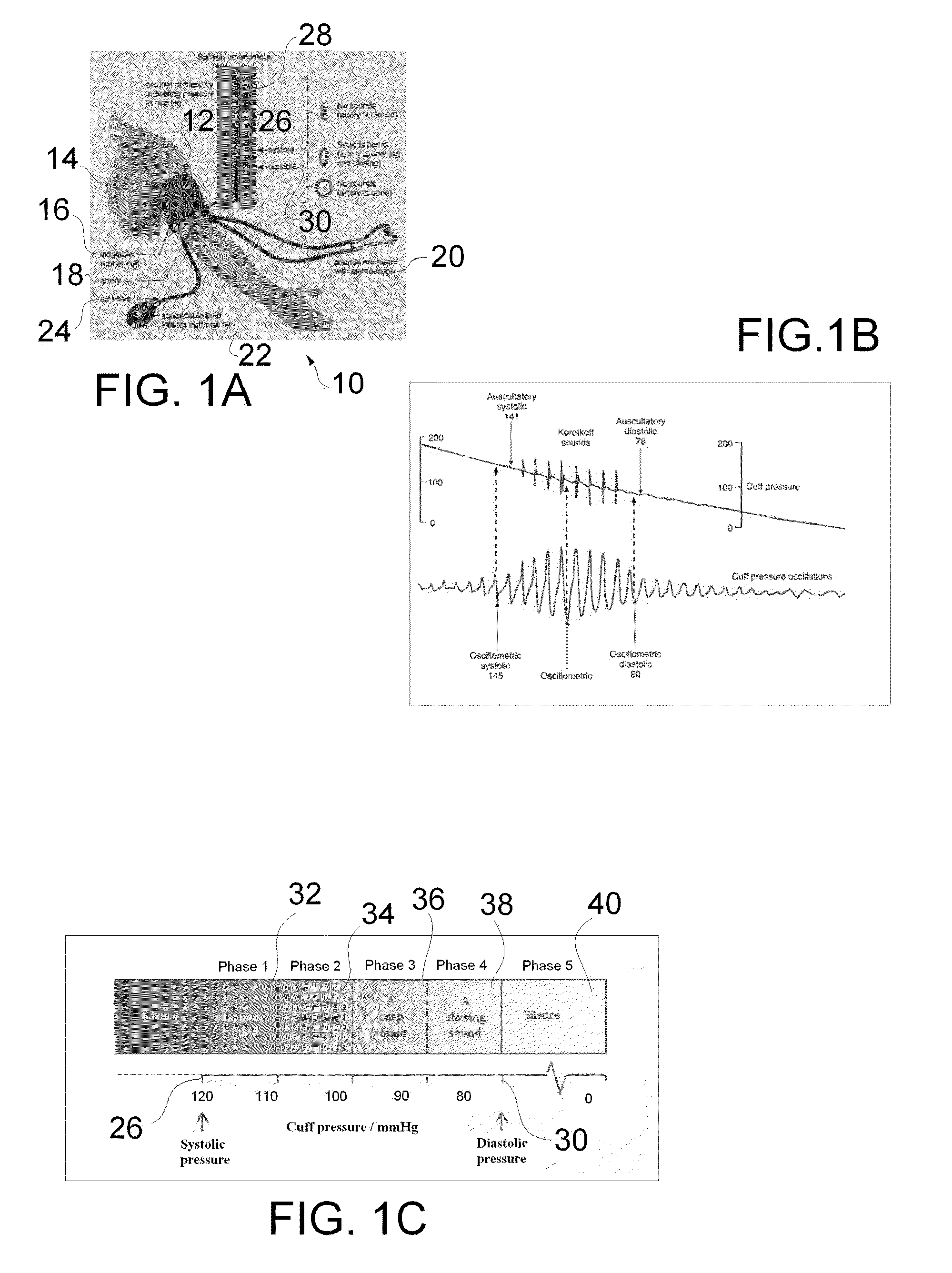
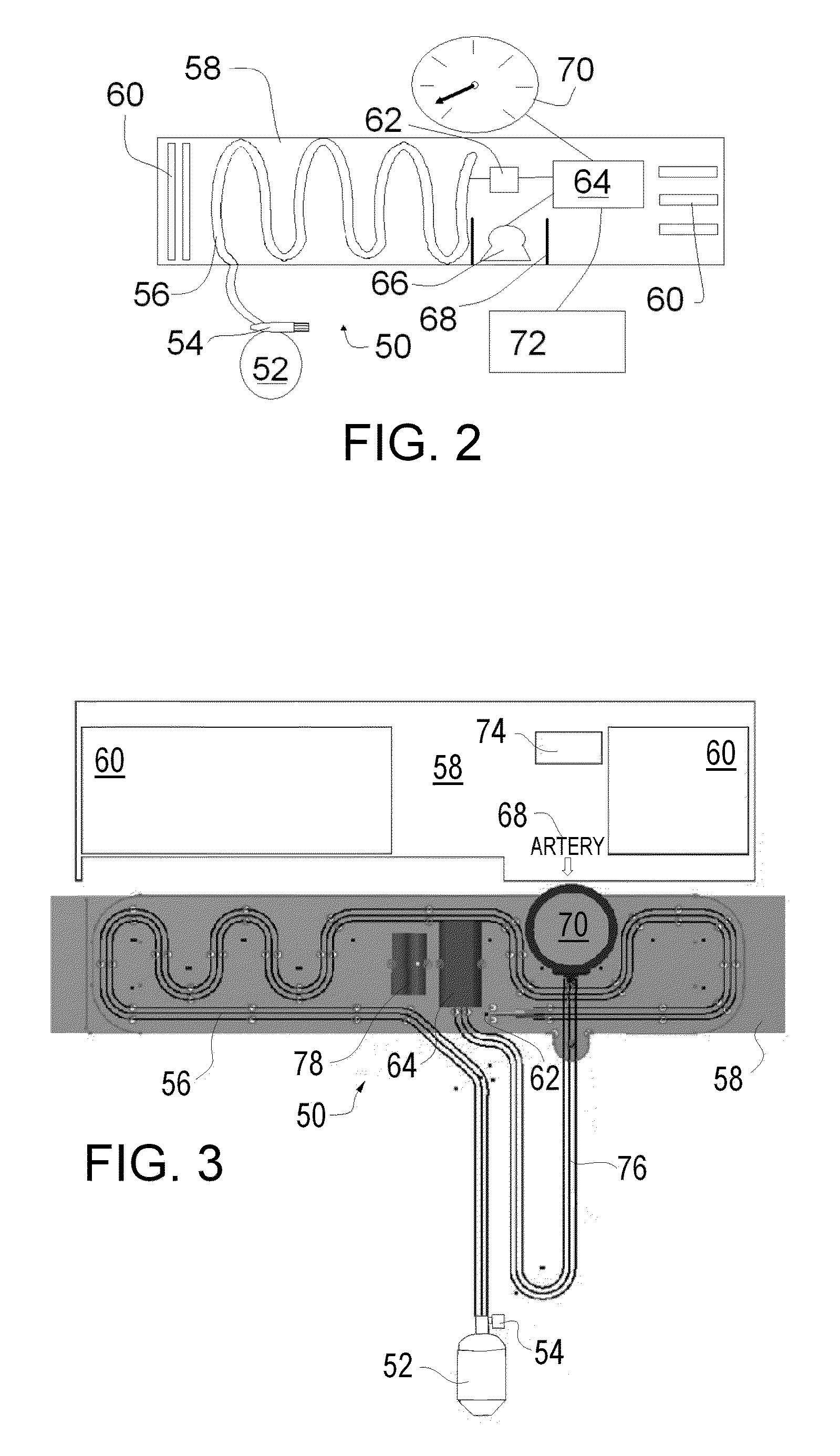
Suite of coordinating diagnostic medical simulators for live training and evaluation
a diagnostic medical simulator and simulator technology, applied in the field of live training and evaluation of diagnostic medical simulators, can solve the problems of not being able to use in environments too noisy to permit hearing the characteristic sounds, and possibly less accurate, and unable to achieve calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0127]A standardized patient is brought to the simulated weight scale, the system detects the proximity of the standardized patient to the simulated weight scale and automatically uploads the patient scenario to the scale.
example 2
[0128]A standardized patient is brought into an examination room containing a wide variety of simulated diagnostic equipment such as a by cuff, pulse ox, etc. The system detects that the patient is in the room containing the equipment and uploads the patient scenario to all of the nearby simulated diagnostic equipment.
[0129]There are multiple ways of getting the standardized patients location within the environment such as RFID, NFC, Video recognition and so on. During facility setup, a map is generated of the environment and the location of various simulated diagnostic equipment. One preferred approach—Medical simulation facilities are usually outfitted with a wide variety of audio / video recording equipment. In addition to the standard microphones normally used, we will strategically place microphones capable of operating in the ultrasonic range above human hearing. A piece of standardized patient worn equipment (probably the vest) will have a wireless transceiver and an ultrasonic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com