Systems and methods for providing lightweight prosthetic components
a prosthetic component and lightweight technology, applied in the field of prosthetics, can solve the problems of inability of knee prosthesis patients to achieve deep knee flexion, also known as full functional flexion, and not allow patients to flex from full extension to 160° and beyond, so as to achieve and greater deep knee flexion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
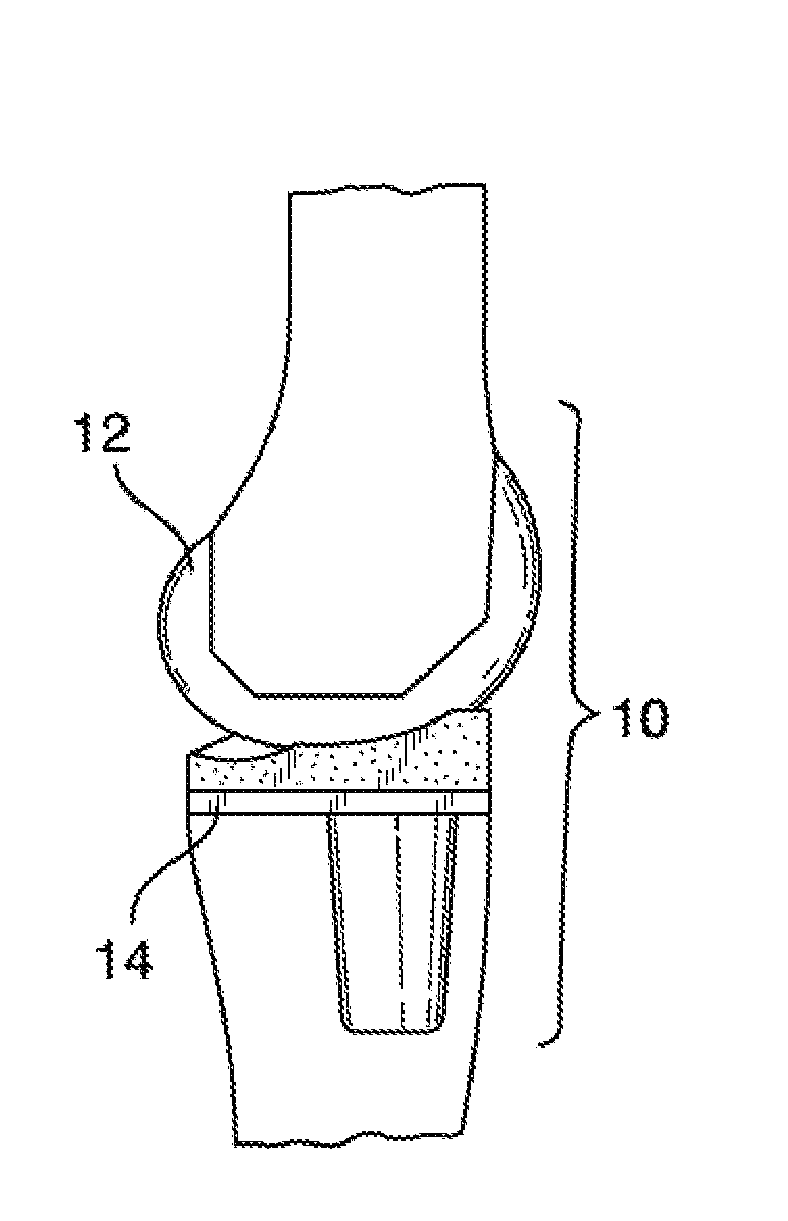
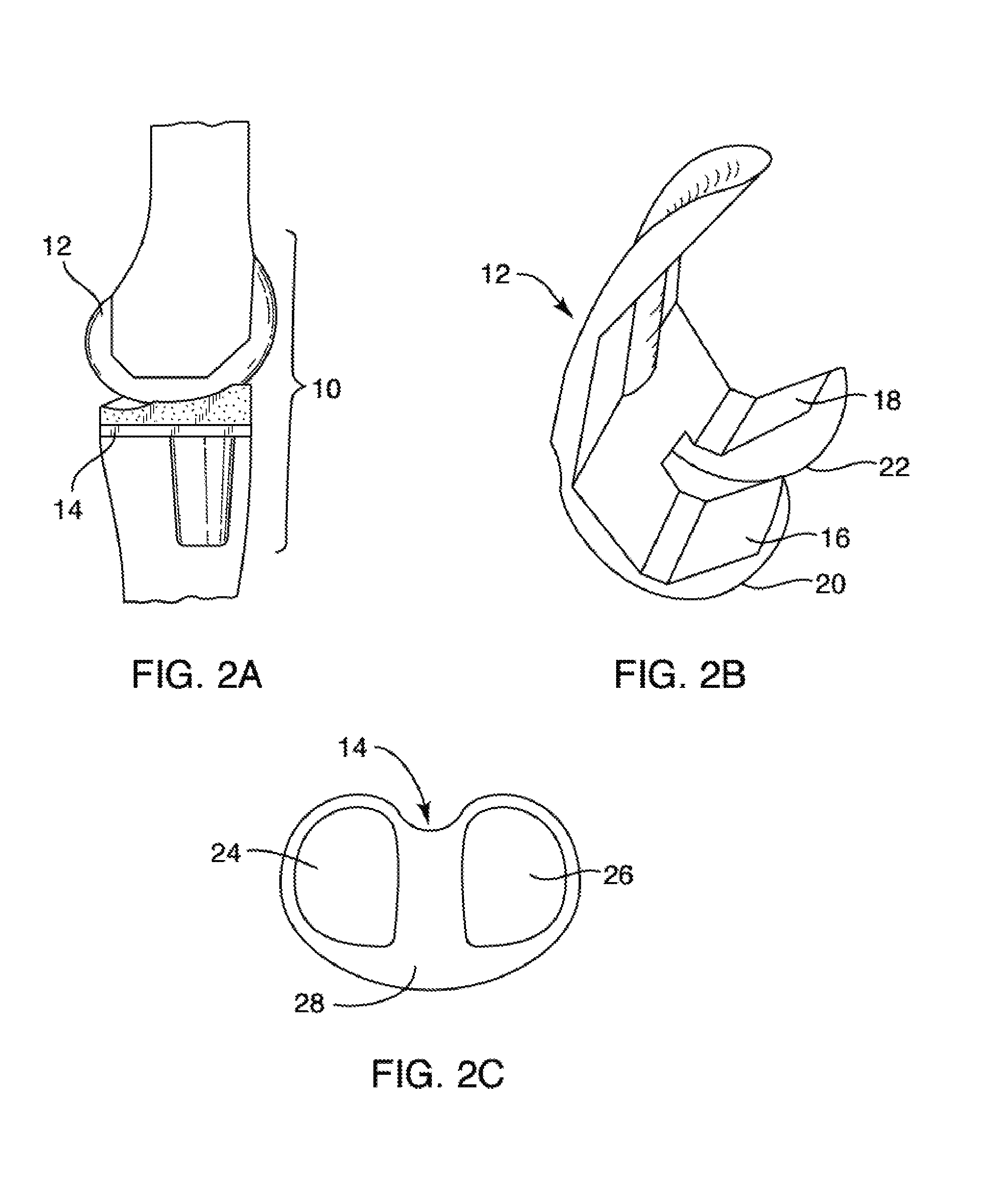
[0117]Some aspects of the present invention relates to prosthetic implants. More specifically, while some aspects of the present invention relate to prosthetic knee implants that allow for a relatively high degree of knee flexion, other aspects relate to systems and methods for providing relatively lightweight prosthetic implants.
[0118]The following disclosure of the present invention is grouped into two subheadings, namely “High Flexion Knee Components” and “Lightweight Prosthetic Implants.” The utilization of subheadings is for convenience of the reader and is not, in any way, to be construed as limiting in any sense.
High Flexion Knee Components
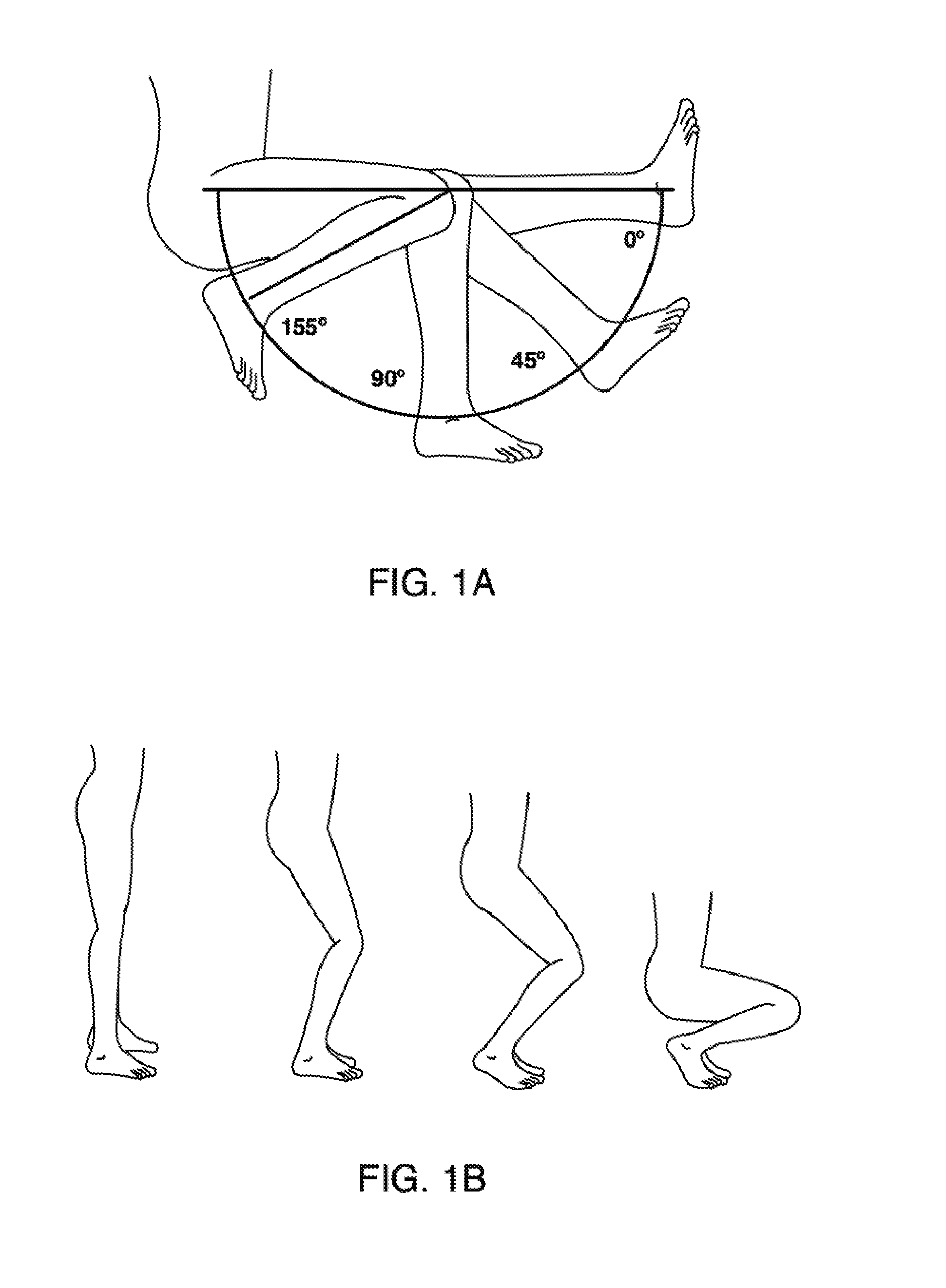
[0119]With respect to the high flexion knee components, some aspects of the present invention relates to knee prostheses. In particular, some implementations of the present invention relate to systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients, and more particularly, to systems and methods for: (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com