Textile Fabric for Martial Arts Clothing
a technology of martial arts clothing and textiles, applied in protective fabrics, knitting, braids, etc., can solve the problems of losing the cooling qualities of cotton, thin cotton fabrics have a tendency to wear prematurely, etc., and achieve the effect of maintaining the flexibility of the formed fabric and enhancing the strength of the formed fabri
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
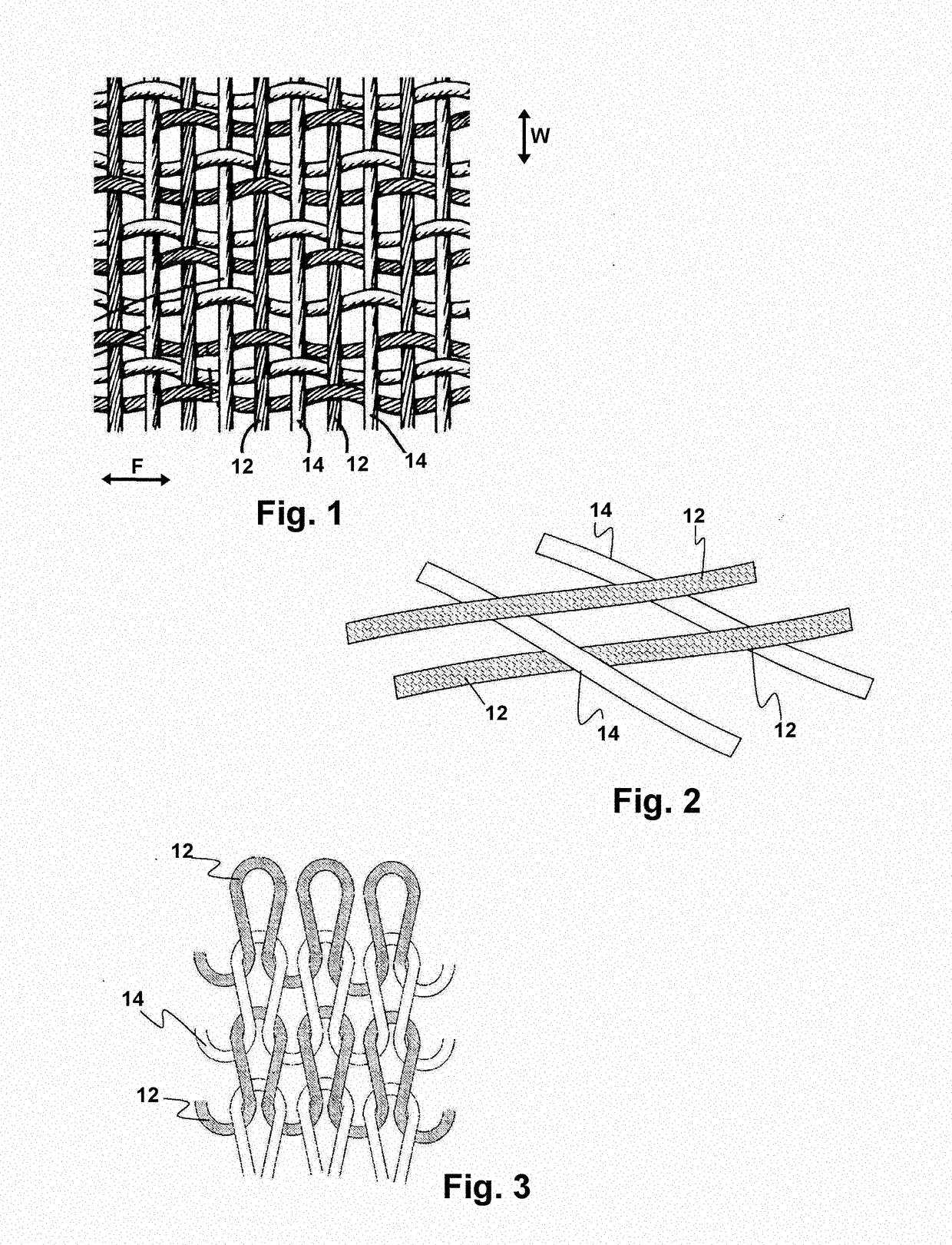
[0029]Now referring to the drawings in FIGS. 1-5, wherein similar components are identified by like reference numerals, in all modes whether woven or knitted, there is included a first yarn 12 formed of cotton, and a second yarn formed of a synthetic or engineered material which imparts strength to the woven material.
[0030]As depicted in FIG. 2, which shows one mode of weaving of both the first yarn 12 and second yarn 14, the first yarn 12 is preferably in both the warp and weft of the formed fabric. The second yarn 14, may be included only in the warp direction W or only the weft or fill direction F, or the second yarn may be included to run both directions which has shown to yield better resistance to tearing and abrasion.
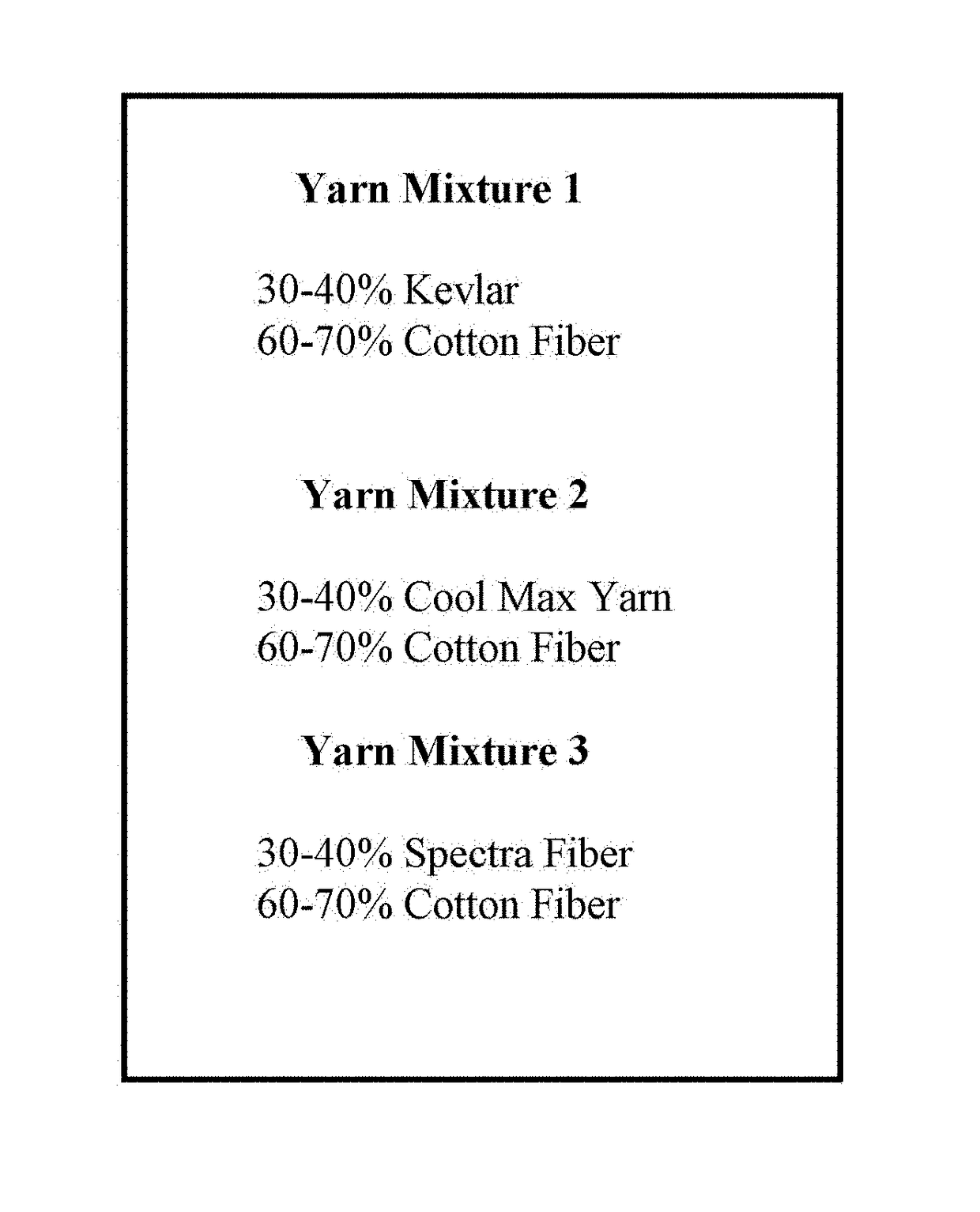
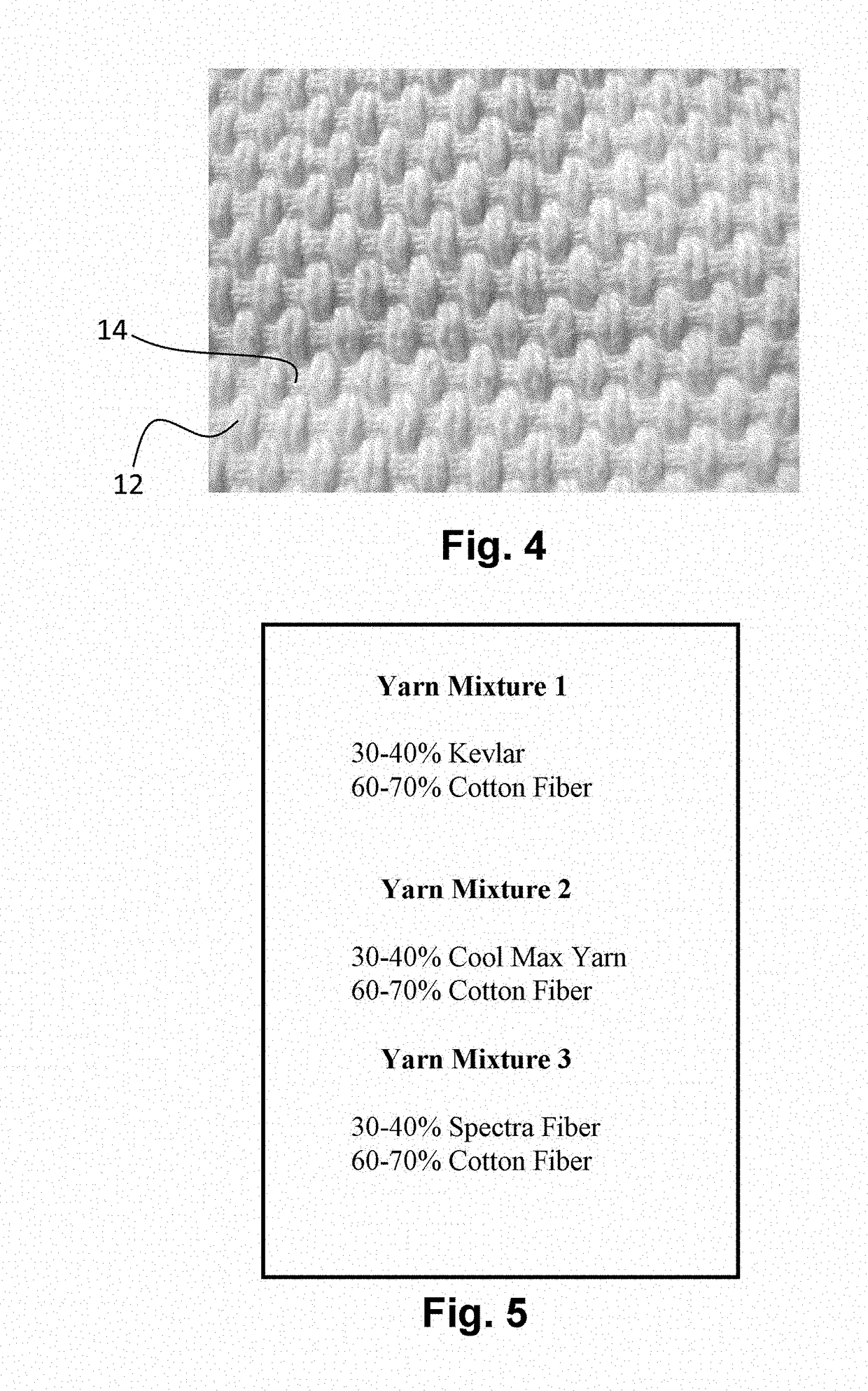
[0031]As noted in all modes of the textile fabric herein, the percentage of first yarn 12 formed of cotton is substantially 60-70% of the total weight of the woven or knitted fabric in all modes of woven or knitted fabric. The second yarn 14 formed of the materia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| constant stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| abrasion resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com