Method, system and computer readable medium for evaluating colonoscopy performance
a colonoscopy and performance evaluation technology, applied in the field of colonoscopy performance evaluation, can solve the problems of inability to accurately detect lesions in spiral colonoscopy, inability to accurately evaluate the quality of colonoscopy examination, and inability to reflect the total withdrawal tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
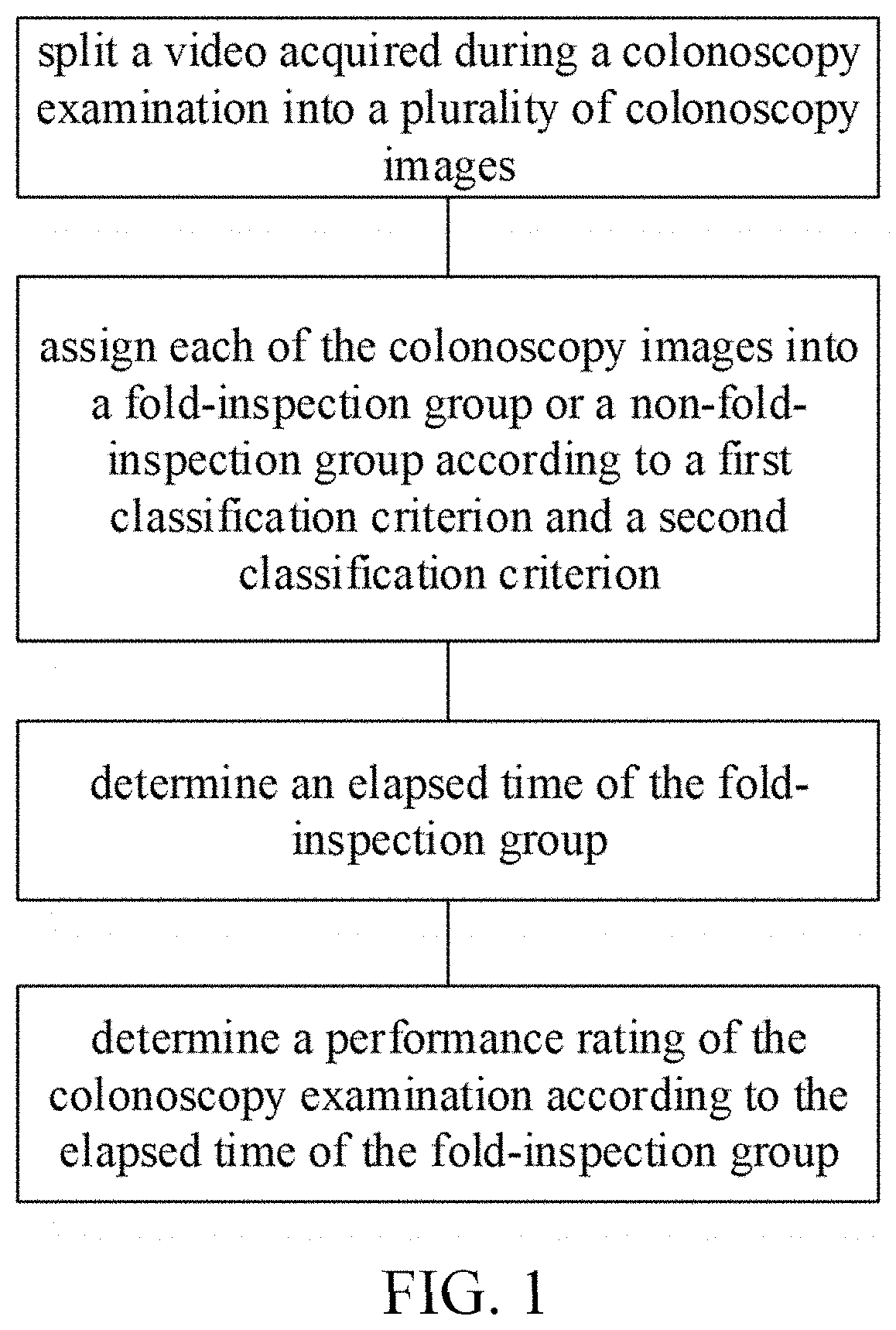
[0070]As shown in FIG. 1, a method for evaluating colonoscopy performance according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes the steps of:
[0071](S1) splitting a video acquired during a colonoscopy examination into a plurality of colonoscopy images;
[0072](S2) assigning each of the colonoscopy images into a fold-inspection group or a non-fold-inspection group according to a first classification criterion and a second classification criterion, wherein the first classification criterion includes at least one of clarity, exposure, level of tissue wrinkling, and level of occlusion in each of the colonoscopy images; and the second classification criterion includes at least one of an amount of haustrum, an amount of colonic lumen, and a position of the colonic lumen in each of the colonoscopy images; and
[0073](S3) determining a performance rating of the colonoscopy examination according to an elapsed time of the fold-inspection group.
[0074]In this embodiment, the video can be a r...
embodiment 2
[0086]In addition to the features of Embodiment 1, this embodiment applies the first classification criterion prior to applying the second classification criterion.
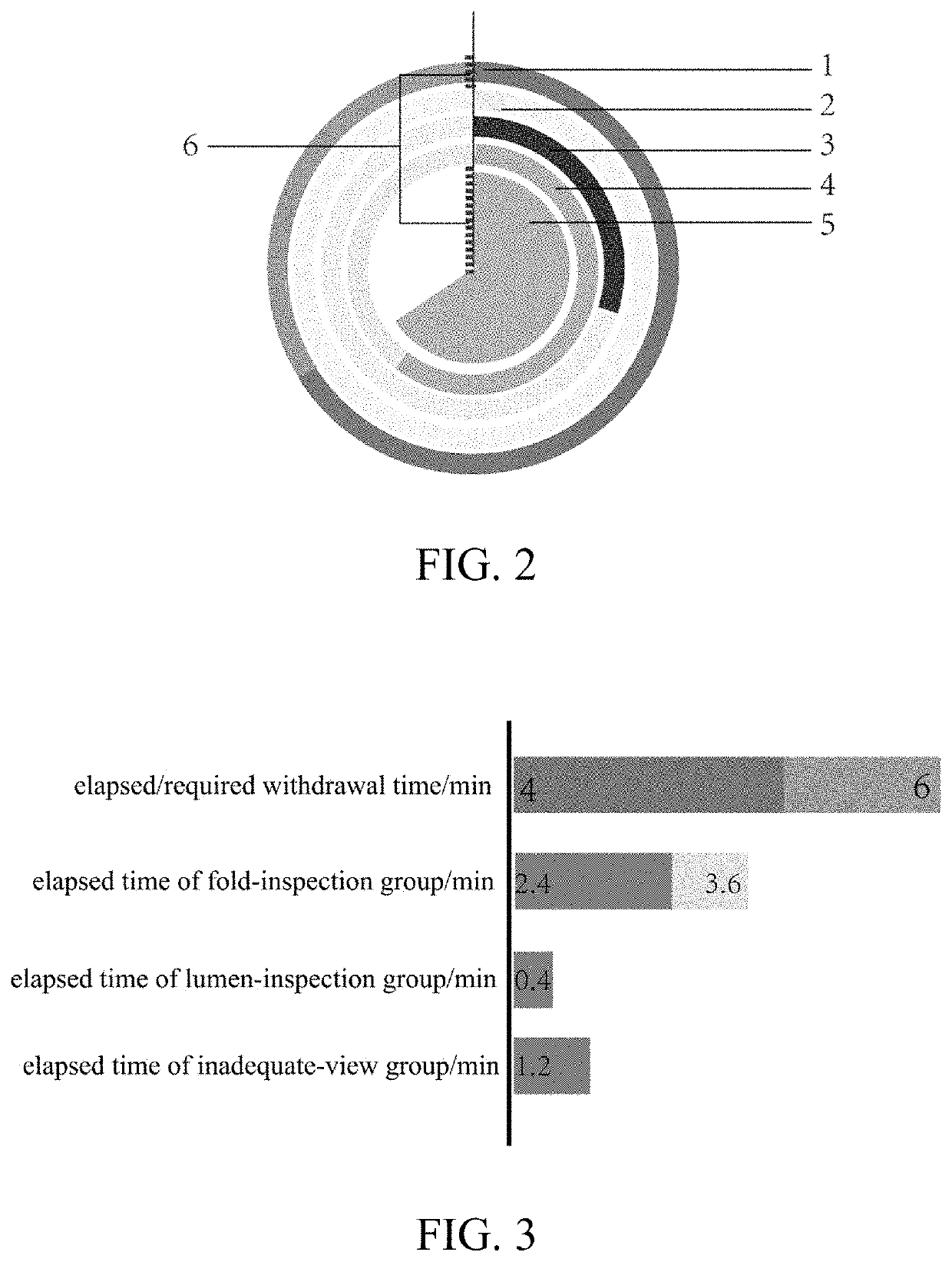
[0087]In this embodiment, the image assignment step (S2) includes: (S21) assigning each of the colonoscopy images into an inadequate-view group or an adequate-view group according to the first classification criterion; and (S22) assigning each image in the adequate-view group into the fold-inspection group or a lumen-inspection group according to the second classification criterion. The rating step (S3) includes: determining the performance rating of the colonoscopy examination according to an elapsed time of at least one of the fold-inspection group, the lumen-inspection group, and the inadequate-view group.
[0088]The three-group classification method provided herein is logically clear and capable of classifying all possible colonoscopy images split frame by frame from a colonoscopy video promptly and reliably.
[0089]After...
embodiment 3
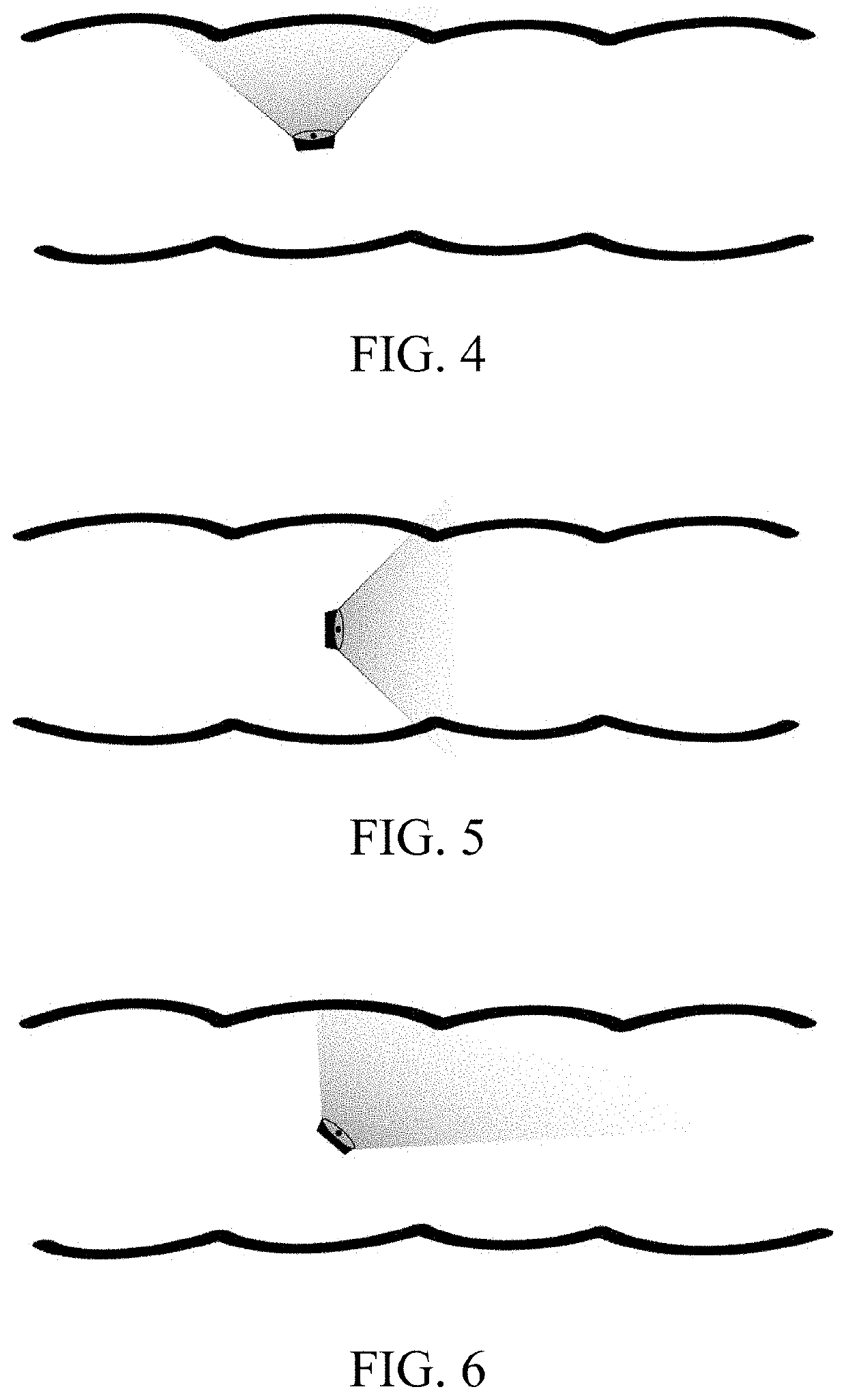
[0092]In addition to the features of the aforementioned embodiments, the image assignment step (S22) may include: assigning the colonoscopy image in the adequate-view group into the fold-inspection group if the image meets one of the requirements of: (R1) colonic wall is shown, but in absence of haustrum or colonic lumen; (R2) colonic wall and haustrum are shown, but in absence of colonic lumen; and (R3) colonic wall, haustrum and colonic lumen are shown, the amount of the haustrum shown falls within a range of 1 to 5, and the colonic lumen falls outside of a central area of the image. Alternatively, if the colonoscopy image does not meet any of the requirements of (R1)-(R3), the image is assigned into the lumen-inspection group.
[0093]In conventional spiral colonoscopy, physicians are required to inspect the colonic mucosa by aiming the colonoscope straight at the colonic wall, as illustrated in FIG. 4. Therefore, common practice in the art has been to regard colonoscopy images take...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com