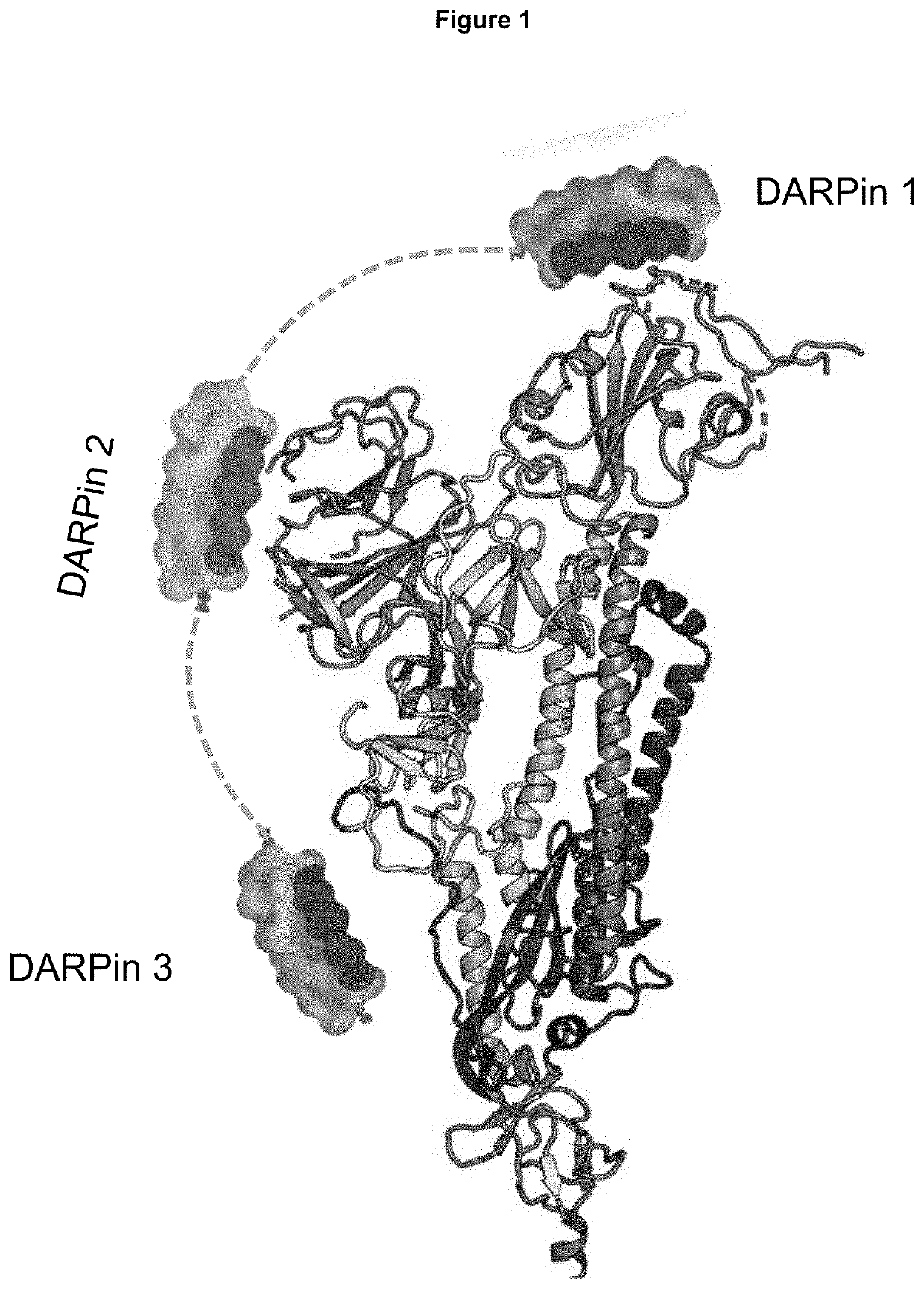
Novel ankyrin repeat binding proteins and their uses
a technology of ankyrin repeat and binding protein, which is applied in the field of recombinant binding proteins, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of treatment options
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of Binding Proteins Comprising an Ankyrin Repeat Domain with Binding Specificity for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
[0387]Summary
[0388]Using ribosome display (Hanes, J. and Plückthun, A., PNAS 94, 4937-42, 1997), multiple ankyrin repeat domains with binding specificity for different domains of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (RBD domain; S1 NTD domain; S2 domain) were selected from DARPin® libraries in a way similar to the one described by Binz et al. 2004 (loc. cit.), with specific conditions and additional de-selection steps. The binding and specificity of the selected clones towards recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein target domains were assessed by E. coli crude extract Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF), indicating that multiple SARS-CoV-2 spike protein specific binding proteins were successfully selected. For example, the ankyrin repeat domains of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 11 constitute amino acid sequences of selected binding proteins comprising an ankyrin repeat domain with binding...
example 2
ng Assays
[0412]Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assays were used to determine the binding affinity of the binding proteins of the invention to the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
[0413]All SPR data were generated using a Bio-Rad ProteOn XPR36 instrument with PBS-T (0.005% Tween20) as running buffer. A new neutravidin sensor chip (NLC) was air-initialized and conditioned according to Bio-Rad manual.
[0414]Mono-domain DARPin proteins: In-house chemically biotinylated (via lysines) SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (Sino Biologics, cat. 40589-V08B1, Lot MF14MA0701) was captured to ˜3400 RUs (30 ug / ml, 30 ul / min, 300s). Two buffer injections (100 ul / min, 60s) followed by two 12.5 mM NaOH regeneration steps (100 ul / min, 18s) were applied before the first injections. Mono-domain DARPin proteins were injected (at 50 / 16.7 / 5.6 / 1.9 / 0.6 nM (or at 16.7 / 5.6 / 1.9 / 0.6 nM for SEQ ID NO: 9 and 10)) for 180s at 100 ul / min for association and dissociation was recorded for 3600s (at 100 ul / min). The ligand was regener...
example 3
l Screening
[0421]This Example describes functional screening of mono-domain and multi domain proteins using the SARS-CoV-2 VSV pseudotype virus assay. The results of this assay are provided in FIGS. 5 to 8.
[0422]Infection inhibition was assessed using a vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) pseudovirus assay (psVSV), where the glycoprotein of VSV was replaced by the Wuhan variant of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein tagged with an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and firefly luciferase (LUC). Inhibition of infection following addition of 1 nM, 10 nM, or 100 nM of candidate was measured by simple quantification of EGFP and LUC activity (see Torriani, G. et al., Virology 531, 57-68 (2019)).
[0423]FIGS. 5 and 7 show pseudotype SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibition at 100 nM of various recombinant binding proteins that bind to a single site on the spike protein (mono-domain DARPin® proteins) and three sites on the spike protein (multi-domain DARPin® proteins), respectively. Shorter bars are in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| equilibrium dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| equilibrium dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com