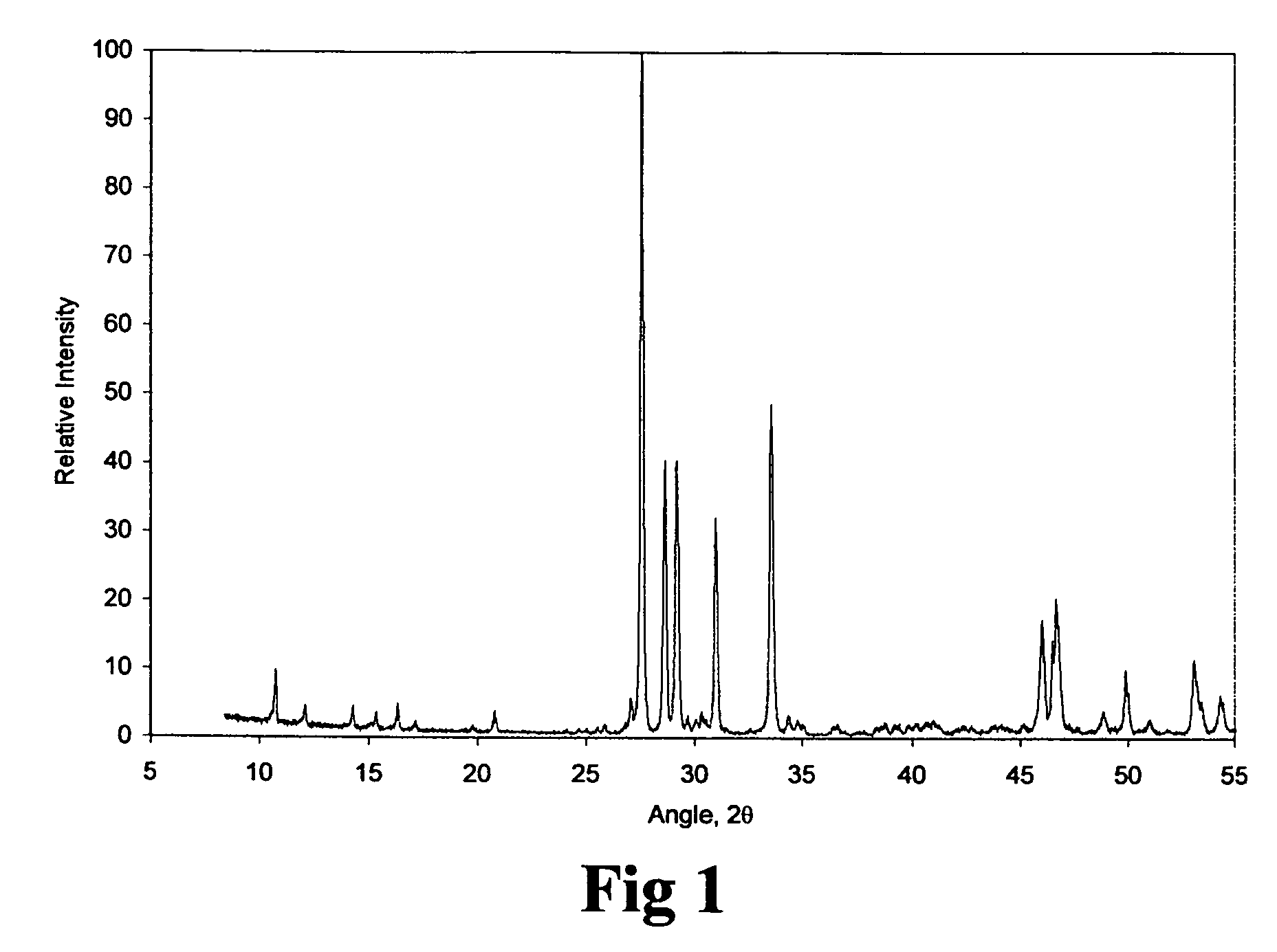
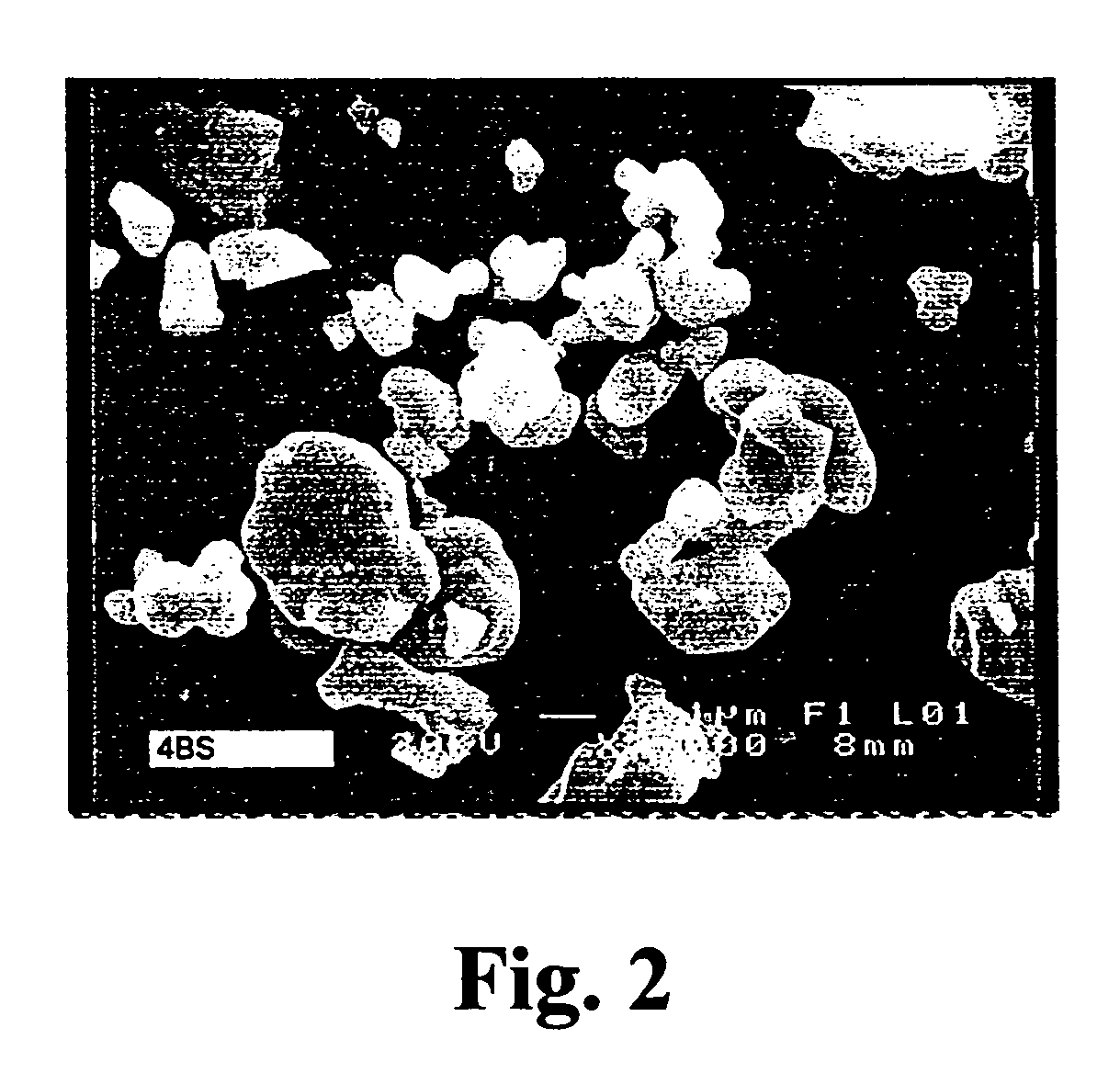
Production of tetrabasic lead sulfate from solid state reactions for the preparation of active plates to be used in lead-acid batteries
a technology of solid state reactions and lead sulfate, which is applied in the manufacture of final products, lead sulfates, cell components, etc., can solve the problems of complex production methods, high cost, and heterogeneous crystal sizes of tetrabasic lead sulfate, and achieve the effect of avoiding any further milling of material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0026]Five mole of lead oxide were intimately mixed up with four mole of lead sulfate. A heat treatment of the reacting mixture at 600° C. for 4 hours made it possible to achieve a degree of transformation of 95%.
3PbO.PbSO4.H2O+PbO+thermal treatment→4PbO.PbSO4+H2O
[0027]In this case a solid state reaction method is proposed for the production of tetrabasic lead sulfate by reacting 3PbO.PbSO4.H2O+PbO. This method comprising the steps of mixing of the stoichiometric mixture of 3PbO.PbSO4.H2O+PbO, heating the stoichiometric mixture of 3PbO.PbSO4.H2O+PbO at a temperature between 500 and 700° C. during 3 to 8 hours and finally deagglomerating and sieving the resulting tetrabasic lead sulfate.
example 2
[0028]A degree of transformation into tetrabasic lead sulfate of 83.4% was achieved by heat treating at 600° C. for 5 hours a mixture of one mole of tribasic lead sulfate with one mole of lead oxide.
[0029]An alternative method to this chemical route to produce tetrabasic lead sulfate is as follows:
[0030]Either by using active materials coming from the pastes used for the preparation of the lead-acid battery plates, or coming from recycled lead-acid battery plates. In this case, a solid state reaction method is proposed for the production of tetrabasic lead sulfate by reacting 3PbO.PbSO4.H2O+PbO. This method comprises the steps of mixing either the paste used for the preparation of the lead-acid battery plates, or the paste recovered from recycled lead-acid battery plates, heating the mixture at a temperature between 500 and 700° C. during 3 to 8 hours, and finally deagglomerating and sieving the resulting tetrabasic lead sulfate.
example 3
[0031]A degree of transformation into tetrabasic lead sulfate of 93% was achieved by heat treating at 650° C. for 5 hours the active materials coming from recycled lead-acid battery plates.
5PbO+H2SO4+thermal treatment→4PbO.PbSO4+H2O
[0032]In this case a solid state reaction method is proposed for the production of tetrabasic lead sulfate by reacting 5PbO+H2SO4. This method comprising the steps of mixing the PbO with 1 mole of a H2SO4 aqueous solution having a specific gravity in the range of 1.100 to 1.400 g / cm3, following this by a temperature rise of the stoichiometric mixture to 500–700° C., holding the mixture at that temperature for 3 to 8 hours, and finally deagglomerating and sieving the resulting tetrabasic lead sulfate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com