Optical displacement sensor and external force detecting device
a technology of optical displacement sensor and detecting device, which is applied in the direction of instruments, instruments, and instruments for force/torque/work measurement, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the accuracy of the measurement, the adjustment of the rotational angle about the z-axis perpendicular to the x- and y-axes is difficult, and the work is laborious, so as to reduce the time, the adjustment is easy, and the effect of reducing the tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
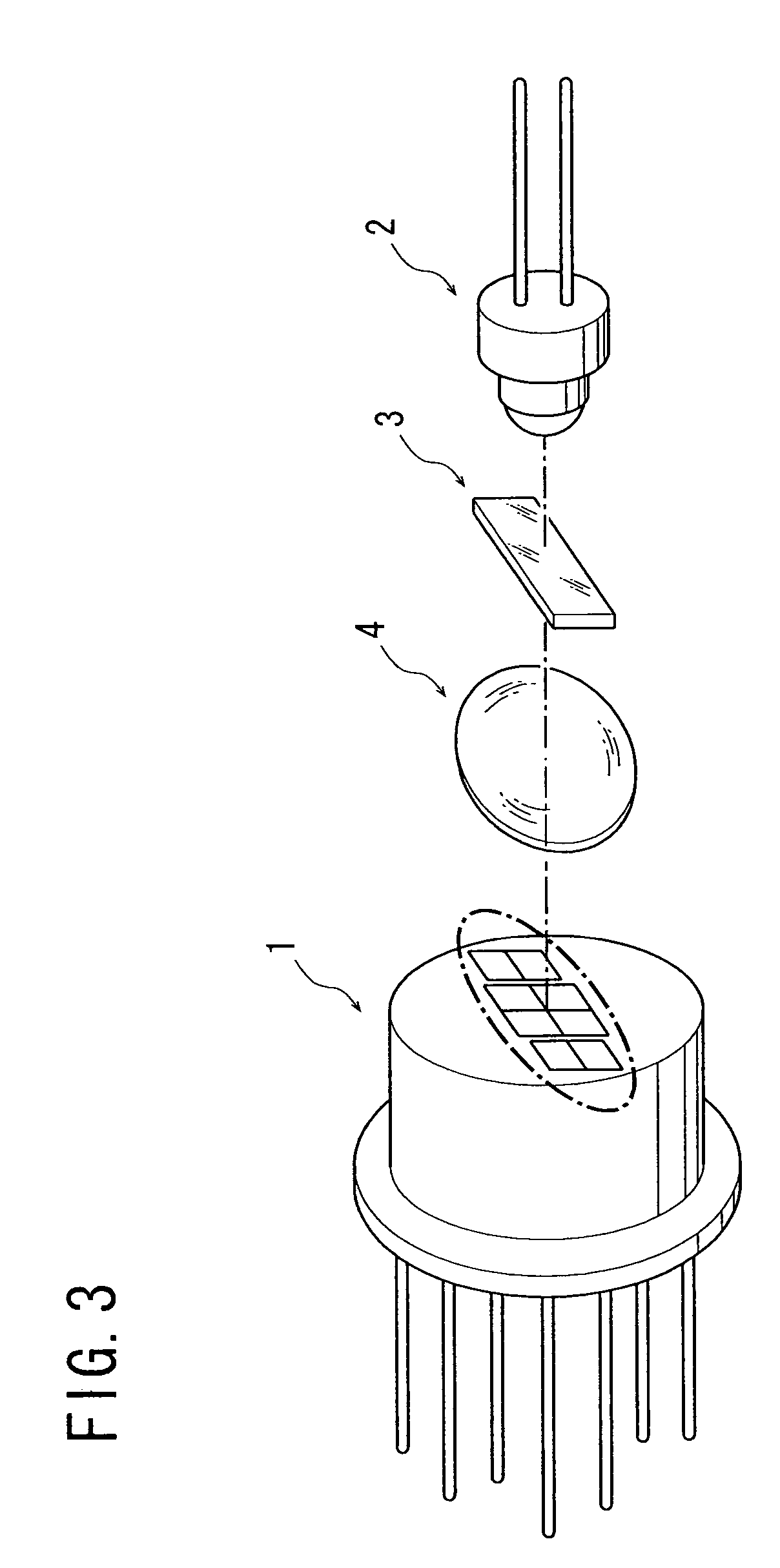
[0035]the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 6. Referring first to FIG. 3, an optical displacement sensor comprises: a photodiode (PD) assembly 1 as a light receiving means; a light emitting diode (LED) 2 which is a light emitting element as a light source; a light diffracting element 3 to disperse one beam into three beams; and a lens 4 to shape and condense beams.
[0036]In the optical displacement sensor shown in FIG. 3, the PD assembly 1 is mounted at one of a reference object and a measurement object, and the LED 2 is mounted at the other one thereof, at which the PD assembly 1 is not mounted, wherein light emitted from the LED 2 is received at the PD assembly 1, and the positional displacement of the measurement object relative to the reference object with respect to two-axis directions in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis of the light emitted from the LED 2 is measured on the basis of the state of light reception at the PD assembly 1. This ...
third embodiment
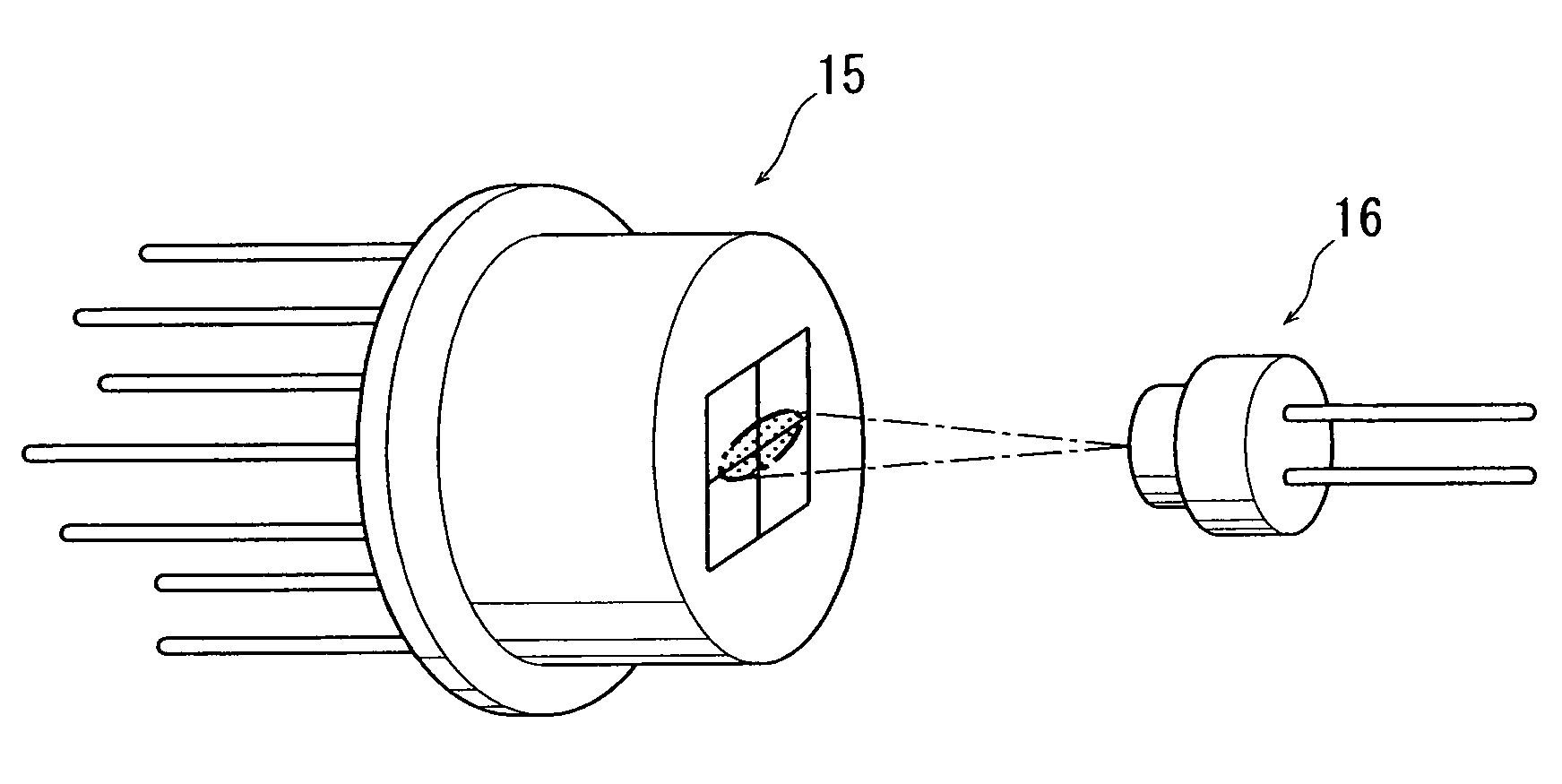
[0051]the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 10. An optical displacement sensor according to the third embodiment comprises a PD assembly 15 (same as employed in the second embodiment) as a light receiving means, an LED 2 (same as employed in the first embodiment) which is a light emitting element as a light source, and a cylindrical lens 17 disposed between the PD assembly 15 and the LED 2.
[0052]Light emitted from the LED 2, which originally is not shaped oval in cross section, has its cross section modified into an oval configuration with two axes of symmetry when passing through the cylindrical lens 17, and is received at the light receiving face of the PD assembly 15. Since the PD assembly 15 is structured in the same way as in the second embodiment, and since the light received by the PD assembly 15 has an oval cross section like in the second embodiment, rotational adjustment about the Z-axis can be performed following the method described in the second...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| light intensity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| external force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com