Radio channel aggregation and segmentation
a technology of radio channel and aggregation, applied in the direction of code conversion, wireless commuication services, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of power consumption, high cost of providing all this hardware, and high hardware cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
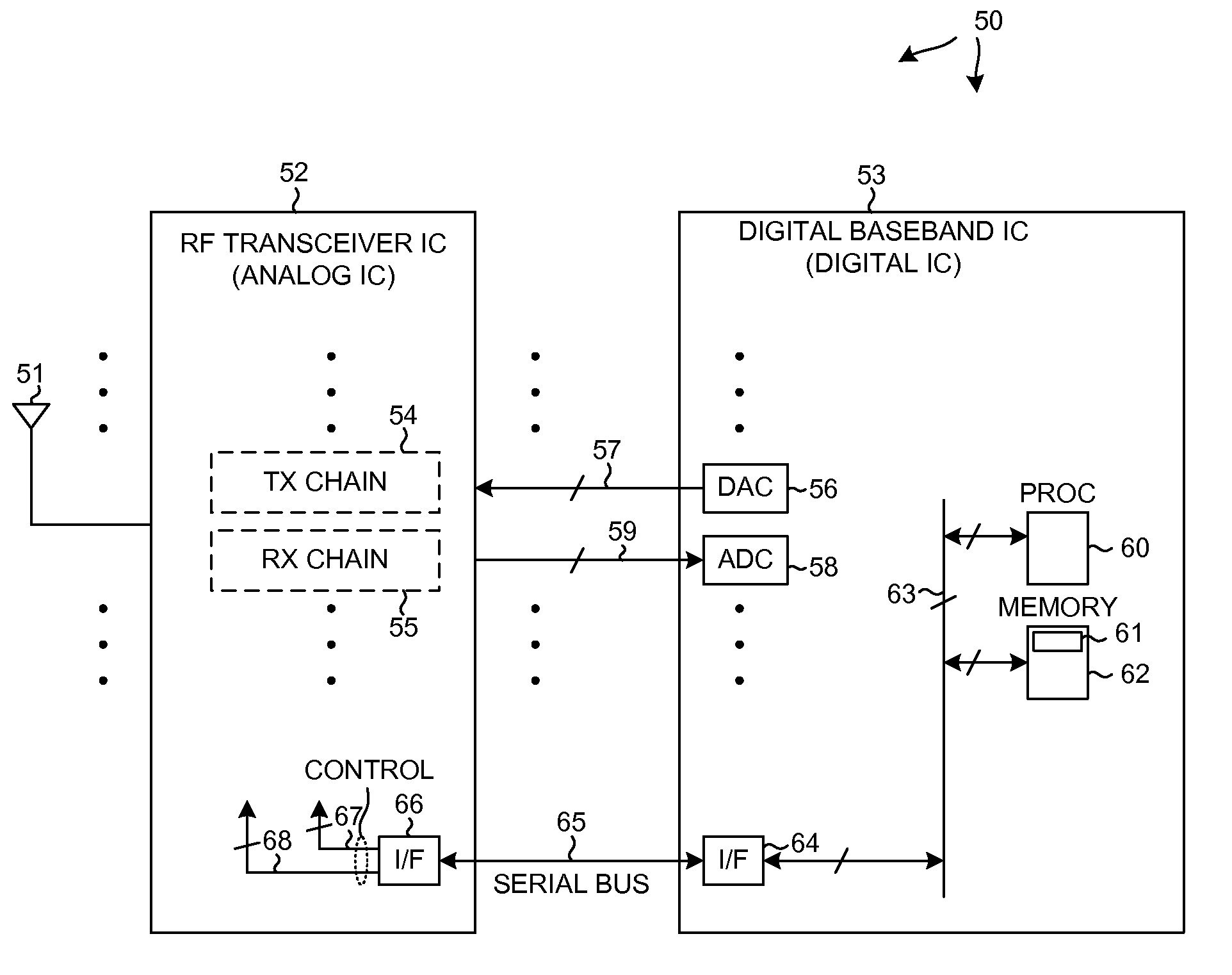
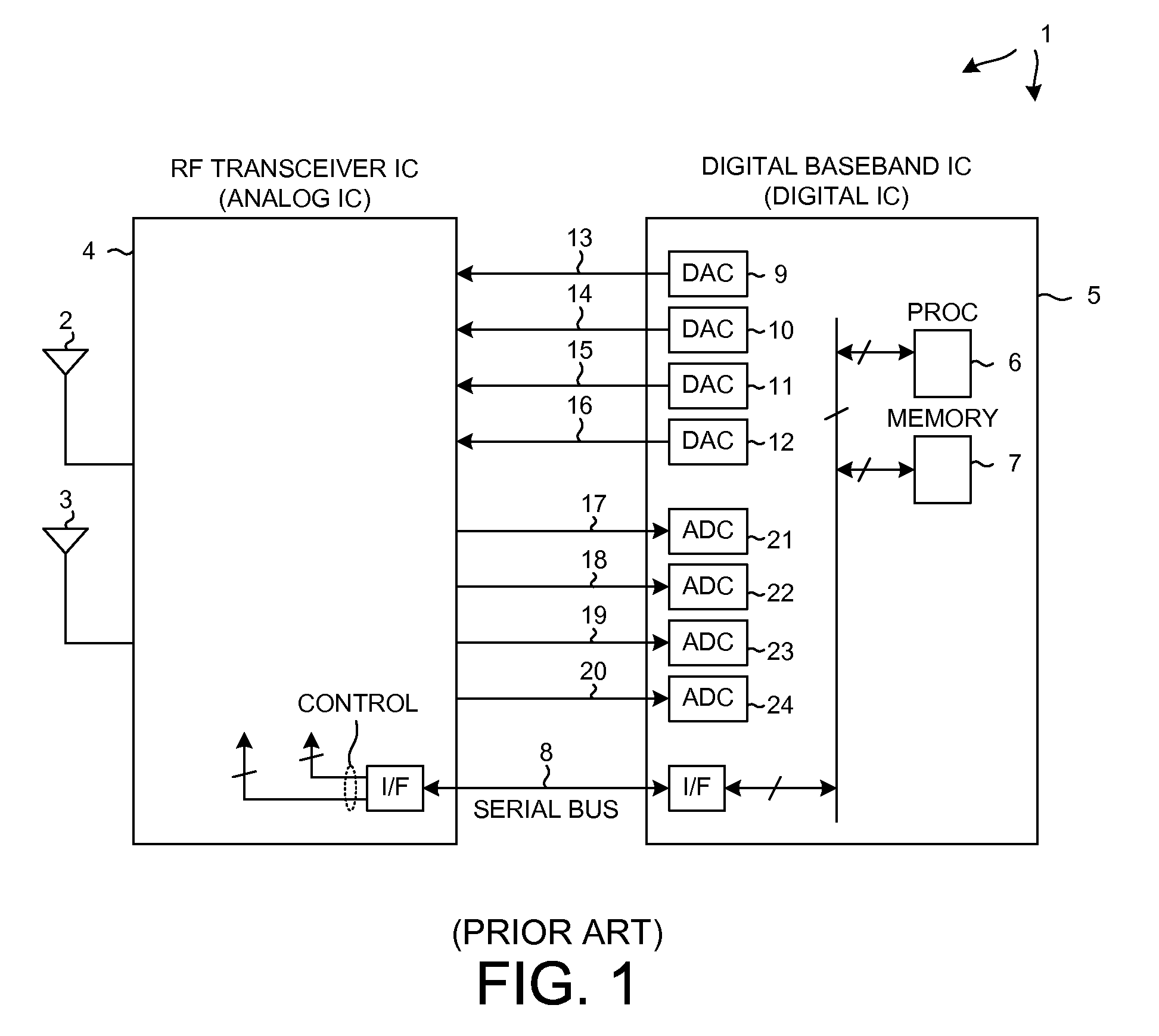
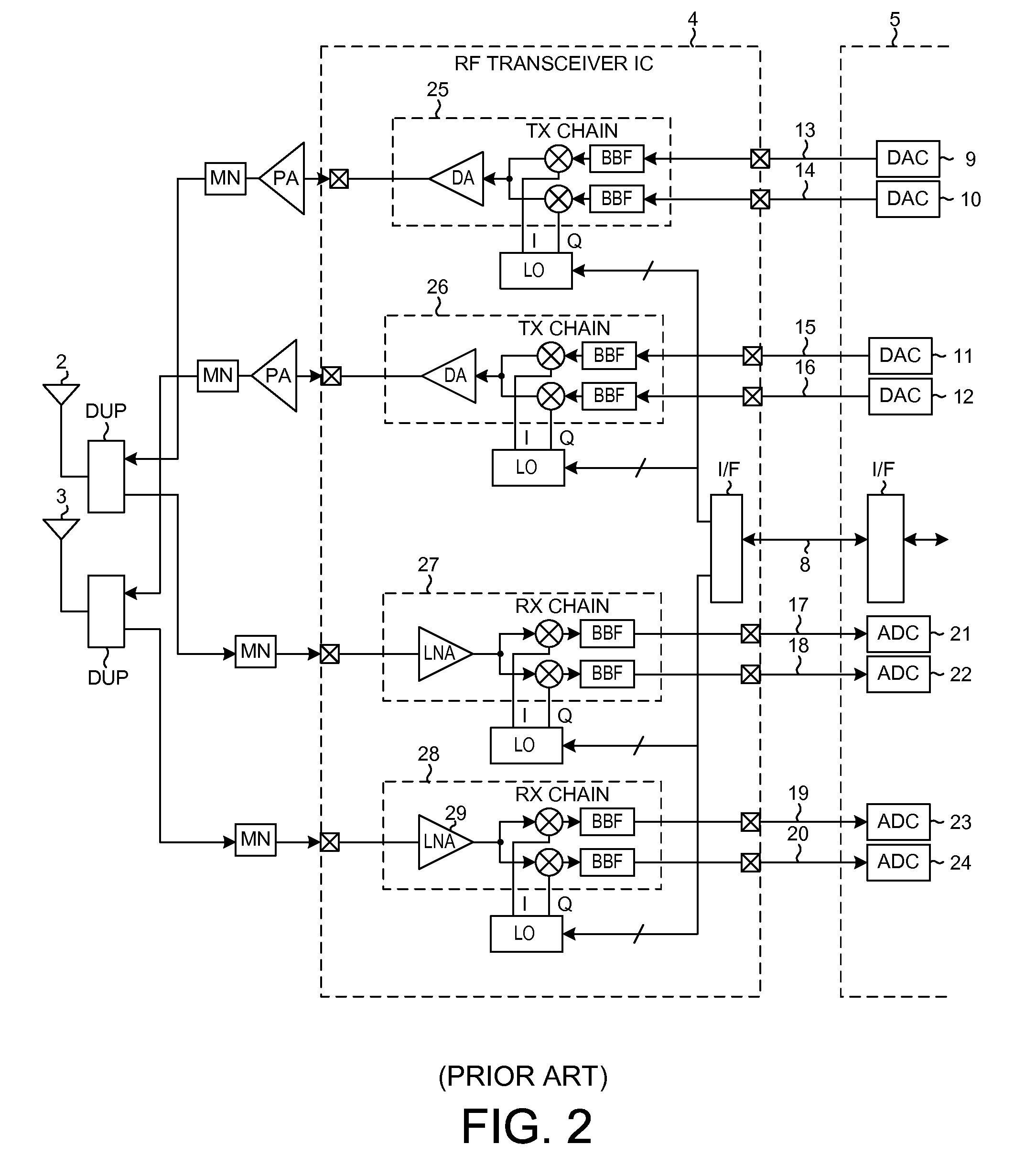
[0039]FIG. 4 is a high-level simplified diagram of an apparatus 50 (a mobile communication device) that includes a specific embodiment of Block-TDM (Block-Time-Division-Multiplexing) aggregation and de-aggregation circuitry and functionality in accordance with a first novel aspect. The Block-TDM aggregation and de-aggregation structures and methods set forth and described in this patent document see wide applicability to both receivers and to transmitters, and to transceiver devices involving different numbers of antennas, and to transceiver devices involving different numbers of communication carriers and different kinds of analog-to-digital conversion circuitry. The analog and digital functionality of the transceivers may be divided and partitioned in different ways in different embodiments. Block-TDM aggregation and de-aggregation can be performed on signals coming from, or going to, multiple antennas. Block-TDM aggregation and de-aggregation can also be performed on signal paths...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com