Method for analyzing continuous glucose monitoring data
a monitoring data and data technology, applied in the field of continuous glucose monitoring data analysis, can solve the problems of lack of useful cgms data indicators, inability to easily aggregate data to facilitate treatment group comparisons, and lack of data for analyzing continuous glucose monitoring data, so as to increase determine the susceptibility to symptomatic hypoglycemia
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
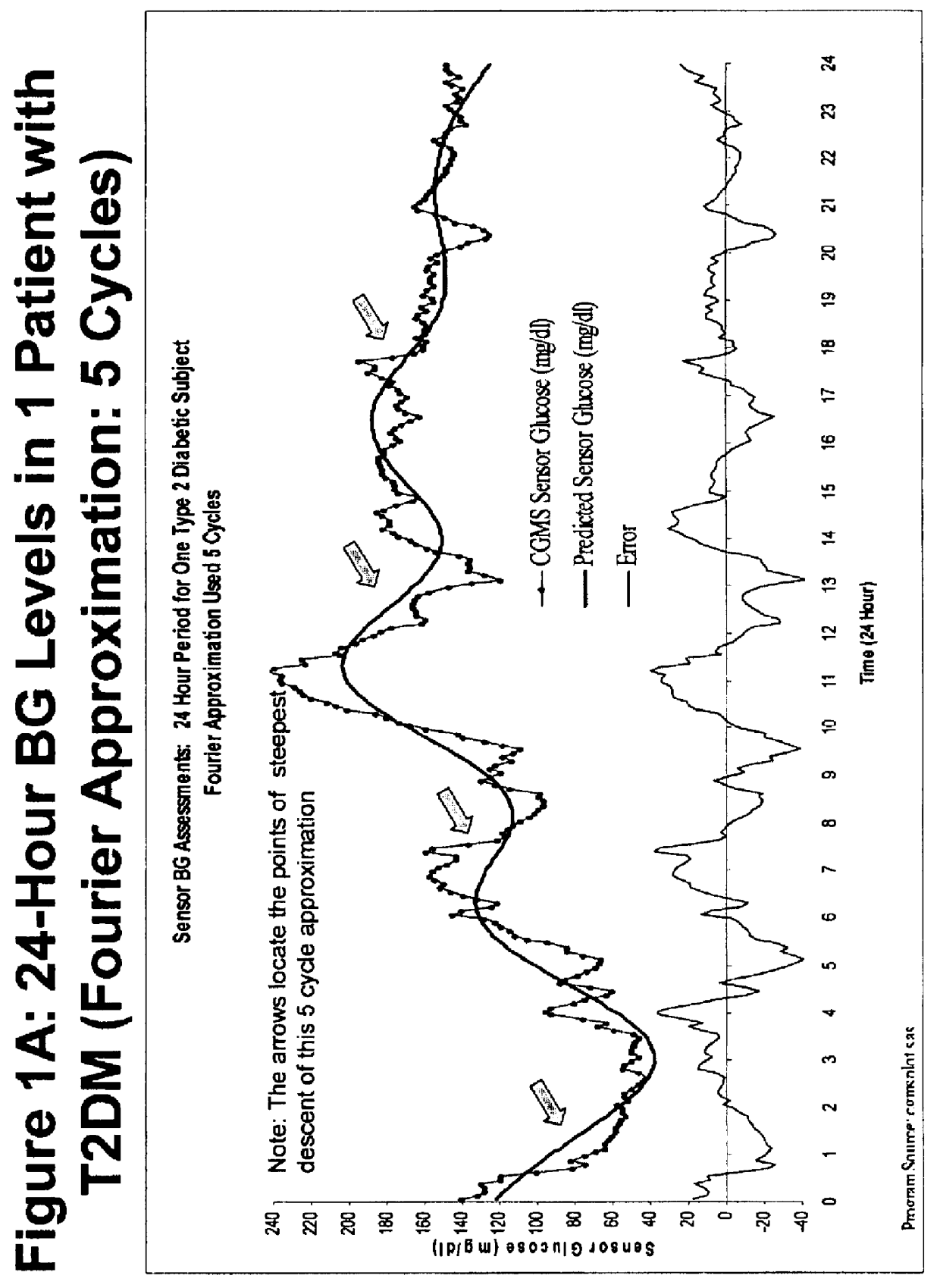
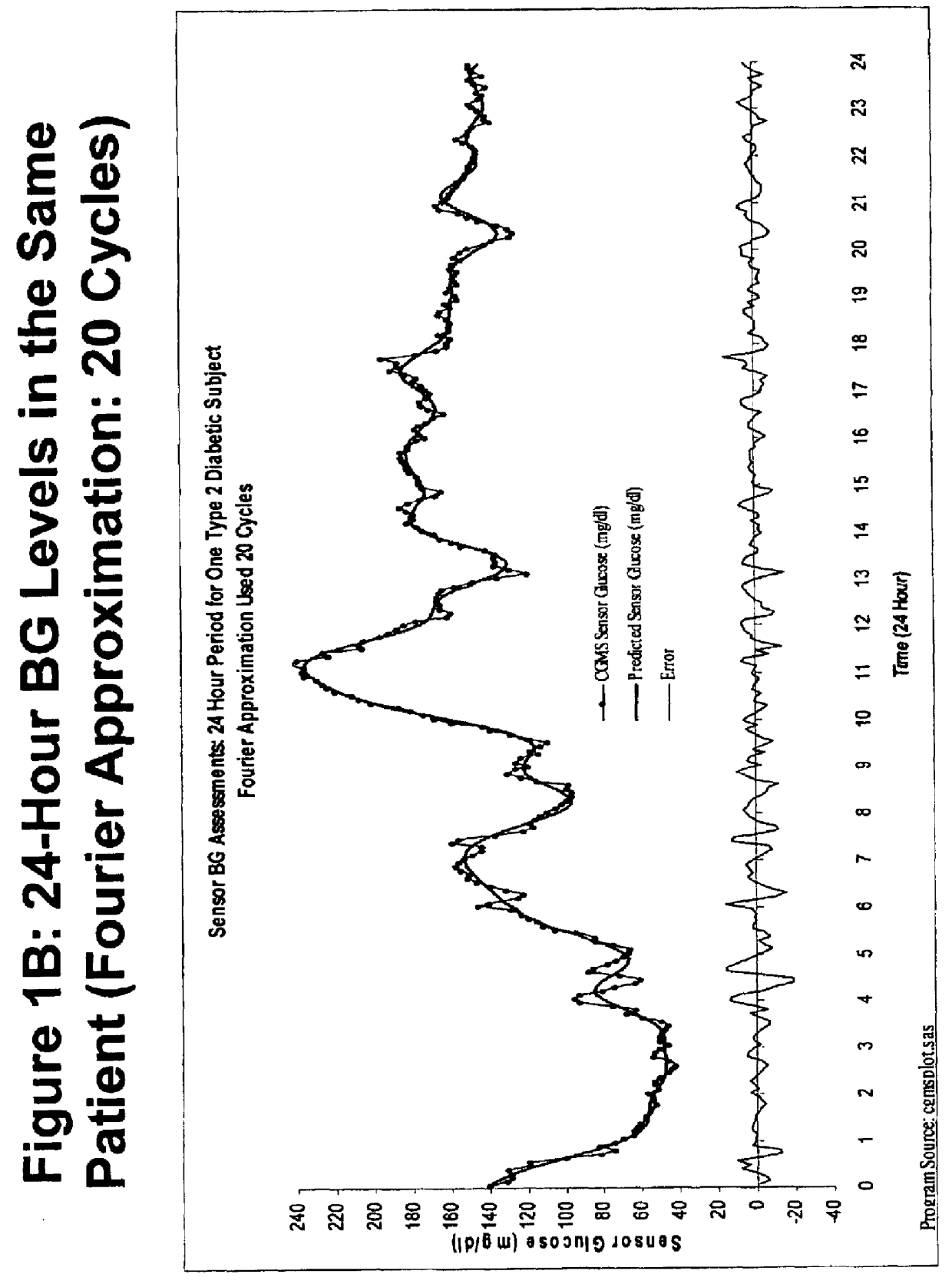
[0023]A Fourier approximation is applied to the observed CGMS blood glucose data for one patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. FIG. 1A shows a Fourier approximation of the CGMS data using five cycles calculated as described above. FIG. 1B shows a Fourier approximation of the same data using twenty cycles. As seen in the FIGS. 1A and 1B, the Fourier approximations tend to smooth out the high-frequency noise observed in the raw CGMS data. As one increases the number of cycles, the Fourier approximation does a better job of approximating the actual CGMS data as shown by the decrease in the fluctuation of the error graph in FIG. 1B as compared to FIG. 1A. As one increases the number of cycles, however, the smoothness of the Fourier approximation curve is decreased, resulting in a curve that is less likely to be useful in identifying prognostic indicators.
example 2
[0024]This study employs CGMS 24-hour blood glucose profiles from the following patient populations:[0025]pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), N=90;[0026]adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), N=34;[0027]normal subjects, N=15; and[0028]patients with T1DM using an insulin pump, N=37.
[0029]For each subject, a seven cycle Fourier approximation is applied to twenty-four hour CGMS data. An aggregate curve is created for each patient population by averaging the subject Fourier coefficients and producing a graph determined by these averages. FIG. 2 shows the resulting graphs for each patient population. An interesting observation is that insulin-pump therapy not only reduces the average blood glucose levels but also reduces the amplitude of the resulting aggregate Fourier approximation. This indicates that type 1 patients using the insulin pump are less likely to experience hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic events.
example 3
[0030]This study employs CGMS 24-hour blood glucose profiles from the pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), N=90; half of the patients are on a typical insulin therapy regimen while half of the patients are using Lantus®. For each subject, a Fourier approximation is applied to twenty-four hour CGMS data. An aggregate curve is created for the patient population by averaging the subject Fourier coefficients and producing a graph determined by these averages. The Fourier approximation is decomposed into its component harmonics. FIG. 3 shows the resulting graph of the mean blood glucose levels from the patient population along with the first, the sum of the second and third, and the sum of the fourth and higher harmonic functions of the aggregate Fourier approximation.
[0031]FIG. 4 shows a graph of week twenty-four HbA1c levels versus the mean baseline amplitude of the sum of the second and third harmonic functions of a Fourier approximation. HbA1c is a specific subtyp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com