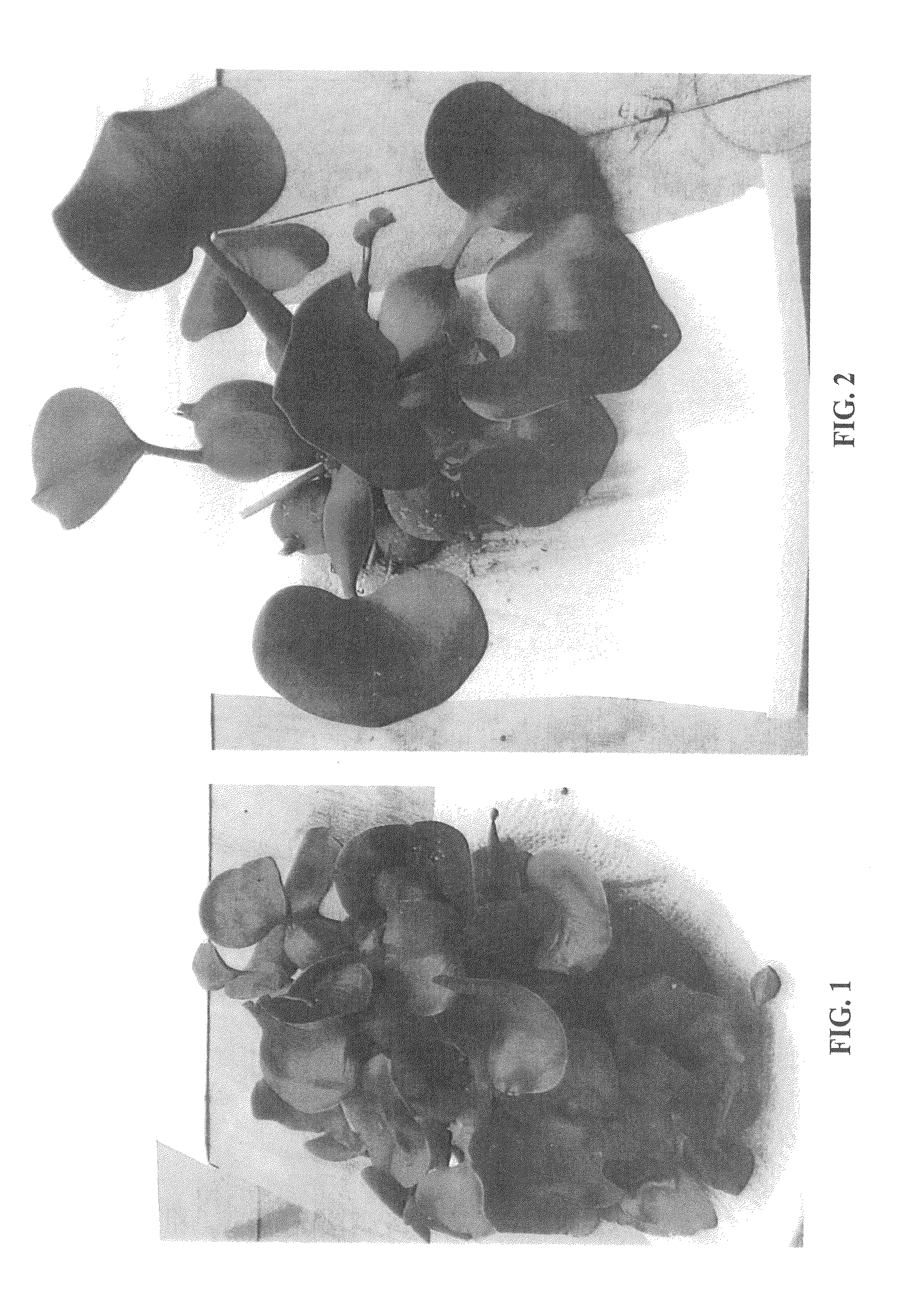
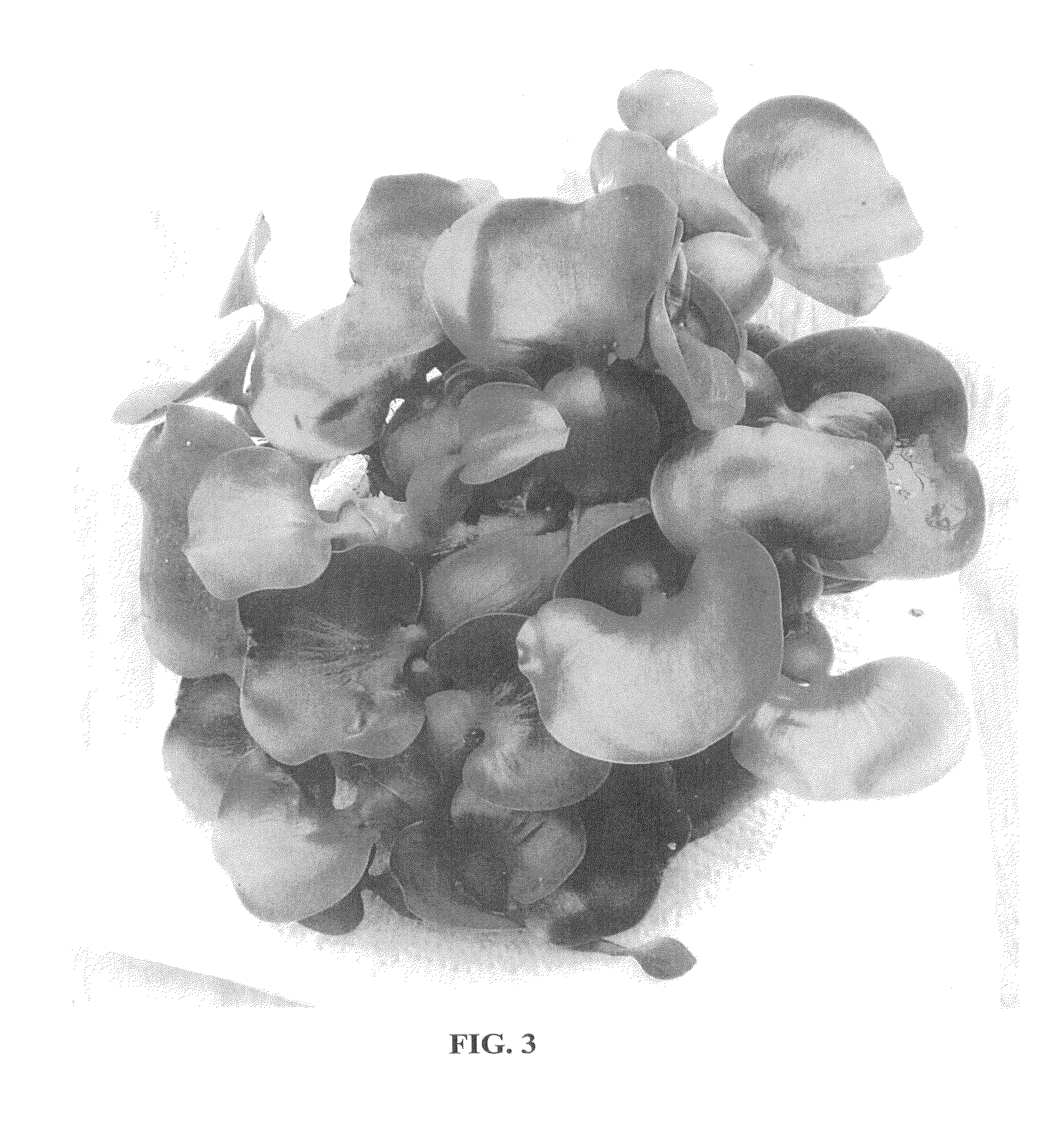
Eichhornia crassipes plant named `Johann Schoofs Sen`
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021]The chart used in the identification of colors is that of The Royal Horticultural Society (R.H.S. Colour Chart), London, England (1995 Edition or equivalent). The observed plants were grown at Kalkar, Germany, and at Naktiunbouw, The Netherlands.[0022]Botanical classification: Eichhornia crassipes, cv Johan Schoofs Sen.[0023]Growth habit: Floats on the surface of water with the roots being substantially completely submerged. The overall growth habit is substantially smaller and substantially more compact than that of typical Eichhornia crassipes plants.[0024]Plant characteristics: The dark green leaves are generally elliptic in configuration, are slightly concave and are slightly wavy in appearance. The leaves are displayed in abundance and are smaller than those typically displayed by Eichhornia crassipes. The leaves commonly are approximately 3 to 9 cm in length and approximately 2.5 to 4.5 cm in width. The coloration of the upper leaf surface commonly ranges from near Green...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com