Battery plates having rounded lower corners
a battery plate and lower corner technology, applied in the field of battery plate manufacturing, can solve the problems of reducing battery life, short circuit of battery, and no process for producing rounded corners on such battery plates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
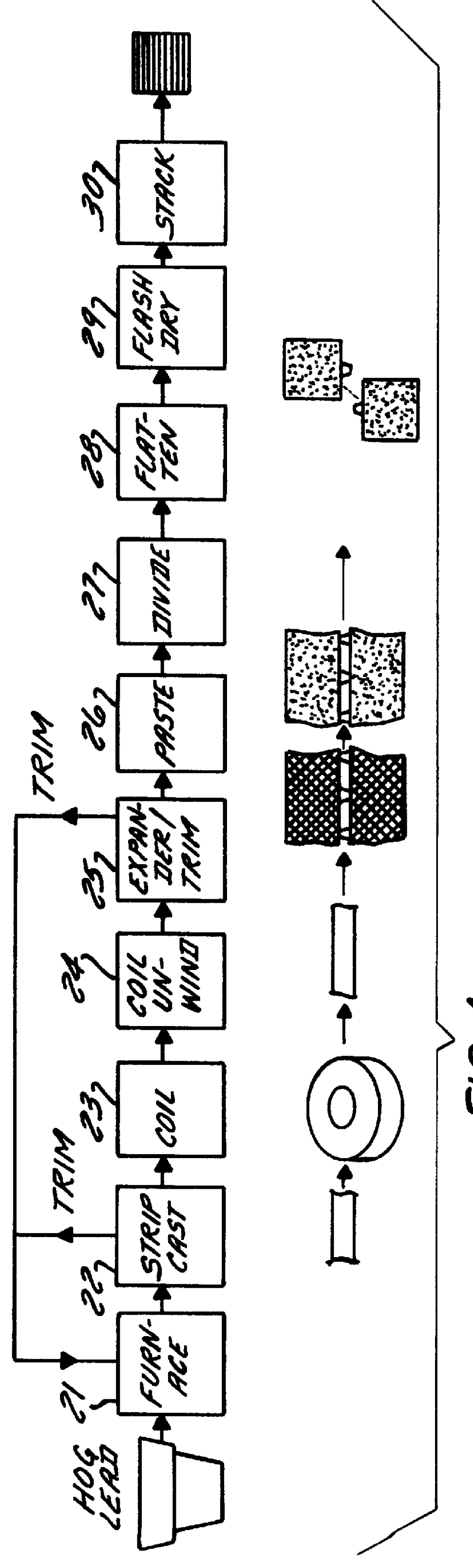
Referring to FIG. 1, the process according to the invention is shown in relation to the other steps conventionally used in a continuous process for making lead-acid battery plates. The known process for making such plates includes an initial step 21 of melting hog lead in a furnace, followed by a step 22 of feeding molten lead alloy to a strip caster. Trim from the caster is recycled to the furnace. The strip is coiled (23) on a winder, and coils of lead alloy strip are stored for later use.
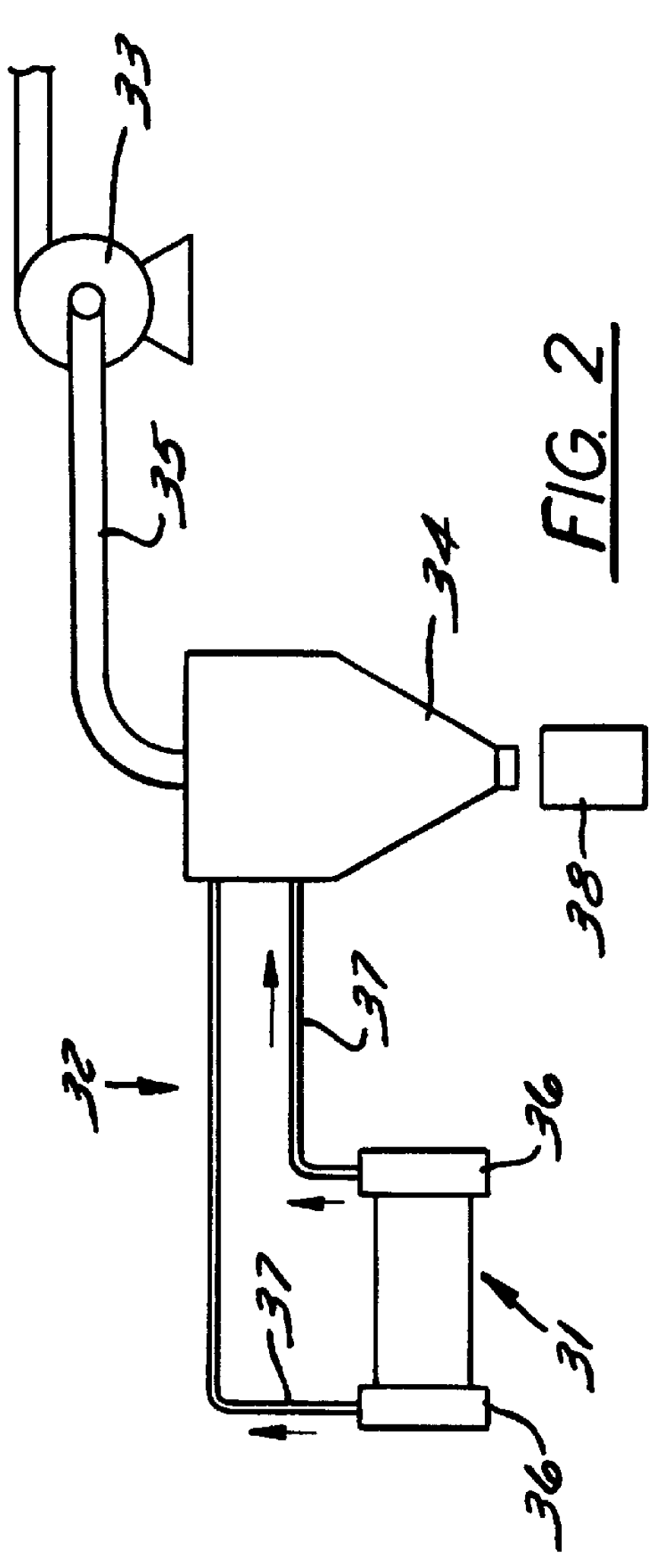
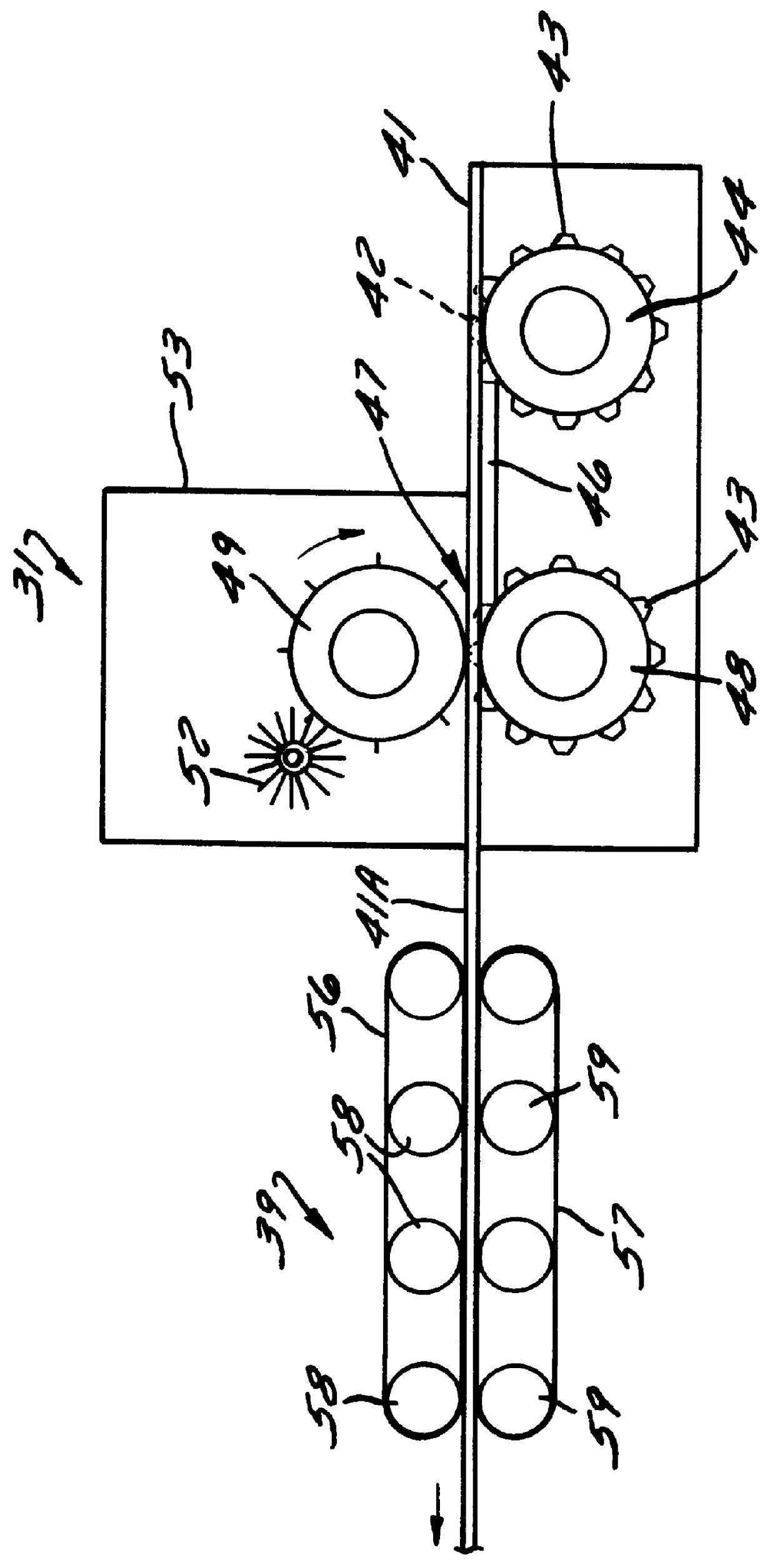
To form a battery grid, the coil is unwound (24) and the free end is fed through an expander that cuts, slits and stretches (25) the strip to form a mesh-like pattern of grid elements. See, for example, the expanders described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 4,315,356 and 4,291,443 assigned to Cominco Ltd., the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. Trim from the expander is recycled to the furnace. The expanded strip is then pasted (26) by a conventional paster, and then fed to the divider ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com