Anti-PMD system
A technology of pulleys and optical fibers, applied in the field of anti-PMD systems, can solve problems such as constant deviation, reduction of twisting torque of anti-PMD pulleys, and reduced effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
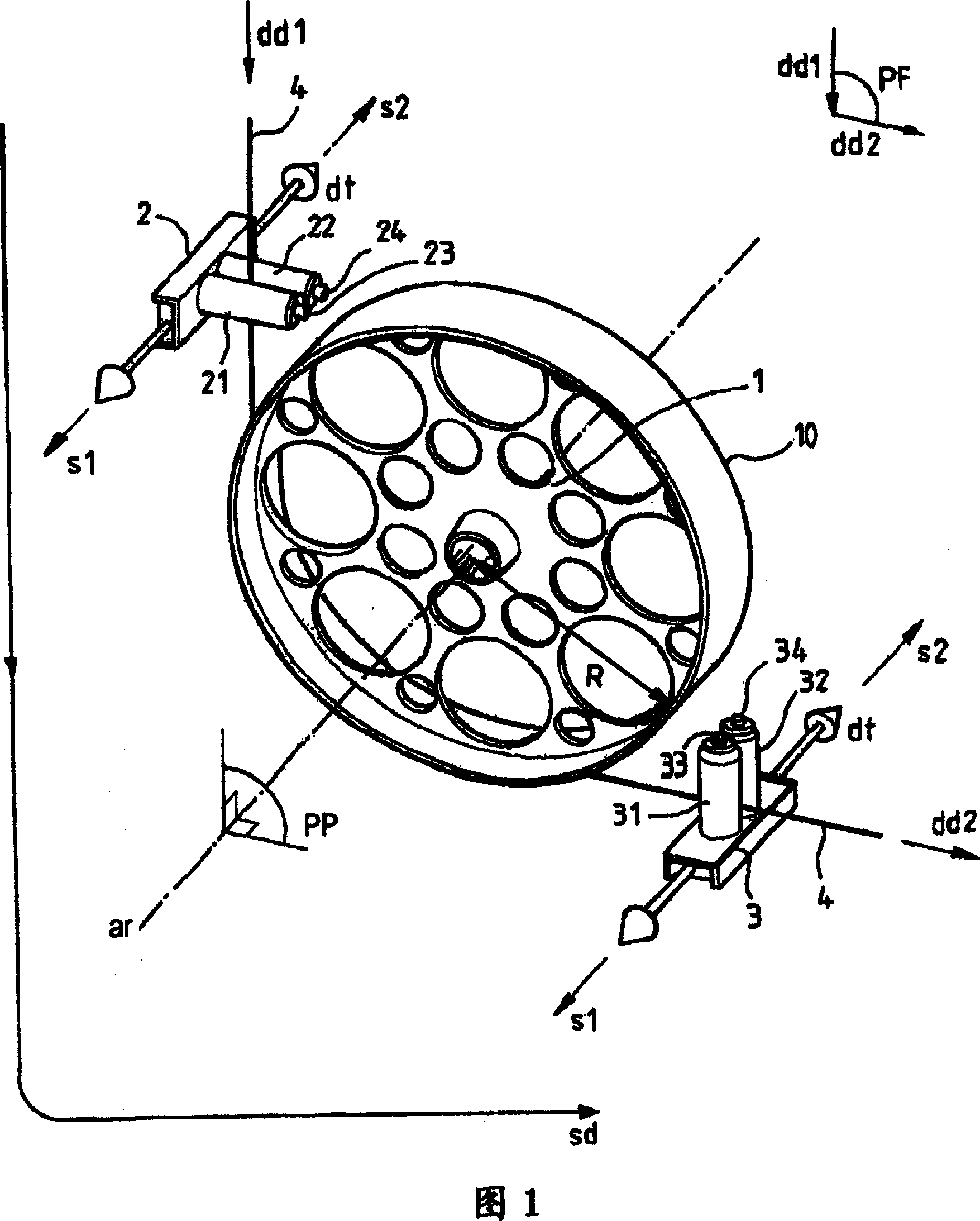
[0010] The various steps of making the optical fiber during the fiber drawing process have a major effect on the ovalization of the refractive index and shape of the preform core, and thus also of the optical fiber, where such ovalization constitutes One of the causes of considerable PMD. Optical fibers in which the PMD is too large cannot be sold because the PMD attenuates the optical signal carried by the optical fiber to an excessive extent. A method for reducing the PMD of an optical fiber during fiber drawing consists in twisting the optical fiber about its own axis alternately in one direction of rotation, eg clockwise, and then in another direction, eg counterclockwise. The anti-PMD system for twisted optical fibers is located at the bottom of the fiber-drawing tower and preferably acts on the optical fiber when it has been covered with two covering layers. The twisting torque applied to the optical fiber is transmitted all the way to the viscous cone of the preform gl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com