Semiconductor integrated circuit and its producing method
A technology of integrated circuits and manufacturing methods, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, circuits, etc., and can solve the problems of storage circuit failure, no consideration, and reduction of storage unit noise margins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
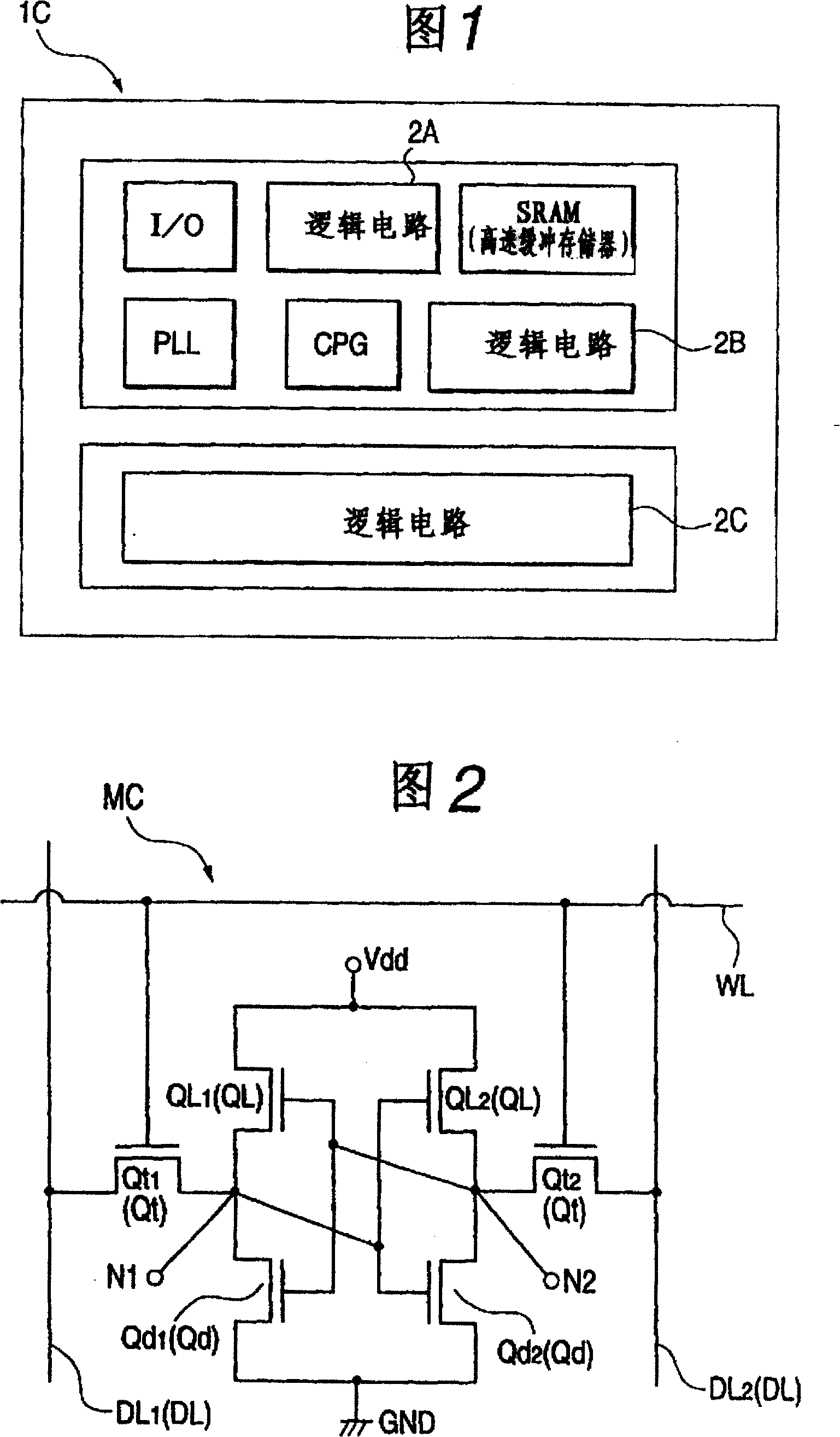
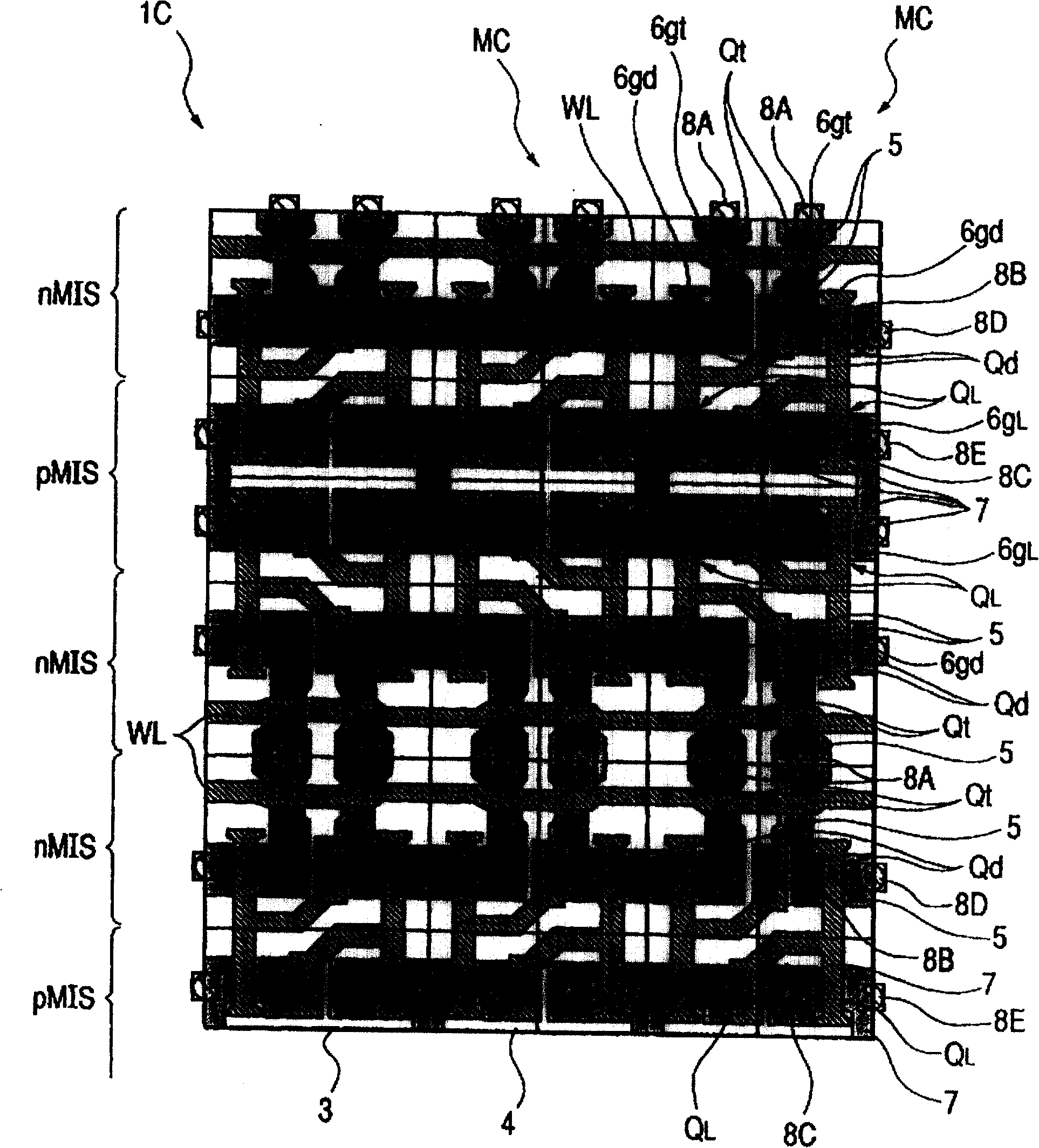
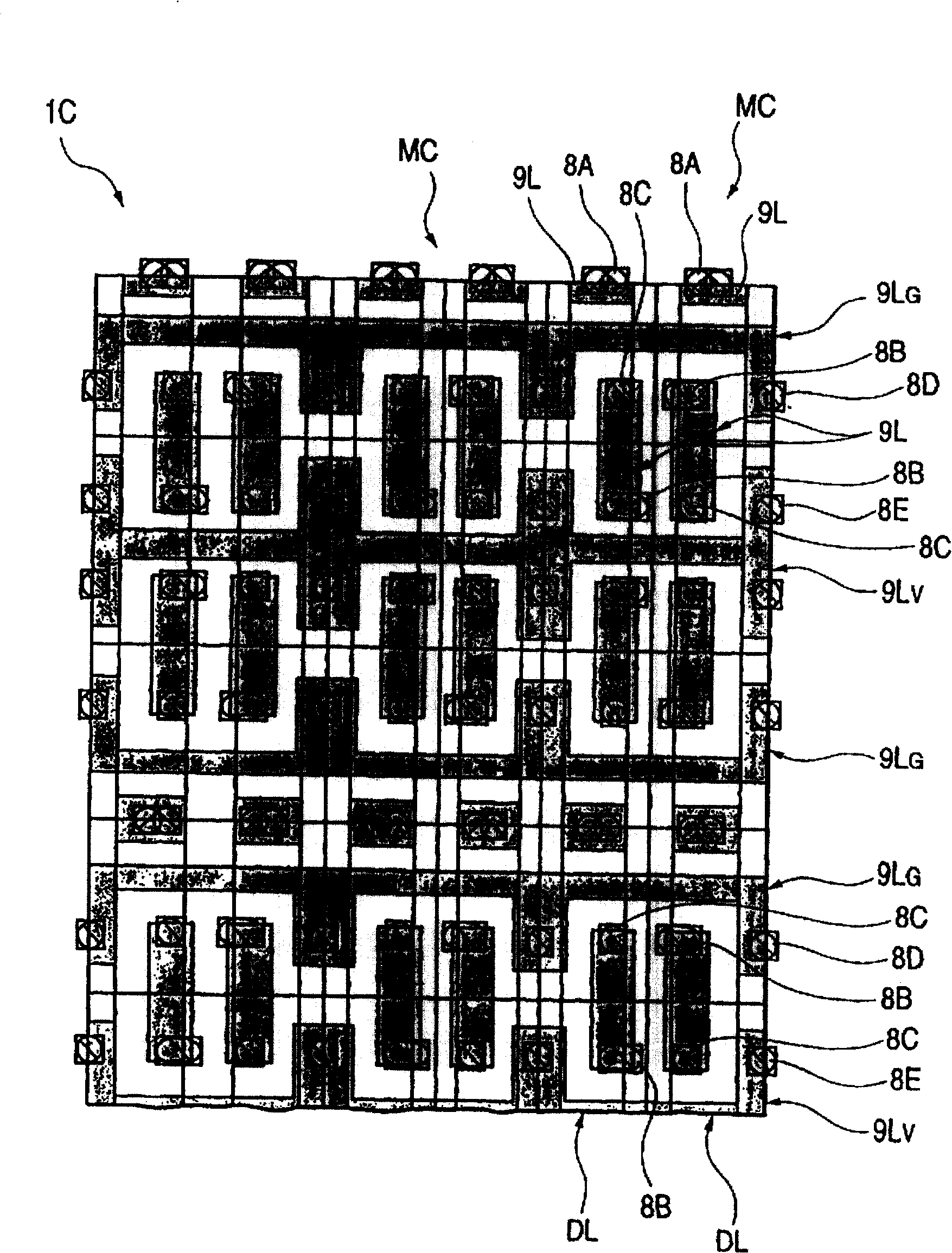
[0044] 1-4 are diagrams for explaining the structure of the semiconductor integrated circuit device of the present invention. 5-17 are cross-sectional views of main parts of the semiconductor integrated circuit device during respective manufacturing steps for explaining a method of manufacturing the semiconductor integrated circuit device in FIG. 1 . Figure 18 is a diagram explaining the effect of the current mode of carrying out the invention. Figure 19 Techniques studied by the inventors are shown to explain the effect of the current mode of carrying out the invention. FIG. 20 is a diagram explaining the effect of the current mode of implementing the present invention.
[0045] With regard to the technical principles of the pertinent field, when it is said that "threshold voltage (hereinafter expressed as Vth) is high", it means that the expected increase in Vth exceeds the increase in Vth due to differences in dimensions such as channel width. In addition, in the techni...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Figure 21 is a plan view of a main part of a semiconductor integrated circuit device of another mode for realizing the invention during manufacture.
[0118] Although said Mode 1 of implementing the invention involves the case of intentionally relatively raising the Vth of all the MISFETs constituting the memory cell of the SRAM, the present invention is not limited thereto, and the Vth of a predetermined MISFET of the memory cell of the SRAM may be relatively raised intentionally. .
[0119] Mode 2 of realizing the invention introduces this way, for example, in order to increase the Vth of the transfer MISFET relatively intentionally, it can be as Figure 21 The photoresist pattern 12A2 is formed on the semiconductor substrate 3 as shown, replacing the first process or the second process described in the mode 1 of realizing the invention. Figure 6 The photoresist pattern 12A is shown so as to expose the region where the transfer MISFET will be formed, while coverin...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Figure 22 is a plan view of a main part of a semiconductor integrated circuit device of another mode for realizing the invention during manufacture.
[0123] Mode 3 for realizing the invention is to introduce the situation where the Vth of the driving MISFET is relatively increased on purpose. In this case, it can be as follows Figure 22 Form photoresist pattern 12A3 on semiconductor substrate 3 as shown, replace said first process or second process introduced in said Mode 1 of realizing the invention (see Figure 6 ) photoresist pattern 12A, in order to expose the area where the driving MISFET will be formed, and cover other areas. Figure 22 Also demonstrated with image 3 , 6 and the same memory cell region, and various elements etc. are shown in order to clearly show the position where the photoresist pattern 12A3 is formed as described above. For the sake of clarity in the attached Figure 22 A photoresist pattern 12A3 is also drawn in . In addition, the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com