Magnetic encoder
A magnetic encoder and magnetic sensor technology, applied in the field of magnetic encoders, can solve problems such as low power consumption and inability to meet high resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
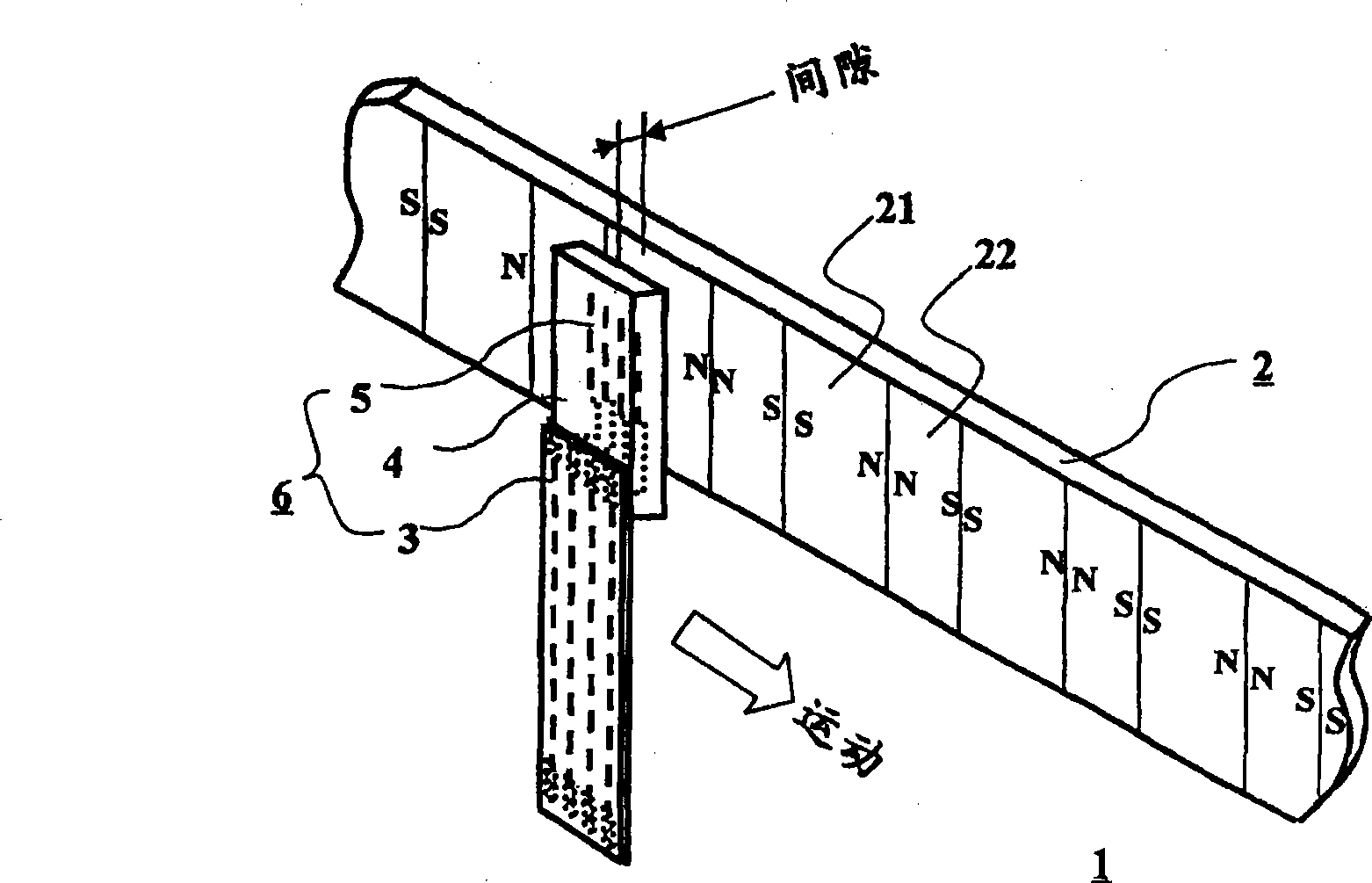
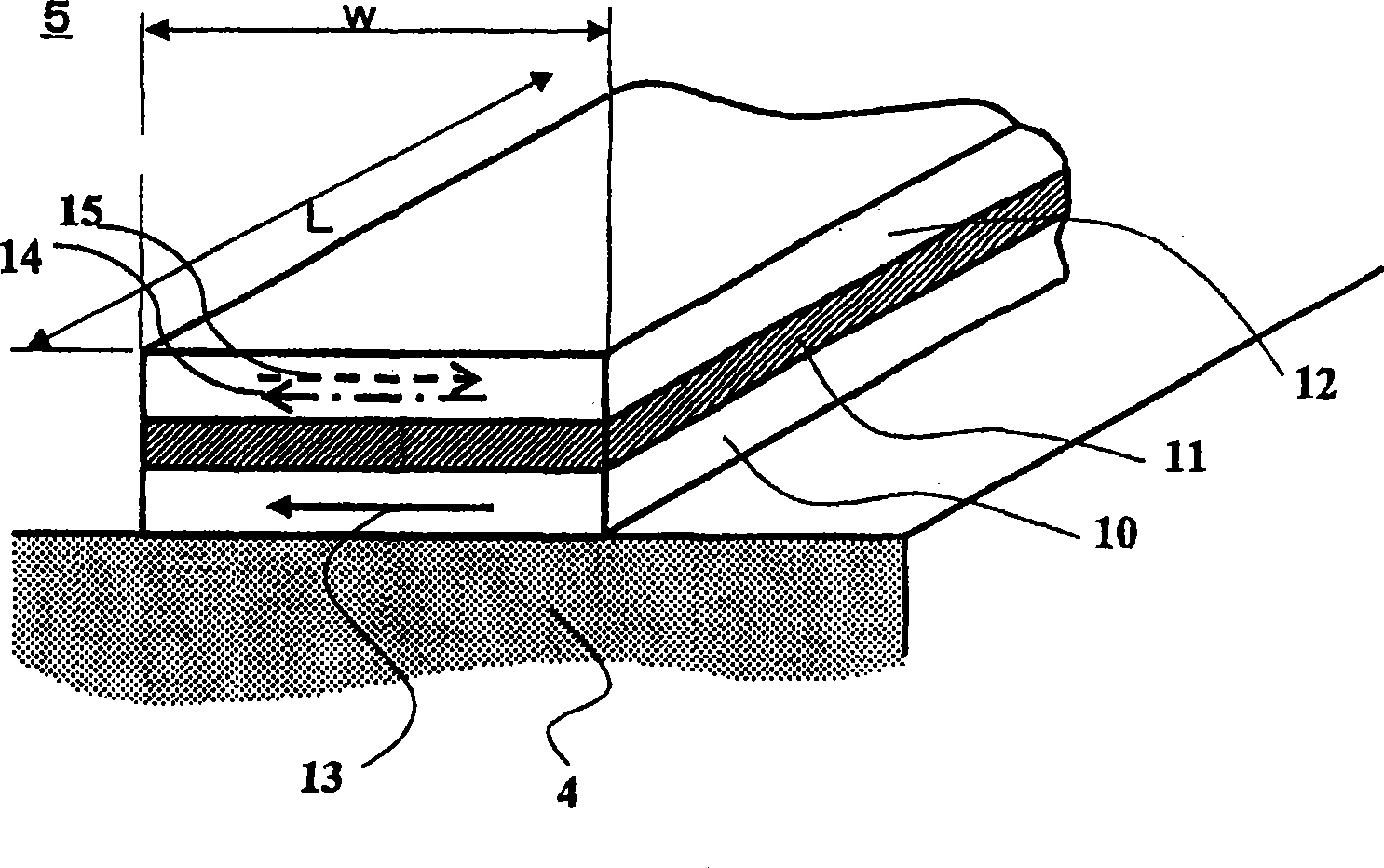
[0042] figure 1 A perspective schematic diagram explaining a magnetic encoder with SVGMR elements is shown. The magnetic encoder 1 consists of a magnetic medium 2 and a magnetic sensor 6 . On the magnetic medium 2, two magnetized regions magnetized opposite to each other, ie, a first magnetized region 21 and a second magnetized region 22, are continuously and alternately arranged along the extending direction of the medium. In the following explanation, it is assumed that the length λl of the first magnetized region 21 is longer than the length λs of the second magnetized region 22 . In the magnetic sensor 6, a plurality of SVGMR elements 5 are formed in a rectangular plane extending perpendicularly to the extending direction of the magnetic medium 2 on the base material 4, and the ends of the SVGMR elements 5 are connected to the flexible printed circuit 3 by wires (not shown). The magnetic medium 2 faces the SVGMR element 5 having a rectangular plane through a predetermine...
example 2
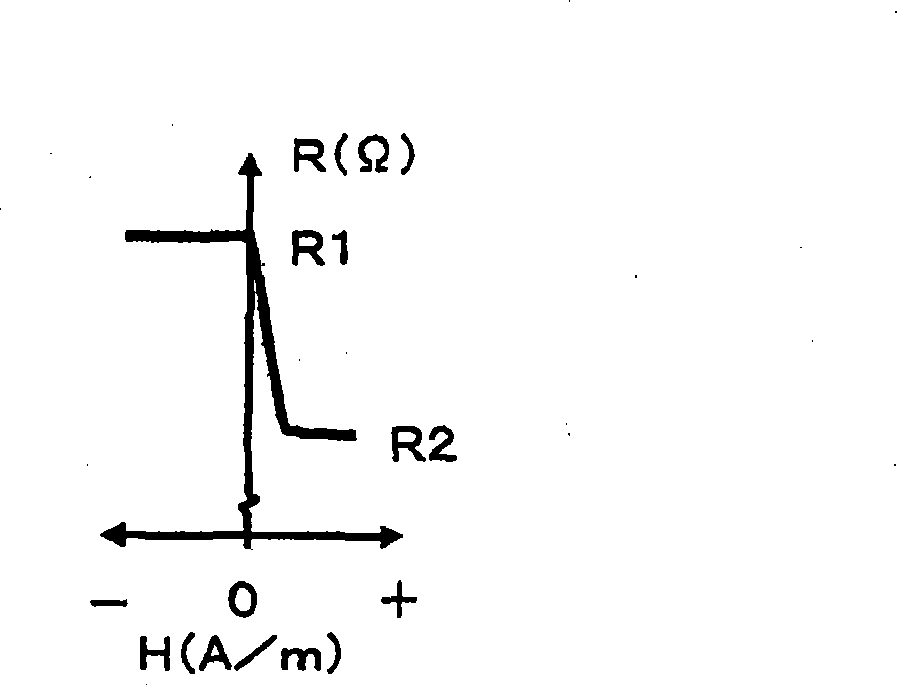
[0047] Referring to FIG. 4, in which the first magnetized region length λl is longer than the second magnetized region length λs on the magnetic medium 2, the operation of the magnetic encoder will be described. Figure 4A The positional relationship between the SVGMR elements 51a to 52b of the magnetic sensor 6 and the magnetic medium 2 is explained, and Figures 4B to 4F A graph of resistance and electrical signal versus location of SVGMR elements 51a to 52b on magnetic medium 2 is shown. The resistance diagrams of the SVGMR element 51a of the first sensor 51, the other SVGMR element 51b of the first sensor 51, the first sensor 51 consisting of SVGMR elements 51a and 51b, and the second sensor 52 consisting of SVGMR elements 52a and 52b are shown respectively exist Figure 4B , 4C , 4D and 4E. In the magnetic sensor 6, four SVGMR elements 51a to 52b are provided on a base material. Each SVGMR element has a cell width w, and the SVGMR elements in each sensor are at a dist...
example 3
[0053] refer to Figures 6A to 6F , a magnetic encoder of Example 3 will be illustrated, with the Figure 4A The magnetic encoder of example 2 in is similar except that the magnetic medium 2 has a first region length that is shorter than a second magnetized region length. Figure 6A The positional relationship between the SVGMR elements 51a to 52b of the magnetic sensor 6 and the magnetic medium 2 is explained, and Figures 6B to 6F A graph of resistance and electrical signal versus location of SVGMR elements 51a to 52b on magnetic medium 2 is shown. The resistance diagrams of the SVGMR element 51a of the first sensor 51, the other SVGMR element 51b of the first sensor 51, the first sensor 51 consisting of SVGMR elements 51a and 51b, and the second sensor 52 consisting of SVGMR elements 52a and 52b are shown respectively exist Figure 6B , 6C , 6D and 6E. In the magnetic sensor 6, four SVGMR elements 51a to 52b are provided on a base material. Each SVGMR element in each ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com