Method of hydrogenation for benzoic acid
A technology of benzoic acid and hydrogen, which is used in the preparation of carboxylic acid by ozone oxidation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of limiting and maintaining the reserves of Ru/C additives, so as to reduce production costs, increase processing capacity, and improve hydrogenation. active effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
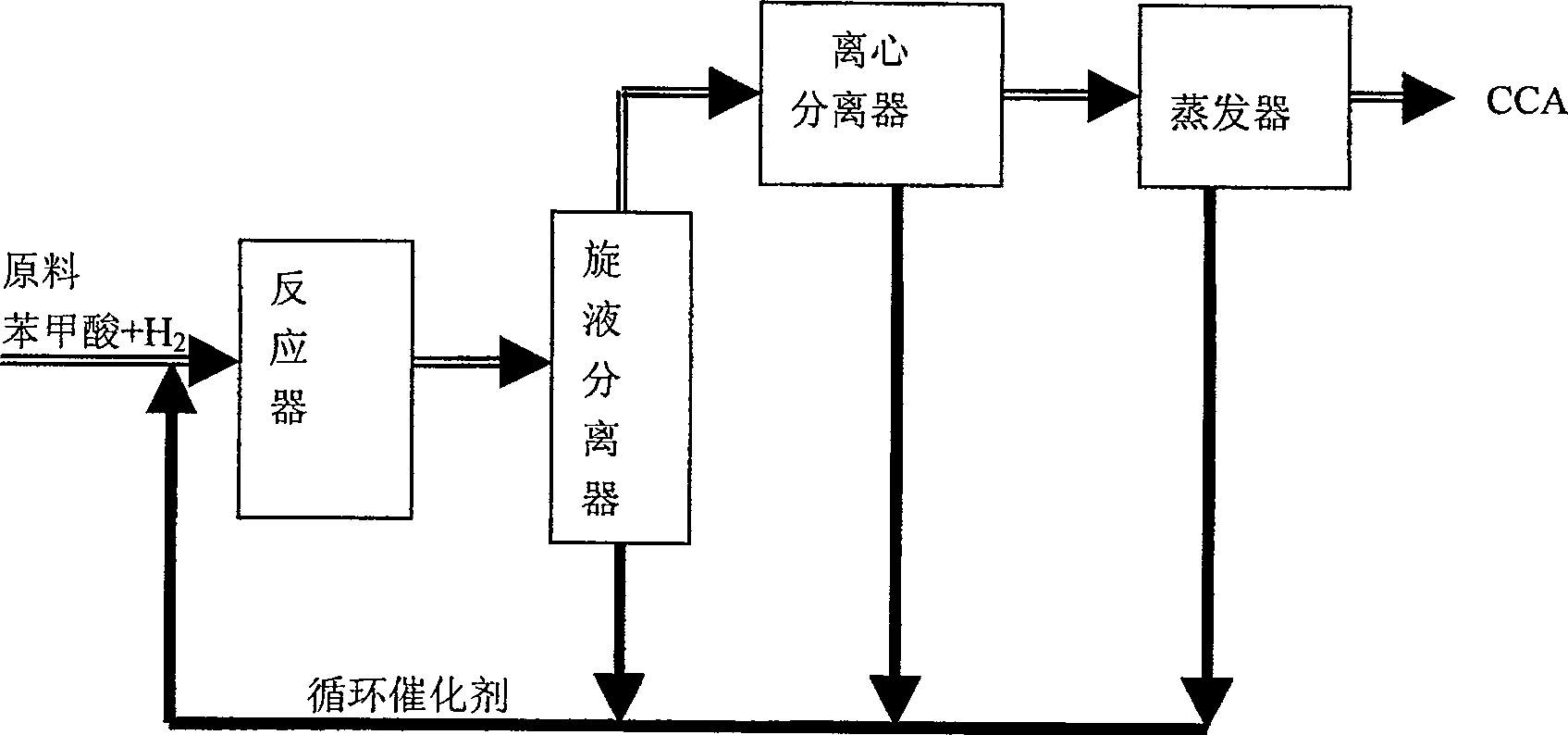
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
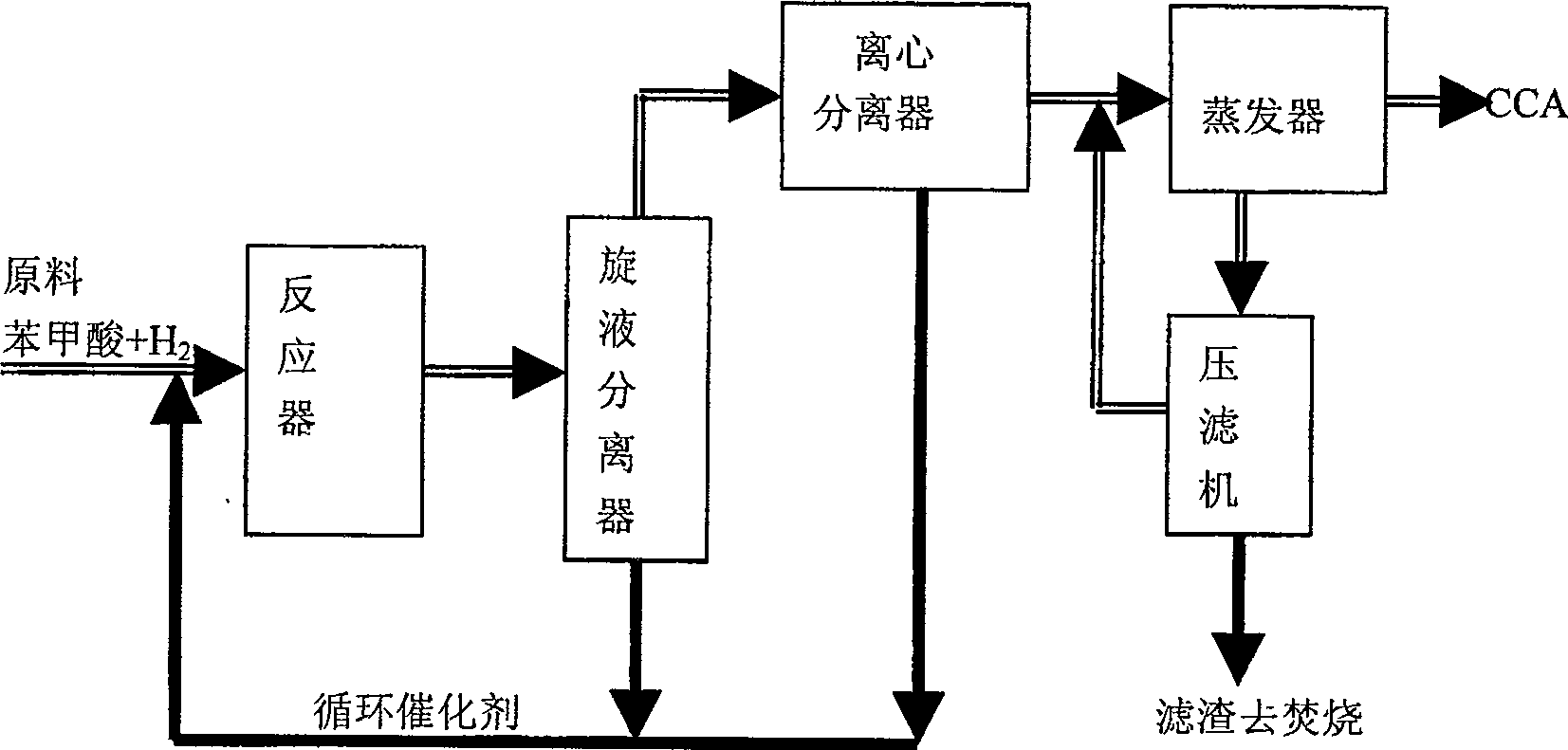
[0017] Such as Figure 2 Show, reactant benzoic acid, hydrogen and Pd / C catalyst, Ru / C auxiliary agent enter reactor system together and carry out benzoic acid hydrogenation reaction, wherein, the consumption of Ru / C auxiliary agent is 3% of Pd / C catalyst weight in the system %, the reaction temperature is 167±2°C, and the pressure is 1.35±0.05MPa. After passing through the four-stage reactor, more than 99% of benzoic acid is converted into products. After the reaction mixture leaves the reactor, it undergoes gas-liquid separation, and the liquid-solid mixture enters the suspension separator, and after hydrocyclone separation, the turbid liquid containing a relatively high concentration of catalysts and additives is circulated back to the reactor from the bottom, containing less solid phase. The supernatant liquid leaves the hydrocyclone from the top, enters the centrifugal separator for liquid-solid separation again, and the separated Pd / C catalyst and Ru / C auxiliary agent a...
Embodiment 2
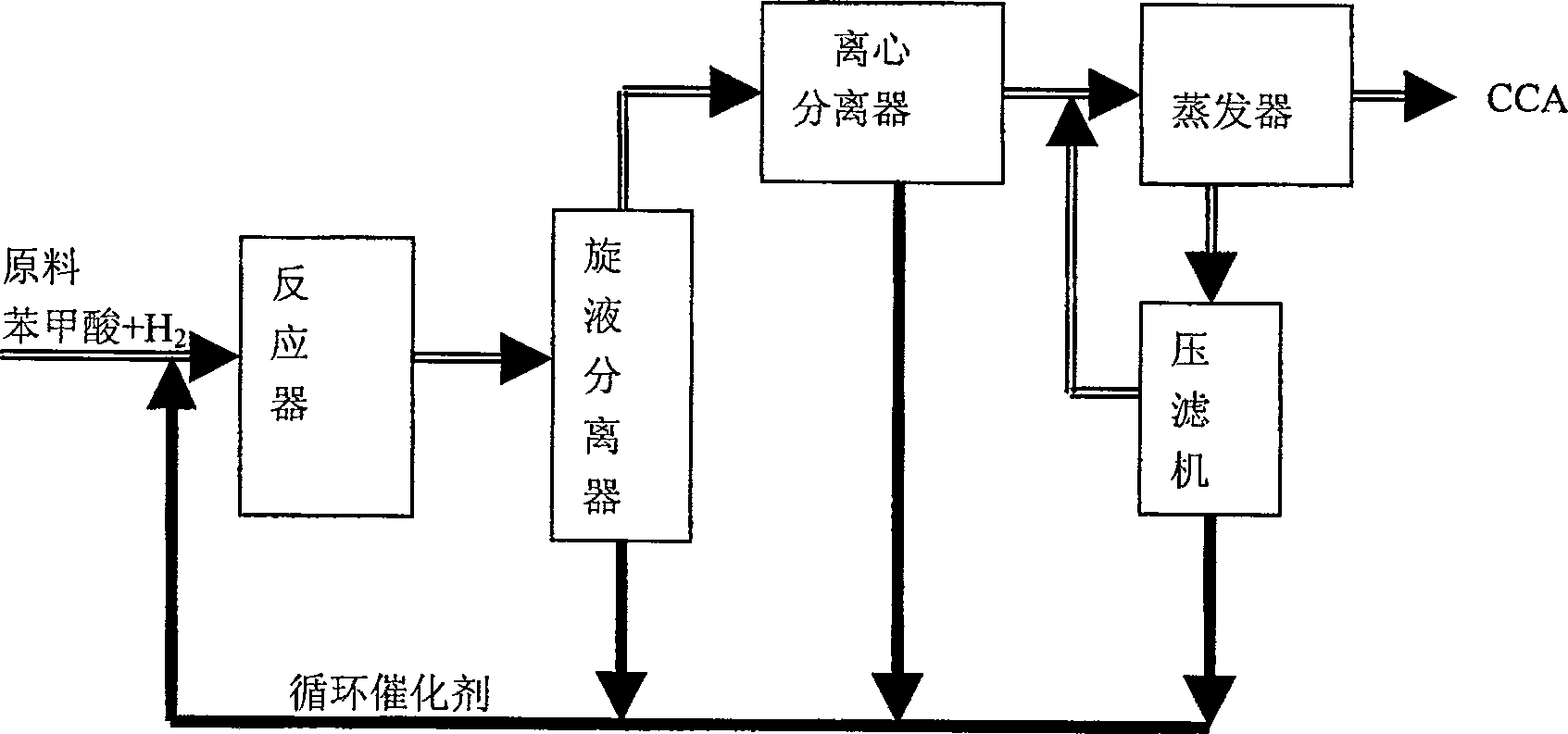
[0019] Another embodiment of the present invention is as Figure 3 Show. Identical with embodiment 1, raw material benzoic acid, hydrogen and catalyzer, auxiliary agent enter reactor and carry out benzoic acid hydrogenation reaction, wherein, the consumption of Ru / C auxiliary agent is 8% of system Pd / C catalyst weight, temperature of reaction 165 ± 2°C, pressure 1.50±0.05MPa. After the reaction, the mixture is separated by hydrocyclone and centrifugal separation, and the turbid liquid with high solid phase concentration is separated and returned to the reactor system. The separated clear liquid enters the evaporator for evaporation, and the evaporated CCA product is discharged from the device and enters the next production process. Unlike Example 1, the effluent from the bottom of the evaporator containing high concentrations of catalyst and adjuvants is directly returned to the reactor system.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Laboratory Pd / C catalyst hydrogenation activity stability test.
[0022] Z for hydrogenation activity of Pd / C catalyst 0 Characterization, which represents the hydrogen consumption rate of the catalyst per unit time. Determination of Z 0 The best method is to use a oscillating high-pressure reactor, add 2 grams of Pd / C catalyst (dry basis) and 200 grams of benzoic acid, replace it with nitrogen three or four times, fill it with nitrogen to 2.0 MPa, heat to 150 ° C, and use high-purity hydrogen Replace three or four times, fill the hydrogen pressure to 11.0MPa, start stirring and start timing at the same time, when the reaction pressure drops from 11.0MPa to 9.0MPa, record the reaction time t (minutes), Z 0 =20 / 4t, recharge to 11.0MPa, carry out 7 consecutive times, and take the average value. Z 0 The larger the value, the higher the hydrogenation activity. Z 0 For the determination method, see (Shijiazhuang Chemical Fiber Co., Ltd.) "Compilation of Analytical Meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com