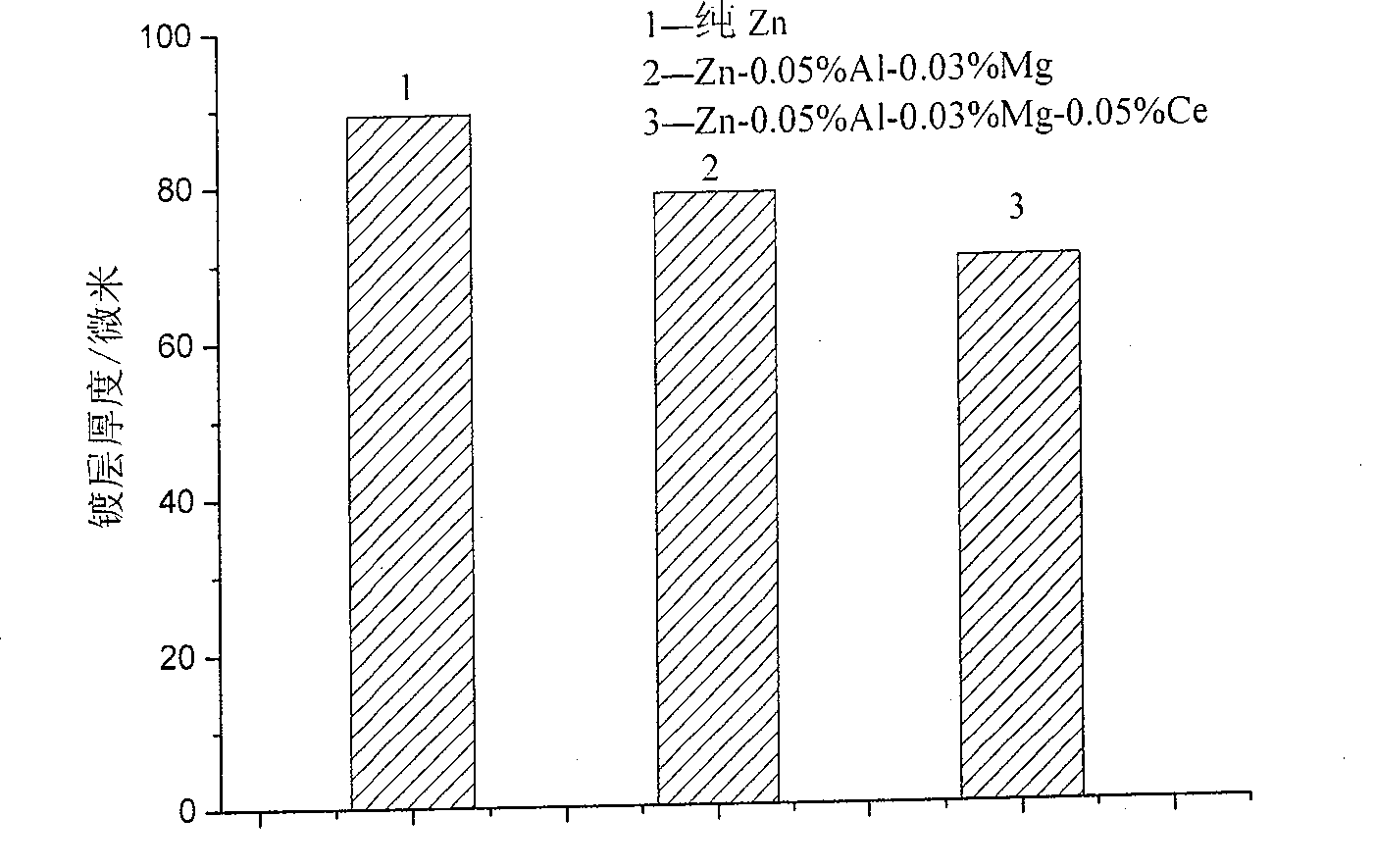
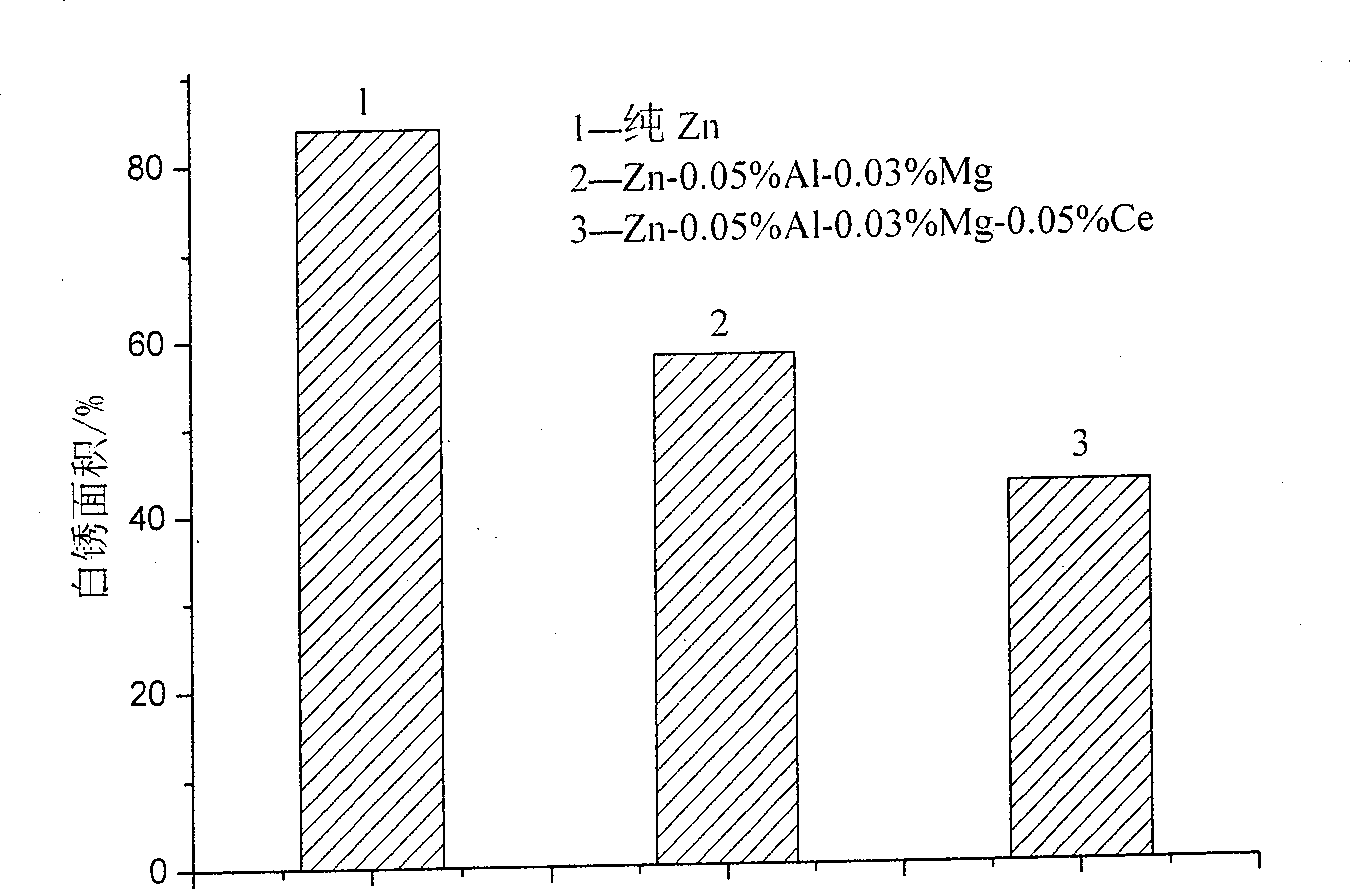
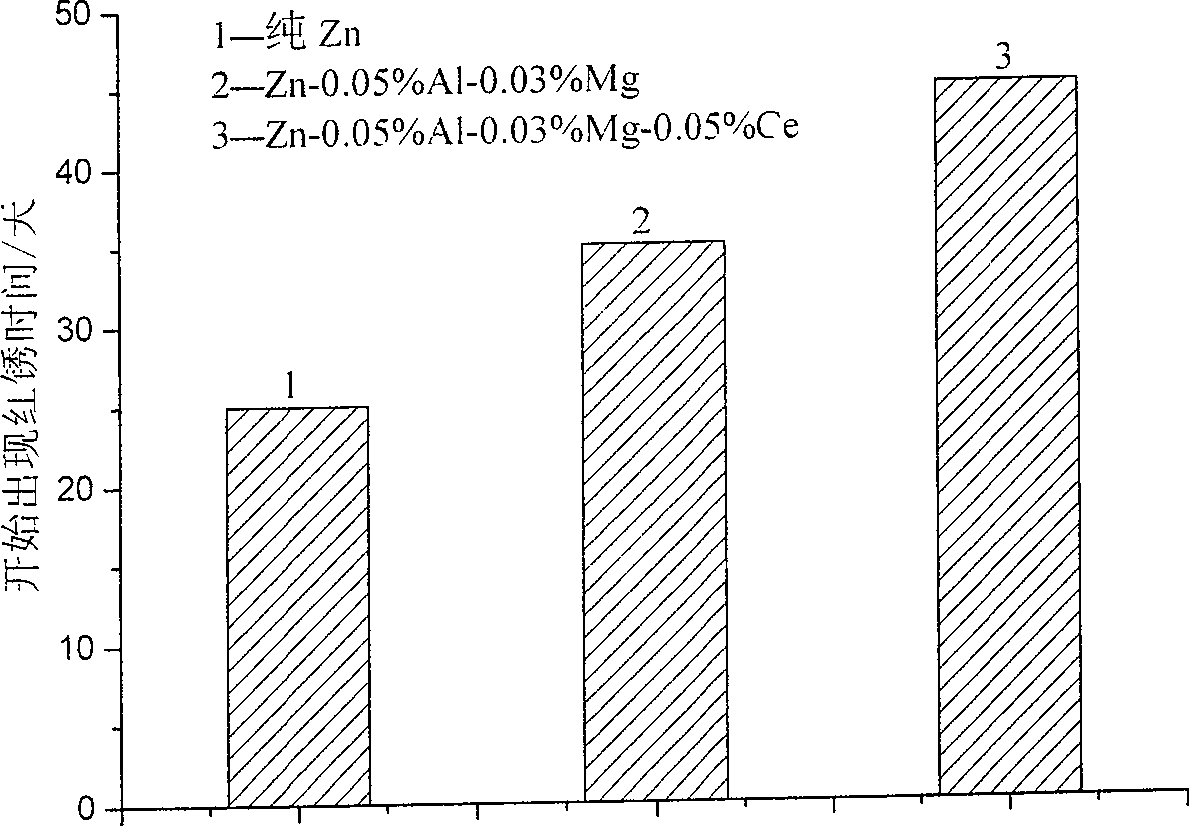
Method adapting to batch quantity hot dipping zinc of rolled steel
A technology of hot-dip galvanizing and steel, applied in chemical variable control, non-electric variable control, multiple fluid ratio control, etc. The formation of white rust, reducing the thickness of the coating, and facilitating the large-scale production of batch hot-dip galvanizing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The steel used for galvanizing is a steel plate containing 0.18% Si, and the chemical composition is shown in Table 1 below. The batch hot-dip galvanizing method adopted includes the following steps and process conditions:
[0023] (1) Binary master alloy refining: Weigh aluminum and zinc, magnesium and zinc, cerium and zinc in proportion by weight, place them in graphite crucibles, and refine them separately. Among them: the aluminum content in the zinc-aluminum binary master alloy is 5%, the melting temperature of the zinc-aluminum master alloy is 680°C, and the holding time is 2 hours; the magnesium content in the zinc-magnesium binary master alloy is 4%, and the zinc-magnesium master alloy The smelting temperature of the zinc-cerium master alloy is 650°C, and the holding time is 4 hours; the cerium content in the zinc-cerium binary master alloy is 3.3%, and the melting temperature of the zinc-cerium master alloy is 760°C, and the holding time is 4 hours. After each...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The steel used for galvanizing is a Q235 (0.22% Si) steel plate, which is hot-dip galvanized for 5 minutes in a pure zinc bath with a bath temperature of 450 ° C and an alloy zinc bath containing aluminum, magnesium and cerium. Wherein the hot-dip galvanizing in the alloy zinc bath comprises the following steps and process conditions:
[0038](1) Refining of binary master alloys: Weigh aluminum and zinc, magnesium and zinc, cerium and zinc by weight, place them in graphite crucibles, and refine them separately. Among them: the aluminum content in the zinc-aluminum binary master alloy is 4%, the smelting temperature of the zinc-aluminum master alloy is 700 ℃, and the holding time is 1 hour; the magnesium content in the zinc-magnesium binary master alloy is 3.6%, and the zinc-magnesium master alloy is 3.6%. The smelting temperature is 680°C, and the holding time is 3 hours; the cerium content in the zinc-cerium binary master alloy is 3%, the melting temperature of the zin...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The steel used for galvanizing is Q235 (containing 0.22% Si) steel sheet, and the test was conducted by hot-dip galvanizing for 5 minutes in a pure zinc bath with a coating bath temperature of 450° C. and an alloy zinc bath containing aluminum, magnesium and cerium. The hot-dip galvanizing in the alloy zinc bath includes the following steps and process conditions:
[0044] (1) Refining of binary master alloys: Weigh aluminum and zinc, magnesium and zinc, cerium and zinc by weight, place them in graphite crucibles, and refine them separately. Among them: the aluminum content in the zinc-aluminum binary master alloy is 4.8%, the smelting temperature of the zinc-aluminum master alloy is 680 ° C, and the holding time is 2 hours; the magnesium content in the zinc-magnesium binary master alloy is 3%, and the zinc-magnesium master alloy is 3%. The smelting temperature is 680°C, and the holding time is 3 hours; the cerium content in the zinc-cerium binary master alloy is 4%, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com