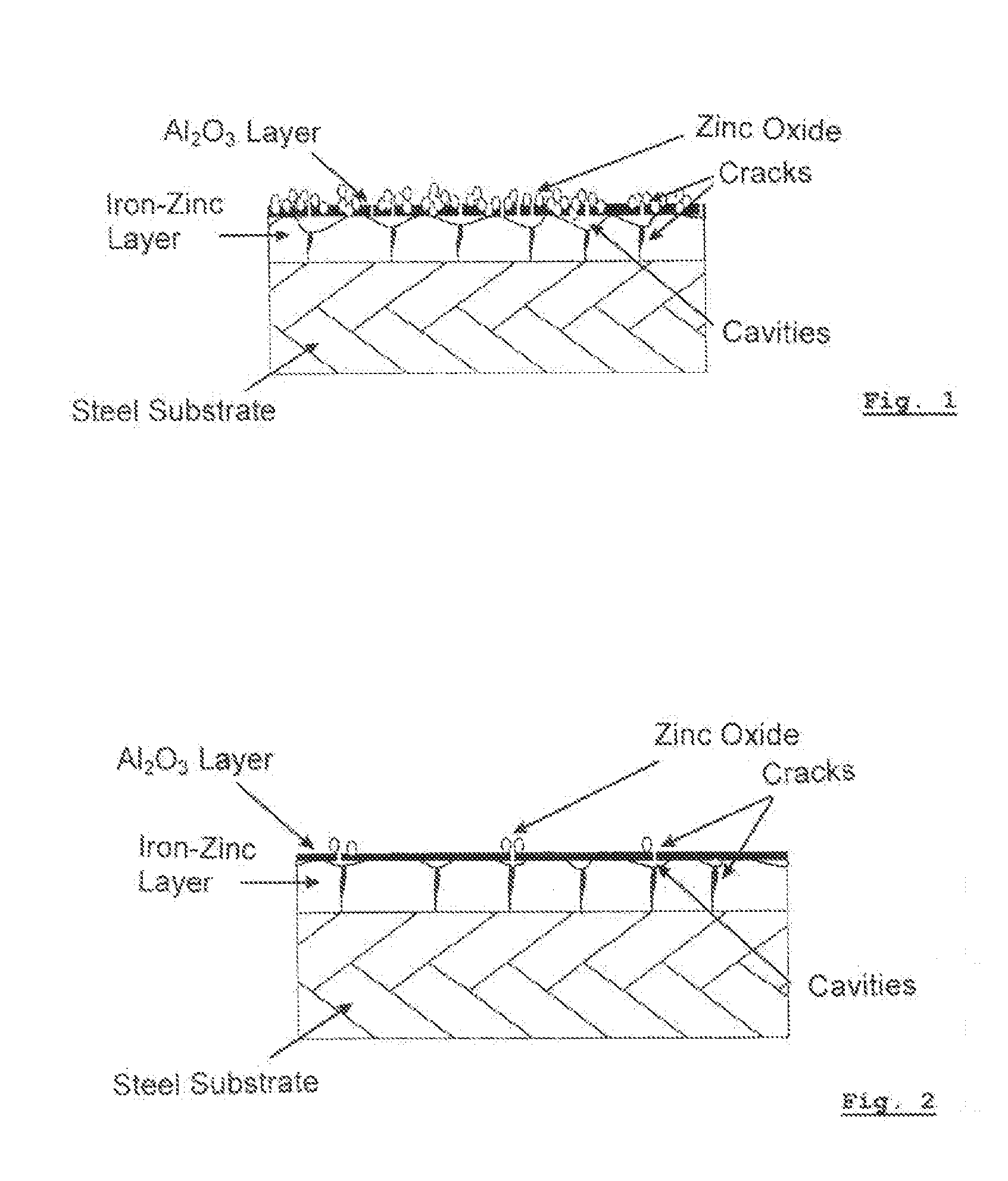
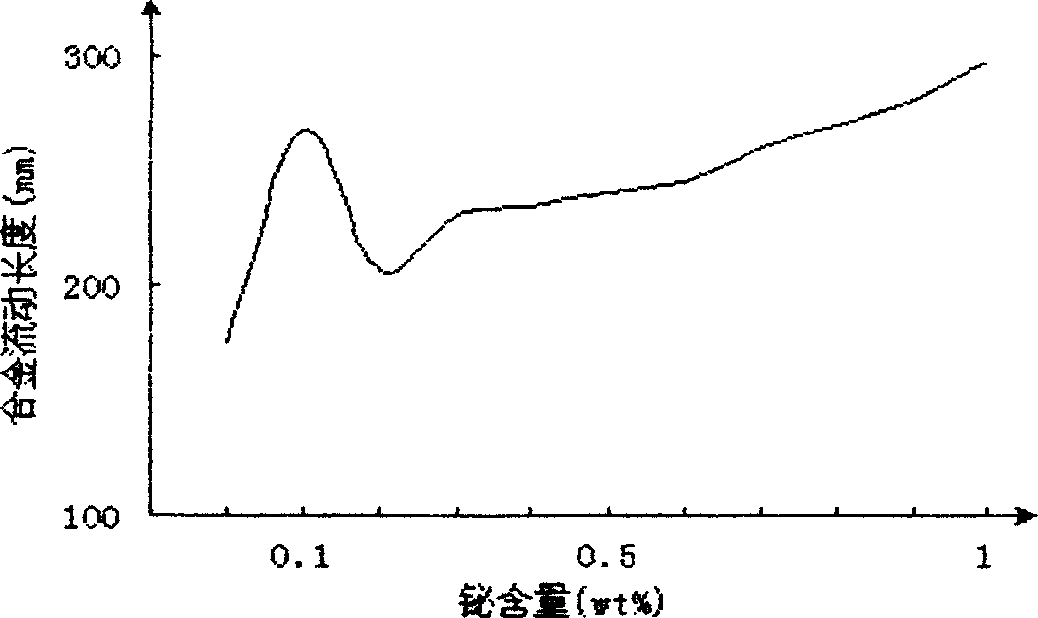
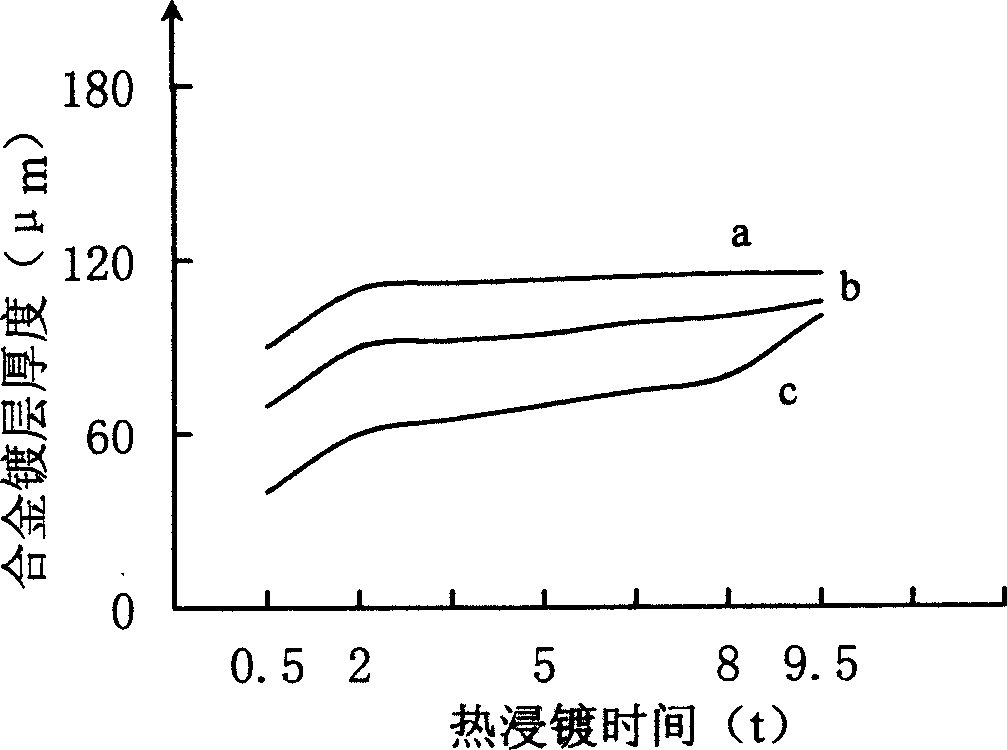
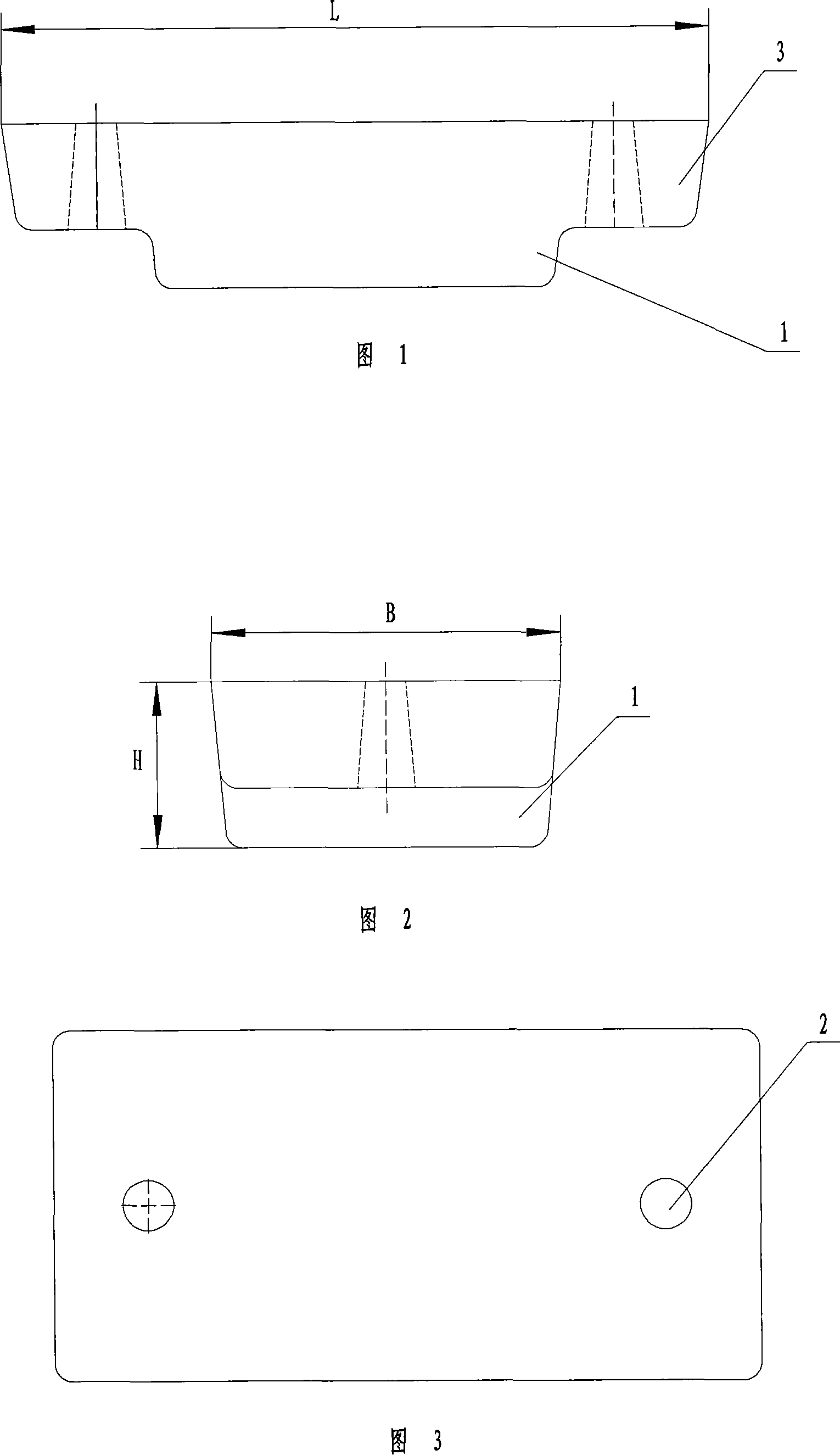
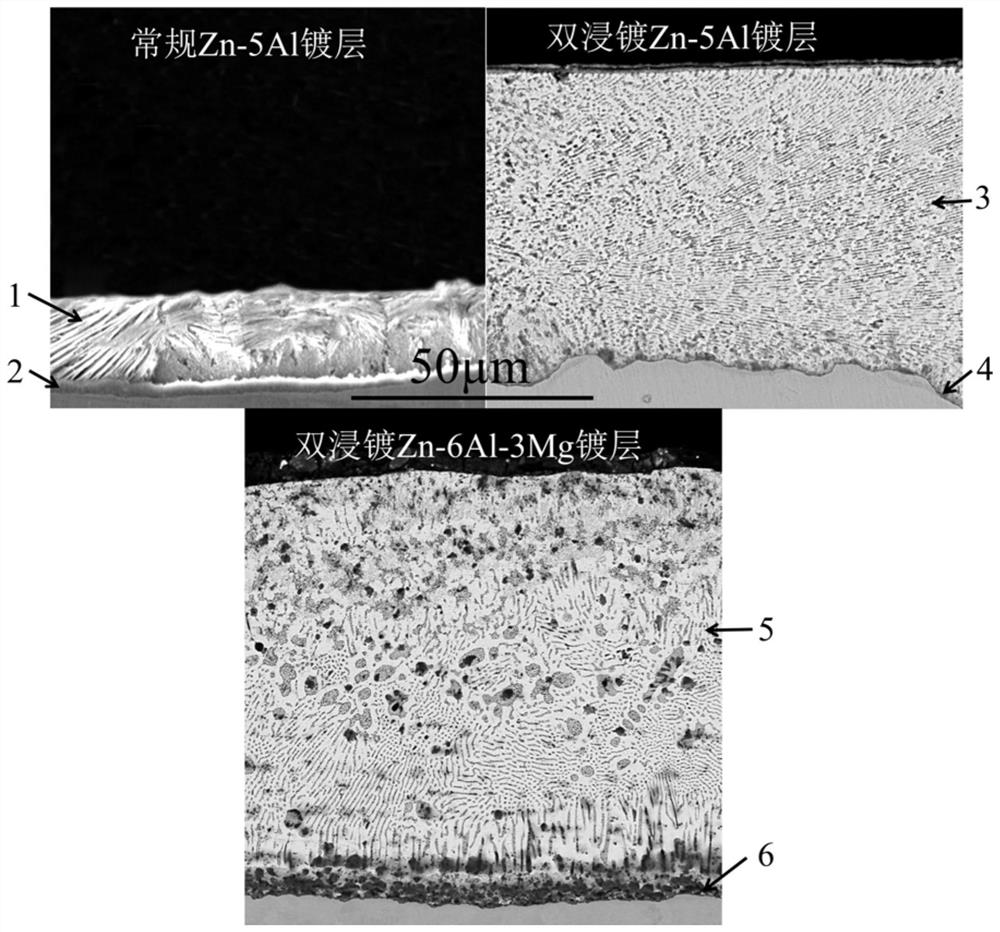
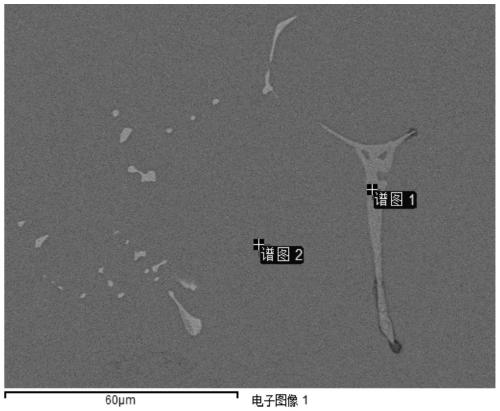
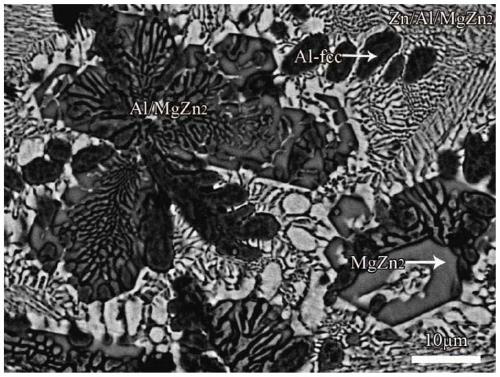
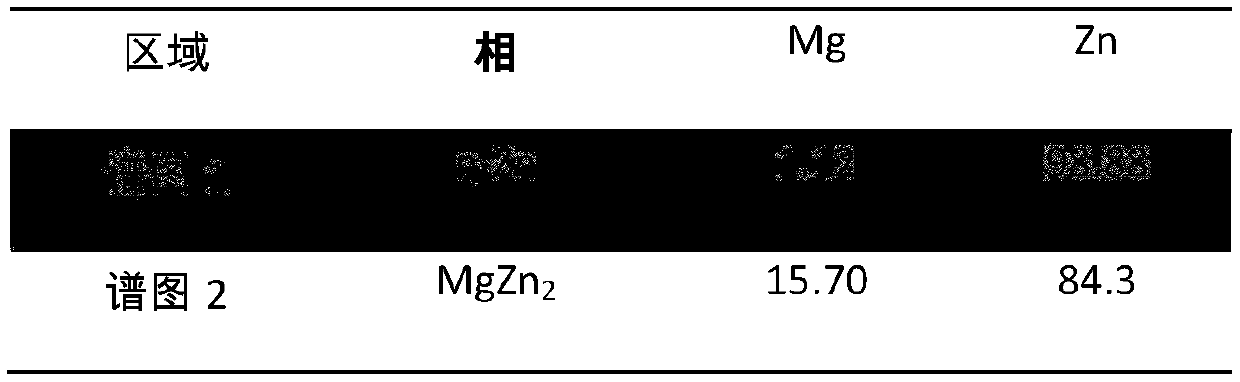
Patents
Literature
85 results about "Zinc bath" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
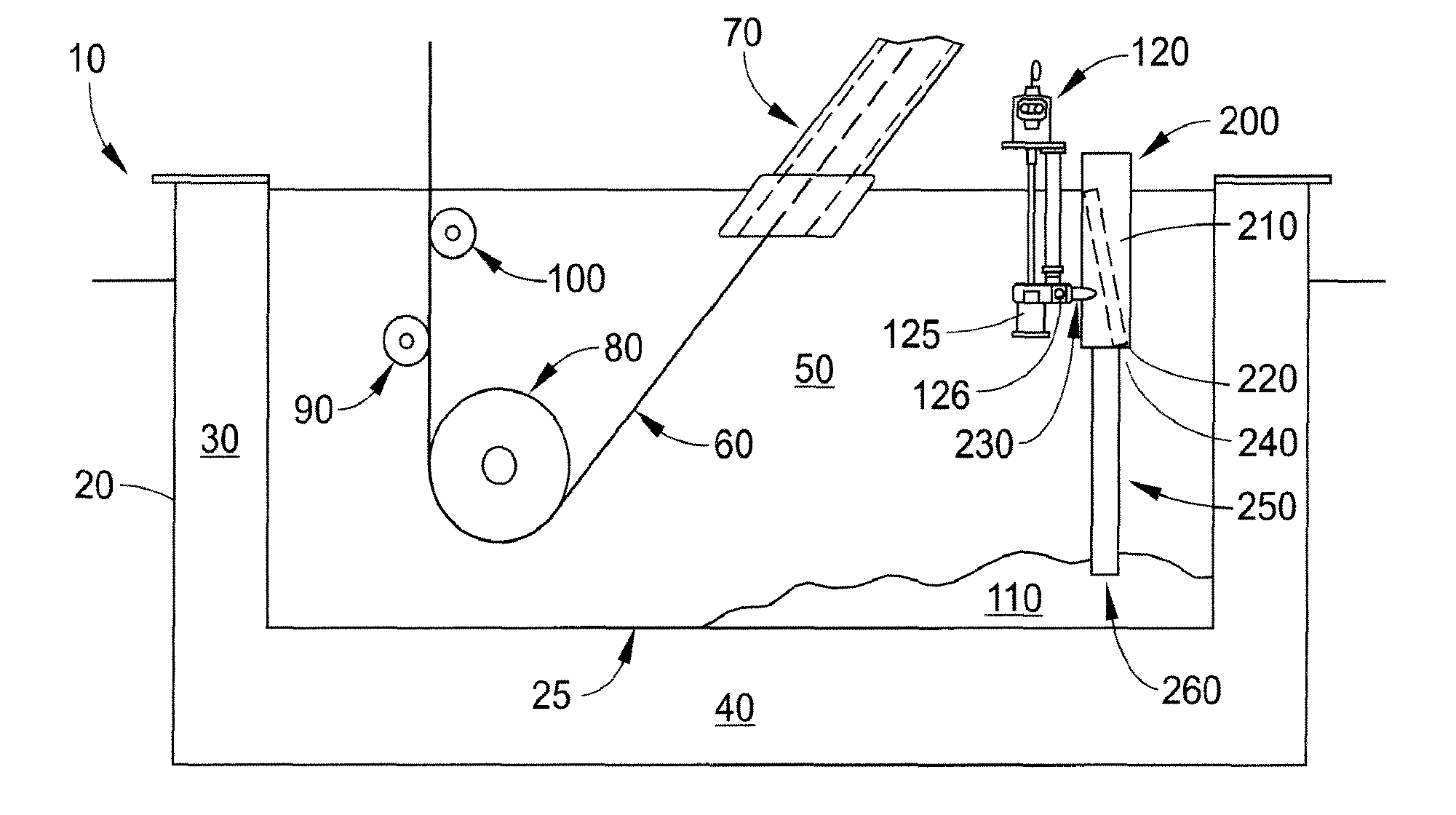
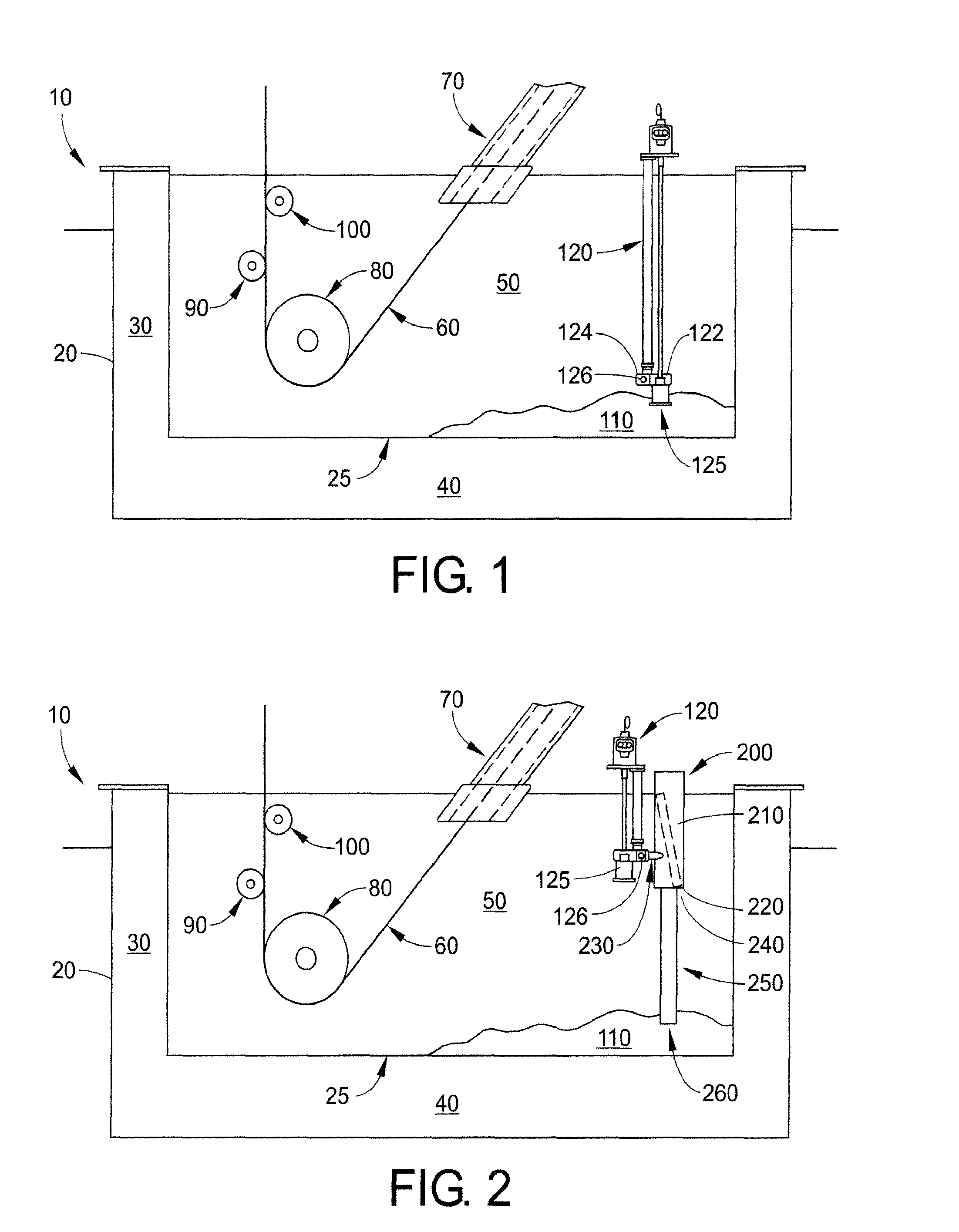
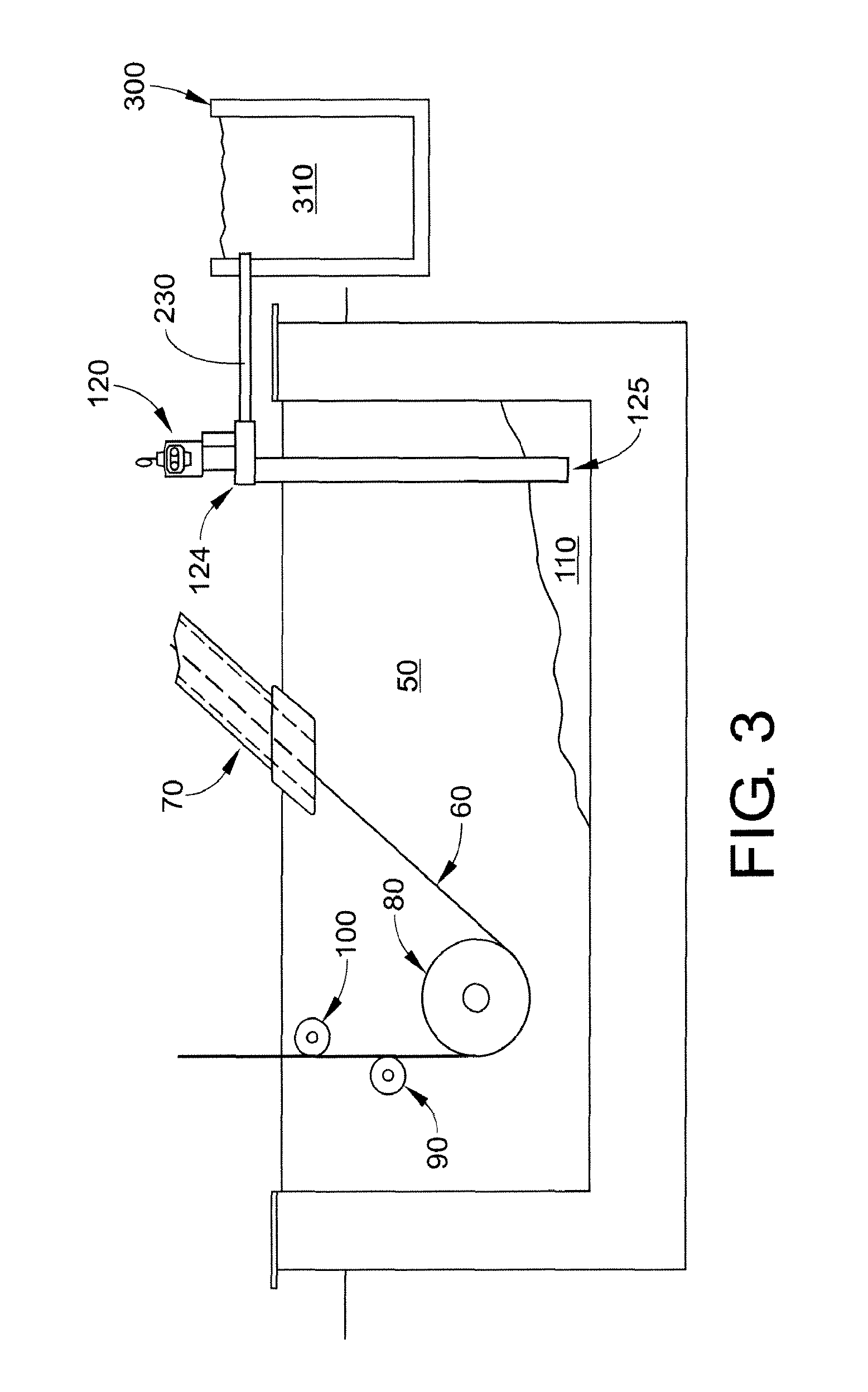
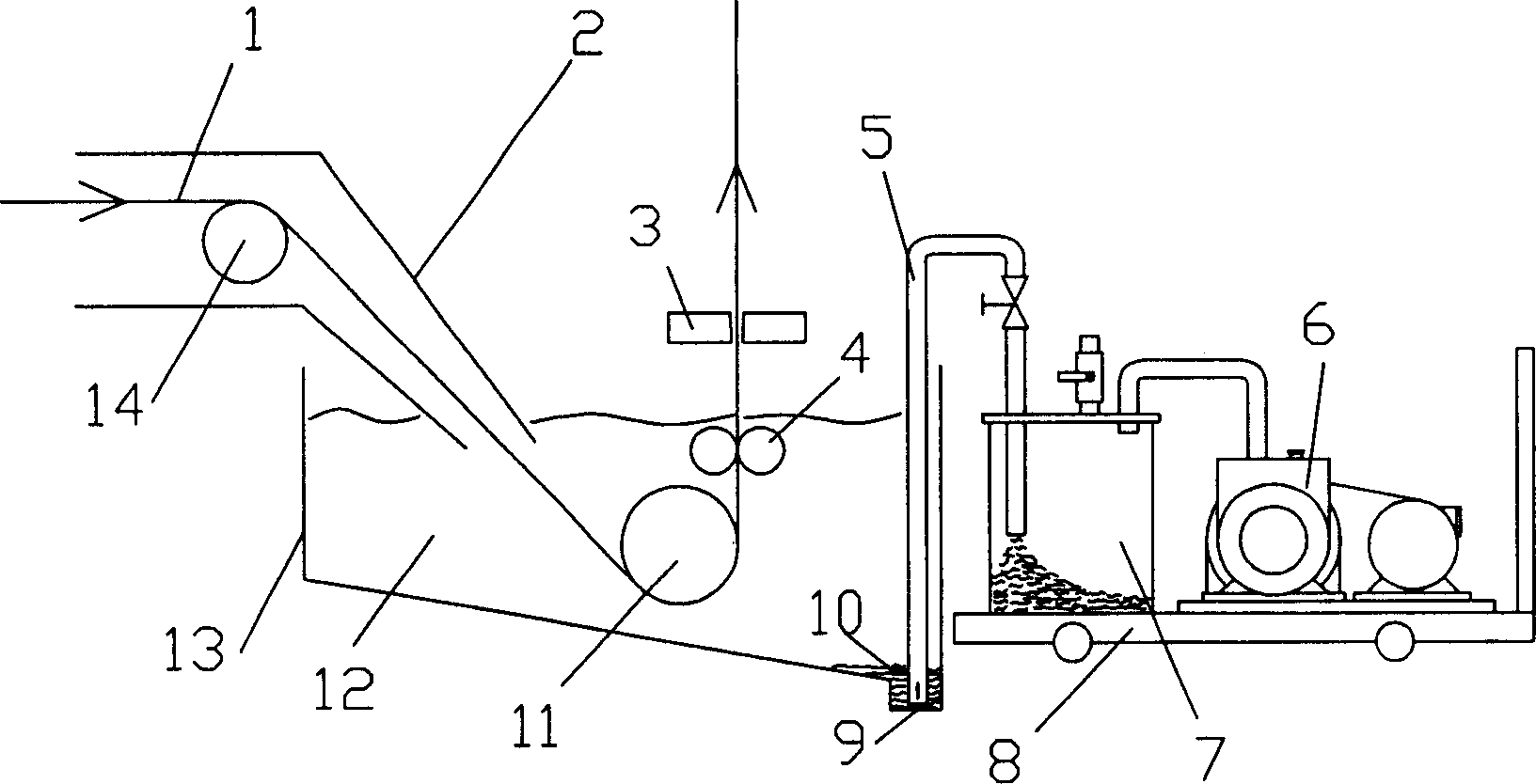
The Berk Zinc Bath helps protect metal objects from rust. It does this by galvanizing the metal, which covers the metal in a protective layer of zinc.
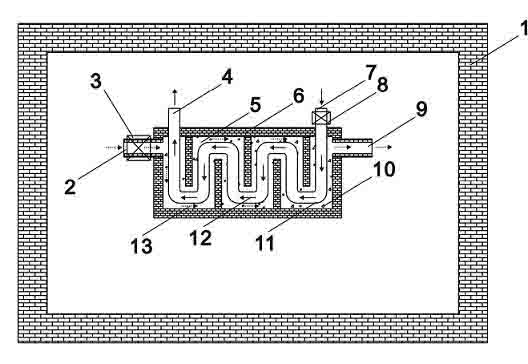
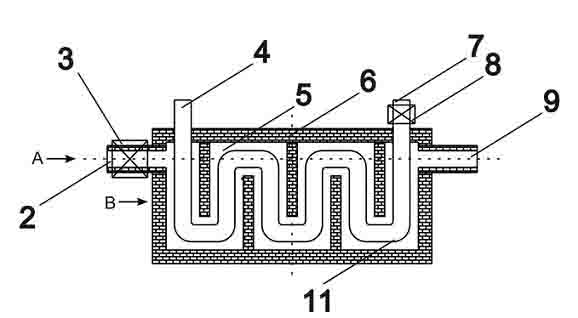
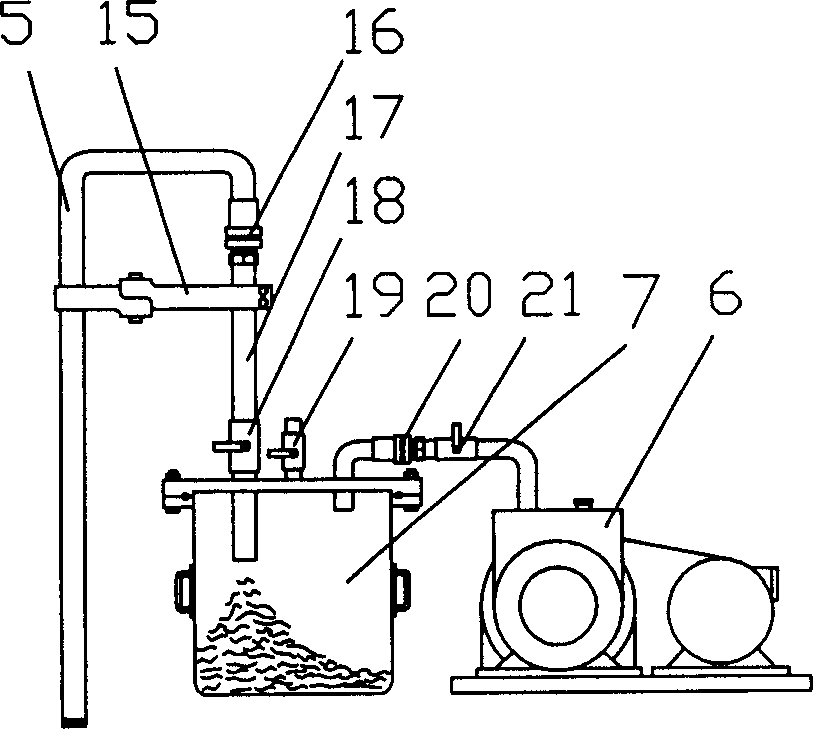
Galvanizing bath apparatus
InactiveUS8475594B2Reduce buildSpeed up the conversion processHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesHigh concentrationDross
A continuous galvanizing line uses a coating pot containing a molten zinc bath having bottom dross and further comprises a pump. The pump agitates the bottom dross so the bottom dross interacts with aluminum and converts to top dross, which can be removed without needing to stop the galvanizing line. A reaction vessel may also be used to provide a higher concentration of aluminum to react with the bottom dross.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
Multifunctional plating assistant agent used for hot dipping
InactiveCN101575691AImprove the plating effectQuality improvementHot-dipping/immersion processesActive agentPotassium
The invention provides a multifunctional plating assistant agent used for hot dip plating, belonging to the technical field of the surface plating technique of steel and iron materials. The technical proposal is as follows: the aqueous solution of the plating assistant agent has the following components of zinc chloride, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium fluoride and a composite surface active agent synthesized by fluorocarbon and hydrocarbon surface active agents with the respective proportion in sequence of 40 to 200g / L, 20 to 50g / L, 20 to 60g / L, 0 to 50g / L, 5 to 30g / L, 0.5 to 5g / L, and the balance of water. The plating assistant agent can improve the plating assistant effect of the plating assistant on the surface of the steel and iron part, prevent the steel and iron part after plating assistance from being oxidized secondarily in air, improve the quality of the surface plating layer of the steel and iron, does not generate zinc burst when in hot dip plating, reduces the dust amount generated by zinc bath surface when in hot dip plating, not only is suitable for hot dip plating, but also is suitable for hot dip aluminium plating.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Surface Coating Material for Molten Zinc Bath Member, Production Method Thereof, and Molten Zinc Bath Member
InactiveUS20100075133A1Improved zinc corrosion resistanceUniform structureHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsAlloyMetal
There are provided a surface coating material for a molten zinc bath member with improved zinc corrosion resistance, a production method thereof, and a molten zinc bath member. The surface coating material comprises WC powder particles and a binder metal. The binder metal comprises Co and a metal element electrochemically nobler than Co and constitutes an alloy structure having a single phase.
Owner:SANYO SPECIAL STEEL COMPANY
Hot-dip galvanizing with electroless ni pre-plating method for controlling thickness of silicon-containing active steel plating
InactiveCN101225518AEffective control of super thick growthControl overthick growthHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelNickel salt
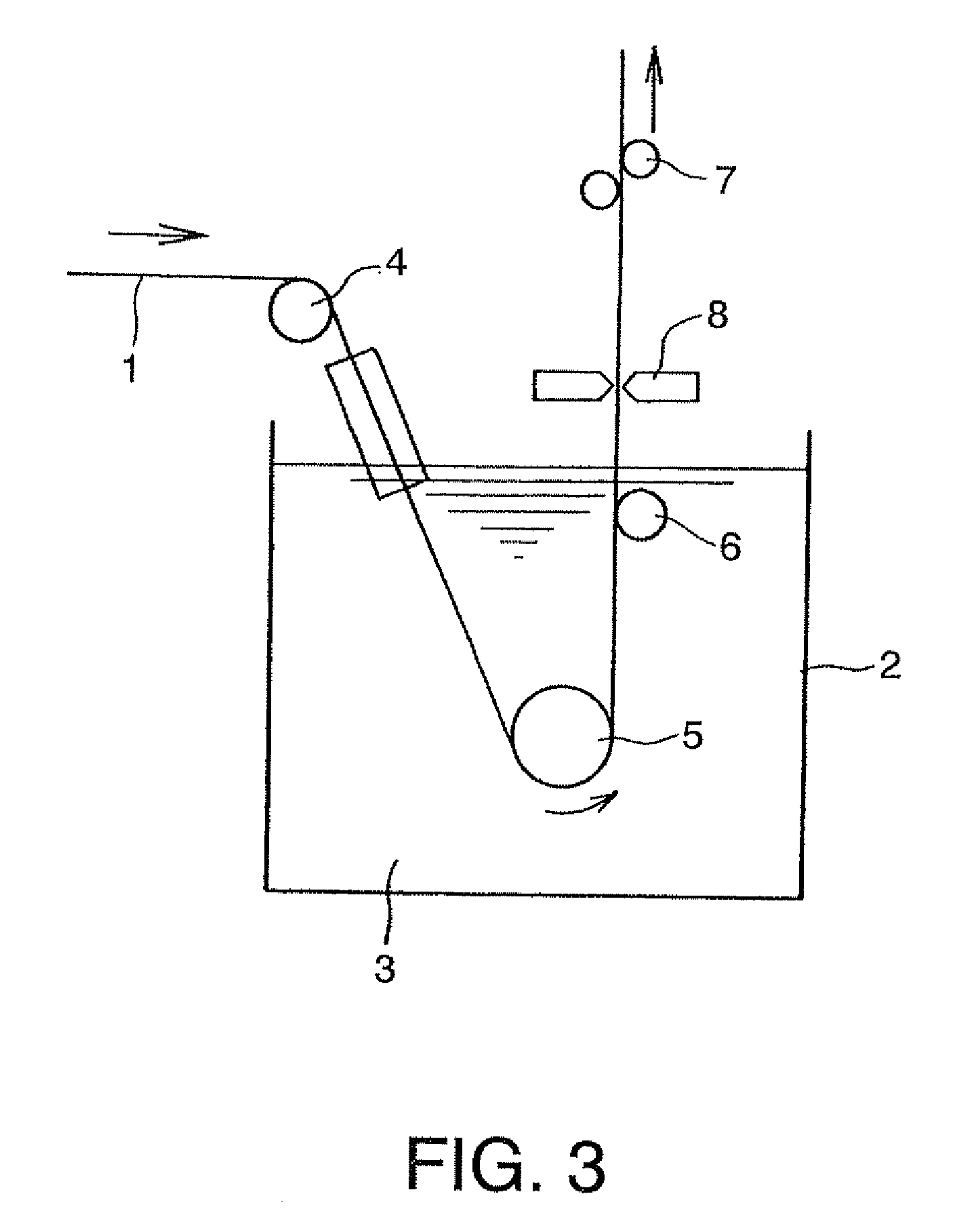
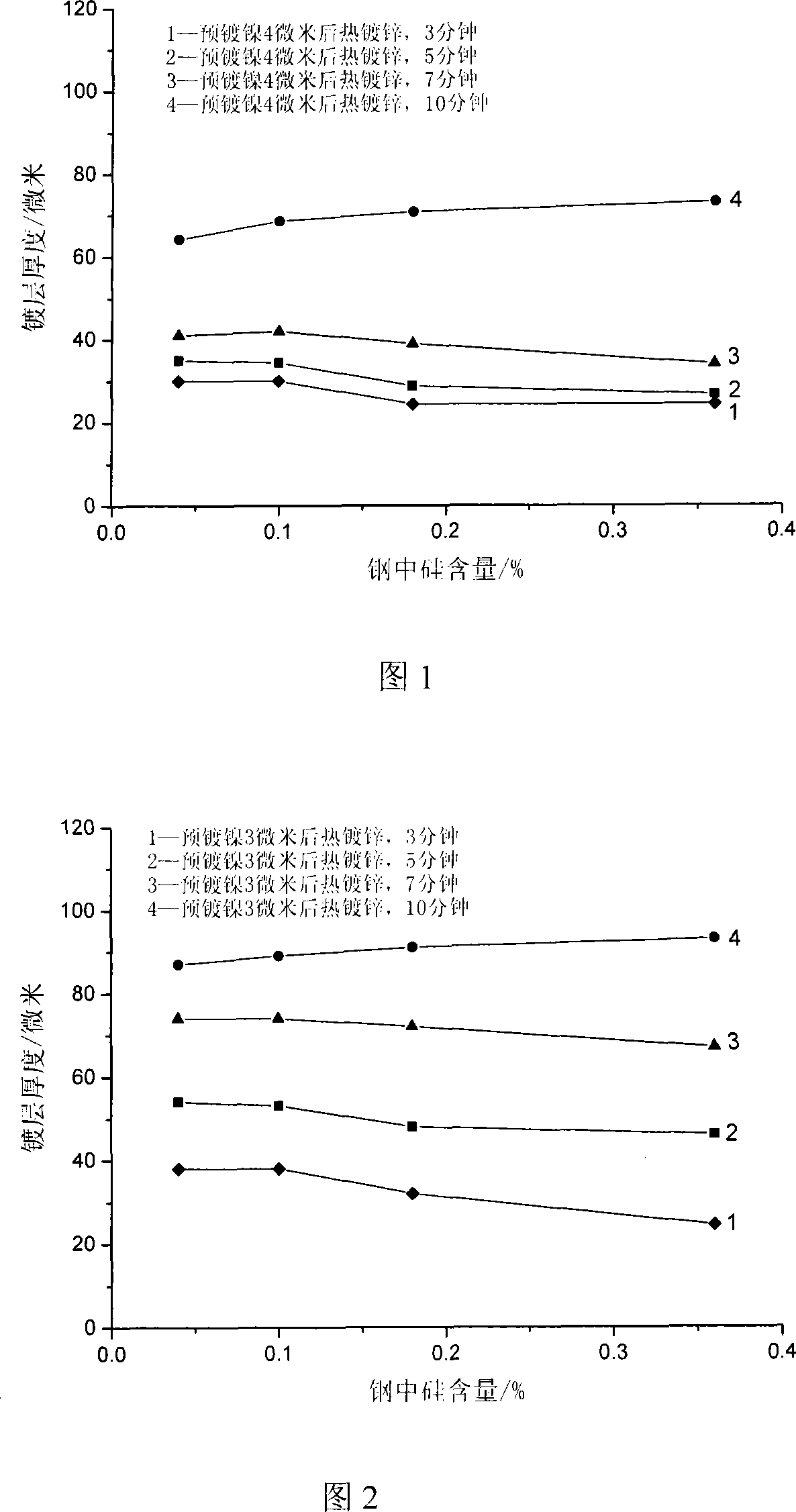
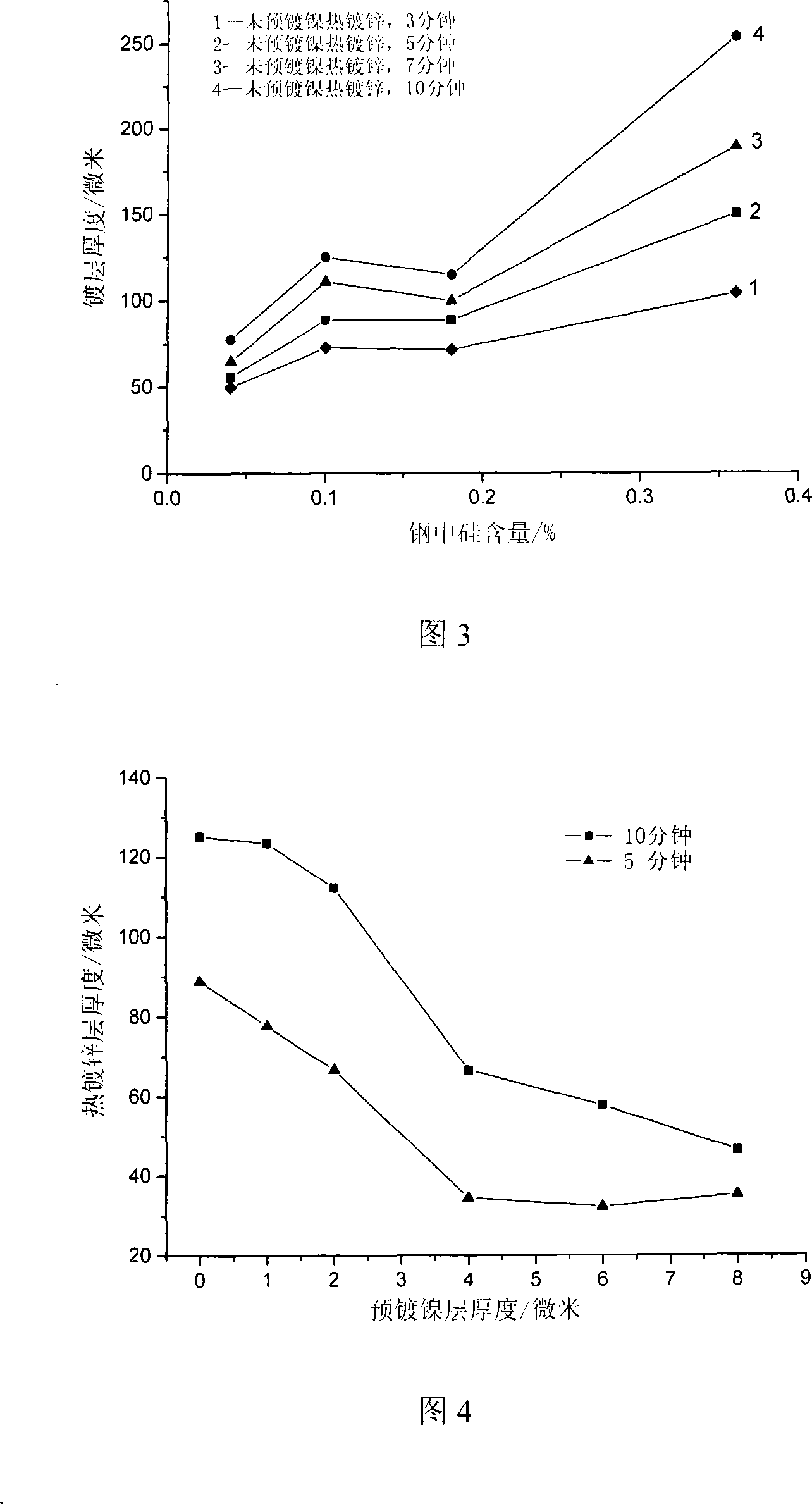
The invention discloses an electroless nickel pre-plating and hot post-galvanizing method for controlling the coating thickness of the silicon-containing reactive steel, which means first performing electroless nickel plating and then hot dip galvanizing on a silicon-containing reactive steel part. The electroless nickel pre-plating and hot post-galvanizing method comprises the following processes: (1) doing pretreatment on the surface of the silicon-containing reactive steel part before electroless nickel plating; (2) carry out electroless nickel plating on the surface of the silicon-containing reactive steel part, wherein, the nickel salt used is NiSO4 x 6H2 O, the reducing agent is NaH2PO2 x H2O, and the complexing agent is C6H5Na3O7 x 2H2O; (3) after drying the silicon-containing reactive steel part undergoing electroless nickel plating, conducting hot dip galvanizing on the reactive steel part. The electroless nickel pre-plating and hot post-galvanizing method for controlling the coating thickness of the silicon-containing reactive steel has the advantages of effectively controlling the coating of the hot galvanized silicon-containing reactive steel from thickening exceedingly, thus obtaining a coating with appropriate thickness, smooth surface and good adhesivity, consuming less nickel, and accomplishing the goal of preventing the hot galvanized coating of the silicon-containing reactive steel from excessively thickening by electrolessly plating a nickel coating with a thickness of 3 to 4 microns on the reactive steel part. Moreover, the pre-plate nickel coating can prevent the iron in steel part from dissolving in the zinc bath, thus greatly reducing the formation amount of zinc dross, and reducing the loss of zinc.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Surfacing welding rod of transition layer of sink roller for melted zinc bath and surfacing technique
InactiveCN101310914AGuaranteed bonding strengthImprove bindingArc welding apparatusFurnace typesMachiningTransition layer
The invention relates to an intermediate layer of a sink roller which is used in a hot galvanizing groove; meanwhile, the invention relates to welding wires used in the surfacing of the intermediate layers of coating roller species and a surfacing method thereof. A surfacing welding wire of the intermediate layer of the sink rolled used in the hot galvanizing groove is provided; the components of the welding wire are as follows (mass percent): 0.04 percent to 0.08 percent of C, 0.3 percent to 0.6 percent of Si, 1.0 percent to 1.5 percent of Mn, 10 percent to 12 percent of Cr, 3 percent to 5 percent of Ni, 0.5 percent to 1.2 percent of Mo and the rest is Fe. The surfacing method of the welding wire comprises the following steps: a surfacing area is processed from the roller surface of the sink roller by a machine; the welding wire is matched with an SJ81 welding flux, 300A to 350A of welding current, 28 V to 30V of welding voltage and 400 mm to 600 mm per minute of welding speed for surfacing; and heat treatment anneal is carried out after being heated to 500 DEG C to 540 DEG C. In the invention, the intermediate layer is produced between the austenitic stainless steel substrate and a hot spraying WC-Co coat of the sink roller and a stabling roller, which are working in the hot galvanizing groove, thus improving the combination between the hot spraying WC-Co coat and substrate material.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSTEEL EQUIP MAINTENANCE CO LTD
Process for Producing a Sheet Steel Product Coated with an Anticorrosion System
InactiveUS20100055344A1Easy to processCheap productionHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesSheet steelEconomic production
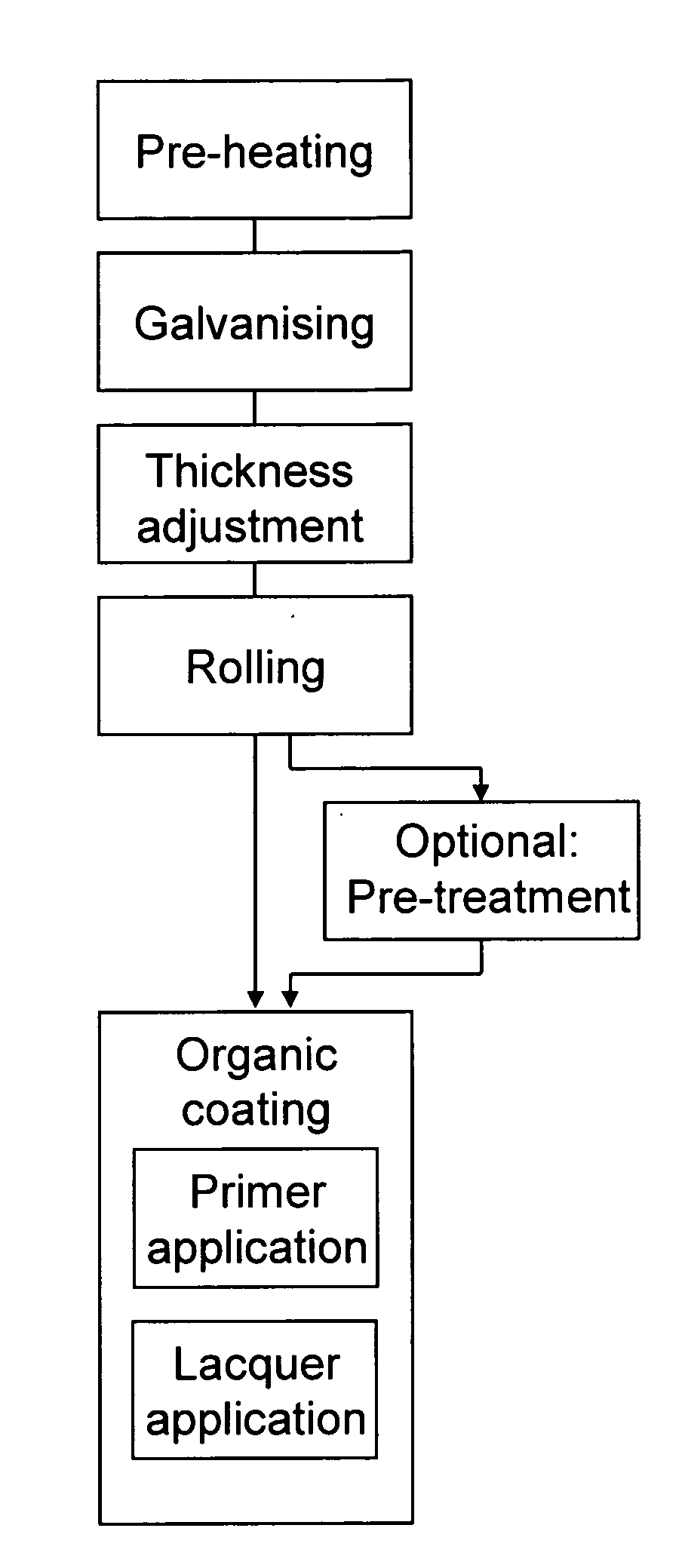
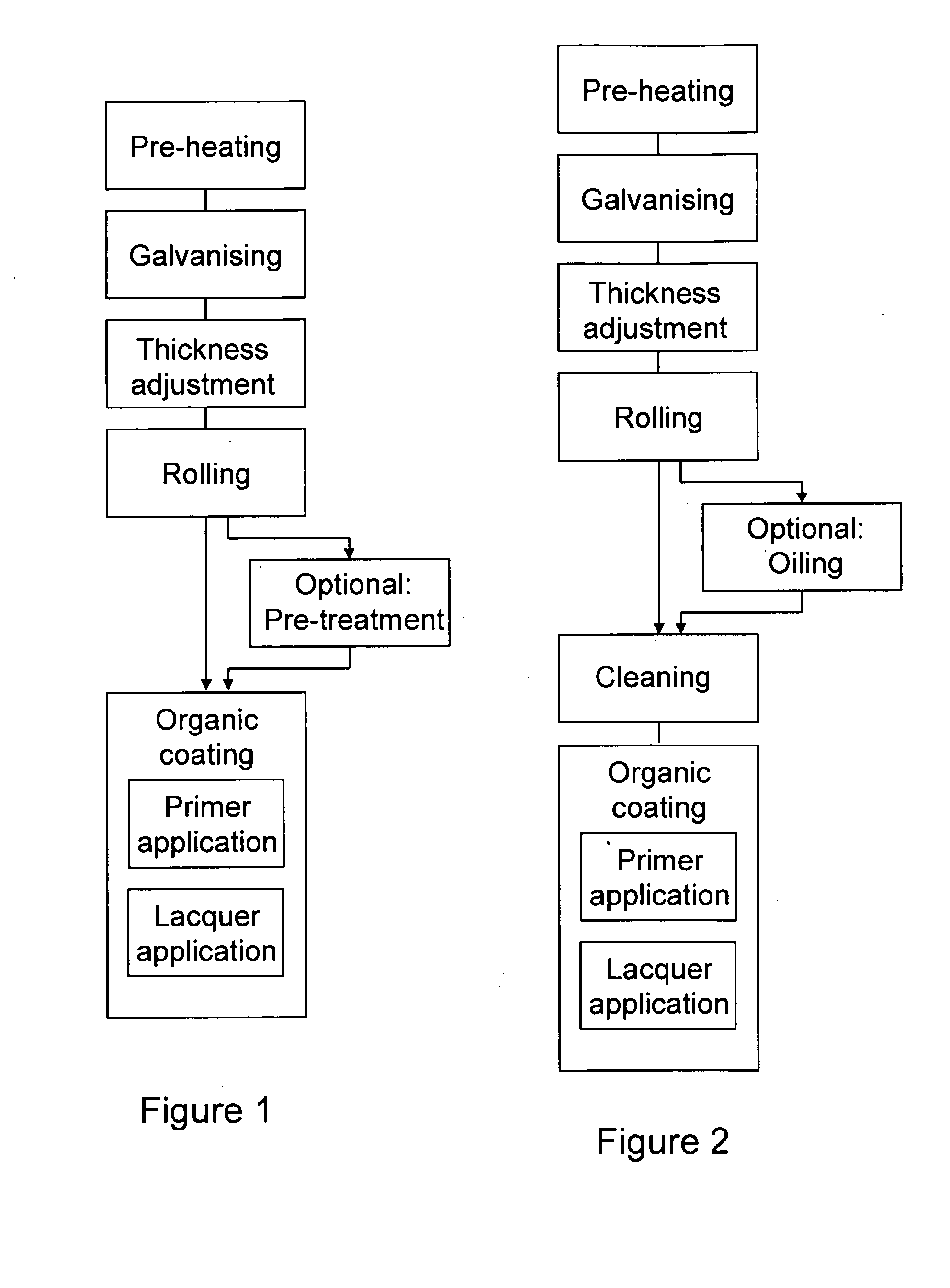
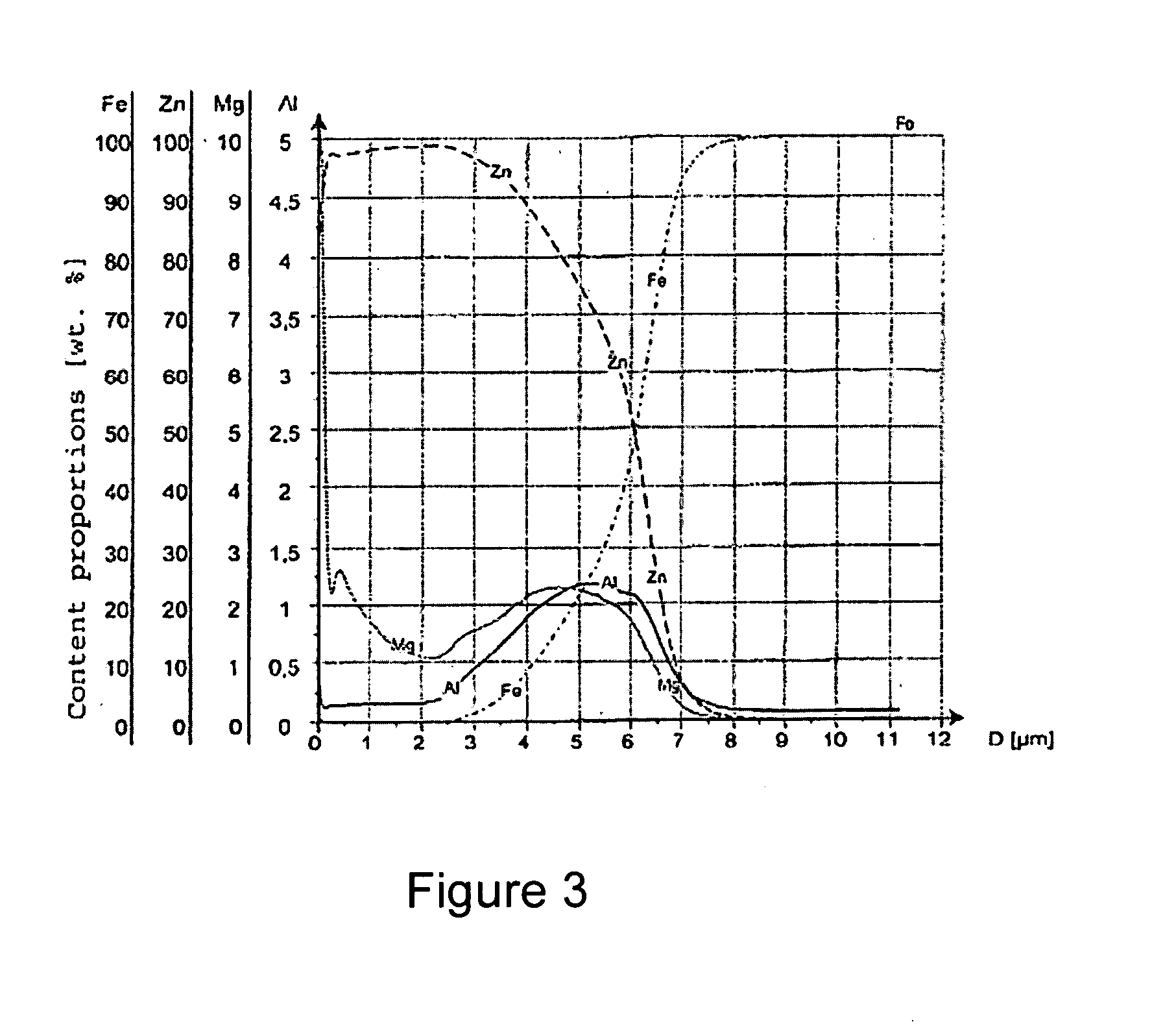
Economic production of highly corrosion-resistant flat steel products with a corrosion protection system, which are at the same time easy to process further, is described. The following work steps are applied: preheating the steel substrate to a strip temperature under inert gas atmosphere; cooling the steel substrate to the strip inlet temperature; hot dip coating of the steel substrate in a zinc bath so that a metallic corrosion protection coating is formed on the steel substrate which has an Al content of max 0.5 wt. % in an intermediate layer; adjusting the thickness of the metallic corrosion protection coating applied to the steel substrate in the melt bath to values of 3 to 20 μm per side by scraping away excess coating material; cooling the steel substrate with the metallic corrosion protection coating; and applying the organic coating to the metallic corrosion protection coating of the steel substrate.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Method for steel product batch hot dip galvanizing
InactiveCN101476099ASolve the problem of different consumption speedInhibition of superthick growthHot-dipping/immersion processesCeriumManganese
The invention discloses a method applicable to rolled-steel lot-quantity hot dipping zinc, namely, performing lot-quantity hot dipping zinc to rolled steels in a zinc alloy plating bath formulated by two kinds of binary intermediate alloy. The zinc alloy plating bath comprises the following components: manganese of 0.3%-0.5%, cerium of 0.005%-0.03% and zincium of the rest, and the two kinds of binary intermediate alloy comprise a zincium-manganese binary intermediate alloy comprising manganese of 2%-3% and zincium of the rest; a zincium-cerium binary intermediate alloy comprising cerium of 2%-3% and zincium of the rest.The invention has advantages of simple alloy coating technique, easy controlling of components of alloy zincium bath; effective control of super-thick growth of the coating layer of silicon-contained reactive steel, improvement of corrosion resistance capability of the coating layer, great delaying of the generation of white rust, elimination of disorder inhomogenous color on the coating layer surface of zincium-manganese alloy for obtaining more bright and smooth coating layers; reduced production cost by because of adopting cheap alloy elements; simple technique without changing original hot dipping zinc equipment, which is propitious to scale-production of lot quantity hot dipping zinc of rolled steels.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A circulating cooling deslagging method in continuous hot dip of zinc-aluminium alloys
ActiveCN102168238AContinuous removalImprove cooling effectHot-dipping/immersion processesHoneycombDross
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
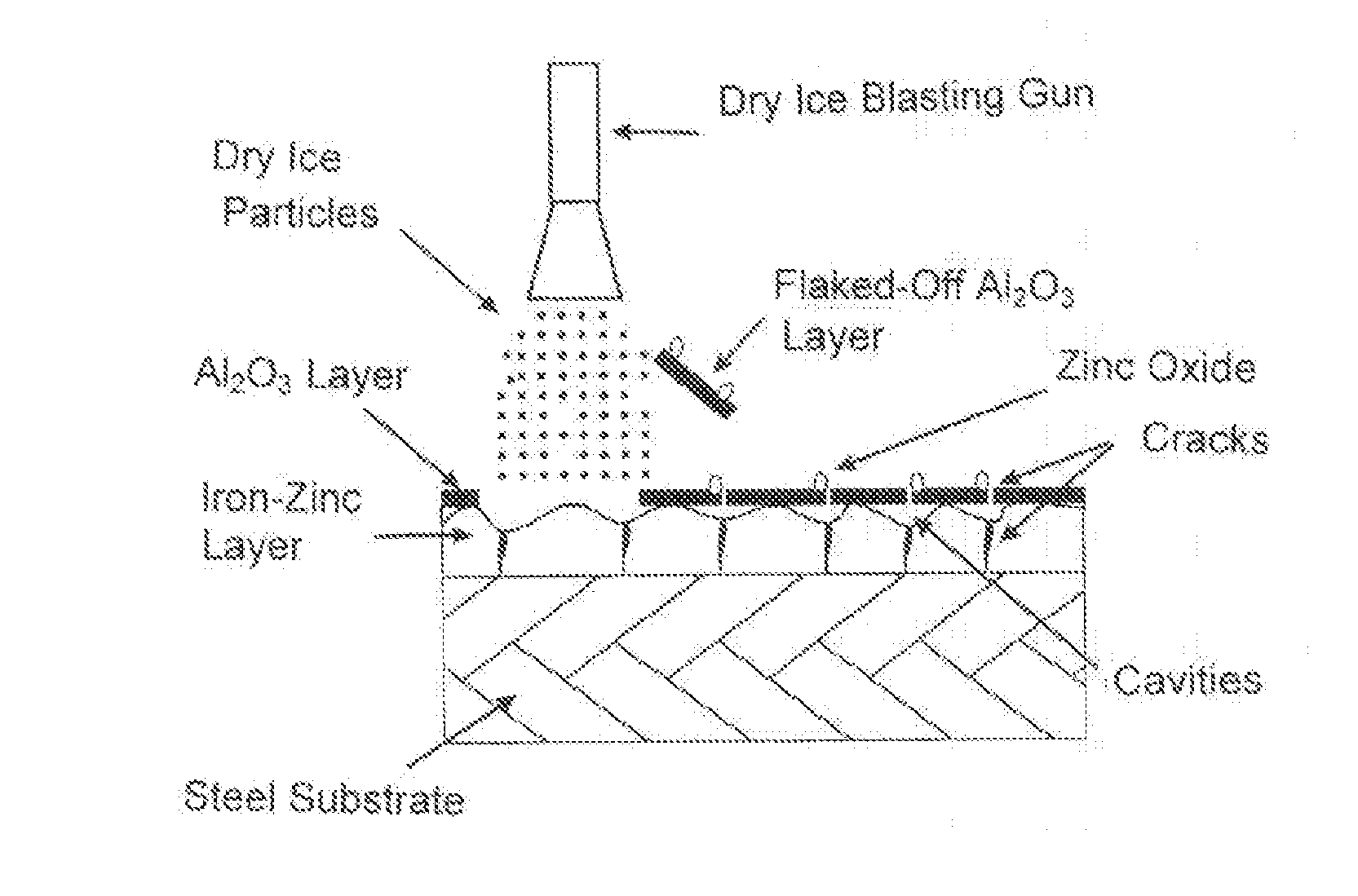
Method for the production and removal of a temporary protective layer for a cathodic coating
ActiveUS20110139308A1Improve attributesImprove adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingDry iceAlloy
The invention relates to a method for the production and removal of a temporary protective layer for a cathodic coating, particularly for the production of a hardened steel component with an easily paintable surface, wherein a steel sheet made of a hardenable steel alloy is subjected to a preoxidation, wherein said preoxidation forms a FeO layer with a thickness of 100 nm to 1,000 nm and subsequently a melt dip coating is conducted, wherein, during the melt dip coating, a zinc layer is applied having a thickness of 5 to 20 μm, preferably 7 to 14 μm, on each side, wherein the melt dip process and the aluminum content of the zinc bath is adjusted such that, during the melt dip coating, an aluminum content for the barrier layer results of 0.15 g / m2 to 0.8 g / m2 and the steel sheet or sheet components made therefrom is subsequently heated to a temperature above the austenitizing temperature and is then cooled at a speed greater than the critical hardening speed in order to cause hardening, wherein oxygen-affine elements are contained in the zinc bath for the melt dip coating in a concentration of 0.10 wt.-% to 15 wt.-% that, during the austenitizing on the surface of the cathodic protective layer, form a thin skin comprised of the oxide of the oxygen-affine elements and said oxide layer is blasted after hardening by irradiation of the sheet component with dry ice particles.
Owner:VOESTALPINE STAHL GMBH
Zinc bismuth multicomponent alloy used for hot dip galvanizing of steel and iron members and hot dip galvanizing method therefor
ActiveCN1654692AImprove liquidityGuaranteed mechanical propertiesHot-dipping/immersion processesRare earthZinc alloys
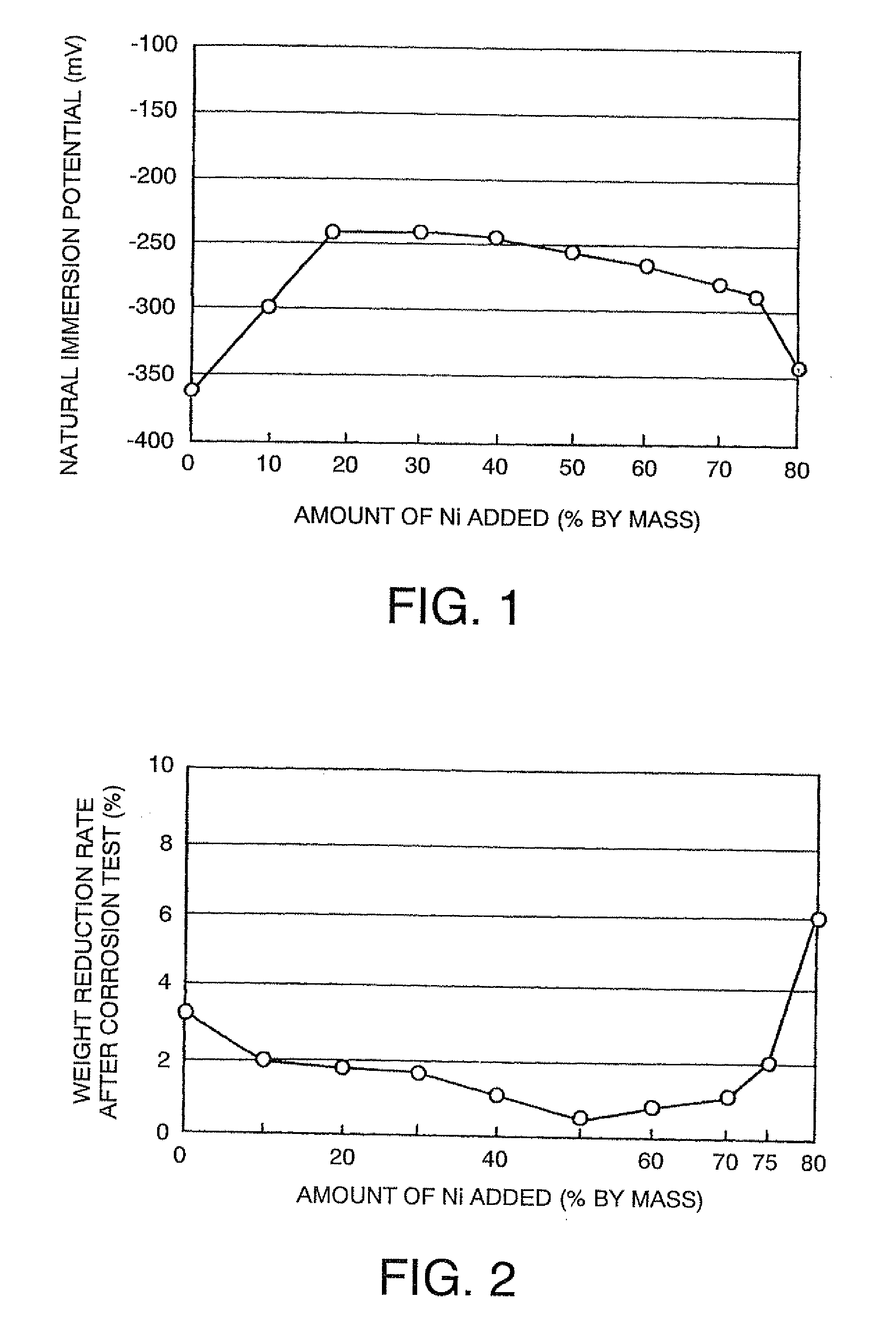
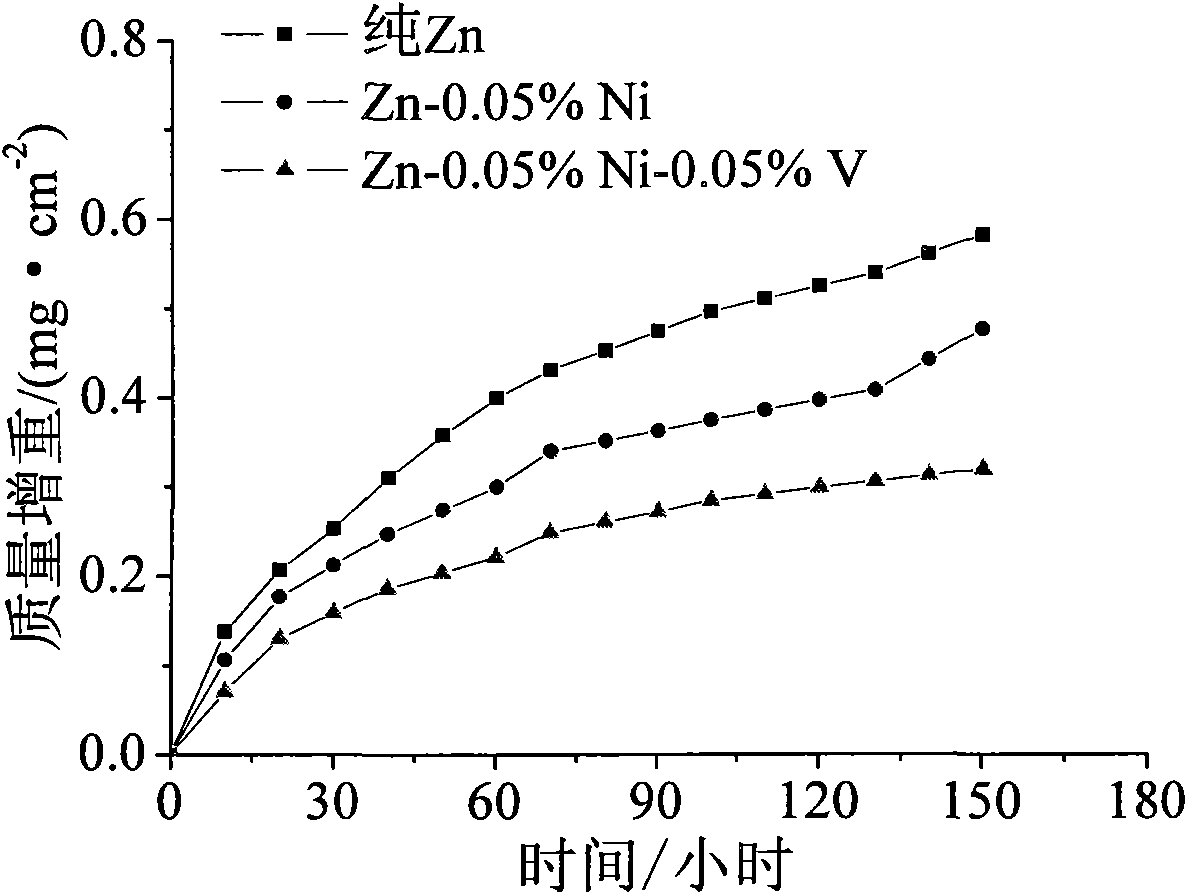
The present invention relates to zinc alloy and its zinc hot immersion plating process. The technological scheme has Zn-Bi alloy for hot immersion plating iron and steel member consists of: Bi 0.05-0.1 wt%, Al 0.05-0.09 wt%, RE 0.01-0.05 wt% and Ni 0-0.05 wt% except Zn and inevitable impurity, with RE being mixture of at least two of La, Ce and Pr. The zinc hot immersion planting of steel product containing Si and / or P is completed in zinc bath with the said Zn-Bi alloy. The present invention has reasonably controlled Al, Ni and RE contents in the alloy and Bi added into the alloy, so that the zinc bath has obviously improved flowability, resulting in appropriately reduced plating thickness while ensuring the anticorrosive performance and mechanical strength of the plating.
Owner:株洲冶炼集团有限责任公司
Hot-dip galvanizing alumino-nickel for steel component hot-dip galvanizing and ingot shape and method thereof
PendingCN101135017AAvoid uneven compositionAvoid burnsHot-dipping/immersion processesIngotZinc alloys
The present invention relates to zinc alloy for hot dip galvanizing steel member and its ingot form and hot dip galvanizing process. The zinc alloy consists of Al 0.008-0.012 wt%, Ni 0.02-0.04 wt%, and Zn and inevitable impurities for the rest. The zinc alloy is shaped in cuboid with ears and hoisting holes for easy hoisting, storing and transporting. When it is applied in hot dip galvanizing steel member, the zinc alloy is melted directly to form one zinc bath for convenient use and lowered galvanizing cost.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Method of constructing highly corrosion-resistant zinc alloy double-coating on surface of steel product
InactiveCN107904532ASolve the problem of thin, poor surface qualityProcess stabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesDouble coatingZinc alloys
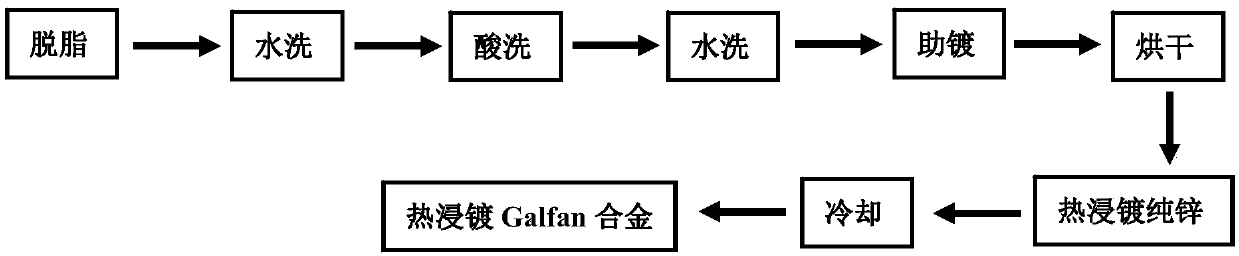
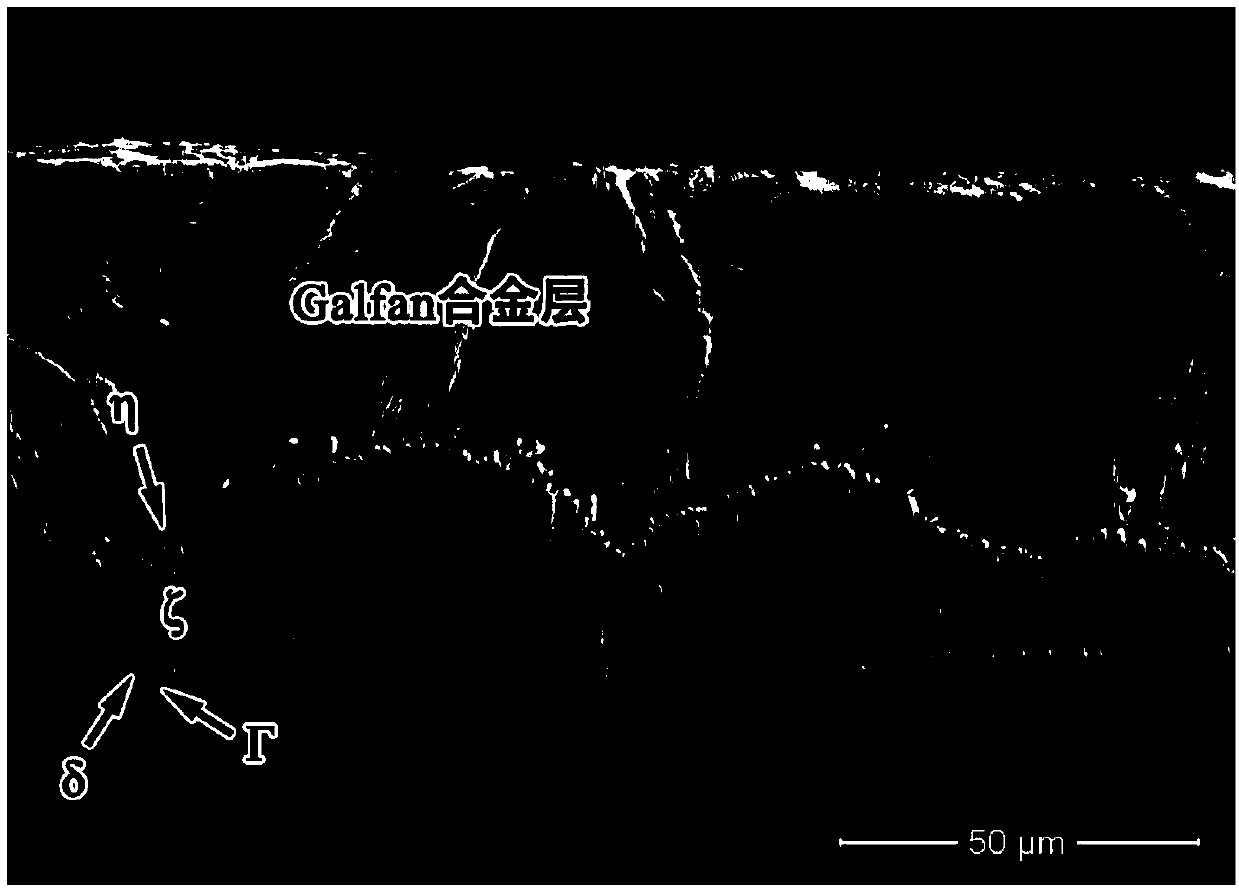
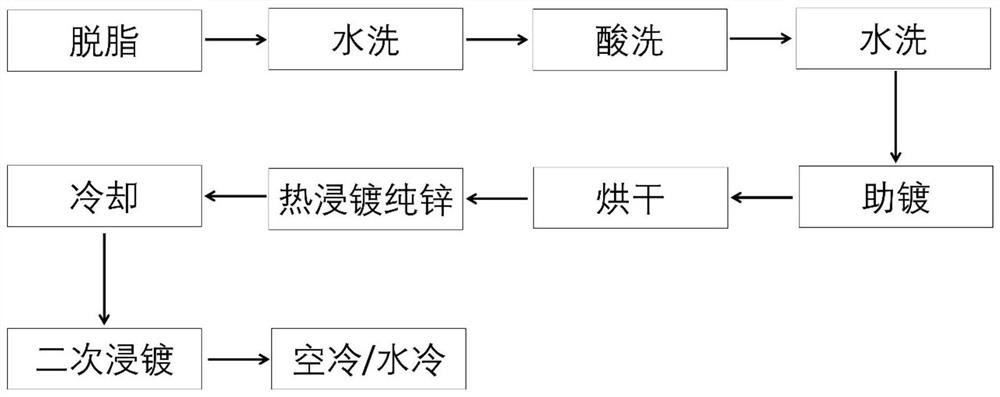
The invention discloses a method of constructing a highly corrosion-resistant zinc alloy double-coating on the surface of a steel product. The method comprises the technological steps of degreasing, water washing, pickling, water washing, assisted plating, drying, hot dipping in pure zinc, cooling, hot dipping in a highly corrosion-resistant zinc alloy, and cooling sequentially. The highly corrosion-resistant zinc alloy is an alloy with a relatively low melting point and high coating corrosion resistance for the hot dipping. The surface of the steel product is subjected to pre-treatment of plating by adopting a conventional batch hot-dip galvanizing process, and after being subjected to hot-dip galvanizing in a 435-460 DEG C pure zinc bath, the surface of the steel product is directly placed in or is cooled and then placed in a 385-450 DEG C alloy bath for dip plating for 5-120 s, and then is cooled. By adopting the method, the problems that the probability of skip plating is high, a coating is thin (less than 20 m) and the surface quality of the coating is poor when steel is directly put in a dip plating aluminum-zinc (the content of Al is greater than 1%) alloy bath are solved, the corrosion resistance of the steel product is improved significantly and the service life is prolonged substantially due to a constructed double-coating superimposed structure, the method is stablein technology, and the coating quality is easy to control.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
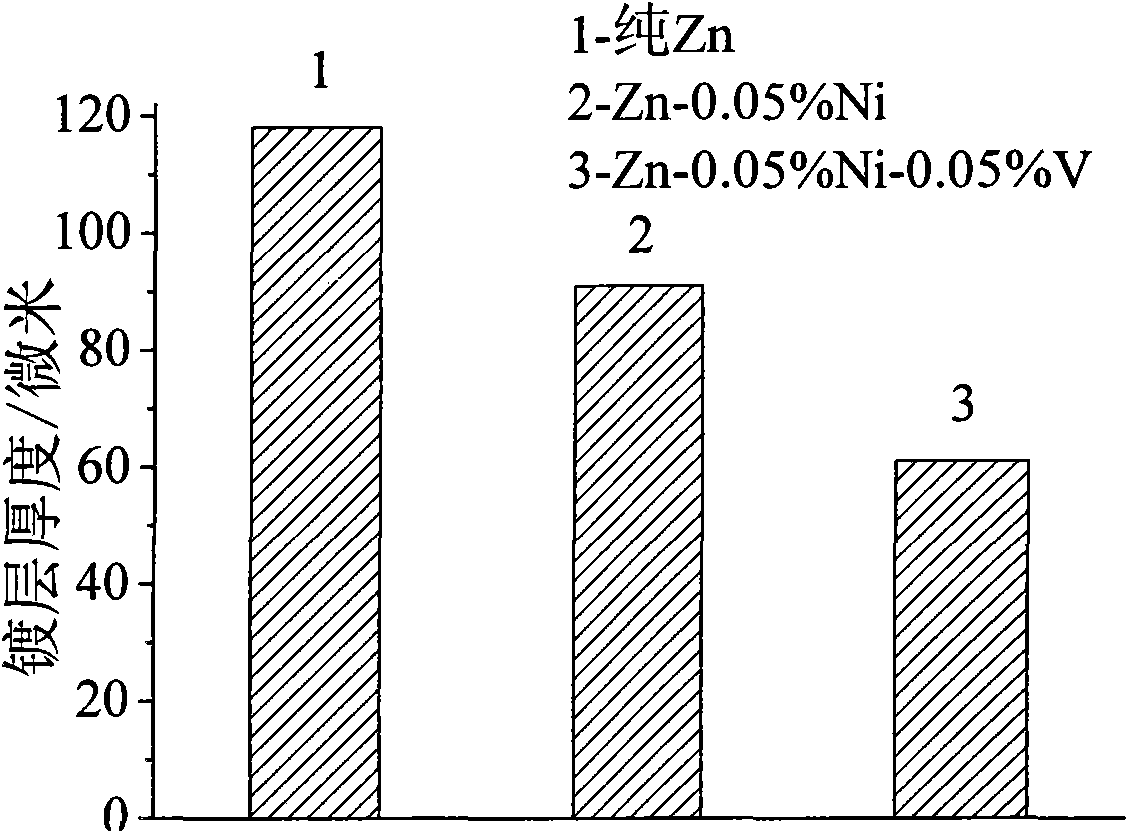
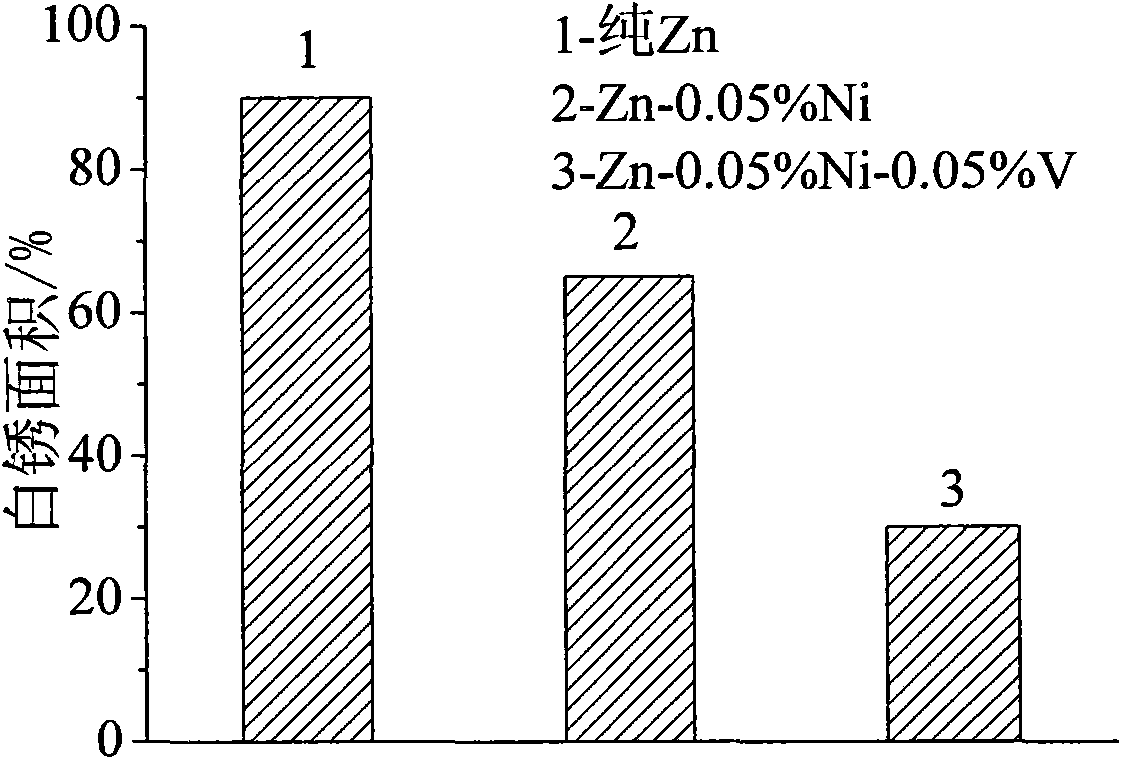
Method for hot dip galvanizing of nickel-vanadium alloy plating coat on rolled steel
InactiveCN101570842ASolve the problem of different consumption speedInhibition of superthick growthHot-dipping/immersion processesZinc alloysSilicon
The invention discloses a method for hot dip galvanizing of nickel-vanadium alloy plating coat on rolled steel, which performs batch hot dip galvanizing on the rolled steel in a zinc alloy plating bath prepared from two binary intermediate alloys. The zinc alloy plating bath comprises the following components by weight percentage: 0.03 to 0.05 percent of nickel, 0.03 to 0.08 percent of vanadium, and the balance of zinc. The two binary intermediate alloys comprise the following components by weight percentage: 2 to 3 percent of the nickel in a zinc-nickel binary intermediate alloy, and the balance of zinc; and 1 to 2 percent of vanadium in a zinc-vanadium binary intermediate alloy, and the balance of the zinc. The alloy plating coat has a simple process, the components of the alloy zinc plating bath are easy to control, adverse effects on the plating coat caused by silicon in the steel for the hot dip galvanizing can be overcome effectively, the thickness of the plating coat is reduced effectively, and simultaneously, the corrosion resistance and the antioxygenic property of the plating coat is further improved and the prior hot dip galvanizing equipment is not necessary to be changed, thus the method is advantageous for the large-scale production of the batch hot dip galvanizing of the rolled steel.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
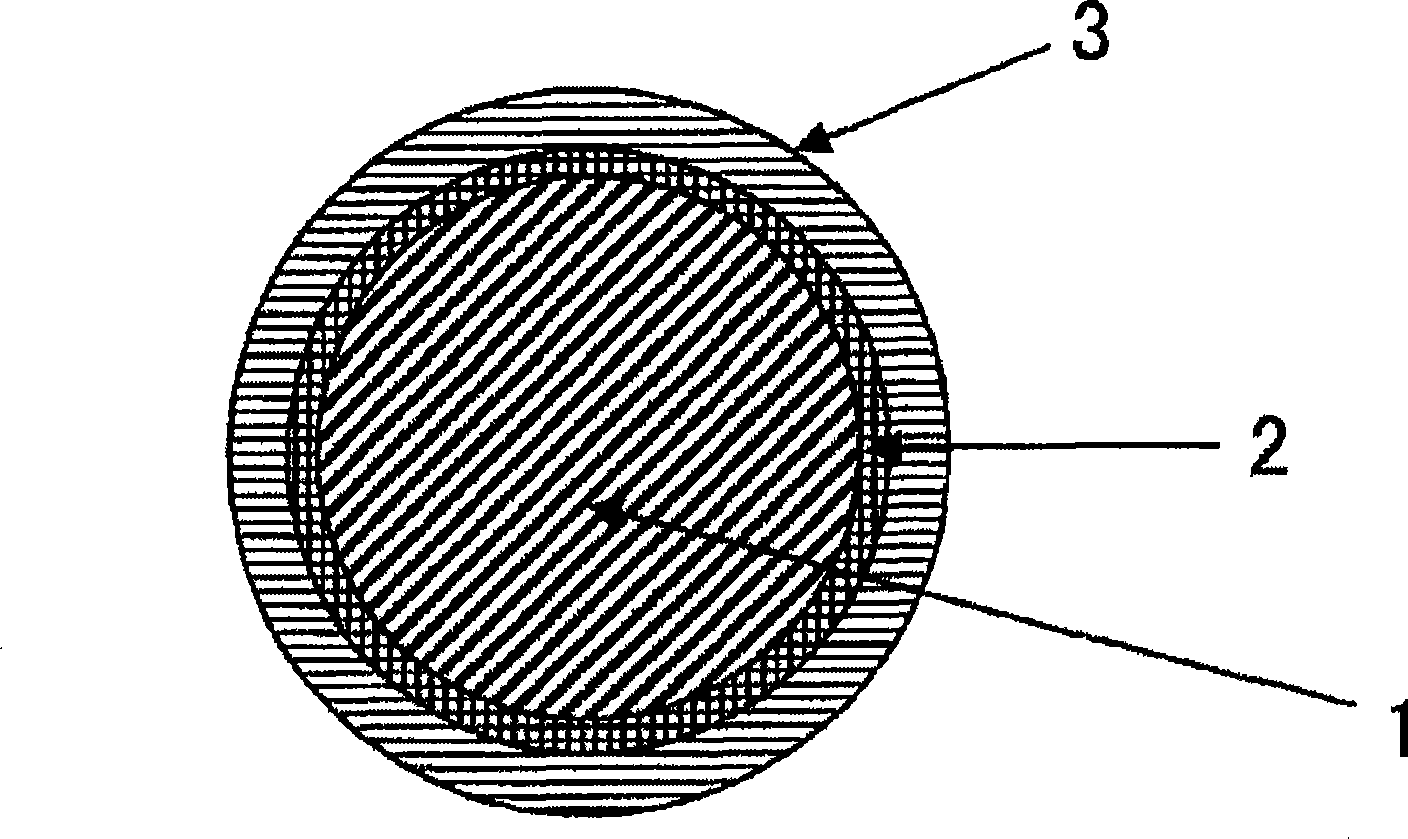
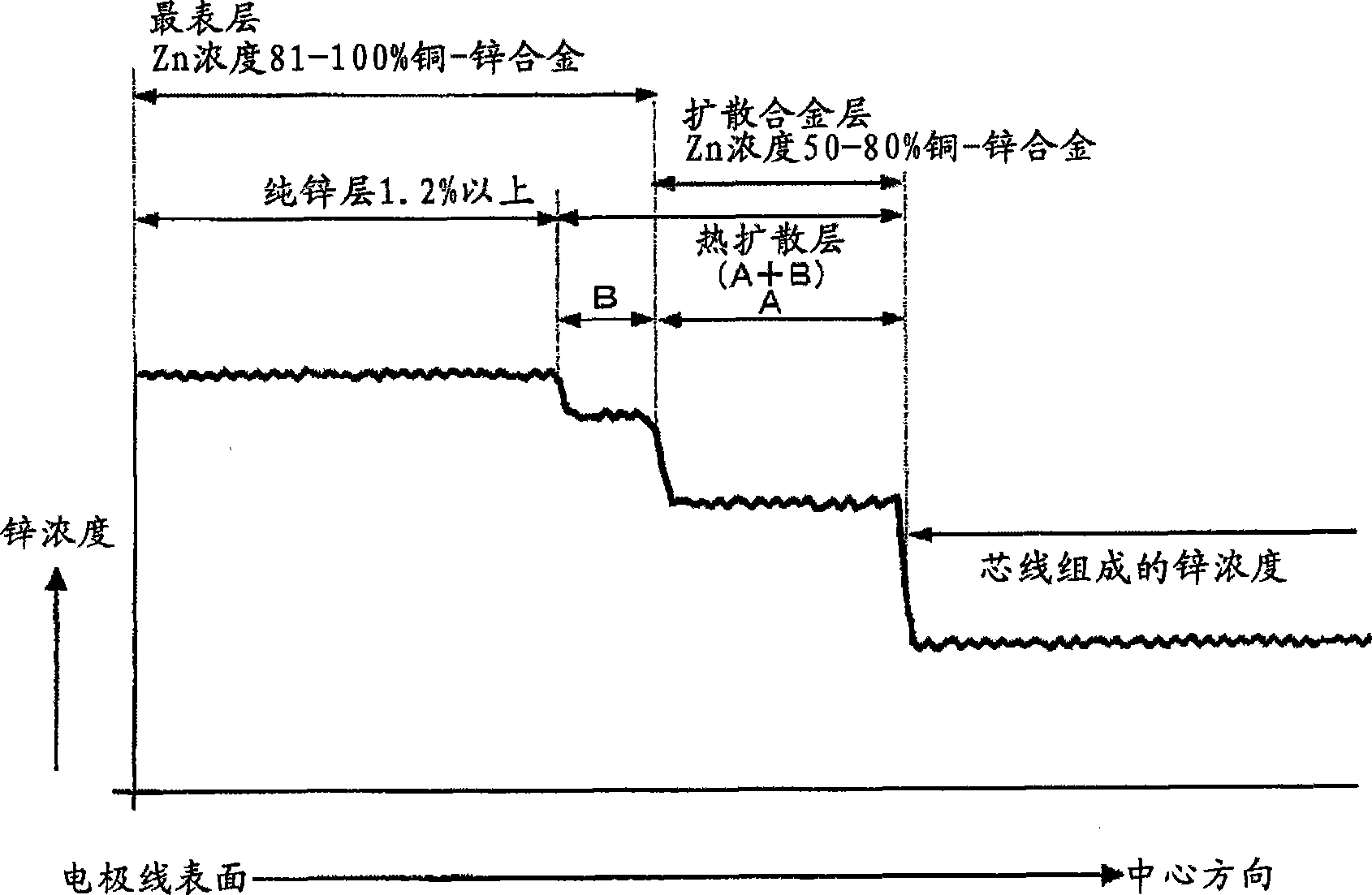
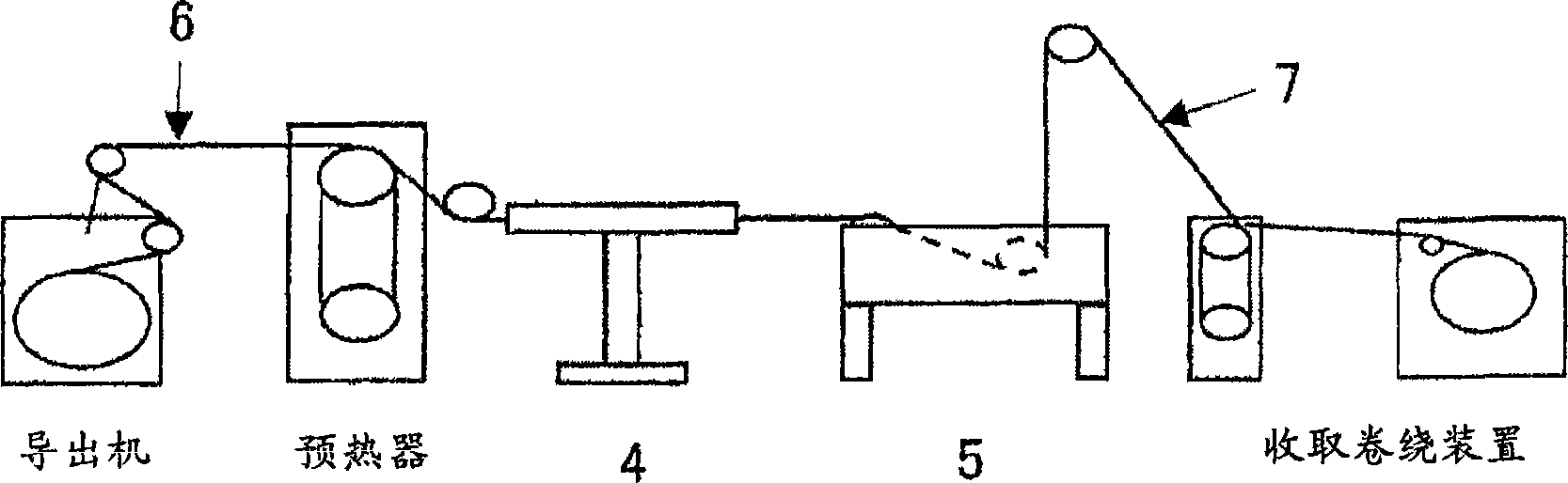
Electrode wire for wire electric discharging, method for manufacturing the electrode wire, and apparatus for manufacturing bus line thereof
InactiveCN101505900AImprove surface roughnessImprove EDM speedHot-dipping/immersion processesElectrical-based machining electrodesZinc alloysConcentration gradient
An electrode wire for wire electrodischarge machining includes a core made of copper or copper alloy, a pure zinc layer formed by hot-dip galvanizing the core, and a relatively thin copper-zinc alloy layer formed by mutual thermal diffusion across the interface between the pure zinc layer and the core and having a zinc concentration gradient. The electrode wire is not cracked during its production. The thickness of the copper-zinc alloy layer, the gradient of zinc concentration, and the thickness of the outermost pure zinc layer can be controlled by selecting the dipping time and the temperature of the hot-dip galvanizing bath as appropriate. By blowing a non-oxidizing gas from a bath surface zinc purifying and wiping device disposed above the bath surface through which the core emerges from the hot-dip galvanizing bath, the pure zinc bath surface is kept exposed and runs and uneven thickness of the galvanizing layer are prevented.
Owner:OKI ELECTRICAL CABLE
Method for continuously and thermally galvanizing pipe
InactiveCN101709445AQuality improvementRealize online full continuous productionHot-dipping/immersion processesSheet steelStack machine
The invention provides a method for continuously and thermally galvanizing a pipe. In the method, the whole process is completed continuously on line, a hot-rolled steel plate is used as a raw material plate, the whole processing process of the steel strip from unrolling to welding a steel pipe, to galvanizing and to shearing is completed on line, and the fully continuous and automatic production of the thermally galvanized pipe integrates unrolling, leveling, rolling, welding, cleaning, blowing with cold wind, specified length shearing and stacking. The method comprises the following steps: delivering the hot-rolled steel strip to a welding stage; delivering the welded continuous steel strip to a disk loop material storing and leveling stage; delivering the welded continuous steel strip to a rolling stage to longitudinally weld a steel pipe; delivering the steel pipe formed by rolling and welding to a zinc bath 12, and controlling the thickness of a zinc layer by using an annular air blade 13; delivering the galvanized steel pipe to a shearing and stacking stage and delivering the galvanized steel pipe to a specified length follow-up shears 16 to shear the steel pipe by required length; and stacking the steel pipes according to a required height with two stacking machines of which one is spared for later use. Production efficiency is improved and cost and expenses are saved.
Owner:BEIJING STAR RIVER INTEGRATED EQUIP TECH
Device for collecting zinc smoke of hot-dip galvanizing workshop
ActiveCN104313526AReduce operating powerEasy to take awayHot-dipping/immersion processesDirt cleaningButt jointZinc bath
The invention discloses a device for collecting zinc smoke of a hot-dip galvanizing workshop and relates to a smoke collecting device. The device comprises a dust collecting cover body fixed on a travelling crane; two load lifting hooks of a crane are hooked by virtue of a vertical guide rope which passes through a cover body rack from top to bottom; the cover body can be used for moving and fetching workpieces with the crane; the fixed device part is supported and guided by upright stands which are distributed on four corners of a zinc pot; for movable baffle plates at the two sides in the length direction of the zinc pot, when the workpieces are soaked in zinc bath, the movable baffle plate at the outer side ascends, so that the top of the movable baffle plate at the outer side is in butt joint with the lower end of the cover body, and the bottom of the movable baffle plate at the outer side is aligned to the top of the movable baffle plate at the inner side, so that the space above the workpieces and the zinc pot is sealed, and thus, the smoke dust is prevented from escaping; meanwhile, the zinc ash on the surface of the zinc bath is prevented from being taken away, so that the zinc consumption is saved; when the zinc ash is scrabbled, the movable baffle plate at the inner side ascends, so that space is made for convenience in operation; when the workpieces are fetched, the movable plates are descended for convenience in conveying the workpieces.
Owner:德州广鑫钢结构有限公司
Multi-purpose ammonium-free fluxing agent for hot dip coating and application method thereof
InactiveCN103741084AAvoid secondary oxidationImprove stabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesDip-coatingAqueous solution
The invention provides a multi-purpose ammonium-free fluxing agent for hot dip coating and an application method thereof. The multi-purpose ammonium-free fluxing agent is suitable for hot dip coating of zinc-aluminum alloys with various aluminum contents, and is good in fluxing effect, small in soot content during hot dip coating and capable of perfecting the production environment. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the matching components of per liter of fluxing solution comprise 240-300 g of ZnCl2, 10-24 g of NaCl, 5-12 g of CaCl2, 20-60 g of SnCl2, 16-60 g of K2ZrF6 and the balance of water. Before the fluxing solution is used, a workpiece is subjected to alkali washing in a 10-25% NaOH solution at 60-80 DEG C for deoiling, is pickled in 20-40% HCL solution at normal temperature for derusting after being washed with water and is washed with water again, then the workpiece is soaked in the ammonium-free fluxing agent for fluxing treatment, the temperature of the fluxing solution is controlled within 40-80 DEG C, and finally, the workpiece is dried in a drying box of 90-120 DEG C after the fluxing treatment. The characteristics of the fluxing solution are as follows: the components of the fluxing agent generate no mutual reaction, corrosion on a matrix is small, oxides on the surface of a molten pool can be cleaned to effectively protect the matrix, decomposition products do not enter zinc bath, and the cost is low.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Device for introducing metal bars into a metal bath
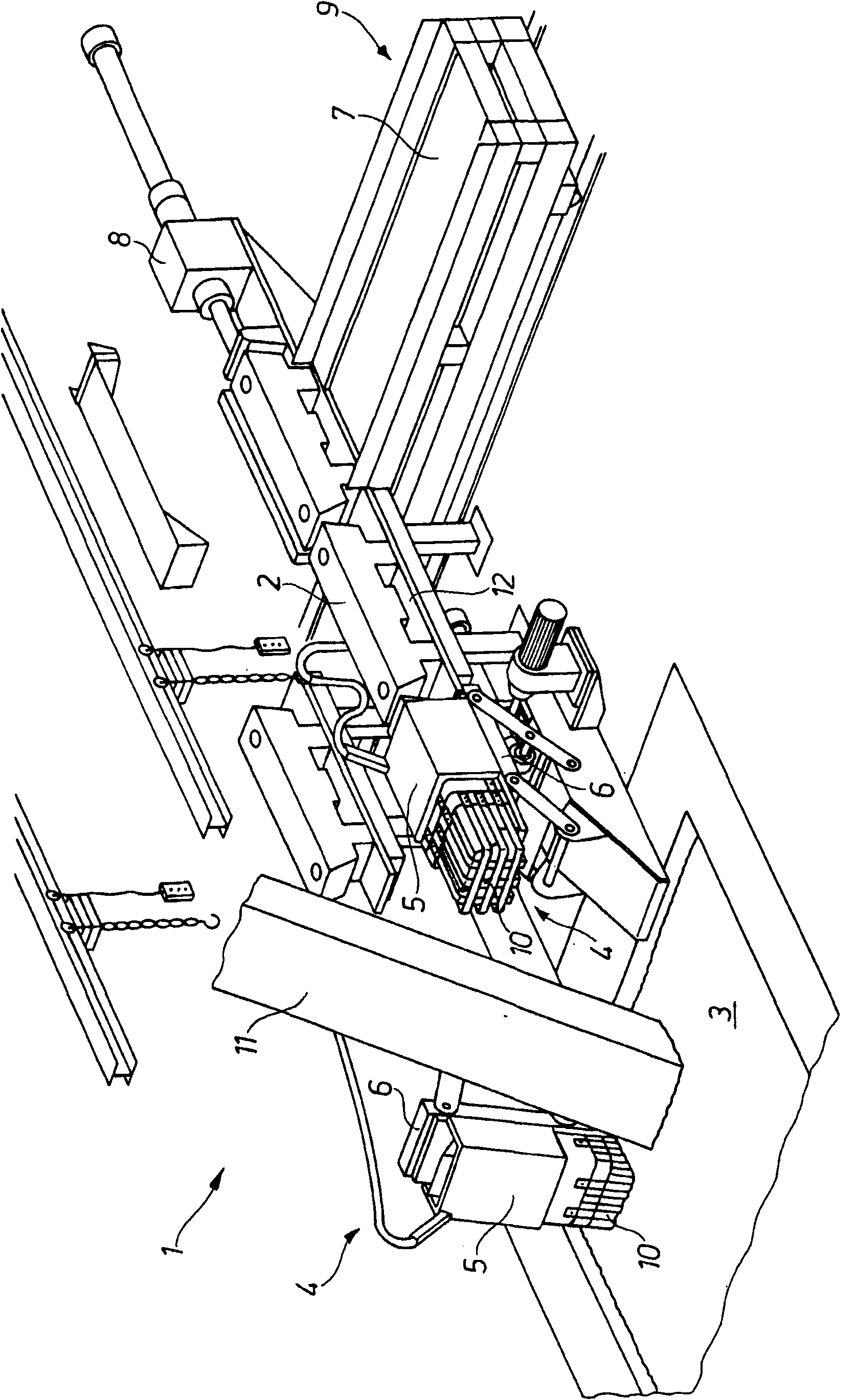
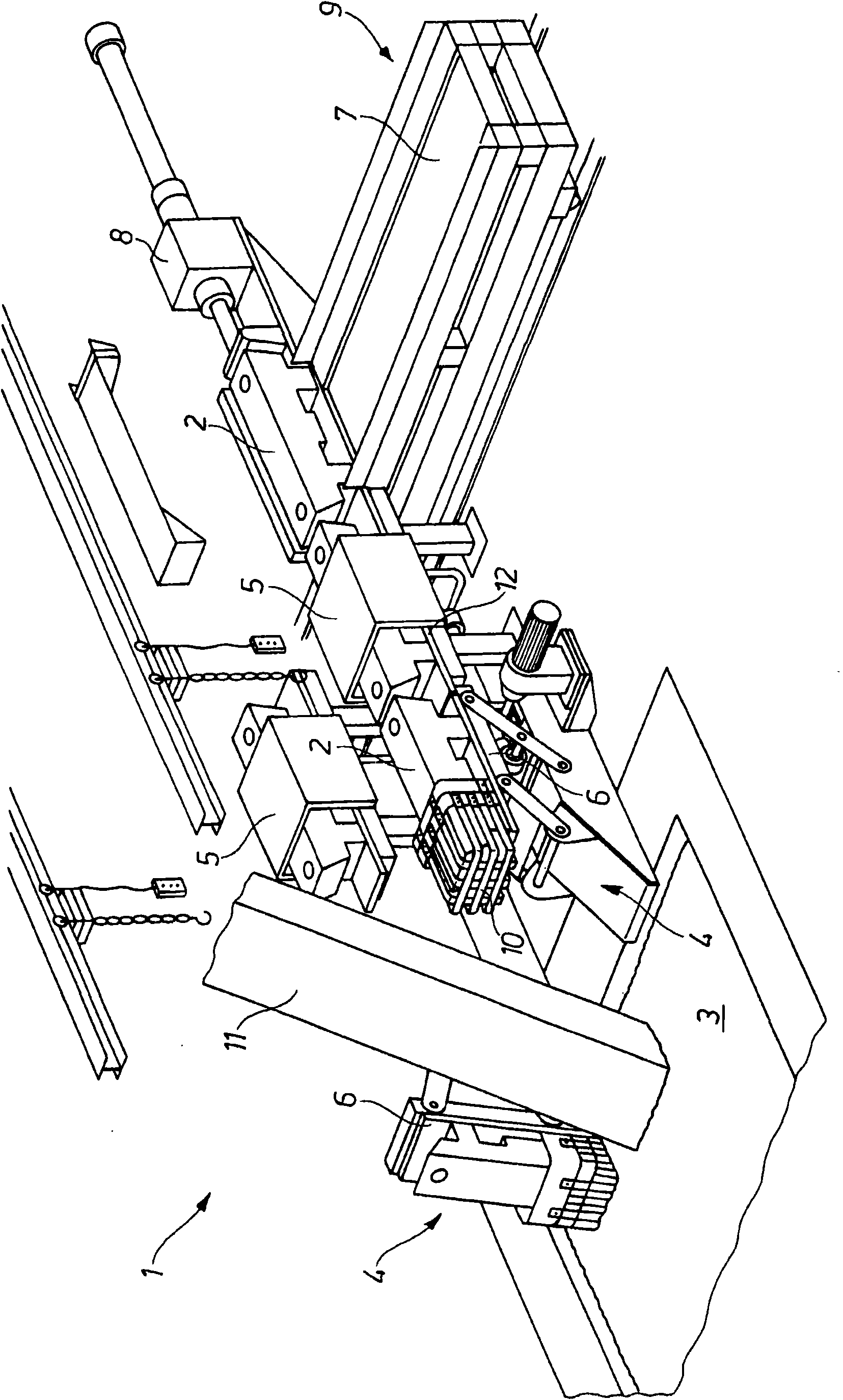
InactiveCN101680716AOptimal process controlSpeed up meltingHot-dipping/immersion processesCharge manipulationIngotMetal
The invention relates to a device (1) for inserting metal ingots (2) into a metal bath (3), in particular zinc ingots into a zinc bath, wherein the device (1) comprises feed means (4) with which an ingot (2) can be fed to the metal bath (3), and wherein the device (1) comprises heating means (5) with which the ingot (2) can be heated to a desired temperature before and / or after its feeding into the metal bath (3). In order to improve the process control, it is provided according to the invention that the heating means (5) comprise at least one independently operated heating element which can be operated independently of other system parts with which the device (1) cooperates.
Owner:SMS DEMAG AG
Production method of zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy for hot dipping
InactiveCN103614592AImprove adhesionReduce manufacturing costHot-dipping/immersion processesSlagManganese
The invention provides a production method of a zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy for hot dipping. The zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy for hot dipping is produced through a preparation process of a zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy and a dosing proportion control process of the zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy. Compared with the traditional zinc alloy for hot dipping, the zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy for hot dipping, provided by the invention, has the advantages that the corrosion resistance and adhesion of a coating are improved, and the manufacturing cost of the alloy is reduced. Meanwhile, due to the addition of the aluminum element, the zinc bath surface oxidation can be reduced, and the coating is thinned and brightened and has good adhesion; due to the addition of the magnesium element, the melting point of the alloy is reduced; due to the addition of the manganese element, the generation of zinc pot bottom slag is reduced, and the zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy better conforms to the requirements for energy conservation and environmental protection and can be widely applied to the fields such as modern buildings, decoration, traffic, home appliance and the like. The production method is suitable to be used as a method for producing a zinc-aluminum-manganese-magnesium alloy for hot dipping.
Owner:HULUDAO ZINC IND CO LTD
Zinc bath bottom slag cleaning device
InactiveCN1827830AReduce disturbanceReduce adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesMechanical apparatusSlagVacuum pump
The invention relates the hot galvanizing, especially the zinc pan slag removal device. The device comprises drafting slag part, vacuum case and vacuum pump. The drafting slag part comprises drafting slag pipe, express connector, slag-off pipe and cut-off valve. One end of slag-off pipe is connected with vacuum case, the other end of it is connected with drafting slag pipe through express connector, and drafting slag pipe extends in the bottom of zinc pan. The vacuum case comprises body and airtight cover, on the airtight cover there are three pore paths, one of which is connected with slag-off pipe, the second of which is connected with aspirator, the third of which is connected with vacuum pump, and the vacuum case body is connected with airtight cover by screw. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and installation, easy operation, high cleaning efficiency and low cost.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Galvanized bath for steel band galvanizing production line
The invention provides a galvanized bath for a steel band galvanizing production line. The galvanized bath comprises a zinc bath, water, a zinc block, an anode strip, a cathode strip, an anode pole and a cathode pole, wherein the zinc bath is an elongated pool made of cement; the anode strip and the cathode strip are arranged along the long outer side wall of the zinc bath in parallel; the anode strip and the cathode strip are insulated from the wall of the pool; the anode pole is supported on the anode strip and is bridged over the zinc bath; the zinc block is connected with the anode pole and then is soaked into water in the zinc bath; and the cathode pole is supported on the cathode strip and is bridged over the middle part of the zinc bath. By adoption of the galvanized bath, steel band products which are very long can be subjected to cold galvanization uninterruptedly with low cost, high efficiency and high quality.
Owner:江苏京生管业有限公司
Method of supplying Zn—Al alloy to molten zinc pot, method of adjusting concentration of Al in molten zinc bath, and apparatus for supplying Zn—Al alloy to molten zinc pot
ActiveUS9458530B2Improve productivitySpread evenlyHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsAlloyZinc bath
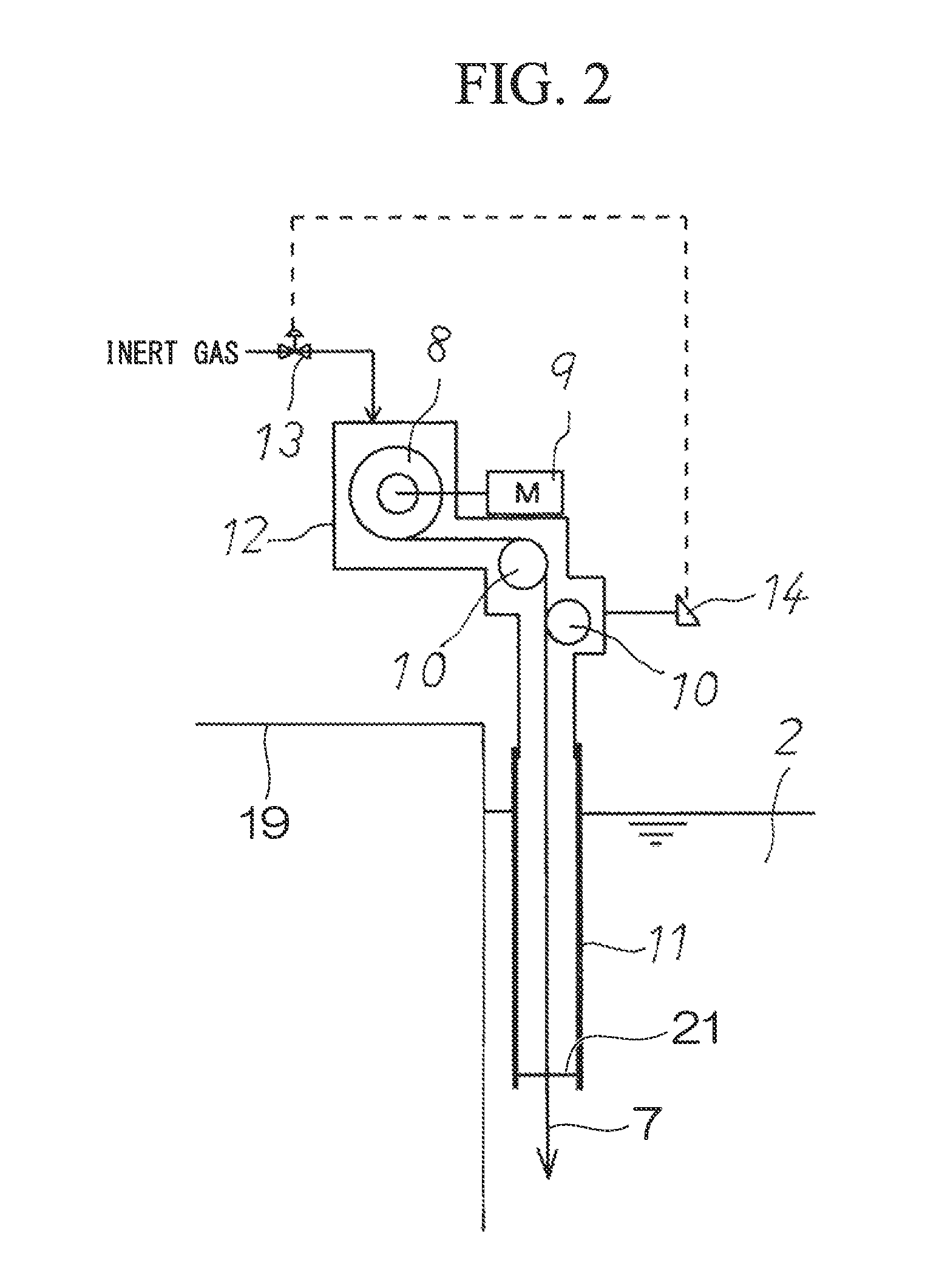
A method of supplying a Zn—Al alloy to a molten zinc pot which accommodates a molten zinc bath in a hot dip galvanizing line, includes: supplying the Zn—Al alloy from a supply portion provided at a lower portion of an insertion guide having a pipe shape, in which the supply portion is immersed between an inner wall of the molten zinc pot on a downstream side in a travelling direction of a steel sheet and a front support roll installed in the molten zinc bath at a depth within ±400 mm from a lower end of the front support roll, and an inside of the insertion guide is pressurized by inert gas to prevent the molten zinc bath from advancing to the inside of the insertion guide.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot dip galvanizing Al rare earth alloy for steel and iron member hot dip galvanizing and its ingot type and method
ActiveCN101086047AAvoid uneven compositionAvoid burnsHot-dipping/immersion processesSymmetrical earsRare earth
The invention relates to a zinc alloy for steel component galvanizing, the ingot shape and the method. The comprised component and weight proportion are as follows: 0.008%-0.012%(wt)Al,0.006%-0.01%(wt)RE, the rest is zinc and unavoidable impurities. The ingot shape is'T'cuboid with two symmetrical ear-warps, the bottom of cuboid is plane, ear-warps are equipped with hoisting holes, and the four sides are inclined plane which is narrow-end-up shape. It is characterized by direct fusion of said alloy to zinc bath, simple utilization, stable and homogeneous Al and rare earth content in zinc alloy, improved coating brightness and zinc flowability, decreased coating thickness, and saved zinc plating cost. The proper zinc alloy ingot shape and weight meets the demand of zinc addition for large-capacity galvanizing equipment, and it is convenient for hoisting and cross transportation, specific surface area is small, which is suitable for multi-layer stacking storage.
Owner:湖南株冶环保科技有限公司
Zinc-manganese-titanium alloy for hot dipping
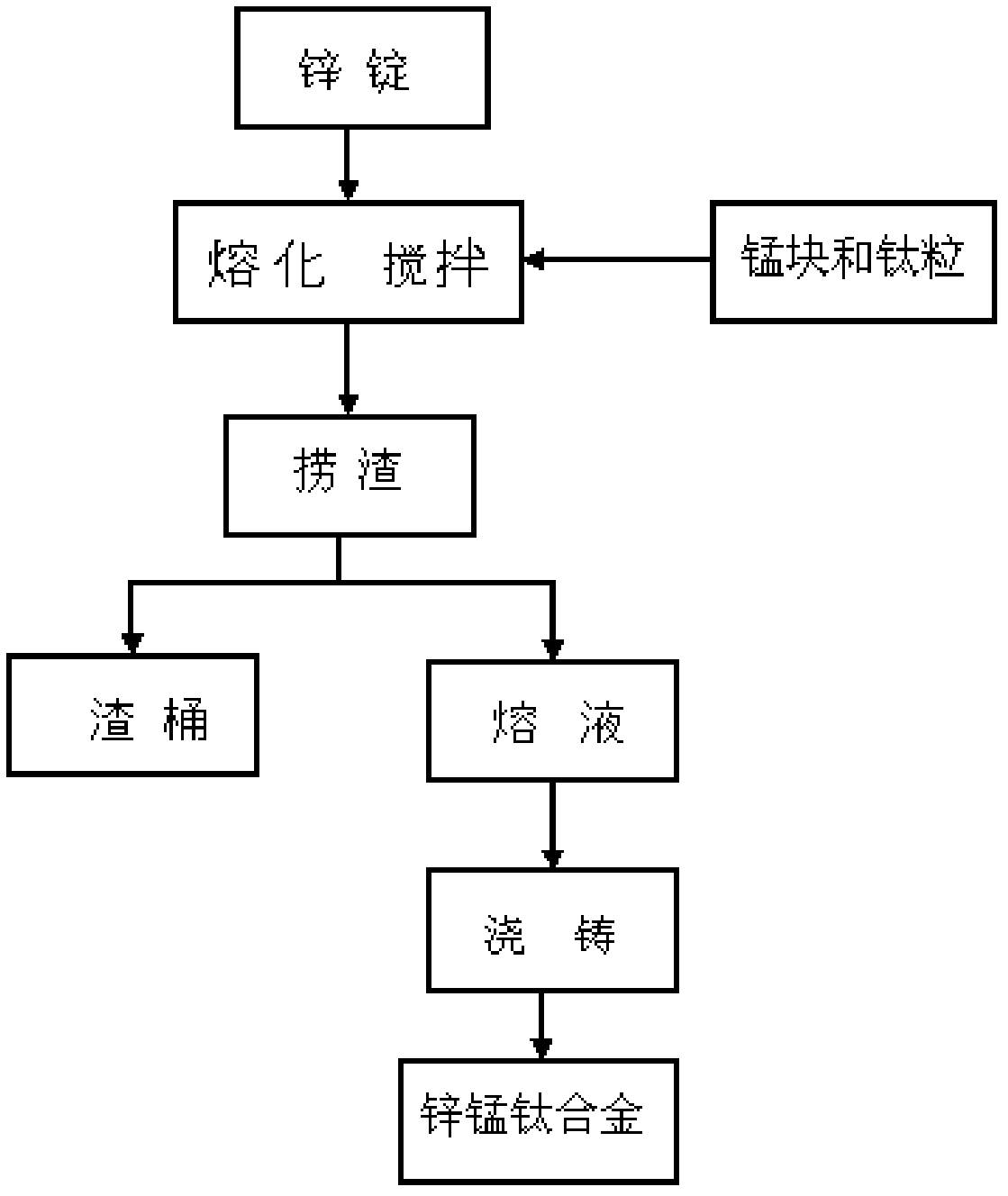
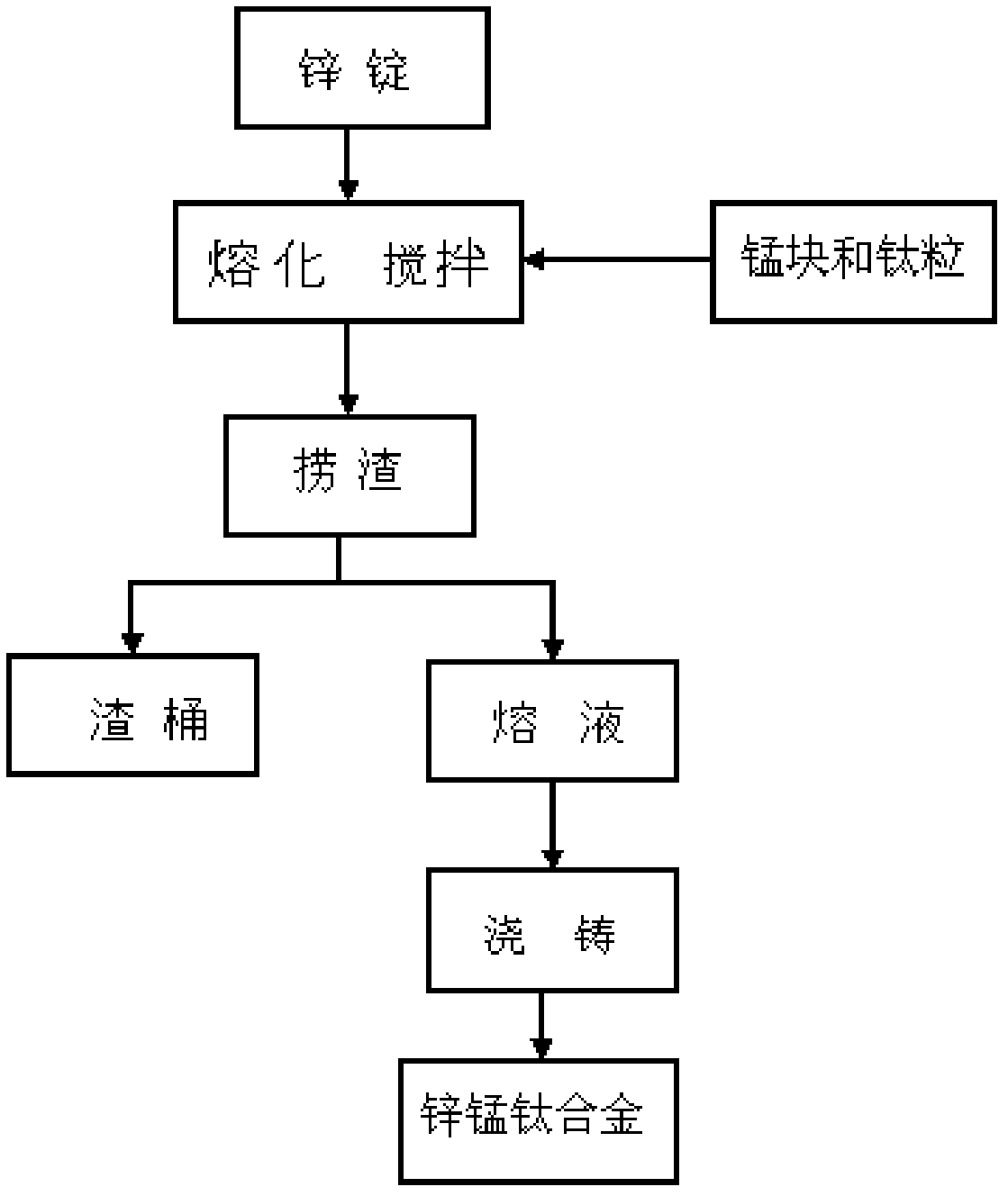
InactiveCN102492913ASimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costsHot-dipping/immersion processesManufacturing technologySlag
The invention relates to a zinc-manganese-titanium alloy for hot dipping. The zinc-manganese-titanium alloy contains the following components of: by weight, 0.5-2.5% of Mn, 0.3-1.5% of Ti and the balance being Zn. The zinc-manganese-titanium alloy is manufactured by the following steps of: heating for fusing, uniformly stirring, dredging slag, casting molding, and cooling at normal temperature to form the massive zinc-manganese-titanium alloy. The zinc-manganese-titanium alloy provided by the invention requires simple manufacturing technology and low manufacturing cost. With the addition of the zinc-manganese-titanium alloy in a zinc bath, fluidity of zinc alloy bath is good; workpiece surface has advantages of uniform thickness, no color difference, no Sandelin effect and no zinc knot; the coating thickness is reduced; corrosion resistance and mechanical property of the alloy coating are enhanced; hot-dipping time is shortened; production cost is reduced; and coating quality and production efficiency are raised.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CHUANGLIN ALLOY
Hot dipping zinc aluminum nickel bismuth rare earth alloy used for steel component hot dipping zinc and ingot case and method thereof
ActiveCN101109053AAvoid uneven compositionImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesRare earthZinc alloys
The invention relates to a zinc alloy used by steel structural component in zinc hot dip plating and the ingot shape and the method thereof. The alloy component and the weight per cent are of 0.008 per cent (wt) to 0.012 per cent (wt) Al, 0.04 per cent (wt) to 0.06 per cent (wt) Ni, 0.02 per cent (wt) to 0.08 per cent (wt) Bi, 0.006 per cent (wt) to 0.01 per cent (wt) RE, and zinc and impurity as the rest composition. The ingot shape is of T-shaped cuboid with two symmetrical ear curls; wherein, the bottom of the cuboid is a plane; the ear curls are provided with hoisting holes; the cuboid is of four included side planes, taking in a big top and small bottom shape. The zinc hot dip plating method is to melt the alloy directly into zinc bath; the application is simple; the zinc bath alloy elements Al, Bi, Ni and RE with stable and uniform content can alleviate or eliminate the Sandelin Effect generated by an active steel galvanization, perfect the wetting behavior and flow property of the iron matrix and the zinc bath, improve corrosion resistance performance and mechanical performance of the coating, reduce the thickness of the coating and lower the cost. With the appropriate shape as well as ingot weight, the zinc alloy ingot shape has the advantages of able to meet zinc adding requirement of the large capacity galvanization equipment, convenient hoisting and fork transport, small specific surface area, suitable for storage and multiple layers stacking tier, saving storing room, and stability as well as safety.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Hot dip coating aluminum zinc lead antimony alloy in use for zinc plating narrow steel strip, method and ingot mold
ActiveCN101092670ALower requirementReduce the amount of zincHot-dipping/immersion processesSurface finishIngot
This invention relates to a hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy, its hot-dip galvanization method and its ingot for narrow steel belt. The hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy comprises: Al 0.4-1.0 wt.%, Pb 0.003-0.1 wt.%, Sb 0.1-0.25 wt.%, and Zn and impurities as balance. The T-shaped ingot of the hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy is a trapezoid with two symmetric warped ears. The ears have lift-off holes. The hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy is directly smelted into a zinc bath. The hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy can improve the fluidity of the zinc bath, decrease the residue rate, and increase the smoothness of the galvanization layer. The hot-galvanized Al-Pb-Sb alloy is used for galvanizing on a narrow steel belt.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Hot dip galvanizing Al Bi rare earth alloy for steel and iron member hot dip galvanizing and its ingot type and method
PendingCN101086048AAvoid uneven compositionAvoid burnsHot-dipping/immersion processesSymmetrical earsRare earth
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Method for hot dipping of composite zinc coating on surface of steel and steel coating composite material
PendingCN112281100AIncreasing the thicknessImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesAlloyCorrosion resistant
The invention discloses a method for hot dipping of a composite zinc coating on the surface of steel and a steel coating composite material, and relates to the field of corrosion protection. The method for hot dipping of the composite zinc coating on the surface of the steel comprises the steps that primary dip plating is carried out on the steel in a zinc bath, and then secondary dip plating is carried out in an alloy bath with a melting point lower than the melting point of pure zinc; and the alloy bath contains zinc and aluminum elements, and a mixed melting point of the alloy bath is lowerthan the melting point of the pure zinc. According to the method for hot dipping of the composite zinc coating on the surface of the steel and the steel coating composite material, primary dip plating is creatively carried out in the zinc bath and then secondary dip plating is carried out in the alloy bath with the melting point lower than the melting point of the pure zinc, the secondary dip plating is equivalent to replacement of other elements except zinc in the alloy bath to form a pure zinc plating layer, a plating layer material with larger thickness and high corrosion resistance can beobtained, and the method is suitable for batch hot dipping of steel surfaces.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MATERIALS & PROCESSING
Zinc-aluminum-magnesium intermediate alloy capable of supplementing lost magnesium element in zinc bath and method thereof
PendingCN109763030AFast dissolutionDissolve evenlyHot-dipping/immersion processesMolten bathZinc alloys
The invention relates to zinc-aluminum-magnesium intermediate alloy capable of supplementing the lost magnesium element in a zinc-6Al-3Mg alloy liquid bath and a method thereof. According to the technical scheme, the zinc-aluminum-magnesium intermediate alloy comprises, by weight, 6wt.% of Al, 4.0-8.0 wt.% of Mg and the balance Zn. The method for supplementing the lost magnesium element in the zinc-6Al-3Mg alloy liquid bath comprises the steps that, granular Zn-6wt.Al-(4.0-8.0)wt.%Mg intermediate alloy accounting for 1.0-2.0wt.% of zinc alloy liquid is added into a zinc-6Al-3Mg alloy molten bath, and the magnesium element in the zinc-6Al-3Mg alloy bath is continuously supplemented. According to the zinc-aluminum-magnesium intermediate alloy and a method thereof, the effect of stabilizing the magnesium content of the zinc-aluminum-magnesium galvanization alloy molten bath is achieved, and the magnesium element supplementing method is simple and reliable.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
On-line automatic pretreatment process for steel pipe hot-dip galvanizing
ActiveCN104195485AEmission reductionReduce energy consumptionHot-dipping/immersion processesRare earthEnergy consumption
The invention relates to an on-line automatic pretreatment process for steel pipe hot-dip galvanizing. The process includes following steps performed on line in order: degreasing, rinsing, washing with an acid to remove rust, rinsing, performing plating assistant treatment and drying. The step of degreasing and the step of washing with the acid to remove the rust are performed at a condition lower than 40 DEG C, thus reducing energy consumption and significantly reducing discharge of acid mist and alkali mist. By adoption of the process, under the conditions of not adding a rare earth plating assistant and not adding rare earth into a zinc bath, hot-dip galvanizing of zinc-aluminum alloys can be achieved, the plating thickness of the zinc-aluminum alloy is uniform, and defects such as skip plating are avoided.
Owner:DANYANG TENGHUANG PIPE GALVANIZATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com