A dual-edge plane three-phase linear permanent magnetic synchronization motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, flat plate technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult design, complex winding insulation, high manufacturing cost, easy insulation process, reduced production cost, and high manufacturing cost. simple craftsmanship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
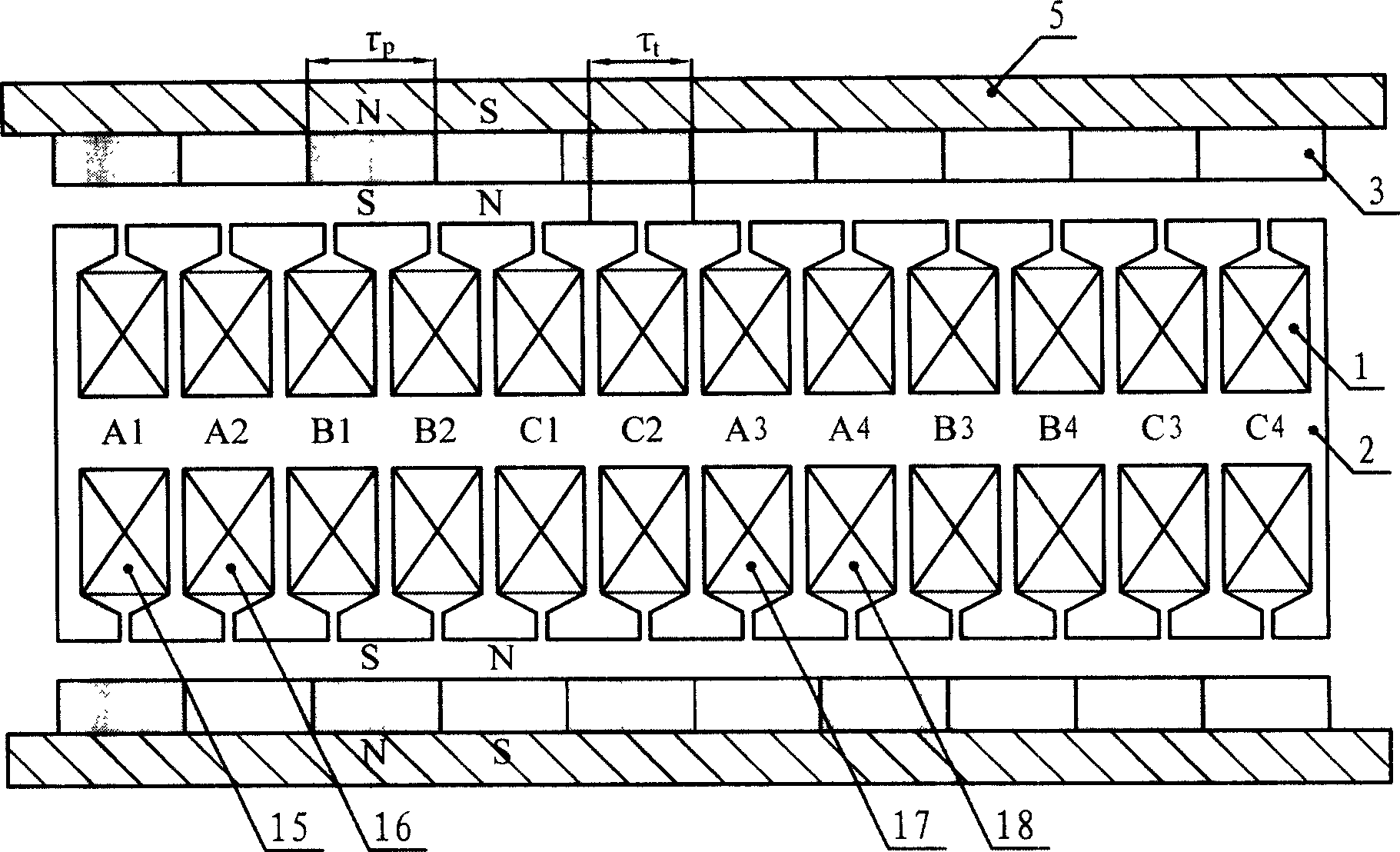
[0012] Specific implementation mode 1: see figure 1 This embodiment will be described. A bilateral flat three-phase linear permanent magnet synchronous motor in this embodiment is composed of a casing 5, an armature part and a permanent magnet excitation part, the casing 5 is made of a magnetically conductive material, and the permanent magnet excitation The component is composed of two groups of flat-shaped permanent magnets 3. The number of poles formed by the permanent magnets 3 is P=2k. The magnetization directions of the permanent magnets at the corresponding positions of the magnets 3 are opposite, that is, the polarities of the directions facing the armature components are the same, and the magnetization directions of the adjacent permanent magnets 3 in the same group of permanent magnets are opposite. The winding 1 and the armature iron core 2 are formed. The armature iron core 2 is fixed in the middle of the two flat plate-shaped permanent magnets 3 and has an air g...
specific Embodiment approach 2
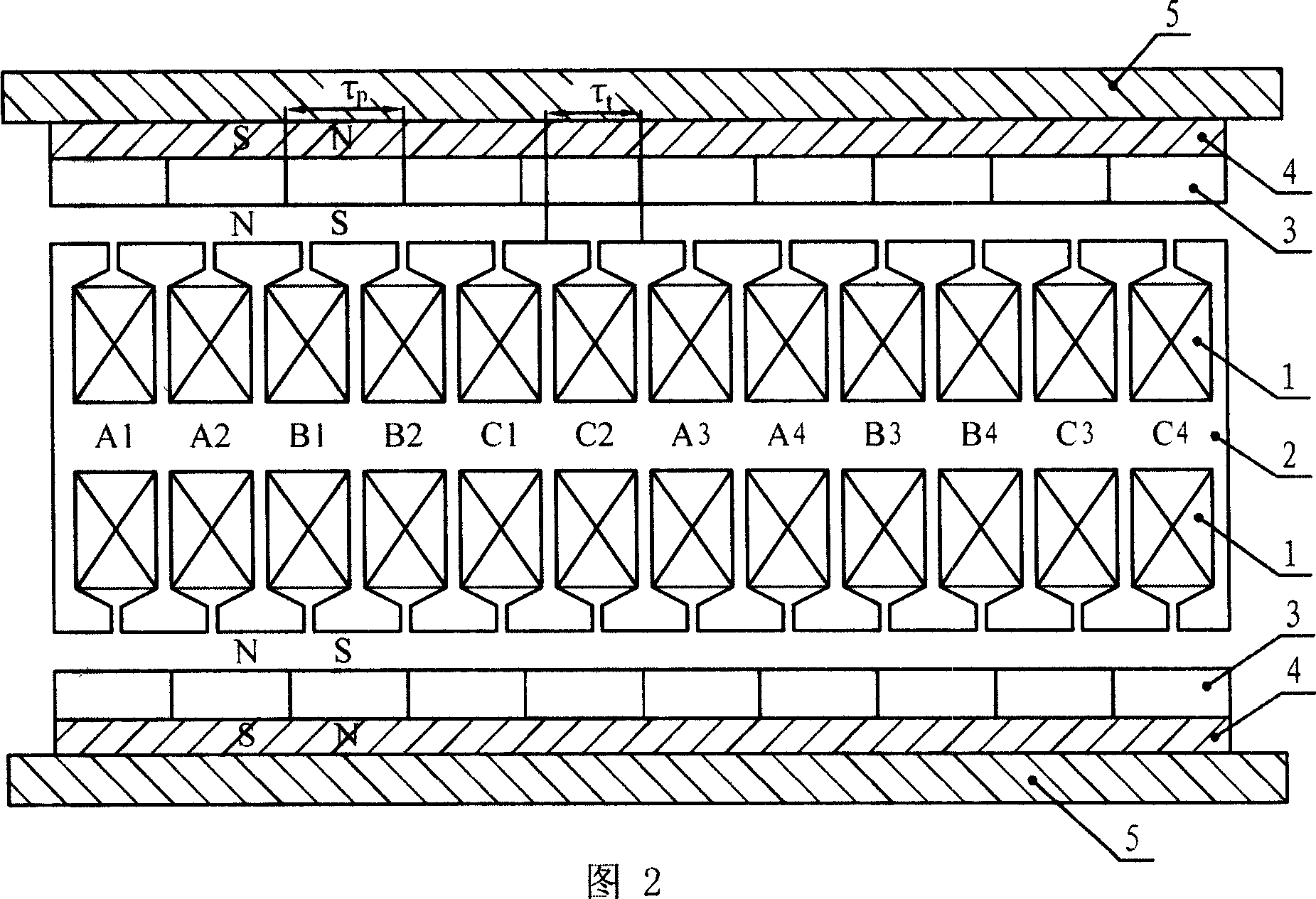
[0014] Specific implementation two: see figure 2 This embodiment will be described. The difference between this embodiment and the one-sided flat-phase three-phase linear permanent magnet synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1 is that the permanent magnet excitation component further includes a flat-plate permanent magnet yoke 4, and the permanent magnet yoke 4 is fixed between the permanent magnet 3 and the casing 5, and the casing 5 in this embodiment may be made of non-magnetic conductive material.
specific Embodiment approach 3
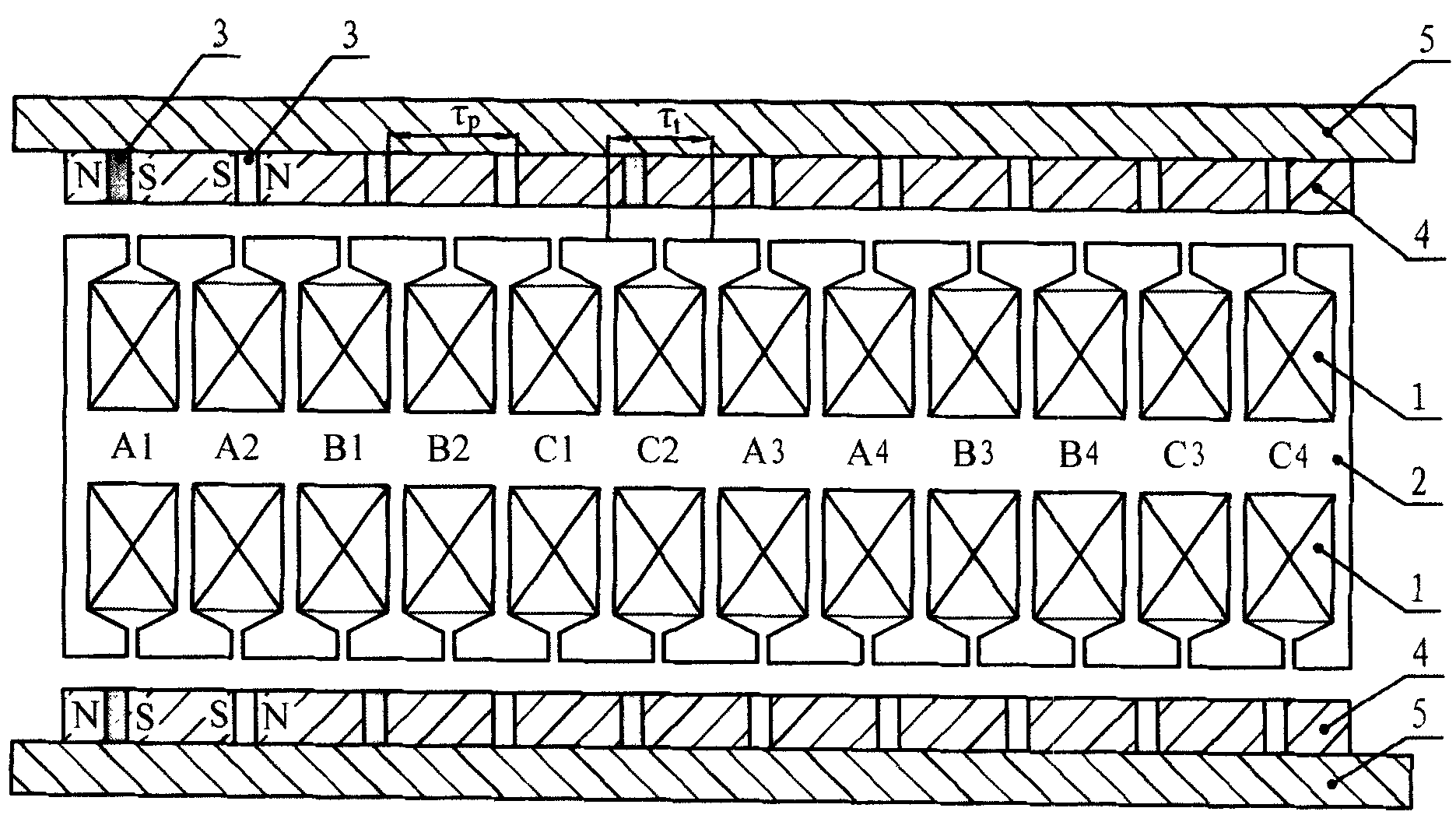
[0015] Specific implementation mode three: see image 3 , Figure 4 This embodiment will be described. The difference between this embodiment and the two-sided flat-phase three-phase linear permanent magnet synchronous motor described in the second embodiment is that the permanent magnets 3 are embedded in the permanent magnet yoke 4 and are arranged at intervals from the permanent magnet yoke, so The permanent magnets 3 are magnetized in parallel, the magnetization direction is parallel to the movement direction, the magnetization directions of the adjacent permanent magnets 3 are opposite, and the magnetization directions of the permanent magnets at the corresponding positions of the two groups of permanent magnets 3 on the bilateral casing 5 are respectively fixed. same.
[0016] When the casing 5 of the bilateral flat motor in this embodiment is made of magnetically conductive material, a layer of magnetic isolation plate 6 is added between the casing 5 and the permanent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com