Motor drive method
A driving method and motor technology, applied in the direction of electronically commutated motor control, single motor speed/torque control, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of areas where the rotor position cannot be detected, reverse rotation or deviation from the same step, and failure to start. To achieve good quality, shorten the period, improve the effect of starting speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
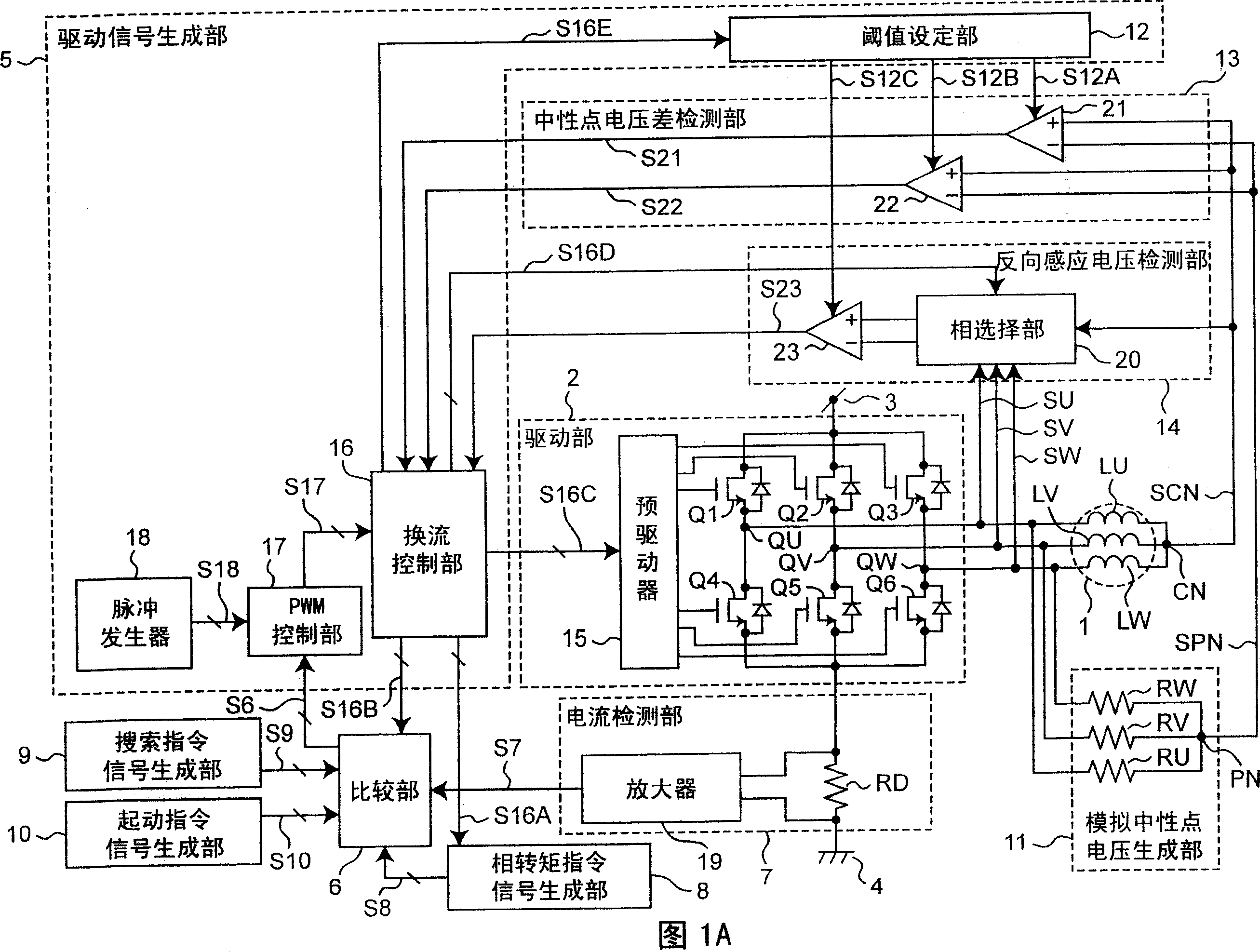
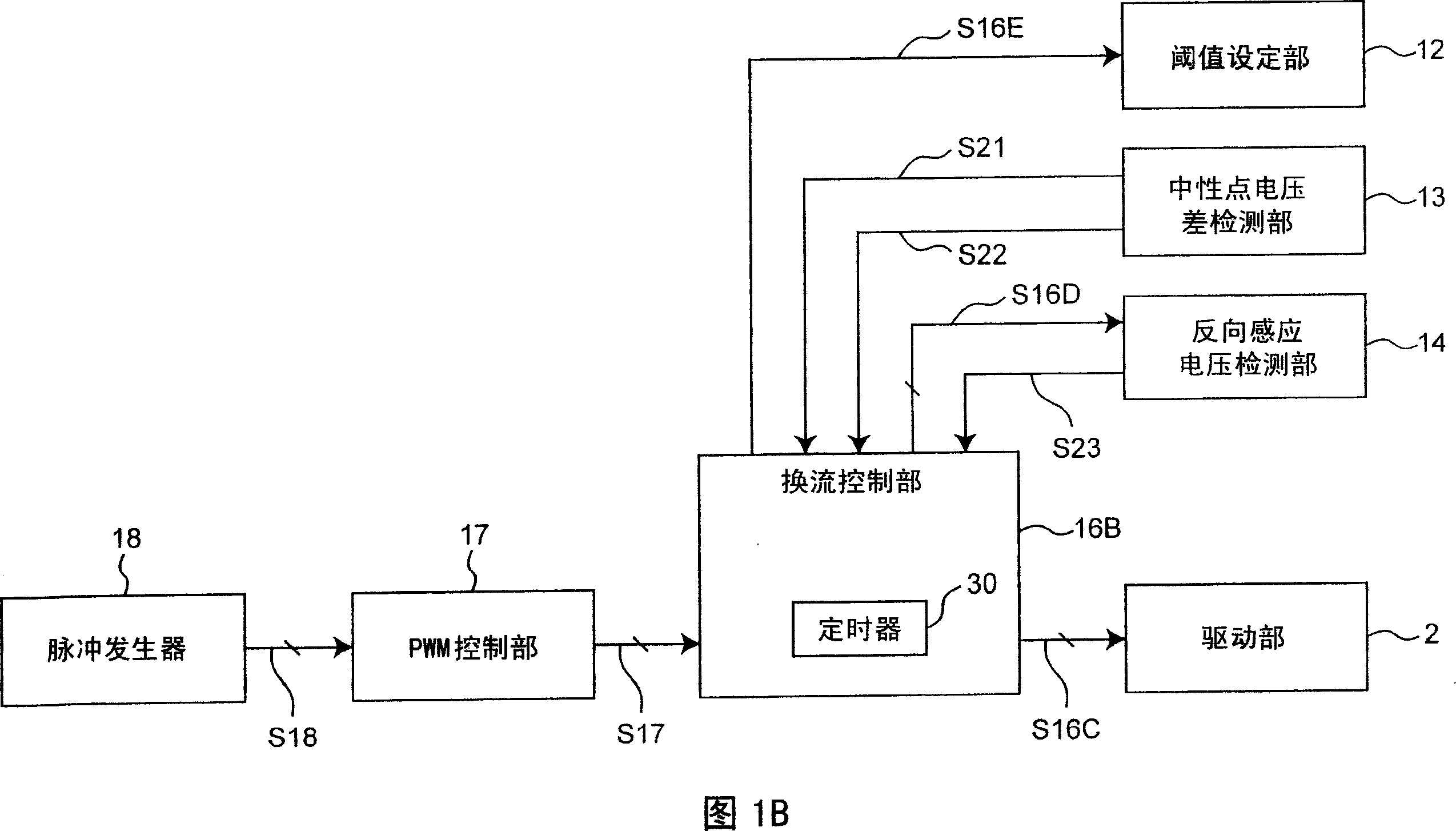
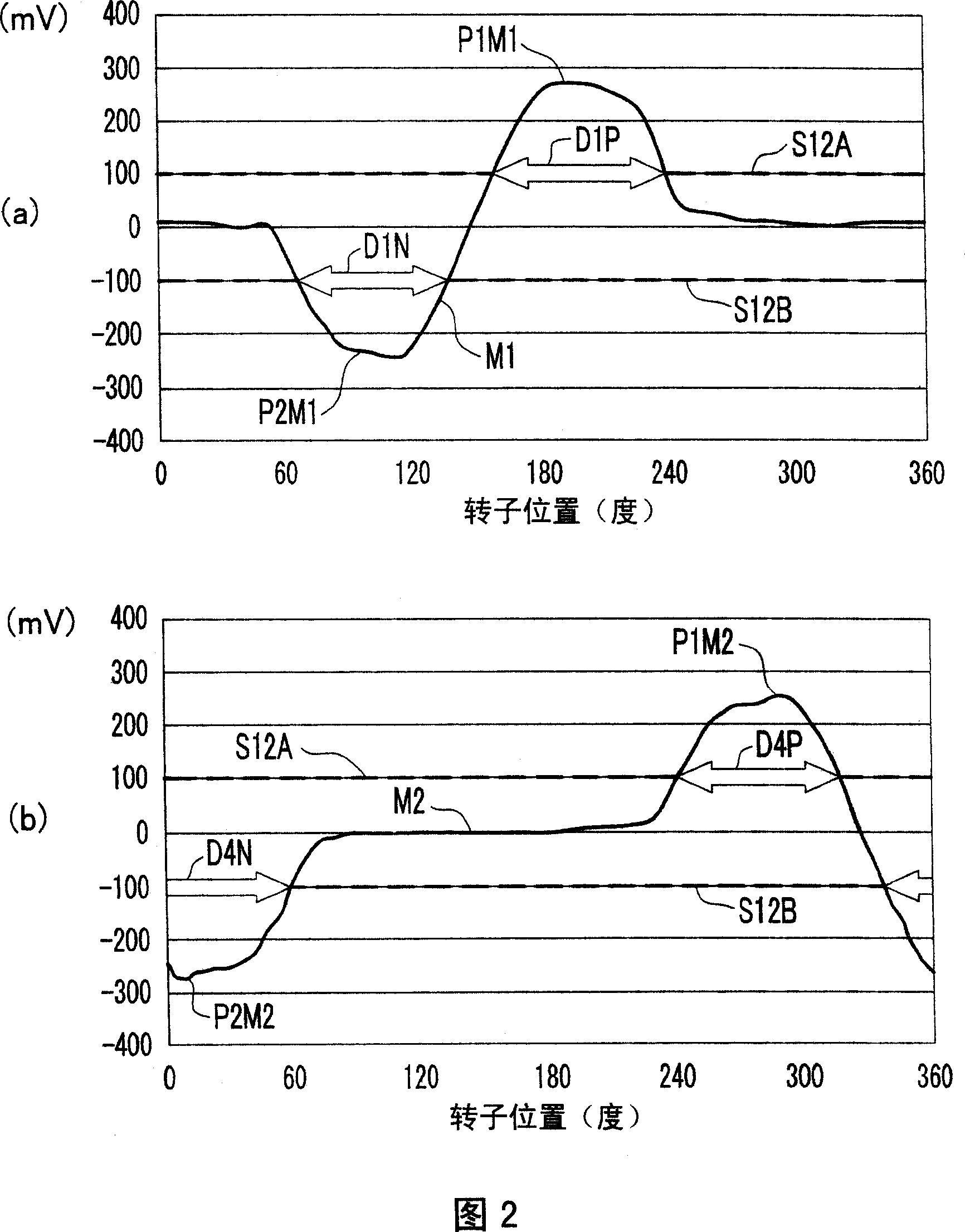
[0066] FIG. 1A shows a circuit configuration in a first embodiment of a motor drive device according to the present invention. In FIG. 1A , the motor drive device includes a motor 1, a drive unit 2, a drive signal generation unit 5, a comparison unit 6, a current detection unit 7, a phase torque command signal generation unit 8, a search command signal generation unit 9, a start command signal A generation unit 10 , an analog neutral point voltage generation unit 11 , a neutral point voltage difference detection unit 13 , and a reverse induced voltage detection unit 14 .
[0067] The motor 1 includes a three-phase stationary stator and a rotor rotating around the stator. In the first embodiment, the three-phase motor 1 is used as the motor, but the present invention can be applied to an N-phase motor by setting N to an integer greater than or equal to 2. The U-phase motor coil LU, V-phase motor coil LV, and W-phase motor coil LW wound in the stator are connected in common thr...
no. 2 approach
[0403] In the first embodiment, the case of two-phase energization has been described. In the second embodiment, the case of three-phase energization will be described focusing on points different from the first embodiment described above. Other configurations, actions, and effects are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0404] FIG. 20 shows a circuit configuration of a second embodiment of the motor drive device according to the present invention. In FIG. 20 , the motor drive device includes a motor 1, a drive unit 2, a drive signal generation unit 5, a comparison unit 6, a current detection unit 7, a phase torque command signal generation unit 8, a search command signal generation unit 9, a start command signal Generating unit 10 , analog neutral point voltage generating unit 11 , neutral point voltage difference detecting unit 13A, and reverse induced voltage detecting unit 14A.
[0405] The motor 1 includes a three-phase fixed stator and a rotor rotating around ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com