Image encoding apparatus, image decoding apparatus and control method therefor
An image encoding and encoding technology, which is applied in image encoding, image communication, image data processing, etc., can solve the problem of K parameter becoming larger and achieve good compression performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
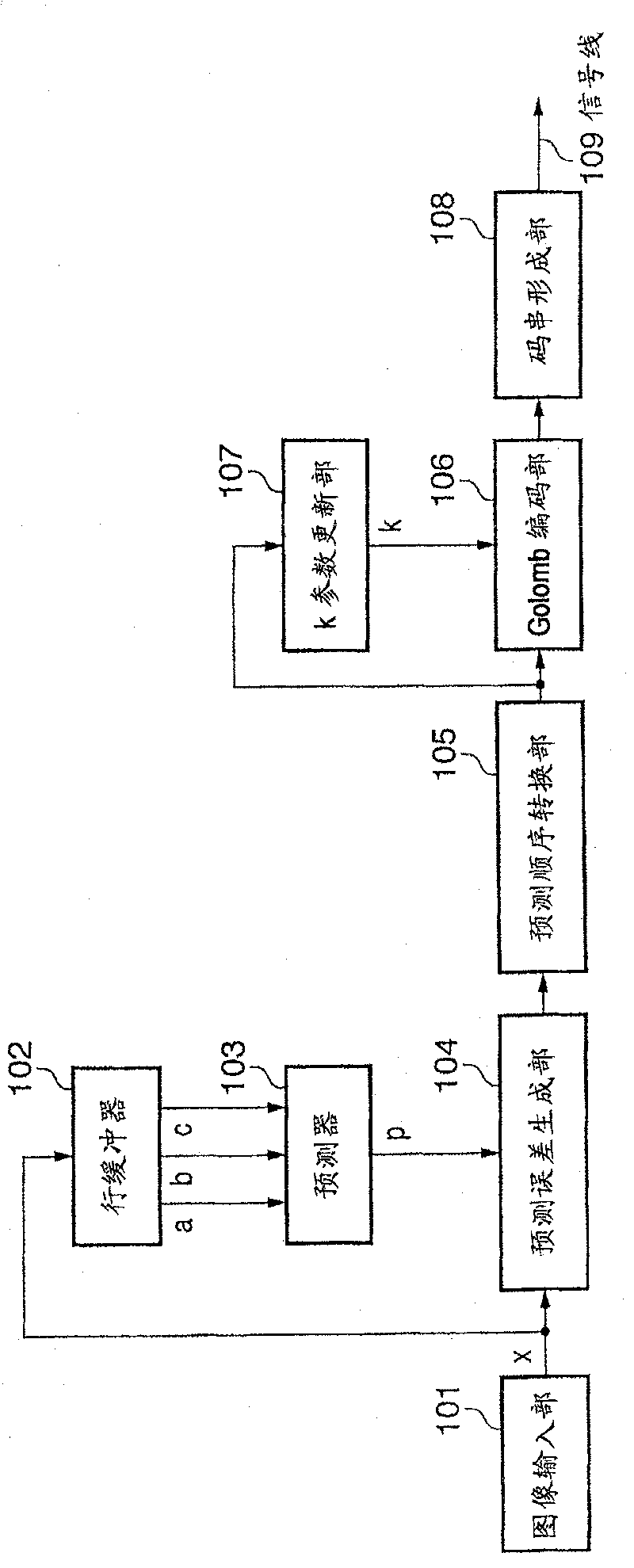
[0060] figure 1 is a block configuration diagram showing the functional configuration of the image processing device according to the present embodiment.
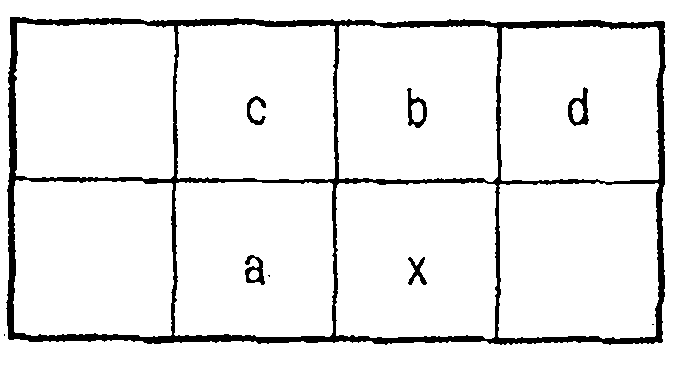
[0061] Such as figure 1 As shown, the image processing device for image coding according to this embodiment includes: an image input unit 101, a line buffer (line buffer) 102, a predictor 103, a prediction error generation unit 104, a prediction order conversion unit 105, a Golomb encoding part 106, k parameter update part 107 and code string forming part 108. exist figure 1 109 represents a signal line.
[0062] Below, refer to figure 1 Image coding processing performed by the image processing device according to this embodiment will be described. Here, the encoding target image is taken as monochrome image data in which each pixel is composed of 8-bit (range of 0 to 255) pixel data representing a luminance value or a density value. However, this method can be similarly applied to color images represented by mult...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0132] Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the image processing device according to the first embodiment, correction is performed by increasing or decreasing the coding parameter k every time the code to be coded is outside the optimum code range. In such a case, there is an advantage of being able to respond quickly to changes in the statistical properties of the information source, but stability will be a problem in information sources whose properties change little.
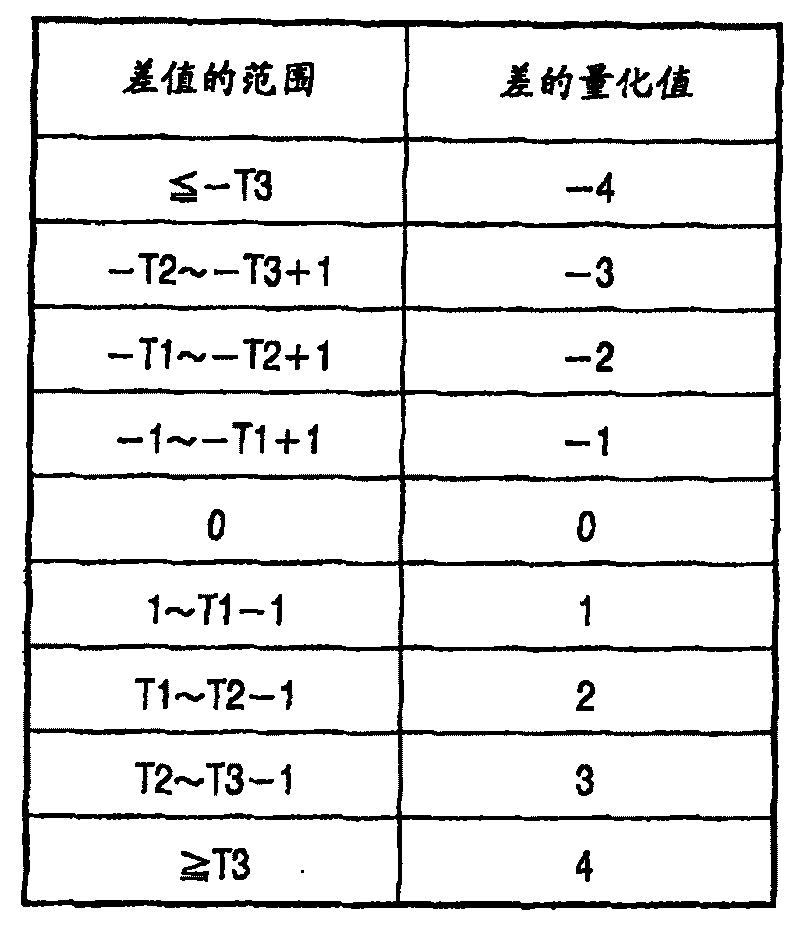
[0133] For example, consider the probability distribution f(n, k)=(1 / 2)^L(n, k) with the maximum coding efficiency among the respective k parameters. L(n, k) is the code length when Golomb encoding is performed on the coding object symbol n with the coding parameter k, and is given by L(n, k)=k+1+floor(n / (2^k)). x^y means x raised to the power of y, and floor(x) means a function that returns the largest integer not exceeding x.
[0134] Figure 7 Indicates the probability distribution f(n, 1) wh...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0170] In the above-mentioned second embodiment, the method of reducing the k parameter when the symbol of the region 51 is generated twice is shown, but the number of occurrences to be updated may be changed according to the k parameter. An example of this will be described as a third embodiment.
[0171] The block diagram of the image processing device according to the third embodiment is different from that described in the second embodiment. Figure 10 The same, only the processing of the k parameter update unit 1002 is different. Hereinafter, the processing of the k-parameter update unit 1002 in the third embodiment will be described.
[0172] The k parameter update unit 1002 of the third embodiment holds Figure 12 The shown correspondence table of index value i and parameter k, and array I[S] storing index value i for 365 state numbers S classified by the context generation unit 1001 . All elements of the array I[S] are set to an initial value (here, 4) at the time o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com