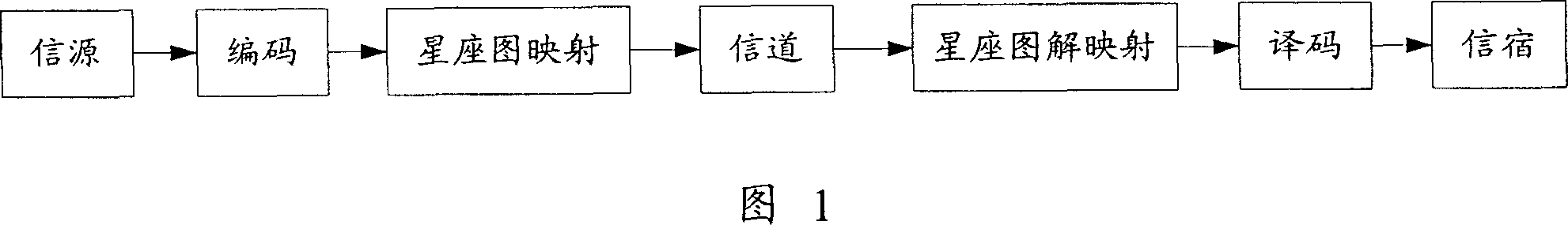
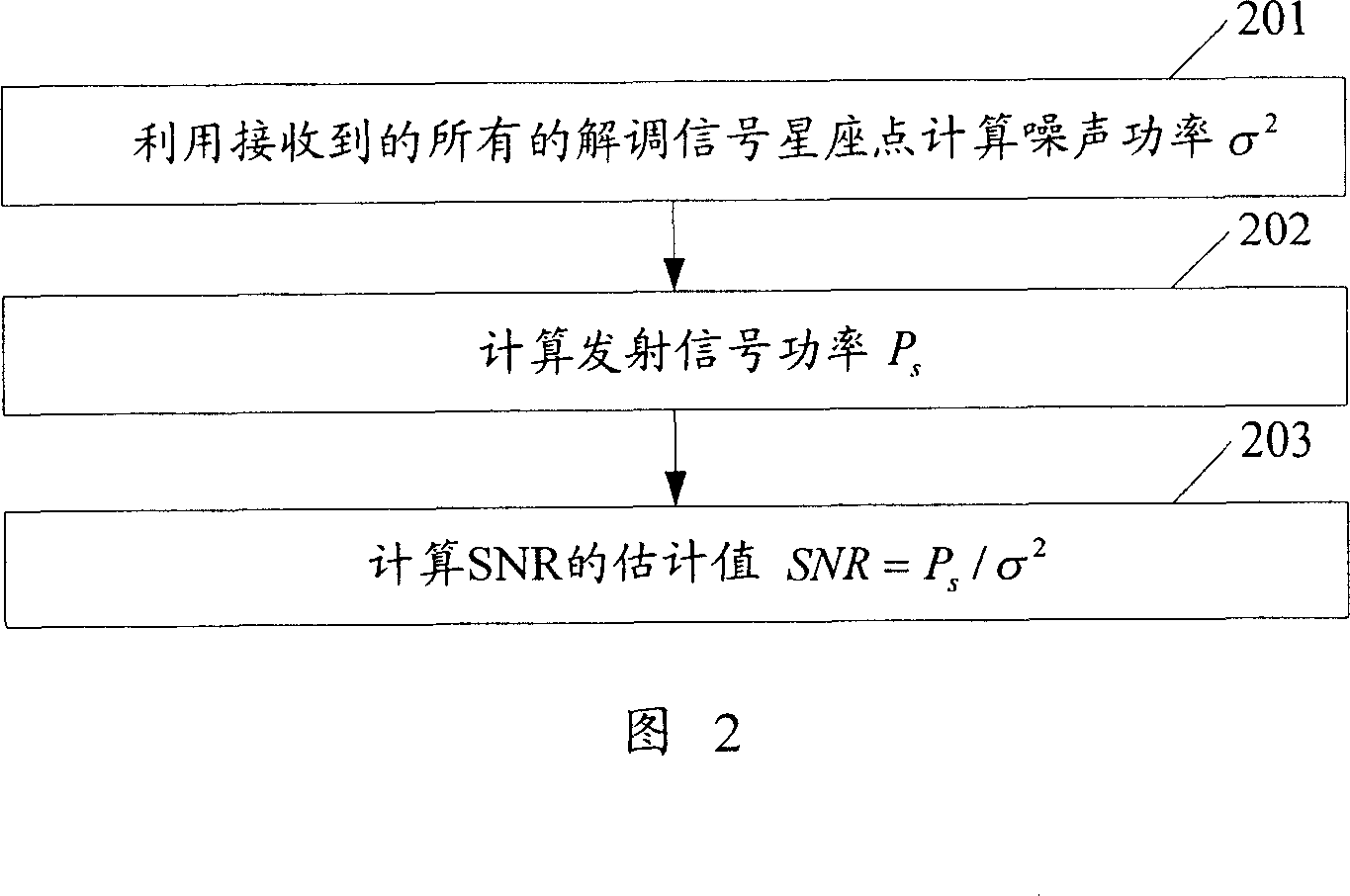
Method and device for estimating signal noise ratio
A technology for signal-to-noise ratio and demodulation signal, applied in the field of estimating signal-to-noise ratio, can solve the problems of noise power calculation error, large estimation error between SNR estimated value and actual value, and easy overlapping of demodulated signal constellation points. Achieve the effect of avoiding noise power error, avoiding error and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Embodiment 1: SNR estimation in the case of AWGN channel QPSK modulation
[0068] In this embodiment, when estimating the SNR, it is not considered that the absolute value of the in-phase component in the constellation point of the QPSK demodulated signal is smaller than the absolute value of the in-phase component of the edge constellation point of the QPSK modulated signal, and the absolute value of the quadrature component is smaller than the positive value of the edge constellation point of the QPSK modulated signal. Constellation point of the absolute value of the quadrature component, only considering that the absolute value of the in-phase component in the constellation point of the QPSK demodulated signal is greater than the absolute value of the in-phase component of the edge constellation point of the QPSK modulated signal or the absolute value of the quadrature component is greater than the quadrature component of the edge constellation point of the QPSK modula...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: SNR estimation in the case of AWGN channel 16QAM modulation
[0083] In this embodiment, when estimating the SNR, it is not considered that the absolute value of the in-phase component in the constellation point of the 16QAM demodulated signal is less than the maximum absolute value of the in-phase component at the edge constellation point of the 16QAM modulated signal, and the absolute value of the quadrature component is less than the edge constellation of the 16QAM modulated signal The constellation point of the maximum absolute value of the quadrature component, only consider the absolute value of the in-phase component in the constellation point of the 16QAM demodulated signal greater than the edge of the 16QAM modulated signal The constellation point of the part of the 16QAM demodulated signal with the maximum absolute value of the quadrature component of the constellation point. Wherein, the edge constellation point of the 16QAM modulated signal is ...
Embodiment 3
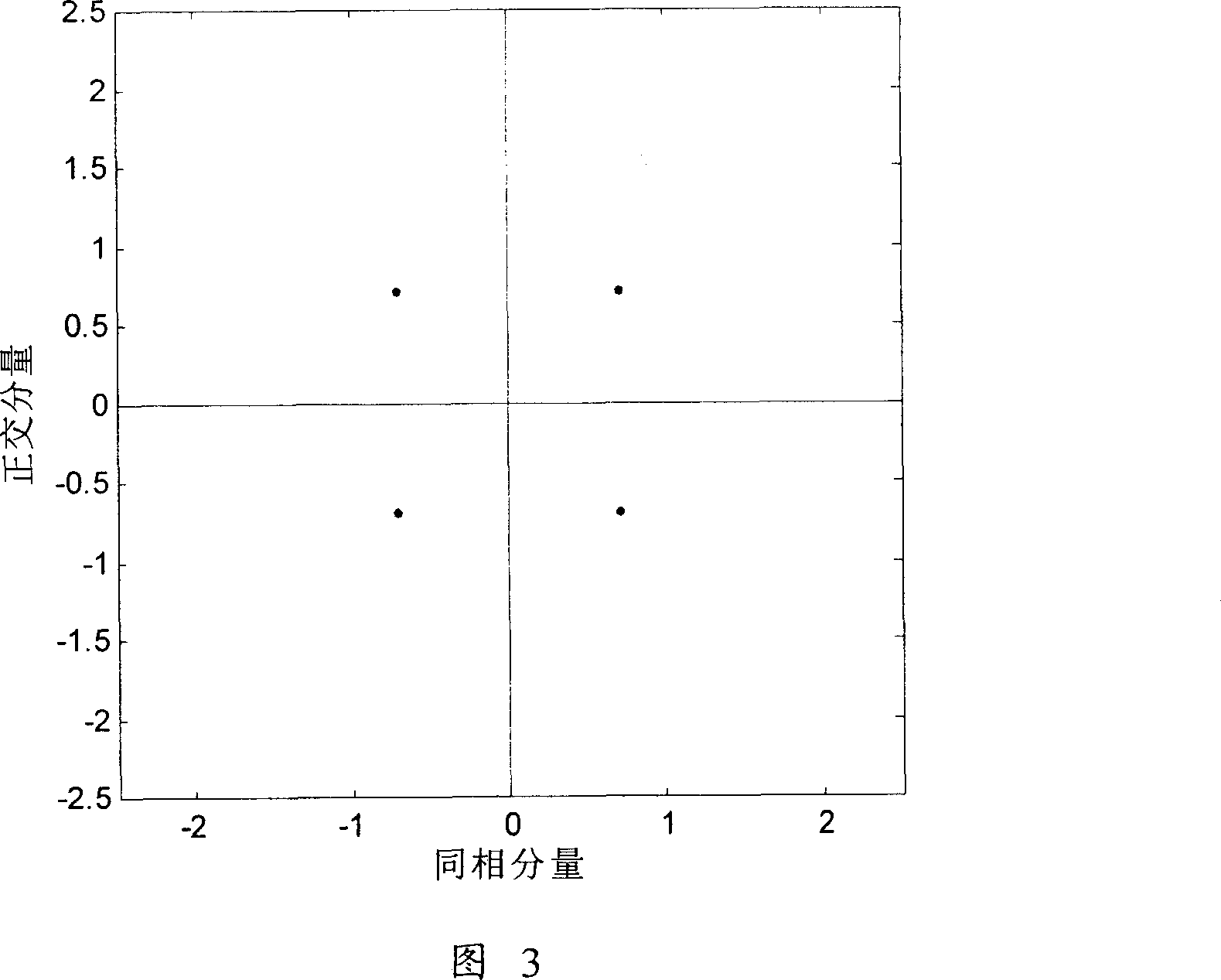
[0101] Embodiment 3: SNR estimation in the case of Rayleigh channel QPSK modulation
[0102] Fig. 5 shows the constellation points obtained by performing channel estimation and equalization on the received signal after receiving the QPSK modulated signal through the Rayleigh channel at the receiving end. It can be seen from Fig. 5 that due to the inaccuracy of equalization, the amplitude of some received constellation points changes greatly, and these constellation points with large amplitude changes have a greater impact on the estimation of SNR. Therefore, in this embodiment, the above-mentioned The method of multiplying the noise power by the probability factor reduces the SNR estimation error.
[0103] In this embodiment, it is also considered that the absolute value of the in-phase component in the constellation point of the QPSK demodulated signal is smaller than the absolute value of the in-phase component at the edge constellation point of the QPSK modulated signal, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com