Semiconductor heterostructure
A heterostructure and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of reducing carrier efficiency and carrier non-resonance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
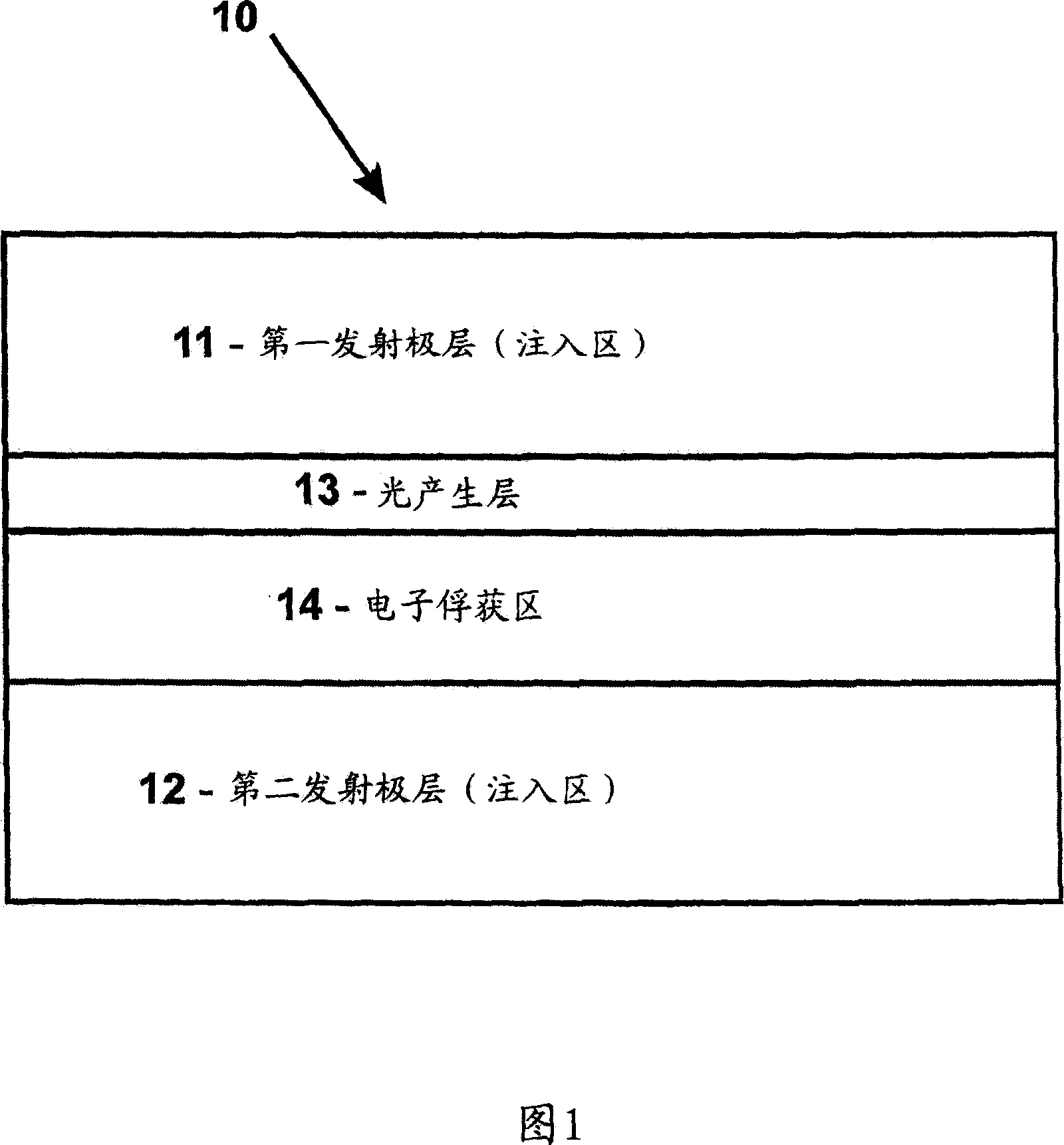
[0046] In FIG. 1 , a schematic diagram of a cross-section of a semiconductor heterostructure is shown. The heterostructure, generally indicated at 10, includes an injection region consisting of a first emitter layer 11 and a second emitter layer 12, a light generating layer 13, and an electron trapping region 14 consisting of a trapping layer and a confinement layer.
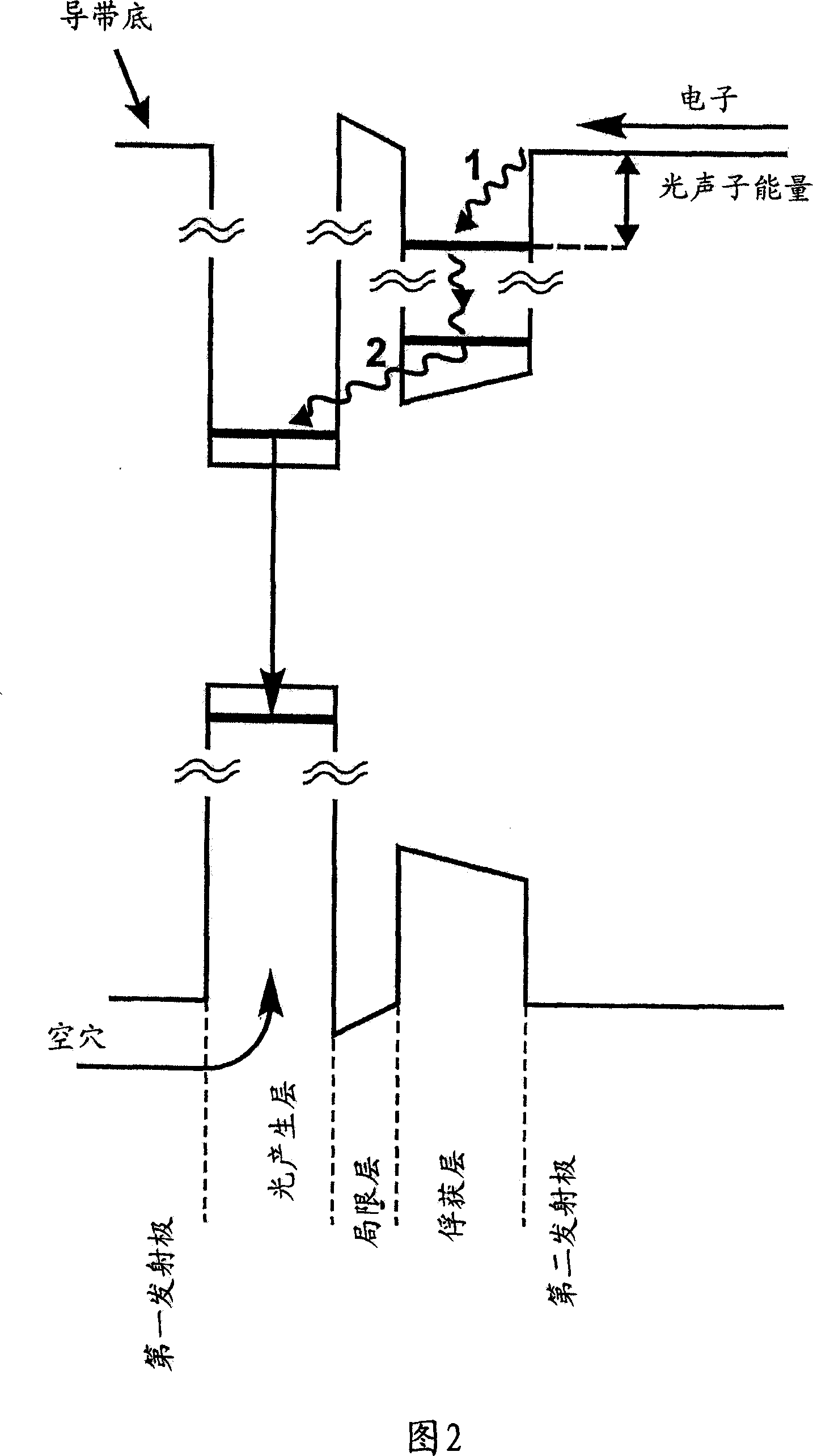
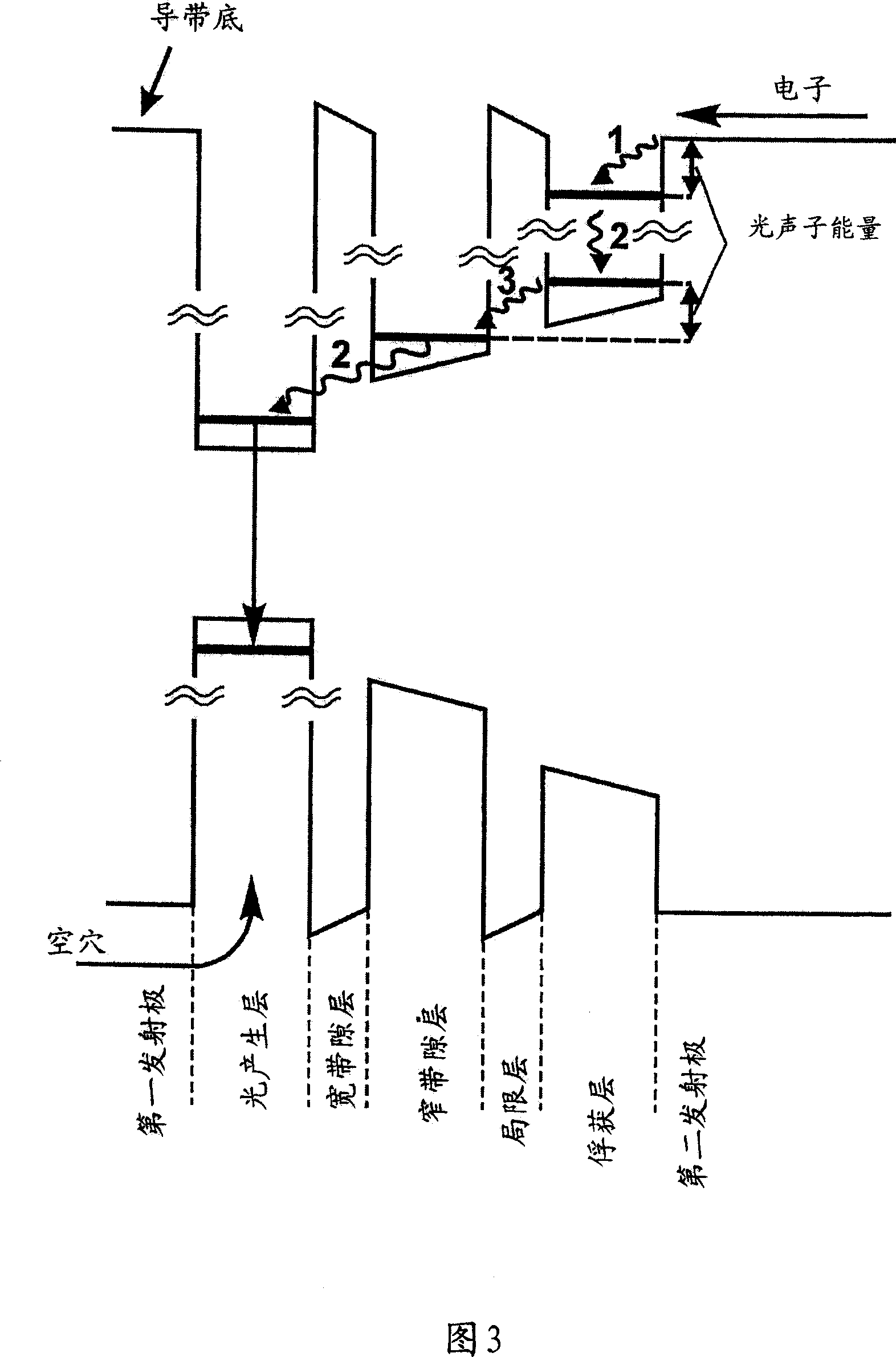
[0047] FIG. 2 depicts a schematic energy band diagram of the heterostructure shown in FIG. 1 . The trapping region is the narrow bandgap layer adjacent to the second emitter layer. A layer with a wide bandgap between the trapping layer and the light generating layer is a confinement layer. The width and composition of the trapping and confinement layers are adjusted so that the energy difference between one of the localized electronic levels of the trapping layer and the bottom of the conduction band in the electron emitter is equal to the photophonon energy. Electron trapping into the narrow bandgap trapping ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electron concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com