Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
A general-sequence, highly advanced technology that can be used in the determination/examination of microorganisms, resistance to vector-borne diseases, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. It can solve the problems of analyte cross-reactions that are difficult to overcome and eliminate, and reduce the effectiveness of multiple bDNA analysis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] The practice of the present invention may employ, unless indicated to the contrary, conventional techniques of synthetic organic chemistry, biochemistry, molecular biology and the like, as known in the art. These techniques are fully described in the literature, see Sambrook, et al., MOLECULAR CLONING: A LABORATORY MANUAL, 2nd edition (1989); OLIGONUCLEOTIDE SYNTHESIS (M.J.Gait, ed., 1984); THE PRACTICE OF PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS (M.Bodanszky and A .Bodanszky, 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1994); NUCLEIC ACID HYBRIDIZATION (B.D. Haines & S.J. Higgins, eds., 1984); and METHODS IN ENZYMOLOGY (Academic Press, Inc.).
[0087] In the following examples, it is to be understood that while efforts have been made to ensure accuracy of experimental parameters (eg, amounts, temperature, etc.), some experimental errors and deviations should be accounted for in repeating the experiments described below. Unless indicated to the contrary, temperature values are in degrees Celsiu...
Embodiment 2
Generation of Best Orthogonal Utility Sequence
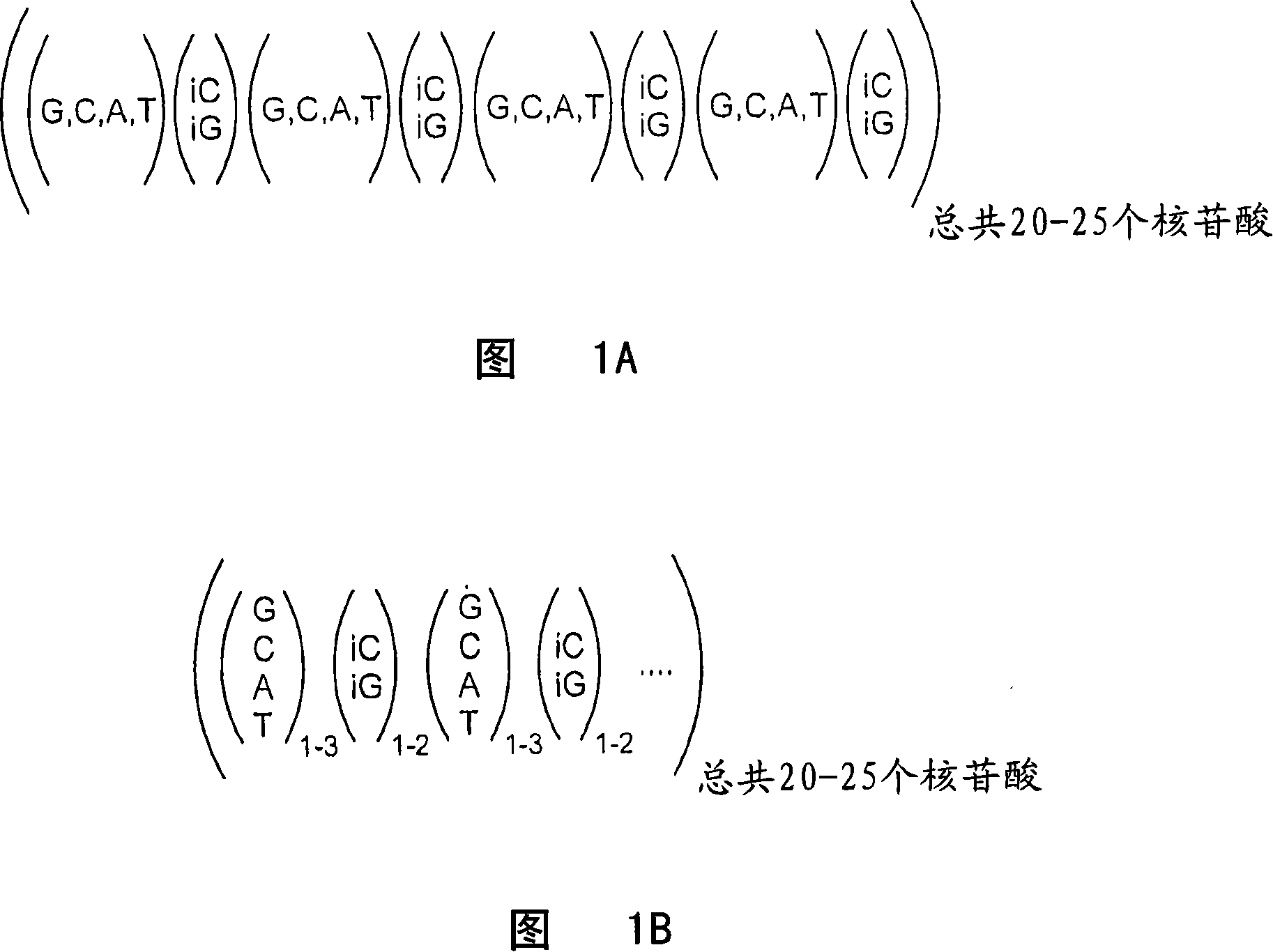
[0094] Multiple optimal CPs were designed from a 20-mer sequence containing a hexabase codon consisting of four natural bases and two unnatural bases, iso-G and iso-C. Figure 1A shows the general structure of the starting 20-mer sequence of the present invention, which consists of four natural bases in no particular order separated by an iso-G or iso-C base. To generate probes from the starting 20-mer sequence, the starting sequence was screened by the method described in Example 1 with the aim of generating 33 CPs and 33 CEs. The resulting sequences were used to design a six-plex cytokine analysis panel. Since the probes showed some cross-reactivity in cytokine assays, the probes were further optimized for minimal cross-reactivity by limiting the melting temperature of the probes to about 85°C. The optimal set of probes resulting from screening and testing is described by the formula in FIG. 1B and shown in Table 1. When the...
Embodiment 3
Specificity of Multiplexed Cytokine mRNA Analysis
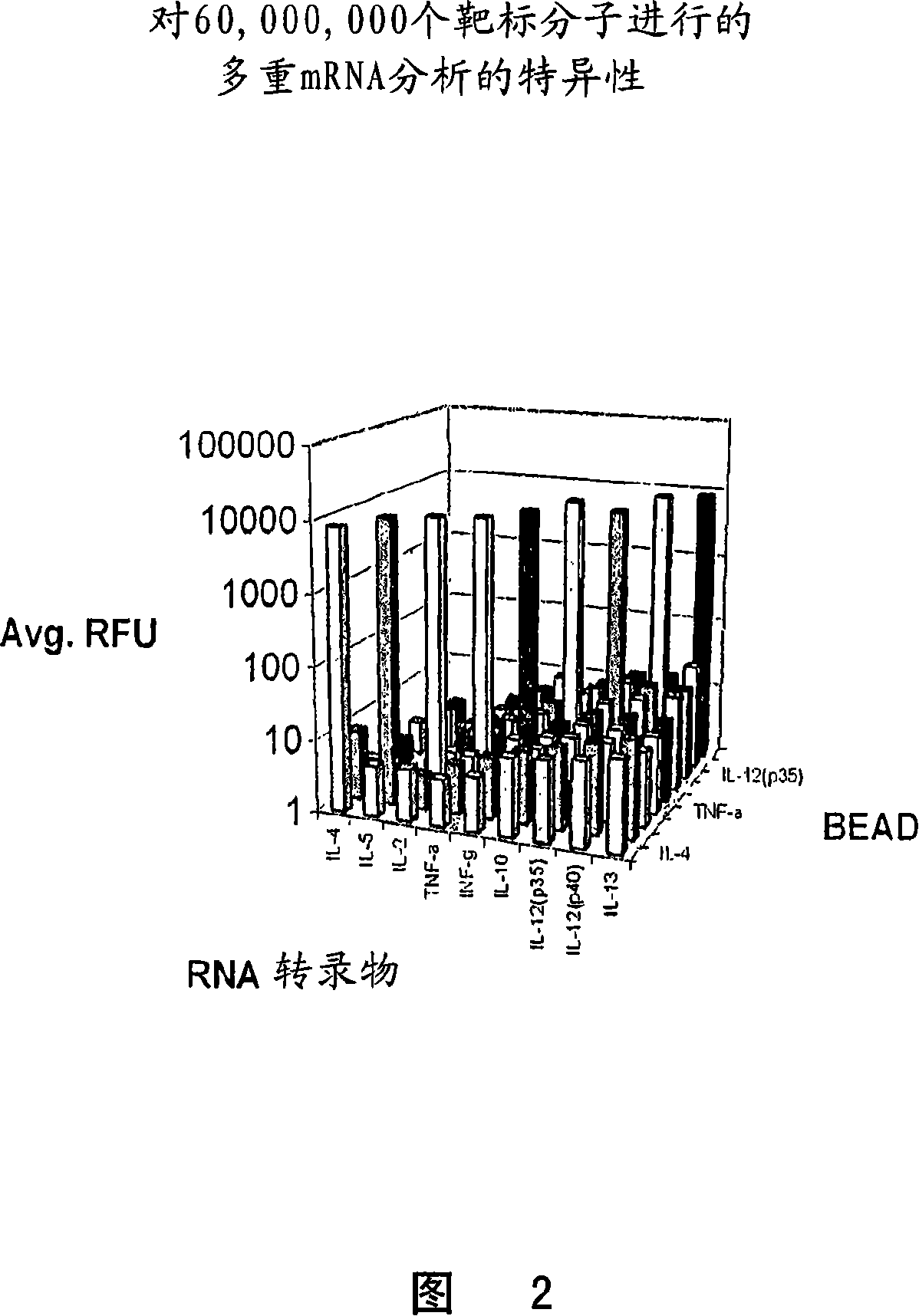
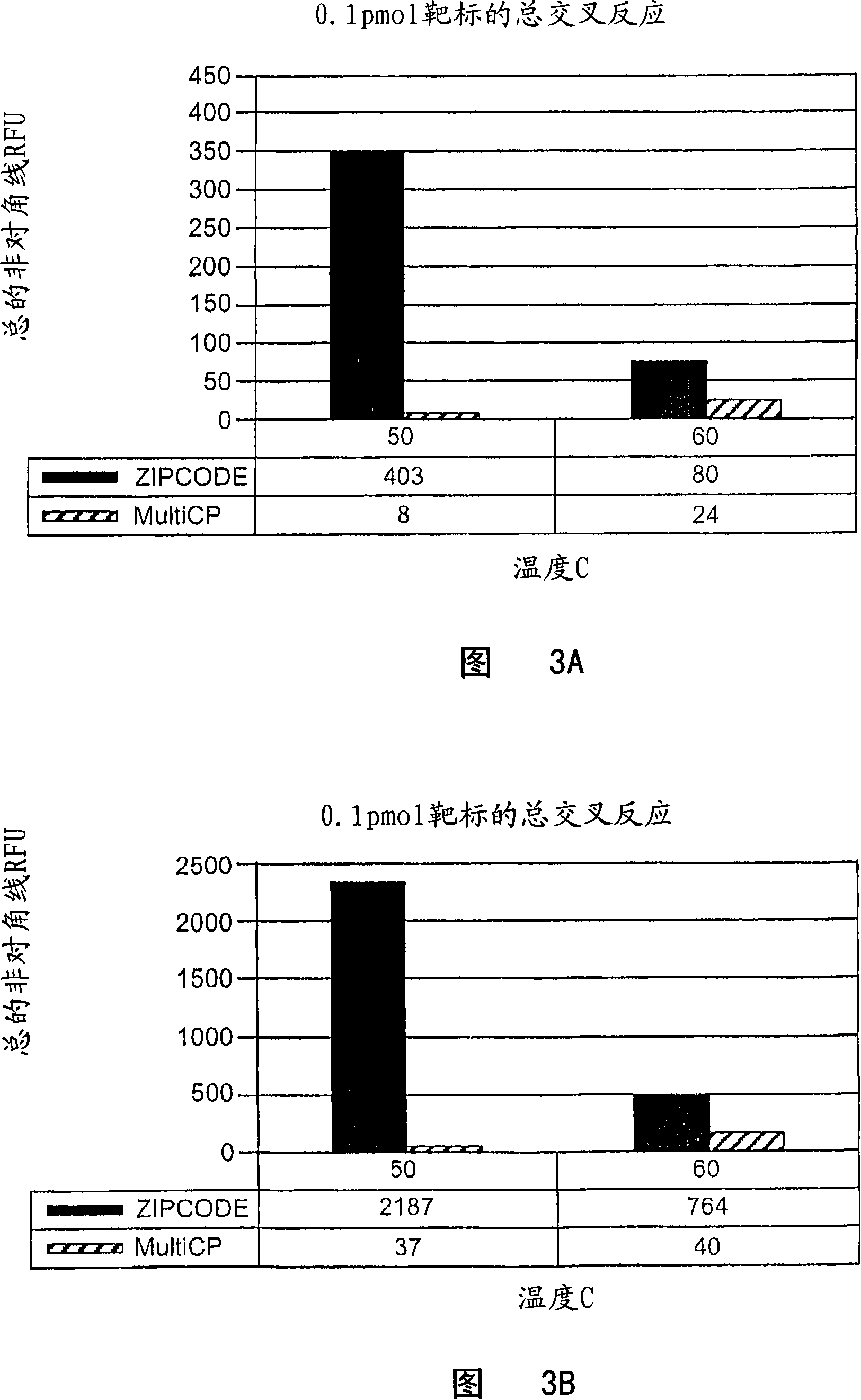
[0095] The universal orthogonal sequences CP1-CP9 and CE1-CE9 (SEQ ID NO. 1-22) of Table 1 were used for multiplex cytokine mRNA quantification using bDNA design principles and Luminex(R) suspension array technology for readout. Table 2 shows the performance of multiplex mRNA profiling using CP1-CP9 and CE1-CE9 for a target of approximately 60,000,000 molecules for nine cytokines. In this experiment, complete bDNA analysis was performed for each cytokine. As shown in Table 2, a very strong RFU signal was observed on the expected bead and there was negligible cross-hybridization of the selected universal sequences compared to the background signal of the assay bead. Figure 2 shows the results of this analysis in a three-dimensional histogram.
Table 2
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com